OO第二次博客作业
目录
1. 前言
2.代码分析
3.三次作业遇到的bug及采坑心得
4.改进建议
5.总结
一、前言
第二次写blug,对于题目的分析已经渐渐孰能生巧了,可以通过SourceMonitor的生成报表内容来分析出自己写过的题目的代码的问题了。
下面是我对三次题目集的大体分析:
题目集4
题量:3道
知识点:正则表达式的运用,类的关系:组合和聚合,java中类的继承性
难度:第一题难度较大,第二题难度虽然不高但过程较复杂,第三题偏易
题目集5
题量:5道
知识点:java集合框架应用,数组的运用,字符串转换,三个排序:冒泡、快排、插入,类的关系
难度:前三题偏简单,第四题运用到Set、List、Map接口难度较大,最后一题跟题目集4中第二题差不多只是类的关系发生了变化
题目集6
题量:6道
知识点:抽象类与接口,类的继承性、多态性,正则表达式的运用
难度:整体难度偏易,第五题可能要有些小技巧
二、代码分析
因学校要求,此次代码分析就分析题目集4的7-2和7-3,题目集5的7-4和7-5,题目集6的7-5和7-6以及这三次作业中所运用的正则表达式分析。
(一)题目集4(7-2)、题目集5(7-5)两种日期类聚合设计的优劣比较
题目集4
7-2
该题代码如下:
import java.util.Scanner; class Year{ private int value; Year(){} Year(int value){ this.setValue(value); } public int getValue() { return value; } public void setValue(int value){ this.value = value; } public boolean isLeapYear() { if(value%4==0&&value%100!=0) return true; else if(value%400==0&&value%100==0) return true; else return false; } public boolean validate() { if(value<=2050&&value>=1900) return true; else return false; } public void yearIncrement() { value++; } public void yearReduction() { value--; } } class Month{ private int value; private Year year; Month(){} Month(int yearValue,int monthValue){ this.year=new Year(yearValue); this.value=monthValue; } public int getValue() { return value; } public void setValue(int value) { this.value = value; } public Year getYear() { return year; } public void setYear(Year year) { this.year=year; } public void resetMin() { this.value=1; } public void resetMax() { this.value=12; } public boolean validate() { if(value>12||value<1) return false; else return true; } public void monehIncrement() { value++; } public void monehReduction() { value--; } } class Day{ private int value; private Month month; int [] mon_maxnum= {31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; Day(){} Day(int yearValue,int monthValue,int dayValue){ this.month=new Month(yearValue,monthValue); this.value=dayValue; } public int getValue() { return value; } public void setValue(int value) { this.value = value; } public Month getMonth() { return month; } public void setMonth(Month month) { this.month = month; } public void resetMin() { value=1; } public void resetMax() { if(month.getYear().isLeapYear()&&month.getValue()==2) value=29; else if(!(month.getYear().isLeapYear())&&month.getValue()==2) value=28; else if(month.getValue()==1||month.getValue()==3||month.getValue()==5||month.getValue()==7||month.getValue()==8||month.getValue()==10||month.getValue()==12) value=31; else if(month.getValue()==4||month.getValue()==6||month.getValue()==9||month.getValue()==11) value=30; } public boolean validate() { if(this.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) mon_maxnum[1]=29; if(value>=1&&mon_maxnum[month.getValue()-1]>=value) return true; return false; } public void dayIncrement() { value++; } public void dayReduction() { value--; } } class DateUtil{ Day day; DateUtil(){} DateUtil(int d,int m,int y){ this.day=new Day(d,m,y); } public Day getDay() { return day; } public void setDay(Day d) { this.day=d; } public boolean checkInputValidity() { if(day.validate()&&this.getDay().getMonth().validate()&&this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().validate()) return true; else return false; } public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date) { if(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()>date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()) return