Spring源码解析二:IOC容器初始化过程详解
IOC容器初始化分为三个步骤,分别是:
1、Resource定位,即BeanDefinition的资源定位。
2、BeanDefinition的载入
3、向IOC容器注册BeanDefinition
下面我们来详细展开这三部分的内容
一、Resource定位
以ApplicationContext的具体实现FileSystemXmlApplicationContext来介绍Resource定位的过程:
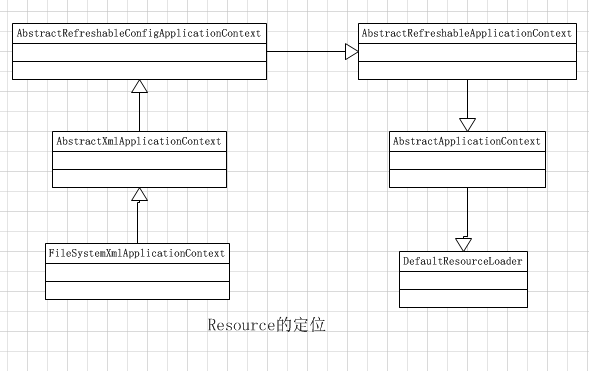
IOC容器初始化类比为用木桶来装水,Resource的定位过程就是寻找水的过程。
它是由ResourceLoader通过统一的Resource接口来完成的,Resource对各种形式的BeanDefinition的使用都提供了统一的接口。
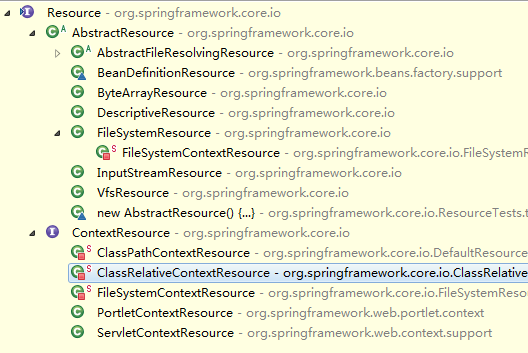
Resource接口有许多实现类,针对不同的BeanDefinition,如:
在文件系统中的Bean定义信息可以使用FileSystemResource来进行抽象。
在类路径中的Bean定义信息可以使用ClassPathResource来进行抽象。
我们来看下FileSystemXmlApplicationContext其中的一个构造函数:
public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, ApplicationContext parent) throws BeansException { super(parent); setConfigLocations(configLocations); if (refresh) { refresh(); } }
这里有个refresh()方法,这个方法非常重要,可以说是IOC容器启动的入口,该方法的实现在AbstractApplicationContext中。
在AbstractApplicationContext的refresh方法中,最终对调用到AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext的refreshBeanFactory,在这里会创建一个基础的IOC容器供ApplicationContext使用,这个基础的BeanFactory就是DefaultListableBeanFactory。
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException { if (hasBeanFactory()) { destroyBeans(); closeBeanFactory(); } try { DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory(); beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId()); customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory); loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory); synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) { this.beanFactory = beanFactory; } } catch (IOException ex) { throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex); } }
再根据loadBeanDefinitions方法一直往下查找,最终会找到DefaultResourceLoader类的getResource方法:
public Resource getResource(String location) { Assert.notNull(location, "Location must not be null"); if (location.startsWith(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX)) { return new ClassPathResource(location.substring(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX.length()), getClassLoader()); } else { try { // Try to parse the location as a URL... URL url = new URL(location); return new UrlResource(url); } catch (MalformedURLException ex) { // No URL -> resolve as resource path. return getResourceByPath(location); } } }
这里的getResourceByPath方法最终被子类重写,该场景下重写该方法的类就是FileSystemXmlApplicationContext
protected Resource getResourceByPath(String path) { if (path != null && path.startsWith("/")) { path = path.substring(1); } return new FileSystemResource(path); }
这样我们从FileSystemXmlApplicationContext的构造函数中的refresh方法开始,最终到getResourceByPath结束,完成了资源定位的解析。但是这个只是容器启动中的一部分,还有载入和解析也是糅合在一起的,只是为了思路清晰,故意对这些地方视而不见。
二、BeanDefinition的载入和解析
在第一部分资源的定位中,我们是以getResourceByPath()结束的,接下来我们要通过该方法返回的Resource对象来进行BeanDefinition的载入了。现在我们已经知道水在哪里了,就可以现在打水和装水之旅了。
这个过程就是将定义的BeanDefinition在IOC容器中转化成一个Spring内部表示的数据结构的过程。我们紧接着前面的源码往下梳理:
AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext的方法refreshBeanFactory中调用loadBeanDefinitions(),往下梳理找到类AbstractXmlApplicationContext,源码片段如下;
