java-线程池+CompletableFuture
使用线程池
线程池的基本概念
线程池,本质上是一种对象池,用于管理线程资源。
在任务执行前,需要从线程池中拿出线程来执行。
在任务执行完成之后,需要把线程放回线程池。
通过线程的这种反复利用机制,可以有效地避免直接创建线程所带来的坏处。
线程池的优缺点
优点
- 降低资源的消耗。线程本身是一种资源,创建和销毁线程会有CPU开销;创建的线程也会占用一定的内存。
- 提高任务执行的响应速度。任务执行时,可以不必等到线程创建完之后再执行。
- 提高线程的可管理性。线程不能无限制地创建,需要进行统一的分配、调优和监控。
缺点
- 频繁的线程创建和销毁会占用更多的CPU和内存
- 频繁的线程创建和销毁会对GC产生比较大的压力
- 线程太多,线程切换带来的开销将不可忽视
- 线程太少,多核CPU得不到充分利用,是一种浪费
线程池创建流程

通过上图,我们看到了线程池的主要处理流程。我们的关注点在于,任务提交之后是怎么执行的。大致如下:
- 判断核心线程池是否已满,如果不是,则创建线程执行任务
- 如果核心线程池满了,判断队列是否满了,如果队列没满,将任务放在队列中
- 如果队列满了,则判断线程池是否已满,如果没满,创建线程执行任务
- 如果线程池也满了,则按照拒绝策略对任务进行处理
在jdk里面,我们可以将处理流程描述得更清楚一点。来看看ThreadPoolExecutor的处理流程。

我们将概念做一下映射。
corePool-> 核心线程池maximumPool-> 线程池BlockQueue-> 队列RejectedExecutionHandler-> 拒绝策略
入门级例子
为了更直观地理解线程池,我们通过一个例子来宏观地了解一下线程池用法。
public class ThreadPoolTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
executor.submit(() -> {
System.out.println("thread id is: " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
try {
Thread.sleep(1000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
}
}
在这个例子中,首先创建了一个固定长度为5的线程池。然后使用循环的方式往线程池中提交了10个任务,每个任务休眠1秒。在任务休眠之前,将任务所在的线程id进行打印输出。
所以,理论上只会打印5个不同的线程id,且每个线程id会被打印2次。

Executors
Executors是一个线程池工厂,提供了很多的工厂方法,我们来看看它大概能创建哪些线程池。
// 创建单一线程的线程池
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor();
// 创建固定数量的线程池
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads);
// 创建带缓存的线程池
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool();
// 创建定时调度的线程池
public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize);
// 创建流式(fork-join)线程池
public static ExecutorService newWorkStealingPool();
1. 创建单一线程的线程池
顾名思义,这个线程池只有一个线程。若多个任务被提交到此线程池,那么会被缓存到队列(队列长度为Integer.MAX_VALUE)。当线程空闲的时候,按照FIFO的方式进行处理。
2. 创建固定数量的线程池
和创建单一线程的线程池类似,只是这儿可以并行处理任务的线程数更多一些罢了。若多个任务被提交到此线程池,会有下面的处理过程。
- 如果线程的数量未达到指定数量,则创建线程来执行任务
- 如果线程池的数量达到了指定数量,并且有线程是空闲的,则取出空闲线程执行任务
- 如果没有线程是空闲的,则将任务缓存到队列(队列长度为
Integer.MAX_VALUE)。当线程空闲的时候,按照FIFO的方式进行处理
3. 创建带缓存的线程池
这种方式创建的线程池,核心线程池的长度为0,线程池最大长度为Integer.MAX_VALUE。由于本身使用SynchronousQueue作为等待队列的缘故,导致往队列里面每插入一个元素,必须等待另一个线程从这个队列删除一个元素。
4. 创建定时调度的线程池
和上面3个工厂方法返回的线程池类型有所不同,它返回的是ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor类型的线程池。平时我们实现定时调度功能的时候,可能更多的是使用第三方类库,比如:quartz等。但是对于更底层的功能,我们仍然需要了解。
我们写一个例子来看看如何使用。
public class ThreadPoolTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ScheduledExecutorService executor = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(2);
// 定时调度,每个调度任务会至少等待`period`的时间,
// 如果任务执行的时间超过`period`,则等待的时间为任务执行的时间
executor.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(10000);
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() / 1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, 0, 2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// 定时调度,第二个任务执行的时间 = 第一个任务执行时间 + `delay`
executor.scheduleWithFixedDelay(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() / 1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, 0, 2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// 定时调度,延迟`delay`后执行,且只执行一次
executor.schedule(() -> System.out.println("5 秒之后执行 schedule"), 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
}
-
scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long period, TimeUnit unit),定时调度,每个调度任务会至少等待period的时间,如果任务执行的时间超过period,则等待的时间为任务执行的时间 -
scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long delay, TimeUnit unit),定时调度,第二个任务执行的时间 = 第一个任务执行时间 +delay -
schedule(Runnable command, long delay, TimeUnit unit),定时调度,延迟delay后执行,且只执行一次
手动创建线程池
理论上,我们可以通过Executors来创建线程池,这种方式非常简单。但正是因为简单,所以限制了线程池的功能。比如:无长度限制的队列,可能因为任务堆积导致OOM,这是非常严重的bug,应尽可能地避免。怎么避免?归根结底,还是需要我们通过更底层的方式来创建线程池。
抛开定时调度的线程池不管,我们看看ThreadPoolExecutor。它提供了好几个构造方法,但是最底层的构造方法却只有一个。那么,我们就从这个构造方法着手分析。
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler);
这个构造方法有7个参数,我们逐一来进行分析。