false; else if(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()==date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()&&this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()>date.getDay().getMonth().getValue()) return false; else if(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()==date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()&&this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()==date.getDay().getMonth().getValue()&&this.getDay().getValue()>date.getDay().getValue()) return false; return true; } public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date) { if(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()==date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()&&this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()==date.getDay().getMonth().getValue()&&this.getDay().getValue()==date.getDay().getValue()) return true; return false; } public String showDate() { return this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()+"-"+this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()+"-"+this.getDay().getValue(); } public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n) { int m=0; int [] mon_maxnum= {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; int year=this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue(); int month=this.getDay().getMonth().getValue(); int day=this.getDay().getValue(); for(int i=this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()+1;i<=12;i++) { m+=mon_maxnum[i]; } m+=mon_maxnum[this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()]-this.getDay().getValue(); if(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()&&this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()<=2) m++; if(n<m) { int days=mon_maxnum[month]; if(month==2&&this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) days++; days-=day; if(days>=n) { day+=n; } else { n-=days; month++; while(n-mon_maxnum[month]>0&&month<=12) { n-=mon_maxnum[month]; month++; } day=n; } } else { n-=m; year++; int x=365; if(new Year(year).isLeapYear()) x++; while(n-x>0) { n-=x; year++; x=365; if(new Year(year).isLeapYear()) x++; } int i=1; while(n-mon_maxnum[i]>0&&i<=12) { n-=mon_maxnum[i]; i++; } month=i; day=n; } return new DateUtil(year,month,day); } public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n) { int m=0; int [] mon_maxnum= {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; int year=this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue(); int month=this.getDay().getMonth().getValue(); int day=this.getDay().getValue(); for(int i=this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()+1;i<=12;i++) { m+=mon_maxnum[i]; } m+=mon_maxnum[this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()]-this.getDay().getValue(); if(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()&&this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()<=2) m++; int q=365-m; if(n<q) { if(day>n) { day=day-n; } else { n-=day; month--; if(month==0) { month=12; year--; } while(n-mon_maxnum[month]>0&&month>=0) { n-=mon_maxnum[month]; month--; } day=mon_maxnum[month]-n; if(new Year(year).isLeapYear()&&month==2) { day++; } } } else { n-=q; year--; int x=365; if(new Year(year).isLeapYear()) { x++; } while(n-x>0) { n-=x; year--; x=365; if(new Year(year).isLeapYear()) { x++; } } int y=12; while(n-mon_maxnum[y]>0&&y>=0) { n-=mon_maxnum[y]; y--; } month=y; day=mon_maxnum[y]-n; if(new Year(year).isLeapYear()&&month==2) { day++; } } return new DateUtil(year,month,day); } public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date) { DateUtil last=this; DateUtil now=date; if(this.equalTwoDates(date)) { return 0; } else if(!this.compareDates(date)) { last=date; now=this; } int [] mon_maxnum= {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; int i,j,d=0; for(i=last.