数据采集与融合技术实验二
作业1
在中国气象网(http://www.weather.com.cn)给定城市集的7日天气预报,并保存在数据库。
一、实验完整代码
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
from bs4 import UnicodeDammit
import urllib.request
import sqlite3
class WeatherDB:
def openDB(self):
self.con=sqlite3.connect("weathers.db")
self.cursor=self.con.cursor()
try:
self.cursor.execute("create table weathers (wCity varchar(16),wDate varchar(16),wWeather varchar(64),wTemp varchar(32),constraint pk_weather primary key (wCity,wDate))")
except:
self.cursor.execute("delete from weathers")
def closeDB(self):
self.con.commit()
self.con.close()
def insert(self,city,date,weather,temp):
try:
self.cursor.execute("insert into weathers (wCity,wDate,wWeather,wTemp) values (?,?,?,?)" ,(city,date,weather,temp))
except Exception as err:
print(err)
def show(self):
self.cursor.execute("select * from weathers")
rows=self.cursor.fetchall()
print("%-16s%-16s%-32s%-16s" % ("city","date","weather","temp"))
for row in rows:
print("%-16s%-16s%-32s%-16s" % (row[0],row[1],row[2],row[3]))
class WeatherForecast:
def __init__(self):
self.headers = {
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 6.0 x64; en-US; rv:1.9pre) Gecko/2008072421 Minefield/3.0.2pre"}
self.cityCode={"北京":"101010100","上海":"101020100","广州":"101280101","深圳":"101280601"}
def forecastCity(self,city):