corePoolSize,线程池中的核心线程数,也是线程池中常驻的线程数,线程池初始化时默认是没有线程的,当任务来临时才开始创建线程去执行任务maximumPoolSize,线程池中的最大线程数,在核心线程数的基础上可能会额外增加一些非核心线程,需要注意的是只有当workQueue队列填满时才会创建多于corePoolSize的线程(线程池总线程数不超过maxPoolSize)keepAliveTime,非核心线程的空闲时间超过keepAliveTime就会被自动终止回收掉,注意当corePoolSize=maxPoolSize时,keepAliveTime参数也就不起作用了(因为不存在非核心线程)unit,keepAliveTime的时间单位,可以是毫秒、秒、分钟、小时和天,等等workQueue,等待队列,线程池中的线程数超过核心线程数corePoolSize时,任务将放在等待队列,它是一个BlockingQueue类型的对象threadFactory,创建线程的工厂类,默认使用Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),也可以使用guava库的ThreadFactoryBuilder来创建handler,拒绝策略,当线程池和等待队列(队列已满且线程数达到maximunPoolSize)都满了之后,需要通过该对象的回调函数进行回调处理
这些参数里面,基本类型的参数都比较简单,我们不做进一步的分析。我们更关心的是workQueue、threadFactory和handler,接下来我们将进一步分析。
1. 等待队列-workQueue
等待队列是BlockingQueue类型的,理论上只要是它的子类,我们都可以用来作为等待队列。
同时,jdk内部自带一些阻塞队列,我们来看看大概有哪些。
ArrayBlockingQueue,(有界队列):队列长度受限,当队列满了就需要创建多余的线程来执行任务LinkedBlockingQueue,队列可以有界,也可以无界。基于链表实现的阻塞队列。当请求越来越多时(任务处理速度跟不上任务提交速度造成请求堆积)可能导致内存占用过多或OOMSynchronousQueue,不存储元素的阻塞队列,每个插入操作必须等到另一个线程调用移除操作,否则插入操作将一直处于阻塞状态。该队列也是Executors.newCachedThreadPool()的默认队列。可以简单理解为队列长度为零PriorityBlockingQueue,带优先级的无界阻塞队列
通常情况下,我们需要指定阻塞队列的上界(比如1024)。另外,如果执行的任务很多,我们可能需要将任务进行分类,然后将不同分类的任务放到不同的线程池中执行。
2. 线程工厂-threadFactory
ThreadFactory是一个接口,只有一个方法。既然是线程工厂,那么我们就可以用它生产一个线程对象。来看看这个接口的定义。
public interface ThreadFactory {
/**
* Constructs a new {@code Thread}. Implementations may also initialize
* priority, name, daemon status, {@code ThreadGroup}, etc.
*
* @param r a runnable to be executed by new thread instance
* @return constructed thread, or {@code null} if the request to
* create a thread is rejected
*/
Thread newThread(Runnable r);
}
Executors的实现使用了默认的线程工厂-DefaultThreadFactory。它的实现主要用于创建一个线程,线程的名字为pool-{poolNum}-thread-{threadNum}
static class DefaultThreadFactory implements ThreadFactory {
private static final AtomicInteger poolNumber = new AtomicInteger(1);
private final ThreadGroup group;
private final AtomicInteger threadNumber = new AtomicInteger(1);
private final String namePrefix;
DefaultThreadFactory() {
SecurityManager s = System.getSecurityManager();
group = (s != null) ? s.getThreadGroup() :
Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup();
namePrefix = "pool-" +
poolNumber.getAndIncrement() +
"-thread-";
}
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
Thread t = new Thread(group, r,
namePrefix + threadNumber.getAndIncrement(),
0);
if (t.isDaemon())
t.setDaemon(false);
if (t.getPriority() != Thread.NORM_PRIORITY)
t.setPriority(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY);
return t;
}
}
很多时候,我们需要自定义线程名字。我们只需要自己实现ThreadFactory,用于创建特定场景的线程即可。
ThreadFactory namedThreadFactory = new ThreadFactoryBuilder().setNameFormat("thread-call-runner-%d").build();
ExecutorService service = new ThreadPoolExecutor(1,1,200L,TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,new LinkedBlockingQueue(),namedThreadFactory);
3. 拒绝策略-handler
所谓拒绝策略,就是当线程池满了、队列也满了的时候,我们对任务采取的措施。或者丢弃、或者执行、或者其他...
jdk自带4种拒绝策略
CallerRunsPolicy// 在调用者线程执行,即让提交任务的线程去执行任务(对比前三种比较友好一丢丢)AbortPolicy// 直接抛出RejectedExecutionException异常DiscardPolicy// 默默丢弃任务,不进行任何通知DiscardOldestPolicy// 丢弃队列里最旧的那个任务,再尝试执行当前任务
这四种策略各有优劣,比较常用的是DiscardPolicy,但是这种策略有一个弊端就是任务执行的轨迹不会被记录下来。所以,我们往往需要实现自定义的拒绝策略, 通过实现RejectedExecutionHandler接口的方式。
提交任务的几种方式
往线程池中提交任务,主要有两种方法,execute()和submit()。
execute()用于提交不需要返回结果的任务,我们看一个例子。
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
executor.execute(() -> System.out.println("hello"));
}
submit()用于提交一个需要返回果的任务。该方法返回一个Future对象,通过调用这个对象的get()方法,我们就能获得返回结果。get()方法会一直阻塞,直到返回结果返回。另外,我们也可以使用它的重载方法get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit),这个方法也会阻塞,但是在超时时间内仍然没有返回结果时,将抛出异常TimeoutException。
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
Future<Long> future = executor.submit(() -> {
System.out.println("task is executed");
return System.currentTimeMillis();
});
System.out.println("task execute time is: " + future.get());
}
关闭线程池
在线程池使用完成之后,我们需要对线程池中的资源进行释放操作,这就涉及到关闭功能。我们可以调用线程池对象的shutdown()和shutdownNow()方法来关闭线程池。
这两个方法都是关闭操作,又有什么不同呢?