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()+1;i<now.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue();i++) { d+=365; if(new Year(i).isLeapYear()) { d++; } } if(last.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()!=now.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()) { for(j=last.getDay().getMonth().getValue()+1;j<=12;j++) { d+=mon_maxnum[j]; } d+=mon_maxnum[last.getDay().getMonth().getValue()]-last.getDay().getValue(); for(j=1;j<now.getDay().getMonth().getValue();j++) { d+=mon_maxnum[j]; } d+=now.getDay().getValue(); if(last.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()&&last.getDay().getMonth().getValue()<=2) { d++; } if(now.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()&&now.getDay().getMonth().getValue()>2) { d++; } } else if(last.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()==now.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()&&last.getDay().getMonth().getValue()!=now.getDay().getMonth().getValue()) { for(j=last.getDay().getMonth().getValue()+1;j<=now.getDay().getMonth().getValue()-1;j++) { d+=mon_maxnum[j]; } d+=mon_maxnum[last.getDay().getMonth().getValue()]-last.getDay().getValue(); d+=now.getDay().getValue(); if(last.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()&&last.getDay().getMonth().getValue()<=2) { d++; } } else if(last.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()==now.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()&&last.getDay().getMonth().getValue()==now.getDay().getMonth().getValue()&&last.getDay().getValue()!=now.getDay().getValue()) { d=now.getDay().getValue()-last.getDay().getValue(); } return d; } } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in); int year,month,day; int choice=in.nextInt(); switch(choice) { case 1: year=in.nextInt(); month=in.nextInt(); day=in.nextInt(); DateUtil date=new DateUtil(year,month,day); if(!date.checkInputValidity()) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } int n=in.nextInt(); if(n<0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } System.out.println(date.getNextNDays(n).showDate()); break; case 2: year=in.nextInt(); month=in.nextInt(); day=in.nextInt(); DateUtil date1=new DateUtil(year,month,day); if(!date1.checkInputValidity()) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } int m=in.nextInt(); if(m<0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } System.out.println(date1.getPreviousNDays(m).showDate()); break; case 3: year=in.nextInt(); month=in.nextInt(); day=in.nextInt(); int behindyear=in.nextInt(); int behindmonth=in.nextInt(); int behindday=in.nextInt(); DateUtil lastdate=new DateUtil(year,month,day); DateUtil nowdate=new DateUtil(behindyear,behindmonth,behindday); if(lastdate.checkInputValidity()&&nowdate.checkInputValidity()) { System.out.println(lastdate.getDaysofDates(nowdate)); } else { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } break; default: System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } } }
度量:
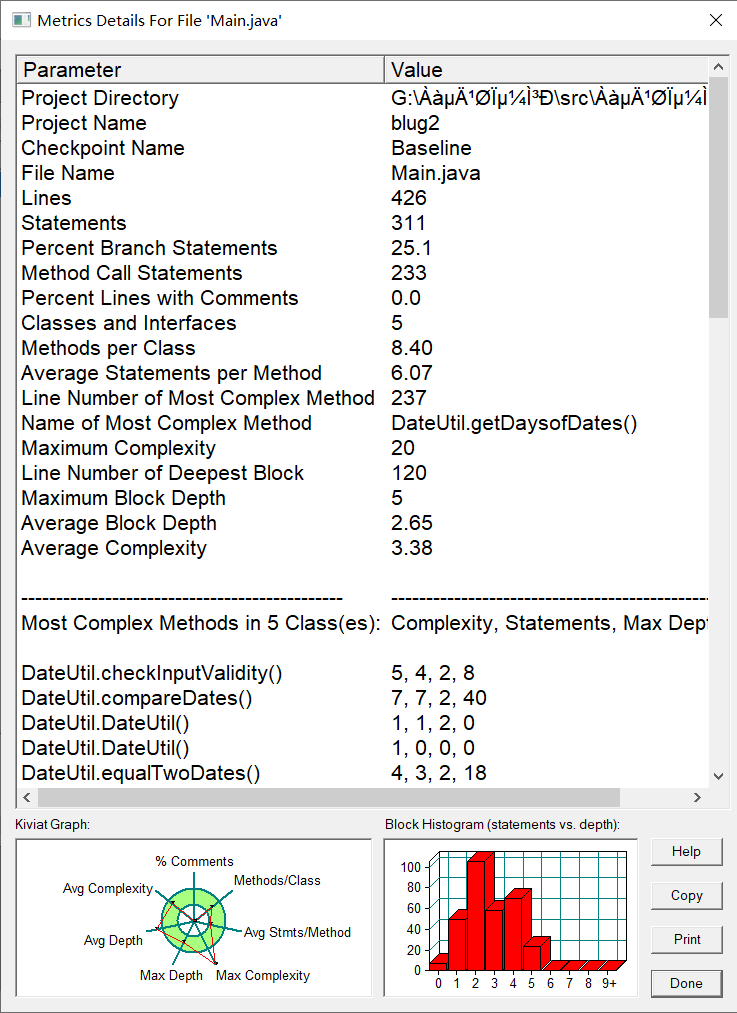
分析:这次作业比较复杂,但方法块并不深,只要理清类之间的关系还要类中方法的运用即可。
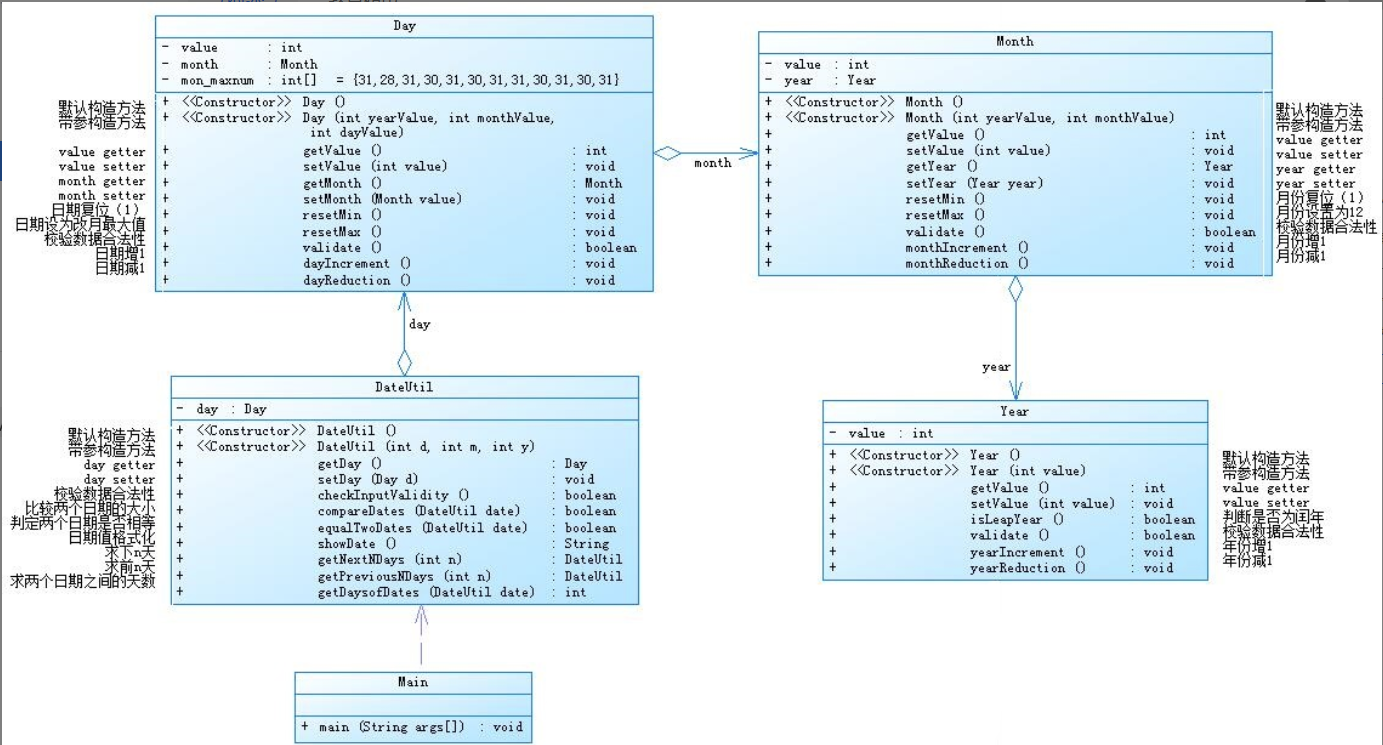
此次作业类图:
题目集5
7-5
此次作业事实上与上一次没什么不同,只是类的关系有所改变,因此就不放入代码和SourceMonitor的生成报表了。
此次作业类图:
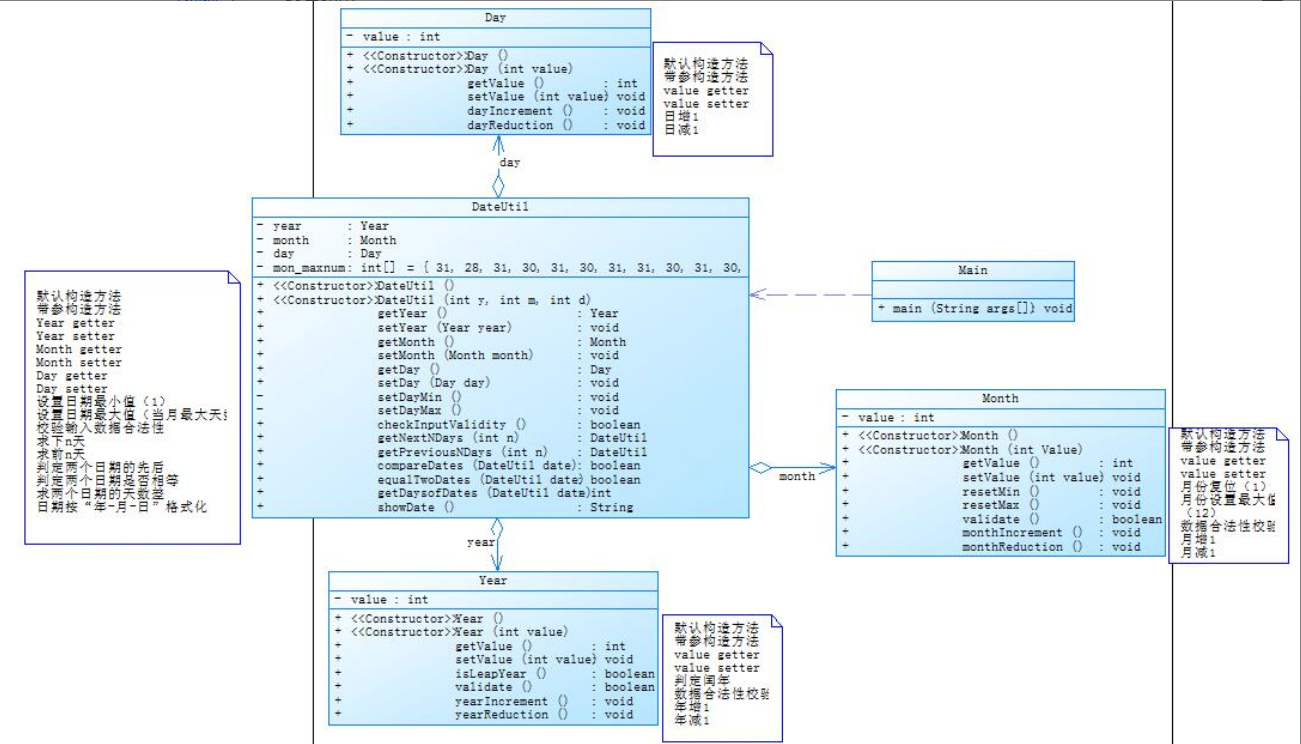
对于两次日期类聚合的分析:题目集4的7-2题是Year类放入Month类,Month类放入Day类,Day类放入DateUtil类,每个类链接在一起,旁边的类成聚合关系;而题目集5的7-5是Year类、Month类、Day类、--DateUtil类都与Main类成聚合关系。从这可以看出,题目集4的7-2题更具有逻辑性,一类套着一类,更容易让人理解,但同时也会给编译器带来负担,导致其时间复杂度可能过大,题目集5的7-5题虽没有题目集4的7-2题更具有逻辑性,但同时也减小了编译器的负担,时间复杂度可能会小点。
(二)题目集4(7-3)、题目集6(7-5、7-6)三种渐进式图形继承设计的思路与技术运用(封装、继承、多态、接口等)
题目集4
7-3
该题运用了类的继承性,以及方法重写,但要切记方法重写和方法重载的区别
该题代码如下:
import java.text.DecimalFormat; import java.util.Scanner; class Shape{ Shape(){ System.out.println("Constructing Shape"); } public double getArea() { return 0.0; } } class Circle extends Shape{ private double radius; Circle(double radius){ this.radius=radius; System.out.println("Constructing Circle"); } public double getRadius() { return radius; } public void setRadius(double radius) { this.radius = radius; } @Override public double getArea() { return Math.PI*radius*radius; } } class Rectangle extends Shape{ private double width,length; Rectangle(double width,double length){ this.length=length; this.width=width; System.out.println("Constructing Rectangle"); } public double getWidth() { return width; } public void setWidth(double width) { this.width = width; } public double getLength() { return length; } public void setLength(double length) { this.length = length; } @Override public double getArea() { return length*width; } } class Ball extends Circle{ Ball(double radius){ super(radius); System.out.println("Constructing Ball"); } @Override public double getArea() { return Math.PI*4*super.getRadius()*super.getRadius(); } public double getVolume() { return Math.PI*super.getRadius()*super.getRadius()*super.getRadius()*(4/3.00); } } class Box extends Rectangle{ private double height; Box(double width,double length,double height){ super(width,length); this.height=height; System.out.println("Constructing Box"); } public double getHeight() { return height; } public void setHeight(double height) { this.height = height; } @Override public double getArea() { return 2*super.getWidth()*super.getLength()+2*super.getLength()*height+2*super.getWidth()*height; } public double getVolume() { return super.getLength()*super.getWidth()*height; } } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in); DecimalFormat df=new DecimalFormat("0.00"); int choice=in.nextInt(); if(choice==1) { double radius=in.nextDouble(); if(radius>0) { Circle circle=new Circle(radius); System.out.println("Circle's area:"+df.format(circle.getArea())); } else { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } } else if(choice==2) { double width=in.nextDouble(); double length=in.nextDouble(); if(width>0&&length>0) { Rectangle rectangle=new Rectangle(width,length); System.out.println("Rectangle's area:"+df.format(rectangle.getArea())); } else { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } } else if(choice==3) { double radius=in.nextDouble(); if(radius>0) { Ball ball=new Ball(radius); System.out.println("Ball's surface area:"+df.format(ball.getArea())); System.out.println("Ball's volume:"+df.format(ball.getVolume())); } else { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } } else if(choice==4) { double width=in.nextDouble(); double length=in.nextDouble(); double height=in.nextDouble(); if(width>0&&length>0&&height>0) { Box box=new Box(width,length,height); System.out.println("Box's surface area:"+df.format(box.getArea())); System.out.println("Box's volume:"+df.format(box.getVolume())); } else { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } } else { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } } }
度量:
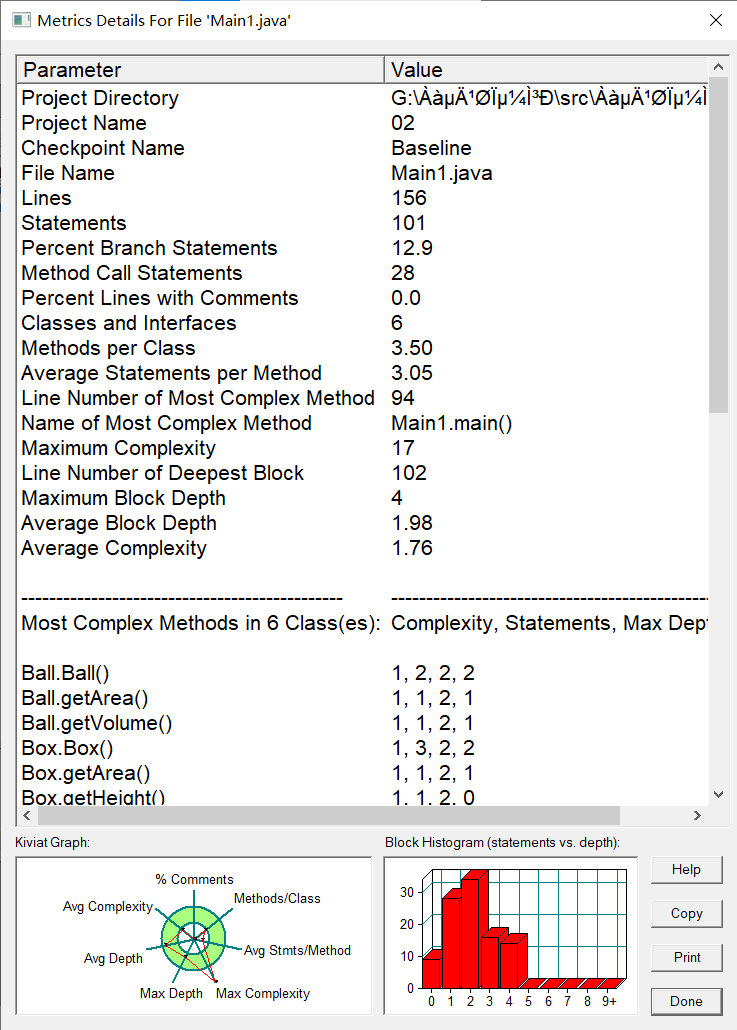
分析:这次作业难度不大,但要记住Shape类中的方法要返回值且子类要运用到方法重写,按照要求写就可以了。
题目集6
7-5
这道题按照题目指导书的要求是先创造一个抽象类,然后再在别的类中将方法补充完整,但我比较叛逆,我是先创造抽象类的接口,再在别的类中实现接口中的方法。
该题代码如下:
import java.text.DecimalFormat; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Scanner; abstract interface Shape{ public double getArea(); public boolean validate(); public String toString(); } class Circle implements Shape{ private double radius; Circle(double radius){ this.radius=radius; } public double getRadius() { return radius; } public void setRadius(double radius) { this.radius = radius; } @Override public double getArea() { return Math.PI*radius*radius; } public boolean validate() { if(radius<=0) return false; return true; } public String toString() { return ""; } } class Rectangle implements Shape{ private double width; private double length; Rectangle(double width,double length){ this.width=width; this.length=length; } public double getWidth() { return width; } public void setWidth(double width) { this.width = width; } public double getLength() { return length; } public void setLength(double length) { this.length = length; } @Override public double getArea() { return length*width; } public boolean validate() { if(width<0||length<0) return false; return true; } public String toString() { return ""; } } class Triangle implements Shape{ private double side1; private double side2; private double side3; Triangle(double side1,double side2,double side3){ this.setSide1(side1); this.setSide2(side2); this.setSide3(side3); } public double getSide1() { return side1; } public void setSide1(double side1) { this.side1 = side1; } public double getSide2() { return side2; } public void setSide2(double side2) { this.side2 = side2; } public double getSide3() { return side3; } public void setSide3(double side3) { this.side3 = side3; } @Override public double getArea() { double p=(side1+side2+side3)/2; double area=Math.sqrt(p*(p-side1)*(p-side2)*(p-side3)); return area; } public boolean validate() { if(side1<0||side2<0||side3<0) return false; if(side1+side2<=side3||side2+side3<=side1||side1+side3<=side2) return false; return true; } public String toString() { return ""; } } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in); DecimalFormat df=new DecimalFormat("0.00"); int a=in.nextInt(); int b=in.nextInt(); int c=in.nextInt(); if(a<0||b<0||c<0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } int i; double sum=0; double [] arr=new double[a+b+c]; for(i=0;i<a;i++) { double radius=in.nextDouble(); Circle circle=new Circle(radius); if(!circle.validate()) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } arr[i]=circle.getArea(); sum+=circle.getArea(); } for(i=0;i<b;i++) { double width=in.nextDouble(); double length=in.nextDouble(); Rectangle rectangle=new Rectangle(width,length); if(!rectangle.validate()) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } arr[a+i]=rectangle.getArea(); sum+=rectangle.getArea(); } for(i=0;i<c;i++) { double side1=in.nextDouble(); double side2=in.nextDouble(); double