if city not in self.cityCode.keys():
print(city+" code cannot be found")
return
url="http://www.weather.com.cn/weather/"+self.cityCode[city]+".shtml"
try:
req=urllib.request.Request(url,headers=self.headers)
data=urllib.request.urlopen(req)
data=data.read()
dammit=UnicodeDammit(data,["utf-8","gbk"])
data=dammit.unicode_markup
soup=BeautifulSoup(data,"lxml")
lis=soup.select("ul[class='t clearfix'] li")
for li in lis:
try:
date=li.select('h1')[0].text
weather=li.select('p[class="wea"]')[0].text
if li==lis[0]:
temp=li.select('p[class="tem"] i')[0].text
else:
temp=li.select('p[class="tem"] span')[0].text+"/"+li.select('p[class="tem"] i')[0].text
print(city,date,weather,temp)
self.db.insert(city,date,weather,temp)
except Exception as err:
print(err)
except Exception as err:
print(err)
def process(self,cities):
self.db=WeatherDB()
self.db.openDB()
for city in cities:
self.forecastCity(city)
#self.db.show()
self.db.closeDB()
ws=WeatherForecast()
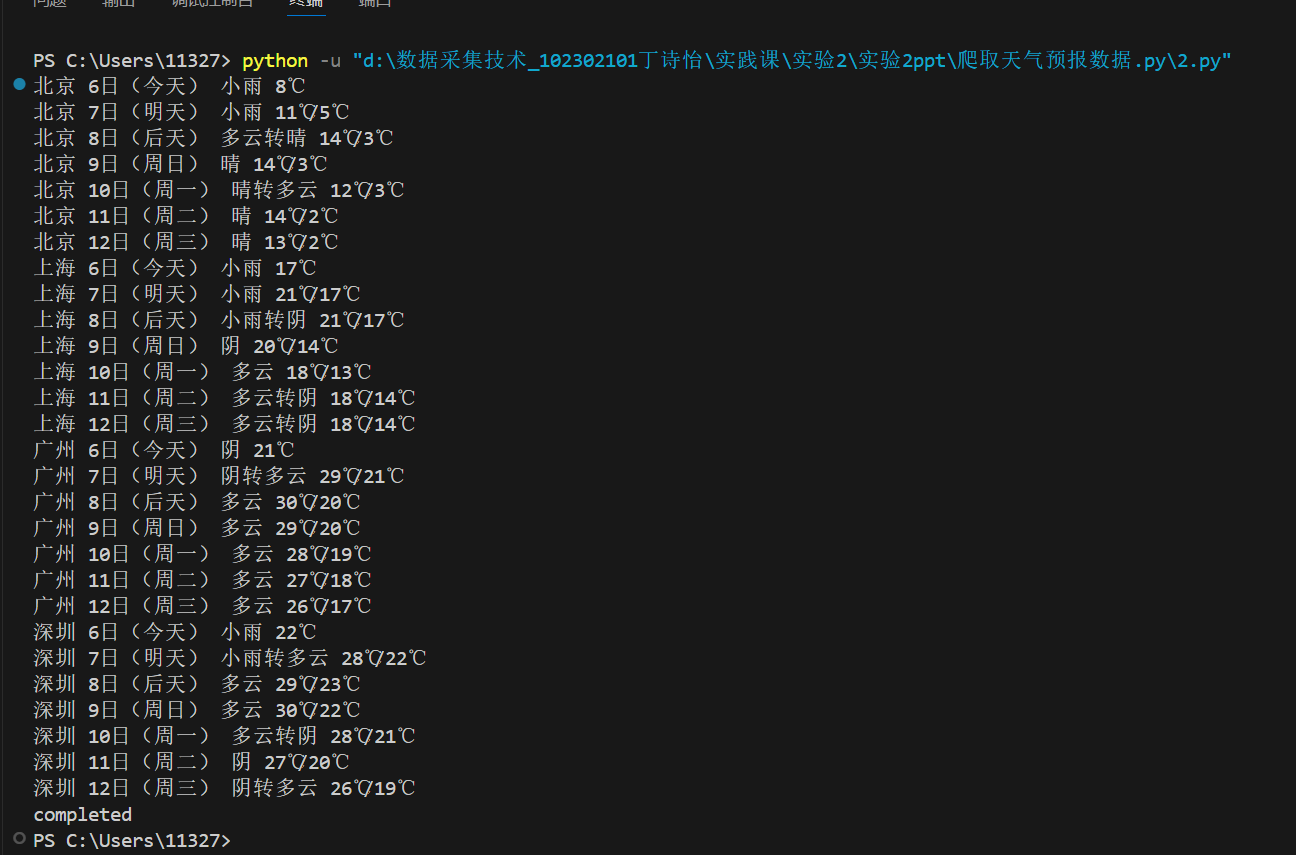
ws.process(["北京","上海","广州","深圳"])
print("completed")
结果
心得体会
通过本次实验,我熟练掌握了 BeautifulSoup 的 CSS 选择器用法
在本实验中,遇到了如下问题,解决方案如下:
爬取气温时发现,当天的气温只显示一个数值(如 "25℃"),而后续日期显示 "最高温 / 最低温"(如 "28℃/18℃"),如果统一提取会导致索引错误。通过判断当前标签是否为第一个li元素,分别处理两种格式,确保了数据提取的完整性。
作业2
用requests和BeautifulSoup库方法定向爬取股票相关信息,并存储在数据库中。
一、实验完整过程
1.打开开发者工具,搜索需要爬取的内容

2.可以发现我们需要的数据在