1 protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException { 2 // Create a new XmlBeanDefinitionReader for the given BeanFactory. 3 XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory); 4 5 // Configure the bean definition reader with this context's 6 // resource loading environment. 7 beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this); 8 beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this)); 9 10 // Allow a subclass to provide custom initialization of the reader, 11 // then proceed with actually loading the bean definitions. 12 initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader); 13 loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader); 14 }
其中第7行是为读取器设置ResourceLoader,为后面的资源读取做准备;第13行就是启动Bean定义信息载入的开始。
1 protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws BeansException, IOException { 2 Resource[] configResources = getConfigResources(); 3 if (configResources != null) { 4 reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configResources); 5 } 6 String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations(); 7 if (configLocations != null) { 8 reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocations); 9 } 10 }
第2行是以Resource的方式获取配置文件的资源位置,而第6行是以String的形式获取配置文件的位置。
reader.loadBeanDefinitions()的实现见XmlBeanDefinitionReader的父类AbstractBeanDefinitionReader
1 public int loadBeanDefinitions(String... locations) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { 2 Assert.notNull(locations, "Location array must not be null"); 3 int counter = 0; 4 for (String location : locations) { 5 counter += loadBeanDefinitions(location); 6 } 7 return counter; 8 }
这里如果Resource为空,则停止BeanDefinition的载入。在启动BeanDefinition的过程中,会遍历整个Resource集合所包含的BeanDefinition的信息。
这里面调用的loadBeanDefinitions()方法具体实现并不在AbstractBeanDefinitionReader,而是在子类里:
1 public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { 2 Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null"); 3 if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { 4 logger.info("Loading XML bean definitions from " + encodedResource.getResource()); 5 } 6 7 Set<EncodedResource> currentResources = this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get(); 8 if (currentResources == null) { 9 currentResources = new HashSet<EncodedResource>(4); 10 this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.set(currentResources); 11 } 12 if (!currentResources.add(encodedResource)) { 13 throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( 14 "Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!"); 15 } 16 try { 17 InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream(); 18 try { 19 InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream); 20 if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) { 21 inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding()); 22 } 23 return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource()); 24 } 25 finally { 26 inputStream.close(); 27 } 28 }
在这里可以拿到代表XML文件的Resource,读取器在打开I/O流后就可以得到XML的文件对象,接下来的事情就是按照Spring的Bean定义规则对这个XML文件做解析并封装了。而这个解析的过程是在类BeanDefinitionParserDelegate
在调用doLoadBeanDefinitions过程中,代码会走到类XmlBeanDefinitionReader中的doLoadBeanDefinitions的方法