side3=in.nextDouble(); Triangle triangle=new Triangle(side1,side2,side3); if(!triangle.validate()) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } arr[a+b+i]=triangle.getArea(); sum+=triangle.getArea(); } System.out.println("Original area:"); for(i=0;i<a+b+c;i++) { System.out.print(df.format(arr[i])+" "); } System.out.println("\nSum of area:"+df.format(sum)); Arrays.parallelSort(arr); System.out.println("Sorted area:"); for(i=0;i<a+b+c;i++) { System.out.print(df.format(arr[i])+" "); } System.out.println("\nSum of area:"+df.format(sum)); } }
度量:
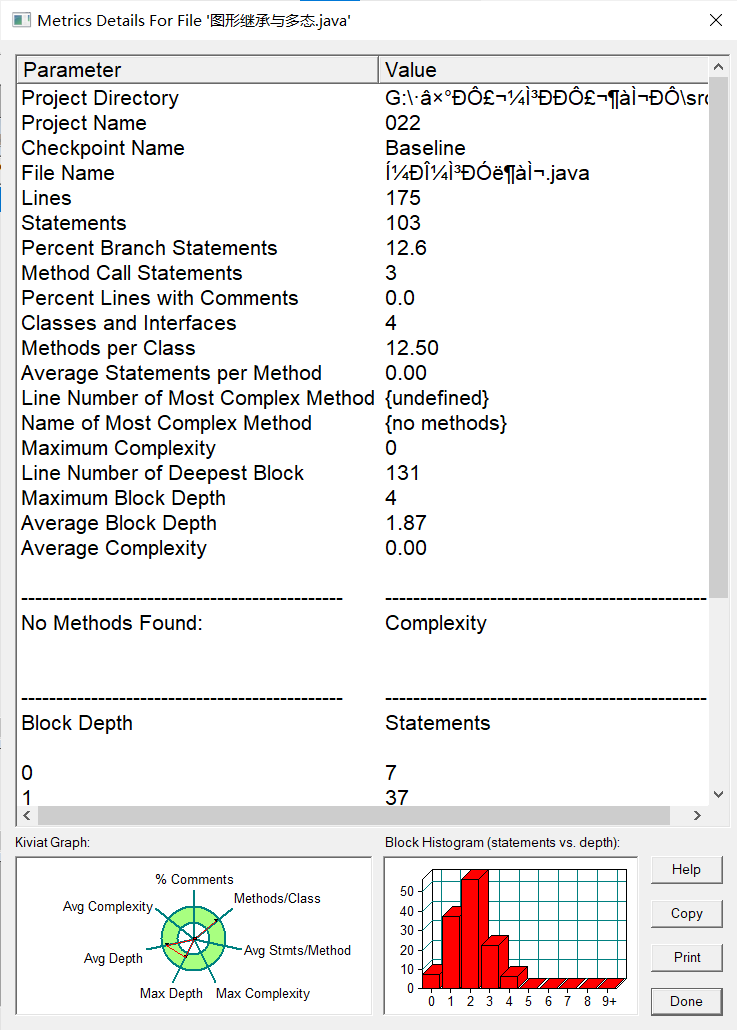
分析:该题因为用了接口的方法和多态性,使得代码复用性搞所以方法块中平均语句较少,按照其指导书的要求就可以写出。
题目集6
7-6
该题运用了接口和抽象类,并在类中实现抽象接口的方法。
该题代码如下:
import java.text.DecimalFormat; import java.util.Scanner; interface GetArea{ public double getArea(); } class Circle implements GetArea{ private double radius; public double getRadius() { return radius; } public void setRadius(double radius) { this.radius = radius; } Circle(double radius){ this.radius=radius; } Circle(){} @Override public double getArea() { return Math.PI*radius*radius; } } class Rectangle implements GetArea{ private double width; private double length; public double getWidth() { return width; } public void setWidth(double width) { this.width = width; } public double getLength() { return length; } public void setLength(double length) { this.length = length; } Rectangle(double width,double length){ this.width=width; this.length=length; } Rectangle(){} @Override public double getArea() { return width*length; } } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in); DecimalFormat df=new DecimalFormat("0.00"); double radius=in.nextDouble(); double width=in.nextDouble(); double length=in.nextDouble(); if(radius<=0||width<=0||length<=0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } else { Circle circle=new Circle(radius); Rectangle rectangle=new Rectangle(width,length); System.out.println(df.format(circle.getArea())); System.out.println(df.format(rectangle.getArea())); } in.close(); } }
度量:
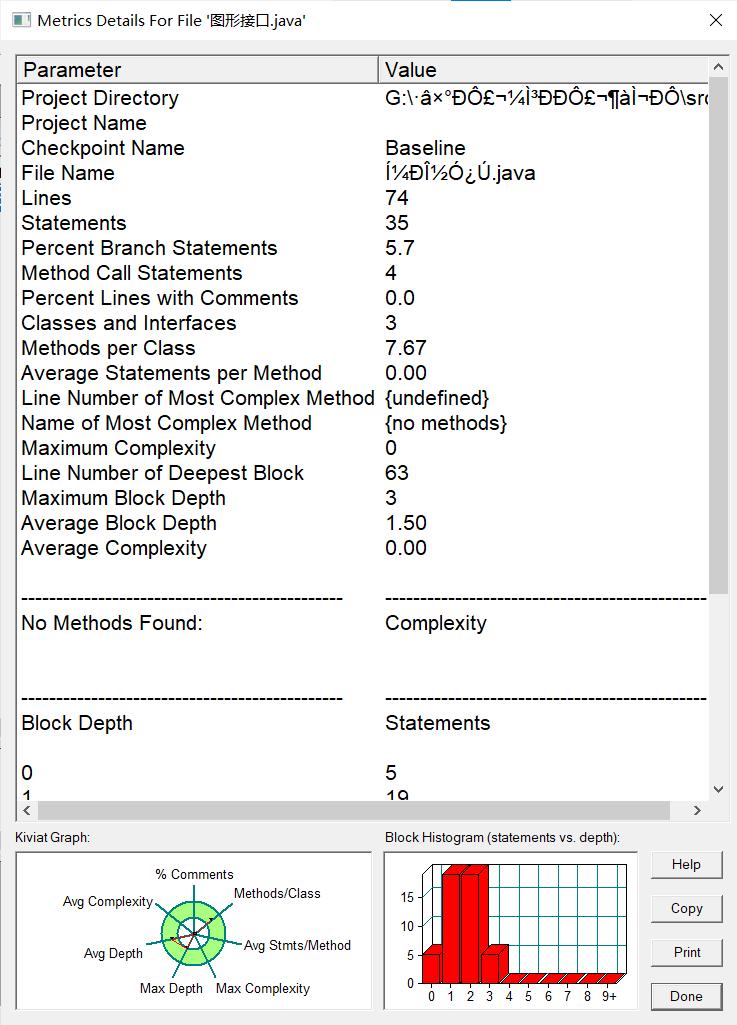
分析:该题运用了抽象接口,并实现了类的封装性、继承性和多态性,故虽然语句较多但其方法块深度较低。
(三)对三次题目集中用到的正则表达式技术的分析总结
通过使用正则表达式,可以:
- 测试字符串内的模式。
例如,可以测试输入字符串,以查看字符串内是否出现电话号码模式或信用卡号码模式。这称为数据验证。 - 替换文本。
可以使用正则表达式来识别文档中的特定文本,完全删除该文本或者用其他文本替换它。 - 基于模式匹配从字符串中提取子字符串。
可以查找文档内或输入域内特定的文本。
这三次作业中正则表达式也多次运用到,如在题目集4中的7-1题、题目集6中的7-1到7-4题都是对于正则表达式的运用。
对于正则表达式编写语法的运用如下:
|
字符 |
说明 |
|---|---|
|
\ |
将下一字符标记为特殊字符、文本、反向引用或八进制转义符。例如,"n"匹配字符"n"。"\n"匹配换行符。序列"\\\\"匹配"\\","\\("匹配"("。 |
|
^ |
匹配输入字符串开始的位置。如果设置了 RegExp 对象的 Multiline 属性,^ 还会与"\n"或"\r"之后的位置匹配。 |
|
$ |
匹配输入字符串结尾的位置。如果设置了 RegExp 对象的 Multiline 属性,$ 还会与"\n"或"\r"之前的位置匹配。 |
|
* |
零次或多次匹配前面的字符或子表达式。例如,zo* 匹配"z"和"zoo"。* 等效于 {0,}。 |
|
+ |
一次或多次匹配前面的字符或子表达式。例如,"zo+"与"zo"和"zoo"匹配,但与"z"不匹配。+ 等效于 {1,}。 |
|
? |
零次或一次匹配前面的字符或子表达式。例如,"do(es)?"匹配"do"或"does"中的"do"。? 等效于 {0,1}。 |
|
{n} |
n 是非负整数。正好匹配 n 次。例如,"o{2}"与"Bob"中的"o"不匹配,但与"food"中的两个"o"匹配。 |
|
{n,} |
n 是非负整数。至少匹配 n 次。例如,"o{2,}"不匹配"Bob"中的"o",而匹配"foooood"中的所有 o。"o{1,}"等效于"o+"。"o{0,}"等效于"o*"。 |
|
{n,m} |
m 和 n 是非负整数,其中 n <= m。匹配至少 n 次,至多 m 次。例如,"o{1,3}"匹配"fooooood"中的头三个 o。'o{0,1}' 等效于 'o?'。注意:您不能将空格插入逗号和数字之间。 |
|
? |
当此字符紧随任何其他限定符(*、+、?、{n}、{n,}、{n,m})之后时,匹配模式是"非贪心的"。"非贪心的"模式匹配搜索到的、尽可能短的字符串,而默认的"贪心的"模式匹配搜索到的、尽可能长的字符串。例如,在字符串"oooo"中,"o+?"只匹配单个"o",而"o+"匹配所有"o"。 |
|
. |
匹配除"\r\n"之外的任何单个字符。若要匹配包括"\r\n"在内的任意字符,请使用诸如"[\s\S]"之类的模式。 |
|
(pattern) |