shutdown()会将线程池状态置为SHUTDOWN,不再接受新的任务,同时会等待线程池中已有的任务执行完成再结束。shutdownNow()会将线程池状态置为SHUTDOWN,对所有线程执行interrupt()操作,清空队列,并将队列中的任务返回回来。
另外,关闭线程池涉及到两个返回boolean的方法,isShutdown()和isTerminated,分别表示是否关闭和是否终止。
如何正确配置线程池的参数
前面我们讲到了手动创建线程池涉及到的几个参数,那么我们要如何设置这些参数才算是正确的应用呢?实际上,需要根据任务的特性来分析。
- 任务的性质:CPU密集型、IO密集型和混杂型
- 任务的优先级:高中低
- 任务执行的时间:长中短
- 任务的依赖性:是否依赖数据库或者其他系统资源
不同的性质的任务,我们采取的配置将有所不同。在《Java并发编程实践》中有相应的计算公式。
通常来说,如果任务属于CPU密集型,那么我们可以将线程池数量设置成CPU的个数,以减少线程切换带来的开销。如果任务属于IO密集型,我们可以将线程池数量设置得更多一些,比如CPU个数*2。
PS:我们可以通过Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors()来获取CPU的个数。
线程池监控
如果系统中大量用到了线程池,那么我们有必要对线程池进行监控。利用监控,我们能在问题出现前提前感知到,也可以根据监控信息来定位可能出现的问题。
那么我们可以监控哪些信息?又有哪些方法可用于我们的扩展支持呢?
首先,ThreadPoolExecutor自带了一些方法。
long getTaskCount(),获取已经执行或正在执行的任务数long getCompletedTaskCount(),获取已经执行的任务数int getLargestPoolSize(),获取线程池曾经创建过的最大线程数,根据这个参数,我们可以知道线程池是否满过int getPoolSize(),获取线程池线程数int getActiveCount(),获取活跃线程数(正在执行任务的线程数)
其次,ThreadPoolExecutor留给我们自行处理的方法有3个,它在ThreadPoolExecutor中为空实现(也就是什么都不做)。
protected void beforeExecute(Thread t, Runnable r)// 任务执行前被调用protected void afterExecute(Runnable r, Throwable t)// 任务执行后被调用protected void terminated()// 线程池结束后被调用
针对这3个方法,我们写一个例子。
public class ThreadPoolTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(1)) {
@Override protected void beforeExecute(Thread t, Runnable r) {
System.out.println("beforeExecute is called");
}
@Override protected void afterExecute(Runnable r, Throwable t) {
System.out.println("afterExecute is called");
}
@Override protected void terminated() {
System.out.println("terminated is called");
}
};
executor.submit(() -> System.out.println("this is a task"));
executor.shutdown();
}
}
输出结果如下:
beforeExecute is called
this is a task
afterExecute is called
terminated is called
一个特殊的问题
任何代码在使用的时候都可能遇到问题,线程池也不例外。楼主在现实的系统中就遇到过很奇葩的问题。我们来看一个例子。
public class ThreadPoolTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
executor.submit(new DivTask(100, i));
}
}
static class DivTask implements Runnable {
int a, b;
public DivTask(int a, int b) {
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
}
@Override public void run() {
double result = a / b;
System.out.println(result);
}
}
}
该代码执行的结果如下。

我们循环了5次,理论上应该有5个结果被输出。可是最终的执行结果却很让人很意外--只有4次输出。我们进一步分析发现,当第一次循环,除数为0时,理论上应该抛出异常才对,但是这儿却没有,异常被莫名其妙地吞掉了!
这又是为什么呢?
我们进一步看看submit()方法,这个方法是一个非阻塞方法,有一个返回对象,返回的是Future对象。那么我们就猜测,会不会是因为没有对Future对象做处理导致的。
我们将代码微调一下,重新运行,异常信息终于打印出来了。
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
Future future= executor.submit(new DivTask(100, i));
try {
future.get();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
PS:在使用submit()的时候一定要注意它的返回对象Future,为了避免任务执行异常被吞掉的问题,我们需要调用Future.get()方法。另外,使用execute()将不会出现这种问题。
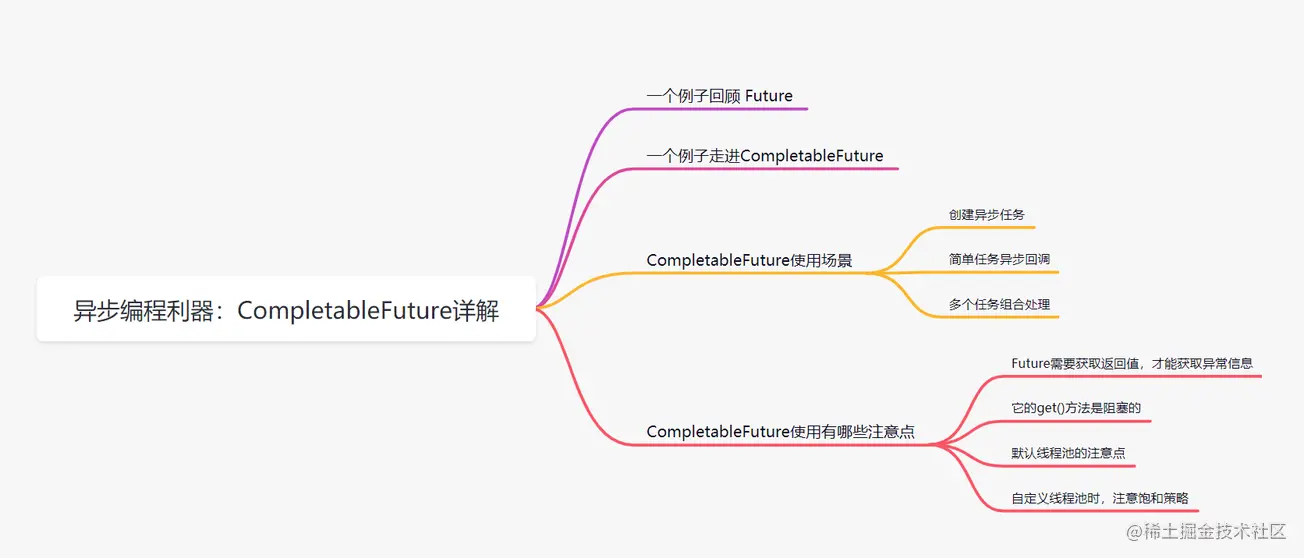
异步编程利器:CompletableFuture
异步编程利器:CompletableFuture详解 |Java 开发实战 - 掘金 (juejin.cn)
我们异步执行一个任务时,一般是用线程池Executor去创建。如果不需要有返回值, 任务实现Runnable接口;如果需要有返回值,任务实现Callable接口,调用Executor的submit方法,再使用Future获取即可。如果多个线程存在依赖组合的话,我们怎么处理呢?可使用同步组件CountDownLatch、CyclicBarrier等,但是比较麻烦。其实有简单的方法,就是用CompeletableFuture。