https://push2.eastmoney.com/api/qt/clist/get
这么一个网址下
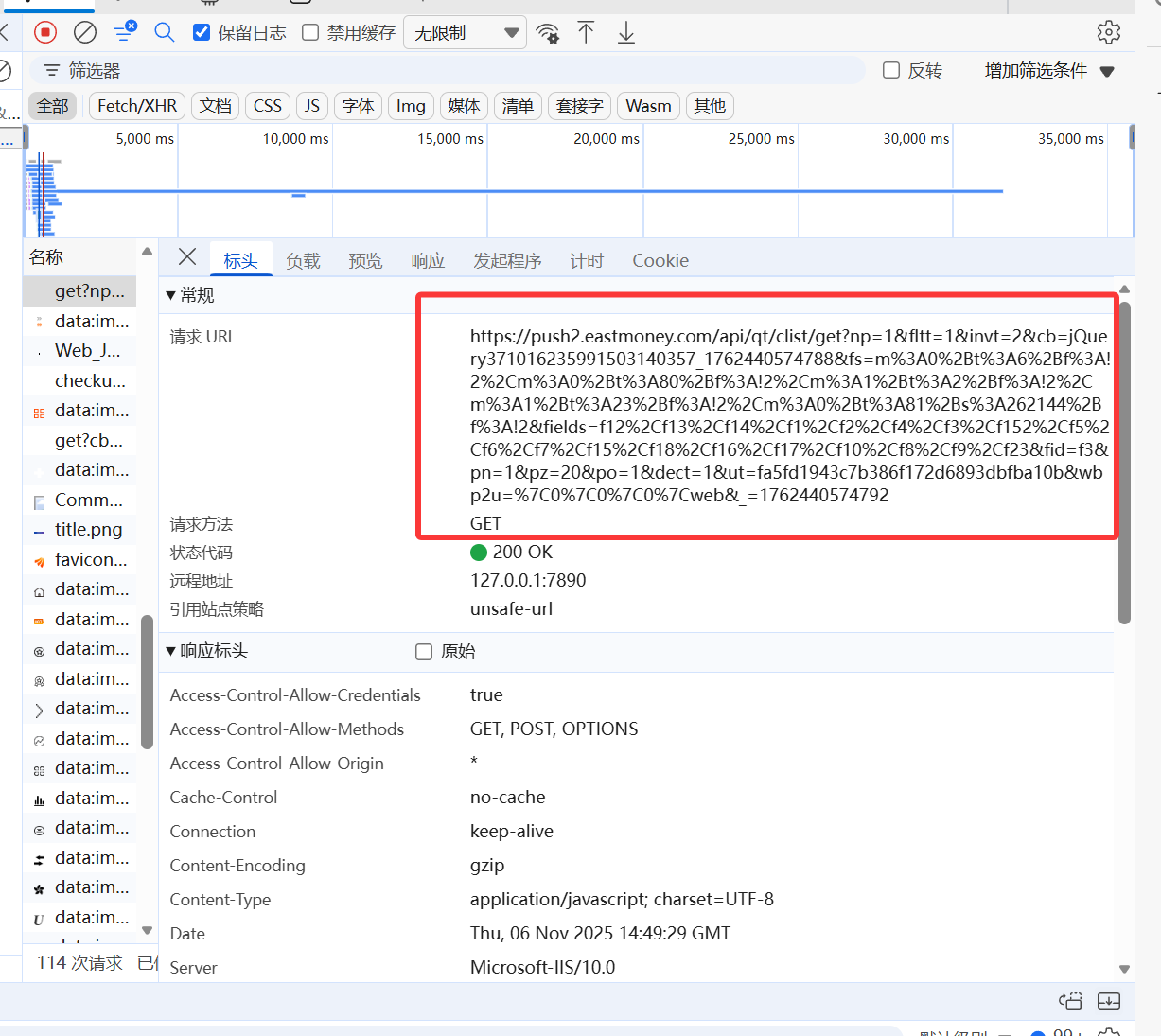
查看载荷
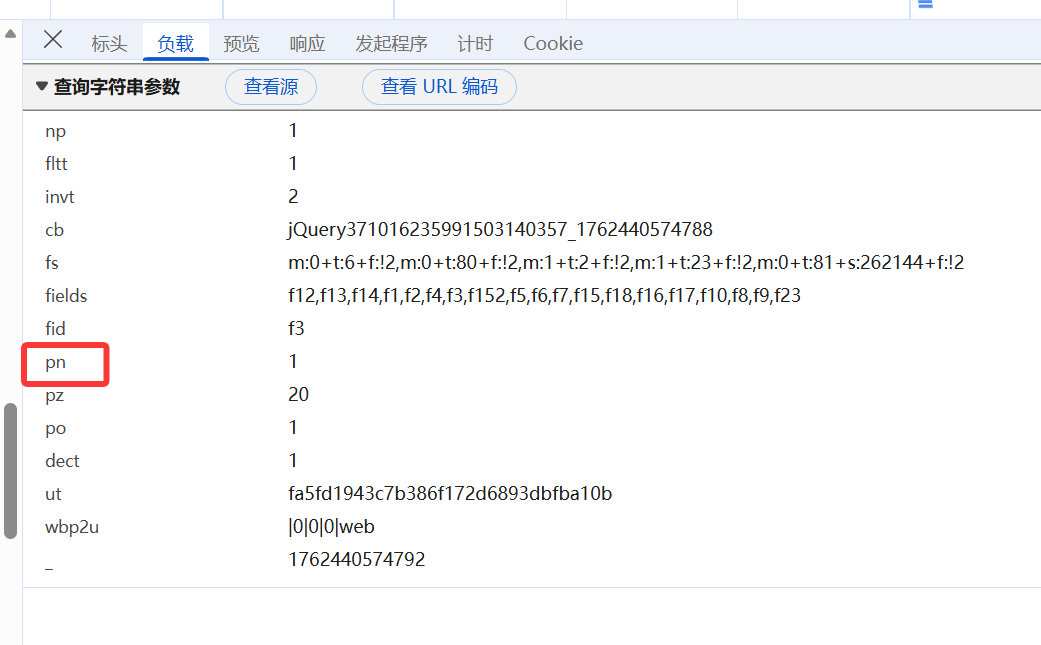
很容易发现pn是实现翻页的参数

我这里把源码提前下载到本地,防止后续因为频繁访问被反爬
因为观察到输出不太整齐,采用下面的方式使输出更加整齐
pd.set_option('display.unicode.ambiguous_as_wide', True)
pd.set_option('display.unicode.east_asian_width', True)
pd.set_option('display.max_columns', None)
pd.set_option('display.width', 200)
pd.set_option('display.precision', 2)
二、实验完整代码
import re
import pandas as pd
import json
import os
import sqlite3
from datetime import datetime
cnt = 1
def init_local_stock_db():
conn = sqlite3.connect('local_stock_data.db')
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 创建与数据字段对应的表
create_sql = '''
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS local_stock_market (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,
serial_num INTEGER NOT NULL,
stock_code TEXT NOT NULL,
stock_name TEXT NOT NULL,
latest_price FLOAT NOT NULL,
price_change TEXT NOT NULL,
price_change_rate TEXT NOT NULL,
volume TEXT NOT NULL,
turnover TEXT NOT NULL,
amplitude FLOAT NOT NULL,
highest_price FLOAT NOT NULL,
lowest_price FLOAT NOT NULL,
opening_price FLOAT NOT NULL,
previous_close FLOAT NOT NULL,
extract_time DATETIME NOT NULL
)
'''
cursor.execute(create_sql)
conn.commit()
conn.close()
def save_local_stock_data(stocks):