匹配 pattern 并捕获该匹配的子表达式。可以使用 $0…$9 属性从结果"匹配"集合中检索捕获的匹配。若要匹配括号字符 ( ),请使用"\("或者"\)"。 |
|
(?:pattern) |
匹配 pattern 但不捕获该匹配的子表达式,即它是一个非捕获匹配,不存储供以后使用的匹配。这对于用"or"字符 (|) 组合模式部件的情况很有用。例如,'industr(?:y|ies) 是比 'industry|industries' 更经济的表达式。 |
|
(?=pattern) |
执行正向预测先行搜索的子表达式,该表达式匹配处于匹配 pattern 的字符串的起始点的字符串。它是一个非捕获匹配,即不能捕获供以后使用的匹配。例如,'Windows (?=95|98|NT|2000)' 匹配"Windows 2000"中的"Windows",但不匹配"Windows 3.1"中的"Windows"。预测先行不占用字符,即发生匹配后,下一匹配的搜索紧随上一匹配之后,而不是在组成预测先行的字符后。 |
|
(?!pattern) |
执行反向预测先行搜索的子表达式,该表达式匹配不处于匹配 pattern 的字符串的起始点的搜索字符串。它是一个非捕获匹配,即不能捕获供以后使用的匹配。例如,'Windows (?!95|98|NT|2000)' 匹配"Windows 3.1"中的 "Windows",但不匹配"Windows 2000"中的"Windows"。预测先行不占用字符,即发生匹配后,下一匹配的搜索紧随上一匹配之后,而不是在组成预测先行的字符后。 |
|
x|y |
匹配 x 或 y。例如,'z|food' 匹配"z"或"food"。'(z|f)ood' 匹配"zood"或"food"。 |
|
[xyz] |
字符集。匹配包含的任一字符。例如,"[abc]"匹配"plain"中的"a"。 |
|
[^xyz] |
反向字符集。匹配未包含的任何字符。例如,"[^abc]"匹配"plain"中"p","l","i","n"。 |
|
[a-z] |
字符范围。匹配指定范围内的任何字符。例如,"[a-z]"匹配"a"到"z"范围内的任何小写字母。 |
|
[^a-z] |
反向范围字符。匹配不在指定的范围内的任何字符。例如,"[^a-z]"匹配任何不在"a"到"z"范围内的任何字符。 |
|
\b |
匹配一个字边界,即字与空格间的位置。例如,"er\b"匹配"never"中的"er",但不匹配"verb"中的"er"。 |
|
\B |
非字边界匹配。"er\B"匹配"verb"中的"er",但不匹配"never"中的"er"。 |
|
\cx |
匹配 x 指示的控制字符。例如,\cM 匹配 Control-M 或回车符。x 的值必须在 A-Z 或 a-z 之间。如果不是这样,则假定 c 就是"c"字符本身。 |
|
\d |
数字字符匹配。等效于 [0-9]。 |
|
\D |
非数字字符匹配。等效于 [^0-9]。 |
|
\f |
换页符匹配。等效于 \x0c 和 \cL。 |
|
\n |
换行符匹配。等效于 \x0a 和 \cJ。 |
|
\r |
匹配一个回车符。等效于 \x0d 和 \cM。 |
|
\s |
匹配任何空白字符,包括空格、制表符、换页符等。与 [ \f\n\r\t\v] 等效。 |
|
\S |
匹配任何非空白字符。与 [^ \f\n\r\t\v] 等效。 |
|
\t |
制表符匹配。与 \x09 和 \cI 等效。 |
|
\v |
垂直制表符匹配。与 \x0b 和 \cK 等效。 |
|
\w |
匹配任何字类字符,包括下划线。与"[A-Za-z0-9_]"等效。 |
|
\W |
与任何非单词字符匹配。与"[^A-Za-z0-9_]"等效。 |
|
\xn |
匹配 n,此处的 n 是一个十六进制转义码。十六进制转义码必须正好是两位数长。例如,"\x41"匹配"A"。"\x041"与"\x04"&"1"等效。允许在正则表达式中使用 ASCII 代码。 |
|
\num |
匹配 num,此处的 num 是一个正整数。到捕获匹配的反向引用。例如,"(.)\1"匹配两个连续的相同字符。 |
|
\n |
标识一个八进制转义码或反向引用。如果 \n 前面至少有 n 个捕获子表达式,那么 n 是反向引用。否则,如果 n 是八进制数 (0-7),那么 n 是八进制转义码。 |
|
\nm |
标识一个八进制转义码或反向引用。如果 \nm 前面至少有 nm 个捕获子表达式,那么 nm 是反向引用。如果 \nm 前面至少有 n 个捕获,则 n 是反向引用,后面跟有字符 m。如果两种前面的情况都不存在,则 \nm 匹配八进制值 nm,其中 n 和 m 是八进制数字 (0-7)。 |
|
\nml |
当 n 是八进制数 (0-3),m 和 l 是八进制数 (0-7) 时,匹配八进制转义码 nml。 |
|
\un |
匹配 n,其中 n 是以四位十六进制数表示的 Unicode 字符。例如,\u00A9 匹配版权符号 (©)。 |
除了正则表达式中这些语法还有其matches、pattern类要掌握,并有替换、匹配、查找等方法,同时在我自学正则表达式中我还发现了正则表达式还有很好玩的地方即正则表达式的三种模式:贪婪模式、懒惰模式、独占模式。
下面是我对这三种模式的了解:
i. ?: 告诉引擎匹配前导字符0次或一次。事实上是表示前导字符是可选的。
ii. +: 告诉引擎匹配前导字符1次或多次。
iii. *: 告诉引擎匹配前导字符0次或多次。
iv. {min, max}: 告诉引擎匹配前导字符min次到max次。min和max都是非负整数。如果有逗号而max被省略了,则表示max没有限制;如果逗号和max都被省略了,则表示重复min次。
把以上三种模式的表达式列出如下:
|
贪婪 |
懒惰 |
独占 |
|
X? |
X?? |
X?+ |
|
X* |
X*? |
X*+ |
|
X+ |
X+? |
X++ |
|
X{n} |
X{n}? |
X{n}+ |
|
X{n,} |
X{n,}? |
X{n,}+ |
|
X{n,m} |
X{n,m}? |
X{n,m}+
|
(四)题目集5(7-4)中Java集合框架应用的分析总结
题目集5
7-4
该题主要运用java中集合框架中Map、Set、List接口,并知道java53个关键词按照正则表达式匹配输出即可。
该题代码如下:
import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.Set; import java.util.regex.Matcher; import java.util.regex.Pattern; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in); String b; StringBuilder wdm=new StringBuilder(); Map<String,Integer> map=new HashMap<String,Integer>(); String[] keywords= { "goto","const","class","interface","byte","short","int","long","float","double","char","boolean","void","true","false","null","if","else","switch","case","default","while", "do","for","break","continue","return","private","protected","public","abstract","final","static","synchronized","extends","implements","new","this","super","instanceof","try","catch","finally", "throw","throws","package","import","native","strictfp","transient","volatile","assert","enum" }; for(int i=0;;i++) { b=in.nextLine(); if(b.equals("exit")) break; if(b.matches("(.