一个例子回顾 Future
因为CompletableFuture实现了Future接口,我们先来回顾Future吧。
Future是Java5新加的一个接口,它提供了一种异步并行计算的功能。如果主线程需要执行一个很耗时的计算任务,我们就可以通过future把这个任务放到异步线程中执行。主线程继续处理其他任务,处理完成后,再通过Future获取计算结果。
来看个简单例子吧,假设我们有两个任务服务,一个查询用户基本信息,一个是查询用户勋章信息。如下,
public class UserInfoService {
public UserInfo getUserInfo(Long userId) throws InterruptedException {
Thread.sleep(300);//模拟调用耗时
return new UserInfo("666", "捡田螺的小男孩", 27); //一般是查数据库,或者远程调用返回的
}
}
public class MedalService {
public MedalInfo getMedalInfo(long userId) throws InterruptedException {
Thread.sleep(500); //模拟调用耗时
return new MedalInfo("666", "守护勋章");
}
}
接下来,我们来演示下,在主线程中是如何使用Future来进行异步调用的。
public class FutureTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
UserInfoService userInfoService = new UserInfoService();
MedalService medalService = new MedalService();
long userId =666L;
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
//调用用户服务获取用户基本信息
FutureTask<UserInfo> userInfoFutureTask = new FutureTask<>(new Callable<UserInfo>() {
@Override
public UserInfo call() throws Exception {
return userInfoService.getUserInfo(userId);
}
});
executorService.submit(userInfoFutureTask);
Thread.sleep(300); //模拟主线程其它操作耗时
FutureTask<MedalInfo> medalInfoFutureTask = new FutureTask<>(new Callable<MedalInfo>() {
@Override
public MedalInfo call() throws Exception {
return medalService.getMedalInfo(userId);
}
});
executorService.submit(medalInfoFutureTask);
UserInfo userInfo = userInfoFutureTask.get();//获取个人信息结果
MedalInfo medalInfo = medalInfoFutureTask.get();//获取勋章信息结果
System.out.println("总共用时" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) + "ms");
}
}
运行结果:
总共用时806ms
如果我们不使用Future进行并行异步调用,而是在主线程串行进行的话,耗时大约为300+500+300 = 1100 ms。可以发现,future+线程池异步配合,提高了程序的执行效率。
但是Future对于结果的获取,不是很友好,只能通过阻塞或者轮询的方式得到任务的结果。
Future.get()就是阻塞调用,在线程获取结果之前get方法会一直阻塞。Future提供了一个isDone方法,可以在程序中轮询这个方法查询执行结果。
阻塞的方式和异步编程的设计理念相违背,而轮询的方式会耗费无谓的CPU资源。因此,JDK8设计出CompletableFuture。CompletableFuture提供了一种观察者模式类似的机制,可以让任务执行完成后通知监听的一方。
CompletableFuture 简介
概述
CompletableFuture是对Future的扩展和增强。CompletableFuture实现了Future接口,并在此基础上进行了丰富的扩展,完美弥补了Future的局限性,同时 CompletableFuture 实现了对任务编排的能力。借助这项能力,可以轻松地组织不同任务的运行顺序、规则以及方式。从某种程度上说,这项能力是它的核心能力。而在以往,虽然通过 CountDownLatch 等工具类也可以实现任务的编排,但需要复杂的逻辑处理,不仅耗费精力且难以维护。
CompletableFuture的继承结构如下:
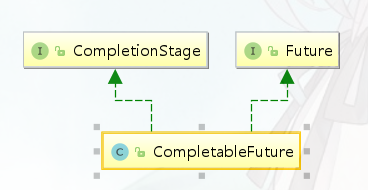
CompletionStage接口定义了任务编排的方法,执行某一阶段,可以向下执行后续阶段。异步执行的,默认线程池是ForkJoinPool.commonPool(),但为了业务之间互不影响,且便于定位问题,强烈推荐使用自定义线程池。
功能
依赖关系
thenApply/thenApplyAsync:第一个任务执行完成后,执行第二个回调方法任务,会将该任务的执行结果,作为入参,传递到回调方法中,并且回调方法是有返回值的。thenCompose():用来连接两个有依赖关系的任务,结果由第二个任务返回
and集合关系
thenCombine:会将两个任务的执行结果作为方法入参,传递到指定方法中,且有返回值thenAcceptBoth: 会将两个任务的执行结果作为方法入参,传递到指定方法中,且无返回值runAfterBoth:不会把执行结果当做方法入参,且没有返回值。
or聚合关系
-
applyToEither():两个任务哪个执行的快,就使用哪一个结果,有返回值 -
acceptEither():两个任务哪个执行的快,就消费哪一个结果,无返回值 -
runAfterEither():任意一个任务执行完成,进行下一步操作(Runnable类型任务)
并行执行
-