1 protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource) 2 throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { 3 try { 4 int validationMode = getValidationModeForResource(resource); 5 Document doc = this.documentLoader.loadDocument( 6 inputSource, getEntityResolver(), this.errorHandler, validationMode, isNamespaceAware()); 7 return registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource); 8 }
这里第5行就是Document对象生成的入口,具体实现在DefaultDocumentLoader中。
第7行就是BeanDefinition解析的入口,我们接着往下走,最终的解析过程在类BeanDefinitionParserDelegate中,源码如下:
1 public BeanDefinitionHolder parseBeanDefinitionElement(Element ele, BeanDefinition containingBean) { 2 String id = ele.getAttribute(ID_ATTRIBUTE); 3 String nameAttr = ele.getAttribute(NAME_ATTRIBUTE); 4 5 List<String> aliases = new ArrayList<String>(); 6 if (StringUtils.hasLength(nameAttr)) { 7 String[] nameArr = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(nameAttr, BEAN_NAME_DELIMITERS); 8 aliases.addAll(Arrays.asList(nameArr)); 9 } 10 11 String beanName = id; 12 if (!StringUtils.hasText(beanName) && !aliases.isEmpty()) { 13 beanName = aliases.remove(0); 14 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 15 logger.debug("No XML 'id' specified - using '" + beanName + 16 "' as bean name and " + aliases + " as aliases"); 17 } 18 } 19 20 if (containingBean == null) { 21 checkNameUniqueness(beanName, aliases, ele); 22 } 23 24 AbstractBeanDefinition beanDefinition = parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele, beanName, containingBean); 25 if (beanDefinition != null) { 26 if (!StringUtils.hasText(beanName)) { 27 try { 28 if (containingBean != null) { 29 beanName = BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.generateBeanName( 30 beanDefinition, this.readerContext.getRegistry(), true); 31 } 32 else { 33 beanName = this.readerContext.generateBeanName(beanDefinition); 34 // Register an alias for the plain bean class name, if still possible, 35 // if the generator returned the class name plus a suffix. 36 // This is expected for Spring 1.2/2.0 backwards compatibility. 37 String beanClassName = beanDefinition.getBeanClassName(); 38 if (beanClassName != null && 39 beanName.startsWith(beanClassName) && beanName.length() > beanClassName.length() && 40 !this.readerContext.getRegistry().isBeanNameInUse(beanClassName)) { 41 aliases.add(beanClassName); 42 } 43 } 44 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 45 logger.debug("Neither XML 'id' nor 'name' specified - " + 46 "using generated bean name [" + beanName + "]"); 47 } 48 } 49 catch (Exception ex) { 50 error(ex.getMessage(), ele); 51 return null; 52 } 53 } 54 String[] aliasesArray = StringUtils.toStringArray(aliases); 55 return new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDefinition, beanName, aliasesArray); 56 } 57 58 return null; 59 }
其中 第24行会触发对Bean元素的详细解析,解析完成后会返回一个AbstractBeanDefinition对象,可以看下这个对象的属性,基本上都是Spring配置文件中的常用属性。
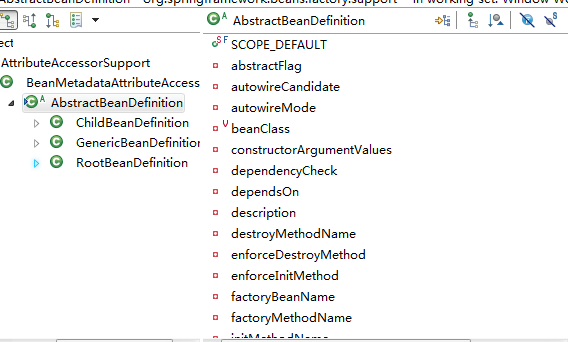
解析方法的具体内容如下:
1 public AbstractBeanDefinition parseBeanDefinitionElement( 2 Element ele, String beanName, BeanDefinition containingBean) { 3 4 this.parseState.push(new BeanEntry(beanName)); 5 6 String className = null; 7 if (ele.hasAttribute(CLASS_ATTRIBUTE)) { 8 className = ele.getAttribute(CLASS_ATTRIBUTE).trim(); 9 } 10 11 try { 12 String parent = null; 13 if (ele.hasAttribute(PARENT_ATTRIBUTE)) { 14 parent = ele.getAttribute(PARENT_ATTRIBUTE); 15 } 16 AbstractBeanDefinition bd = createBeanDefinition(className, parent); 17 18 parseBeanDefinitionAttributes(ele, beanName, containingBean, bd); 19 bd.setDescription(DomUtils.getChildElementValueByTagName(ele, DESCRIPTION_ELEMENT)); 20 21 parseMetaElements(ele, bd); 22 parseLookupOverrideSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides()); 23 parseReplacedMethodSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides()); 24 25 parseConstructorArgElements(ele, bd); 26 parsePropertyElements(ele, bd); 27 parseQualifierElements(ele, bd); 28 29 bd.setResource(this.readerContext.getResource()); 30 bd.setSource(extractSource(ele)); 31 32 return bd; 33 }
其中第18行-27行,都是对Spring配置文件中不同<Bean>节点的解析,可以每个都深入去研究下。最终返回一个AbstractBeanDefinition对象。
到这里,XML文件中定义的BeanDefinition就被整个载入到IOC容器中,建立了对应的数据结构,可以看成是POJO在容器中的抽象。但是这个时候容器中还只是有一些静态的配置信息,完成了管理Bean对象的数据准备工作,但是容器还没有完全发挥作用。
三、BeanDefinition注册过程
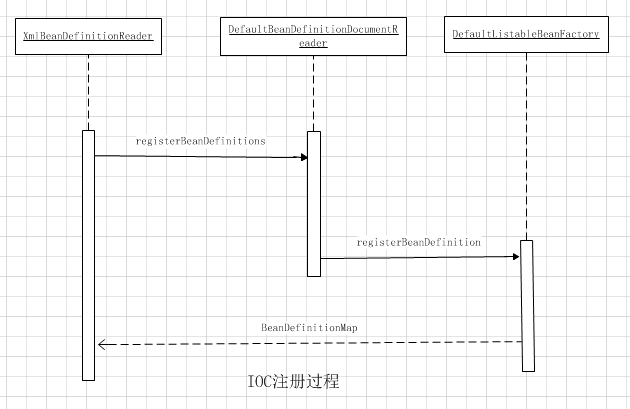
这个源码中方法调用过程比较简单,我们直接来看注册的核心代码:
1 public void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition) 2 throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { 3 4 Assert.hasText(beanName, "Bean name must not be empty"); 5 Assert.notNull(beanDefinition, "BeanDefinition must not be null"); 6 7 if (beanDefinition instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) { 8 try { 9 ((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDefinition).validate(); 10 } 11 catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) { 12 throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), beanName, 13 "Validation of bean definition failed", ex); 14 } 15 } 16 17 synchronized (this.beanDefinitionMap) { 18 Object oldBeanDefinition = this.beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName); 19 if (oldBeanDefinition != null) { 20 if (!this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding) { 21 throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), beanName, 22 "Cannot register bean definition [" + beanDefinition + "] for bean '" + beanName + 23 "': There is already [" + oldBeanDefinition + "] bound."); 24 } 25 else { 26 if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) { 27 this.logger.info("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName + 28 "': replacing [" + oldBeanDefinition + "] with [" + beanDefinition + "]"); 29 } 30 } 31 } 32 else { 33 this.beanDefinitionNames.add(beanName); 34 this.frozenBeanDefinitionNames = null; 35 } 36 this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition); 37 38 resetBeanDefinition(beanName); 39 } 40 }
最关键的一步就是第36行,所谓的注册就是将解析得到的BeanDefinition设置到hashMap中去。至此就完成了整个IOC容器初始化的工作,这样一来就可以在beanDefinition里检索和使用已经配置好的Bean了。ICO容器的作用就是维护和处理里面的Bean。
最后,我们来回答下这个问题,spring 容器中bean是什么时候被初始化的?
通过前面的分析,我们知道bean的实例化是伴随着容器的初始化而同时进行的(但是也有特例),并且默认情况下是单例的。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号