*)//(.*)")) { String []c=b.split("//"); wdm.append(c[0]+" "); } else { wdm.append(b+" "); } } String x=wdm.toString(); Pattern p=Pattern.compile("\"(.*?)\""); Matcher m=p.matcher(x); while(m.find()) { x=x.replace(m.group()," "); p=Pattern.compile("\"(.*?)\""); m=p.matcher(x); } p=Pattern.compile("/\\**(.*?)/"); m=p.matcher(x); while(m.find()) { x=x.replace(m.group()," "); m=p.matcher(x); } if(x.isEmpty()) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } x=x.replace("["," "); x=x.replace("]"," "); x=x.replace("-","a"); x=x.replace("*","a"); x=x.replace("/","a"); x=x.replace("+","a"); x=x.replace(">","a"); x=x.replace("=","a"); x=x.replace("!","a"); x=x.replace(":","a"); x=x.replace("\\","a"); x=x.replaceAll("[^a-zA-Z]", " "); String[]y=x.split("[ ' ']"); for(int i=0;i<y.length;i++) { for(int j=0;j<keywords.length;j++) { if(y[i].equals(keywords[j])) { map.put(keywords[j], 0); } } } int cnt=0; for(int i=0;i<y.length;i++) { for(int j=0;j<keywords.length;j++) { if(y[i].equals(keywords[j])) { cnt=map.get(keywords[j]); map.put(keywords[j], cnt+1); } } } Set set=map.keySet(); Object[] str=set.toArray(); Arrays.sort(str); for(Object f:str) { System.out.println(map.get(f)+"\t"+f); } } }
度量:
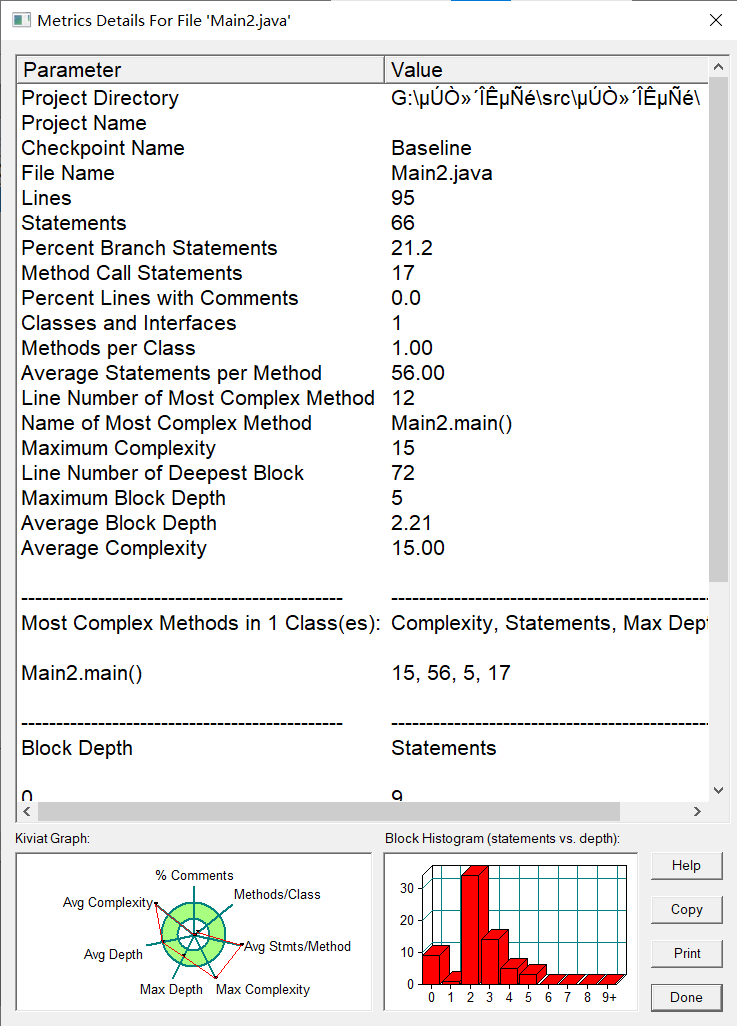
分析:该题平均复杂度比较高可能是因为用了Map、Set接口的原因,但块的深度并不高是因为主要用正则表达式的匹配、修改和列表储存。
java集合框架的应用分析:
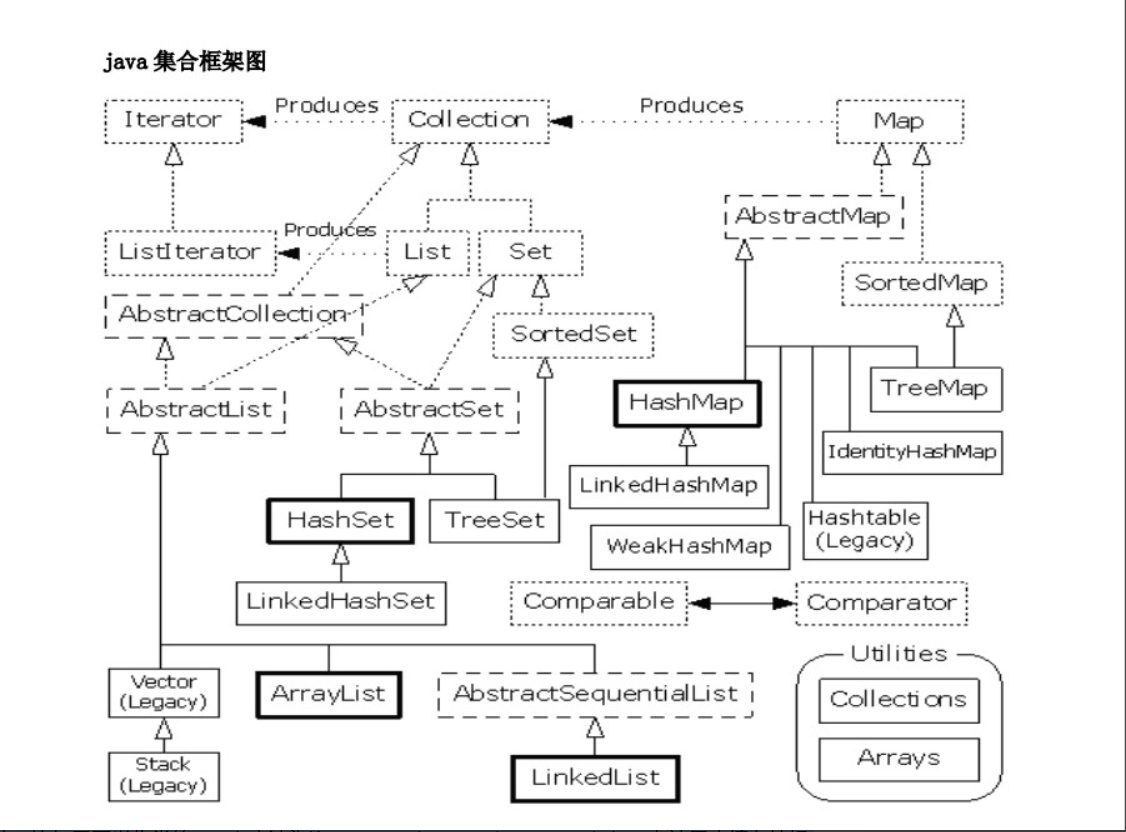
先从最常用的List接口说起,主要的实现类有ArrayList,LinkedList,Vector这三类。其中ArrayList、Vector的底层的实现是数组,而LinkedList的底层实现是链表。了解数据结构的同学应该就明白了,相对另两种而言,LinkedList相对而言在插入和删除数据时更快,而慢于查询。而ArrayList、Vector在查询上更优,慢于增删。
而这其中Vector与另两者的区别是Vector是线程安全的,因为Vector的方法是线程同步的。因此在涉及多线程编程中,例如多人抢票等情境下更为适用。
再说Set接口,Set接口与List接口的不同在于Set集合中的元素不允许重复。当Set集合存放的是字符串,整数等数据时,重复这个概念很容易理解。但是当Set集合存放的例如学生,狗这样的实体类时,怎么样才叫重复呢。这就需要人来定义了。这可以通过重写equals()方法来实现,因为Set集合是通过两个对象是否equals来判断对象是否重复的。比如重写学生类的equals方法为if(a.name==b.name)then a.equals(b)。在这里小编友情提醒,重写equals方法必须重写hashcode方法。并且这里有一个编程规范。就是两个对象equals与他们的hashcode相等最好等价。Set接口有两个实现类——HashSet与TreeSet。其中HashSet底层由HashMap实现,待会讲Map时再详述;TreeSet 底层由树实现。这两者的主要区别是TreeSet是有序的,而HashSet是无序散列的。
最后谈一谈Map接口。Map类型的数据很好理解。就是和Json一样的键值对。Map的实现类主要有HashMap与TreeMap 两种,主要的区别与HashSet与TreeSet相似。一个有序一个无序。另外这里还想提一提HashMap的底层实现。HashMap的底层实现可以认为是hash表上面挂上链表的形式,在增删元素时,先查找Key是否如果。如果不存在则新建并插入,如果存在则找到对应链表,并向对应链表插入值。
目前我对集合框架也就掌握了这么些,后面我会继续努力学习的。
三、三次作业遇到的bug及采坑心得
题目集4
这次作业第一题与上一次博客时的最后一题很相似都是运用正则表达式进行检验和输出,第二道题和第三道题难度不高,只要按照学校发的类图就可以完成了。
题目集5
这次作业前三题都比较简单并没有遇到什么BUG,但第四题学习了比较长时间的集合框架才开始做题,这题遇到了一些BUG,比如java53个关键字缺少,写第五题自己并没有遇到BUG,与上一次作业的第二题只是类的关系发生了变化而已。
题目集6
这次作业整体都比较简单,但有些同学问我方法重载和方法重写的区别,下面我就写一下我对于这两个的理解:
方法重载:
1、同一个类中
2、方法名相同,参数列表不同(参数顺序、个数、类型)
3、方法返回值、访问修饰符任意
4、与方法的参数名无关
方法重写:
1、有继承关系的子类中
2、方法名相同,参数列表相同(参数顺序、个数、类型),方法返回值相同
3、访问修饰符,访问范围需要大于等于父类的访问范围
4、与方法的参数名无关
要记住一点,方法重载的方法参数要改变,而方法重写参数必须与原来的一样。
四、改进建议
题目集4
7-1题可以将正则表达式再简略点,7-2题可以再次简化点,并不一定要按照学校发的类图来完成,可以将判断方法放在一起。
题目集5
7-4题不一定一定要使用Map、Set接口可以使用List接口来简化,用列表来动态存储正则表达式,7-5题可以适当改写减小一下时间复杂度。
题目集6
7-5题可以用抽象类的接口来完成然后用别的类来实现方法,7-6题也可以用抽象类来完成。
五、总结
这三次作业我收获颇多,对于java面向对象的概率有了更深的理解,以及加深了对于java集合框架应用的掌握,会使用抽象类和接口以及对于类的关系、类图等的运用,同时在OO的学习中也改变了我写代码不喜欢换行加空格的风格。对于日后的学习我会继续加深对于集合框架的理解,还有Set、Map、List接口的应用使其真正的成为自己的“武器”。最后也希望在学习OO的过程中能在课堂上学习到更多书上本没有的但对我编代码十分有用的知识,写到更加具有代表性的题型,扩展自己的视野。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号