allOf():当所有给定的CompletableFuture完成时,返回一个新的CompletableFuture -
anyOf():当任何一个给定的CompletablFuture完成时,返回一个新的CompletableFuture结果处理
-
whenComplete:当任务完成时,将使用结果(或 null)和此阶段的异常(或 null如果没有)执行给定操作 -
exceptionally:返回一个新的CompletableFuture,当前面的CompletableFuture完成时,它也完成,当它异常完成时,给定函数的异常触发这个CompletableFuture的完成
异步操作
CompletableFuture提供了四个静态方法来创建一个异步操作:
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable)
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable, Executor executor)
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier)
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier, Executor executor)
这四个方法的区别:
runAsync()以Runnable函数式接口类型为参数,没有返回结果,supplyAsync()以Supplier函数式接口类型为参数,返回结果类型为U;Supplier接口的get()是有返回值的(会阻塞)- 使用没有指定
Executor的方法时,内部使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool()作为它的线程池执行异步代码。如果指定线程池,则使用指定的线程池运行。 - 默认情况下
CompletableFuture会使用公共的ForkJoinPool线程池,这个线程池默认创建的线程数是 CPU 的核数(也可以通过JVM option:-Djava.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool.common.parallelism来设置ForkJoinPool线程池的线程数)。如果所有CompletableFuture共享一个线程池,那么一旦有任务执行一些很慢的 I/O 操作,就会导致线程池中所有线程都阻塞在 I/O 操作上,从而造成线程饥饿,进而影响整个系统的性能。所以,强烈建议你要根据不同的业务类型创建不同的线程池,以避免互相干扰。
异步操作例子
Runnable runnable = () -> System.out.println("无返回结果异步任务");
CompletableFuture.runAsync(runnable);
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("有返回值的异步任务");
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "Hello World";
});
String result = future.get();
获取结果(join&get)
join() 和 get() 方法都是用来获取 CompletableFuture 异步之后的返回值。join() 方法抛出的是 uncheck 异常(即未经检查的异常),不会强制开发者抛出。get() 方法抛出的是经过检查的异常,ExecutionException, InterruptedException 需要用户手动处理(抛出或者 try catch)
结果处理
当 CompletableFuture 的计算结果完成,或者抛出异常的时候,我们可以执行特定的 Action。主要是下面的方法:
public CompletableFuture<T> whenComplete(BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable> action)
public CompletableFuture<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable> action)
public CompletableFuture<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable> action, Executor executor)
Action的类型是BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable>,它可以处理正常的计算结果,或者异常情况。- 方法不以
Async结尾,意味着Action使用相同的线程执行,而Async可能会使用其它的线程去执行(如果使用相同的线程池,也可能会被同一个线程选中执行)。 - 这几个方法都会返回
CompletableFuture,当Action执行完毕后它的结果返回原始的CompletableFuture的计算结果或者返回异常
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
if (new Random().nextInt(10) % 2 == 0) {
int i = 12 / 0;
}
System.out.println("执行结束!");
return "test";
});
// 任务完成或异常方法完成时执行该方法
// 如果出现了异常,任务结果为null
future.whenComplete(new BiConsumer<String, Throwable>() {
@Override
public void accept(String t, Throwable action) {
System.out.println(t+" 执行完成!");
}
});
// 出现异常时先执行该方法
future.exceptionally(new Function<Throwable, String>() {
@Override
public String apply(Throwable t) {
System.out.println("执行失败:" + t.getMessage());
return "异常xxxx";
}
});
future.get();
上面的代码当出现异常时,输出结果如下
执行失败:java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
null 执行完成!