conn = sqlite3.connect('local_stock_data.db')
cursor = conn.cursor()
extract_time = datetime.now().strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S') # 提取时间
# 构造插入数据(与股票数据列表结构完全对应)
insert_list = [(*stock, extract_time) for stock in stocks]
# 批量插入SQL
insert_sql = '''
INSERT INTO local_stock_market (
serial_num, stock_code, stock_name, latest_price, price_change,
price_change_rate, volume, turnover, amplitude, highest_price,
lowest_price, opening_price, previous_close, extract_time
) VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)
'''
cursor.executemany(insert_sql, insert_list)
conn.commit()
conn.close()
def getOnePageFromLocal(page_num):
global cnt
file_path = "实验2ppt/股票源码.txt"
if not os.path.exists(file_path):
print(f"本地文件不存在:{file_path}")
return []
try:
with open(file_path, "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
source_content = f.read()
pat = r'"diff":\[(.*?)\]'
data_str_list = re.compile(pat, re.S).findall(source_content)
if not data_str_list or data_str_list[0].strip() == "":
print(f"第{page_num}页无有效数据")
return []
data_str = data_str_list[0]
data = json.loads(f"[{data_str}]")
stocks = []
for item in data:
stock = [
cnt,
item.get('f12', ''),
item.get('f14', ''),
round(item.get('f2', 0)/100, 2),
f"{round(item.get('f4', 0)/100, 2)}",
f"{round(item.get('f3', 0)/100, 2)}%",