应用场景
结果转换
将上一段任务的执行结果作为下一阶段任务的入参参与重新计算,产生新的结果。
thenApply/thenApplyAsync
thenApply接收一个函数作为参数,使用该函数处理上一个CompletableFuture调用的结果,并返回一个具有处理结果的Future对象。
常用使用:
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApply(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn)
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn)
具体使用:
CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
int result = 100;
System.out.println("第一次运算:" + result);
return result;
}).thenApply(number -> {
int result = number * 3;
System.out.println("第二次运算:" + result);
return result;
});
或者
public class FutureThenApplyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<String> orgFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(
()->{
System.out.println("原始CompletableFuture方法任务");
return "捡田螺的小男孩";
}
);
CompletableFuture<String> thenApplyFuture = orgFuture.thenApply((a) -> {
if ("捡田螺的小男孩".equals(a)) {
return "关注了";
}
return "先考虑考虑";
});
System.out.println(thenApplyFuture.get());
}
}
//输出
原始CompletableFuture方法任务
关注了
thenCompose
thenCompose的参数为一个返回CompletableFuture实例的函数,该函数的参数是先前计算步骤的结果。
常用方法:
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenCompose(Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn);
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenComposeAsync(Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn) ;
具体使用:
CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(new Supplier<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer get() {
int number = new Random().nextInt(30);
System.out.println("第一次运算:" + number);
return number;
}
})
.thenCompose(new Function<Integer, CompletionStage<Integer>>() {
@Override
public CompletionStage<Integer> apply(Integer param) {
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(new Supplier<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer get() {
int number = param * 2;
System.out.println("第二次运算:" + number);
return number;
}
});
}
});
thenApply 和 thenCompose的区别:
thenApply转换的是泛型中的类型,返回的是同一个CompletableFuture;thenCompose将内部的CompletableFuture调用展开来并使用上一个CompletableFutre调用的结果在下一步的CompletableFuture调用中进行运算,是生成一个新的CompletableFuture
结果消费
与 结果处理 和 结果转换 系列函数返回一个新的 CompletableFuture 不同,结果消费系列函数只对结果执行Action,而不返回新的计算值。
根据对结果的处理方式,结果消费函数又可以分为下面三大类:
thenAccept():对单个结果进行消费thenAcceptBoth():对两个结果进行消费thenRun():不关心结果,只对结果执行Action
thenAccept
观察该系列函数的参数类型可知,它们是函数式接口 Consumer,这个接口只有输入,没有返回值。
常用方法:
public CompletionStage<Void> thenAccept(Consumer<? super T> action);
public CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action);
具体使用:
CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(() -> {
int number = new Random().nextInt(10);
System.out.println("第一次运算:" + number);
return number;
}).thenAccept(number ->
System.out.println("第二次运算:" + number * 5));
thenAcceptBoth
thenAcceptBoth 函数的作用是,当两个 CompletionStage 都正常完成计算的时候,就会执行提供的 action 消费两个异步的结果。
常用方法:
public <U> CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptBoth(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action);
public <U> CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptBothAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action);
具体使用:
CompletableFuture<Integer> futrue1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(new Supplier<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer get() {
int number = new Random().nextInt(3) + 1;
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(number);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("任务1结果:" + number);
return number;
}
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(new Supplier<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer get() {
int number = new Random().nextInt(3) + 1;
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(number);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("任务2结果:" + number);
return number;
}
});
futrue1.thenAcceptBoth(future2, new BiConsumer<Integer, Integer>() {
@Override
public void accept(Integer x, Integer y) {
System.out.println("最终结果:" + (x + y));
}
});
thenRun
thenRun也是对线程任务结果的一种消费函数,与thenAccept不同的是,thenRun会在上一阶段 CompletableFuture计算完成的时候执行一个Runnable,而Runnable并不使用该CompletableFuture计算的结果。
常用方法:
public CompletionStage<Void> thenRun(Runnable action);
public CompletionStage<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action);
具体使用:
CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
int number = new Random().nextInt(10);
System.out.println("第一阶段:" + number);
return number;
}).thenRun(() ->
System.out.println("thenRun 执行"));
结果组合
thenCombine
合并两个线程任务的结果,并进一步处理。
常用方法:
public <U,V> CompletableFuture<V> thenCombine(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn);
public <U,V> CompletableFuture<V> thenCombineAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn);
public <U,V> CompletableFuture<V> thenCombineAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn, Executor executor);
具体使用:
CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(new Supplier<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer get() {
int number = new Random().nextInt(10);
System.out.println("任务1结果:" + number);
return number;
}
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(new Supplier<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer get() {
int number = new Random().nextInt(10);
System.out.println("任务2结果:" + number);
return number;
}
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> result = future1
.thenCombine(future2, new BiFunction<Integer, Integer, Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer apply(Integer x, Integer y) {
return x + y;
}
});
System.out.println("组合后结果:" + result.get());
...
import java.time.Instant;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.junit.Test;
@Slf4j
public class dytest {
@Test
public void test() throws Exception {
ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(16,
100,
0L,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(1024),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
// 任务1:计算1秒,得答案2
CompletableFuture<Integer> task_1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
sleepSeconds(1L);
return 2;
},executor);
// 任务2:计算2秒,得答案5
CompletableFuture<Integer> task_2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
sleepSeconds(2L);
return 5;
},executor);
// 将任务1与任务2得结果,进行加法,得结果
// 当任务1 与 2,都结束后,执行
CompletableFuture<Integer> objectCompletableFuture = task_1.thenCombine(task_2, (integer1,integer2) -> {
log.info("加法的结果:{}",integer1 + integer2);
return integer1 + integer2;
});
// 老写法对比
Integer integer3 = null;
try {
integer3 = task_1.get();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error(e.getMessage(), e);
}
Integer integer4 = null;
try {
integer4 = task_2.get();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error(e.getMessage(), e);
}
int result = integer3 + integer4;
log.info("加法的结果2:{}", result);
// 将任务1与任务2得结果,进行乘法,得结果
// 与 thenCombine 差别,就是此方法无返回值
CompletableFuture<Void> objectCompletableFuture2 = task_1.thenAcceptBoth(task_2, (integer1, integer2) -> {
log.info("乘法的结果:{}",integer1 * integer2);
});
// 阻塞
Integer result2 = objectCompletableFuture.get();
objectCompletableFuture2.get();
log.info("加法的结果2:{}", result2);
executor.shutdown();
}
private void sleepSeconds(long seconds) {
try {
Thread.sleep(seconds * 1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
任务交互
线程交互指 将两个线程任务获取结果的速度相比较,按一定的规则进行下一步处理。
applyToEither
两个线程任务相比较,先获得执行结果的,就对该结果进行下一步的转化操作。
常用方法:
public <U> CompletionStage<U> applyToEither(CompletionStage<? extends T> other,Function<? super T, U> fn);
public <U> CompletionStage<U> applyToEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other,Function<? super T, U> fn);
具体使用:
CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(new Supplier<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer get() {
int number = new Random().nextInt(10);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(number);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("任务1结果:" + number);
return number;
}
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(new Supplier<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer get() {
int number = new Random().nextInt(10);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(number);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("任务2结果:" + number);
return number;
}
});
future1.applyToEither(future2, new Function<Integer, Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer apply(Integer number) {
System.out.println("最快结果:" + number);
return number * 2;
}
});
runAfterEither
两个线程任务相比较,有任何一个执行完成,就进行下一步操作,不关心运行结果。
常用方法:
public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterEither(CompletionStage<?> other,Runnable action);
public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterEitherAsync(CompletionStage<?> other,Runnable action);
具体使用:
CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(new Supplier<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer get() {
int number = new Random().nextInt(5);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(number);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("任务1结果:" + number);
return number;
}
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(new Supplier<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer get() {
int number = new Random().nextInt(5);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(number);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("任务2结果:" + number);
return number;
}
});
future1.runAfterEither(future2, new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("已经有一个任务完成了");
}
}).join();
anyOf
anyOf()的参数是多个给定的 CompletableFuture,当其中的任何一个完成时,方法返回这个 CompletableFuture。
常用方法:
public static CompletableFuture<Object> anyOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs)
具体使用:
Random random = new Random();
CompletableFuture<String> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(random.nextInt(5));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "hello";
});
CompletableFuture<String> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(random.nextInt(1));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "world";
});
CompletableFuture<Object> result = CompletableFuture.anyOf(future1, future2);
allOf
allOf 方法用来实现多 CompletableFuture 的同时返回。
常用方法:
public static CompletableFuture<Void> allOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs)
具体使用:
旧写法
import java.time.Instant;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.junit.Test;
@Slf4j
public class dytest {
@Test
public void test2() throws Exception {
ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(16,
100,
0L,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(1024),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
List<Future> futureList = new ArrayList<>();
// 任务1,计算1秒,得答案2
futureList.add(executor.submit(new Callable<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
sleepSeconds(1L);
return 2;
}
}));
// 任务2,计算2秒,得答案5
futureList.add(executor.submit(() -> {
sleepSeconds(2L);
return 5;
}));
// 任务3,计算3秒,得答案
futureList.add(executor.submit(() -> {
sleepSeconds(3L);
return 5;
}));
// ...假设还有很多任务,想等任务全部结束,再干一些事情
try {
Long localDateTimeStart = Instant.now().toEpochMilli();
// LocalDateTime localDateTimeStart = LocalDateTime.now();
for (Future futue : futureList) {
futue.get();
}
Long localDateTimeEnd = Instant.now().toEpochMilli();
// LocalDateTime localDateTimeEnd = LocalDateTime.now();
// DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss");
// 这里的时间,约等于花费时间最长的那个线程,即3秒
log.info("花费的时间(mill):{}", String.valueOf(localDateTimeEnd - localDateTimeStart));
}catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
};
private void sleepSeconds(long seconds) {
try {
Thread.sleep(seconds * 1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
CompletableFuture 的写法
package com.netease.qa;
import java.time.Instant;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
import com.netease.qa.controller.CodeRelationController;
//import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.slf4j.MDC;
import org.junit.Test;
//@Slf4j
public class dytest {
private static Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(CodeRelationController.class);
@Test
public void test3() throws Exception {
ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(16,
100,
0L,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(1024),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
List<Future> futureList = new ArrayList<>();
// 任务1,计算1秒,得答案2
CompletableFuture<Integer> task_1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
sleepSeconds(1L);
return 2;
}, executor);
// 任务2,计算2秒,得答案5
CompletableFuture<Integer> task_2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
sleepSeconds(2L);
return 5;
}, executor);
// 任务3,计算3秒,得答案5
CompletableFuture<Integer> task_3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
sleepSeconds(2L);
return 5;
}, executor);
CompletableFuture<Void> voidCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.allOf(task_1, task_2, task_3).whenComplete((value, throwable) -> {
log.info("value:{}", String.valueOf(value));
log.info("throwable:{}", String.valueOf(throwable));
});
long starttime = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info("get之前");
voidCompletableFuture.get();
long endtime = System.currentTimeMillis();
log.info(String.valueOf(endtime - starttime));
}
private void sleepSeconds(long seconds) {
try {
Thread.sleep(seconds * 1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
CompletableFuture常用方法总结:
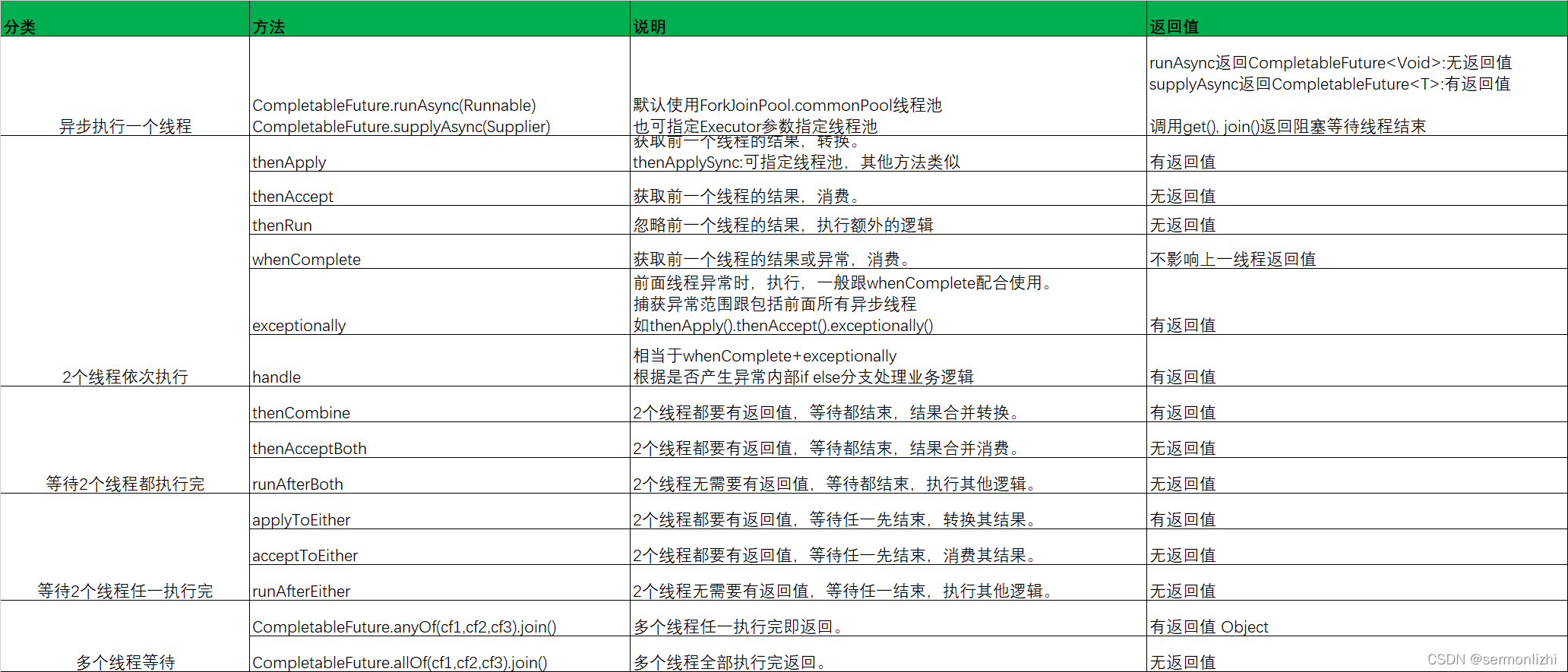
注:CompletableFuture中还有很多功能丰富的方法,这里就不一一列举。
使用案例
实现最优的“烧水泡茶”程序
著名数学家华罗庚先生在《统筹方法》这篇文章里介绍了一个烧水泡茶的例子,文中提到最优的工序应该是下面这样:
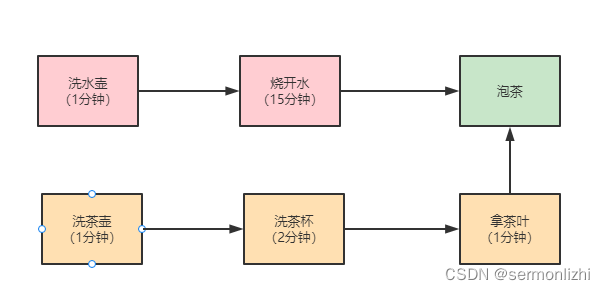
对于烧水泡茶这个程序,一种最优的分工方案:用两个线程 T1 和 T2 来完成烧水泡茶程序,T1 负责洗水壶、烧开水、泡茶这三道工序,T2 负责洗茶壶、洗茶杯、拿茶叶三道工序,其中 T1 在执行泡茶这道工序时需要等待 T2 完成拿茶叶的工序。
基于Future实现
public class FutureTaskTest{
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
// 创建任务T2的FutureTask
FutureTask<String> ft2 = new FutureTask<>(new T2Task());
// 创建任务T1的FutureTask
FutureTask<String> ft1 = new FutureTask<>(new T1Task(ft2));
// 线程T1执行任务ft1
Thread T1 = new Thread(ft2);
T1.start();
// 线程T2执行任务ft2
Thread T2 = new Thread();
T2.start();
// 等待线程T1执行结果
System.out.println(ft1.get());
}
}
// T1Task需要执行的任务:
// 洗水壶、烧开水、泡茶
class T1Task implements Callable<String> {
FutureTask<String> ft2;
// T1任务需要T2任务的FutureTask
T1Task(FutureTask<String> ft2){
this.ft2 = ft2;
}
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("T1:洗水壶...");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
System.out.println("T1:烧开水...");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(15);
// 获取T2线程的茶叶
String tf = ft2.get();
System.out.println("T1:拿到茶叶:"+tf);
System.out.println("T1:泡茶...");
return "上茶:" + tf;
}
}
// T2Task需要执行的任务:
// 洗茶壶、洗茶杯、拿茶叶
class T2Task implements Callable<String> {
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("T2:洗茶壶...");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
System.out.println("T2:洗茶杯...");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
System.out.println("T2:拿茶叶...");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
return "龙井";
}
}
基于CompletableFuture实现
public class CompletableFutureTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//任务1:洗水壶->烧开水
CompletableFuture<Void> f1 = CompletableFuture
.runAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("T1:洗水壶...");
sleep(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println("T1:烧开水...");
sleep(15, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
});
//任务2:洗茶壶->洗茶杯->拿茶叶
CompletableFuture<String> f2 = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("T2:洗茶壶...");
sleep(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println("T2:洗茶杯...");
sleep(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println("T2:拿茶叶...");
sleep(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
return "龙井";
});
//任务3:任务1和任务2完成后执行:泡茶
CompletableFuture<String> f3 = f1.thenCombine(f2, (__, tf) -> {
System.out.println("T1:拿到茶叶:" + tf);
System.out.println("T1:泡茶...");
return "上茶:" + tf;
});
//等待任务3执行结果
System.out.println(f3.join());
}
static void sleep(int t, TimeUnit u){
try {
u.sleep(t);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号