f"{round(item.get('f5', 0)/10000, 2)}万",
f"{round(item.get('f6', 0)/1e8, 2)}亿",
round(item.get('f7', 0)/100, 2),
round(item.get('f15', 0)/100, 2),
round(item.get('f16', 0)/100, 2),
round(item.get('f17', 0)/100, 2),
round(item.get('f18', 0)/100, 2)
]
cnt += 1
stocks.append(stock)
print(f"已从本地文件提取第{page_num}页数据")
return stocks
except Exception as e:
print(f"处理第{page_num}页失败:{e}")
return []
def main():
init_local_stock_db()
all_stocks = []
total_pages = 1
for page in range(1, total_pages + 1):
current_page_data = getOnePageFromLocal(page)
if current_page_data:
all_stocks.extend(current_page_data)
else:
print(f"第{page}页无有效数据,跳过")
columns = ["序号", "股票代码", "股票名称", "最新价格", "涨跌额", "涨跌幅(%)",
"成交量", "成交额", "振幅(%)", "最高", "最低", "今开", "昨收"]
df = pd.DataFrame(all_stocks, columns=columns)
pd.set_option('display.unicode.ambiguous_as_wide', True)
pd.set_option('display.unicode.east_asian_width', True)
pd.set_option('display.max_columns', None)
pd.set_option('display.width', 200)
pd.set_option('display.precision', 2)
# 输出整齐的表格
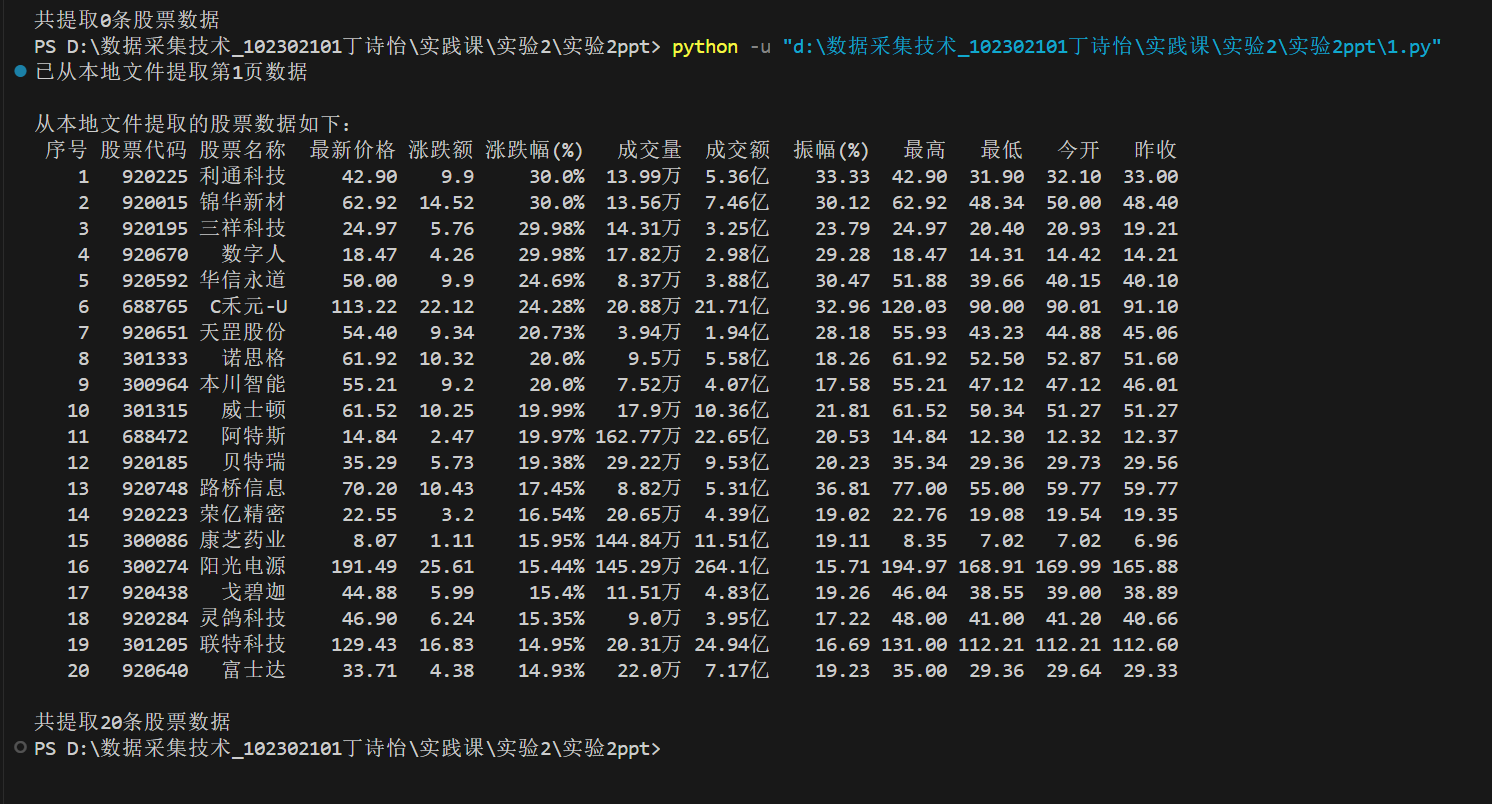
print("\n从本地文件提取的股票数据如下:")
print(df.to_string(index=False)) # 不显示索引列
print(f"\n共提取{len(df)}条股票数据")
save_local_stock_data(all_stocks)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
三、结果
四、实验心得
1.我学会了在谷歌浏览器中进入F12调试模式进行抓包,查找股票列表加载使用的url,并分析api返回的值,并根据所要求的参数可适当更改api的请求参数。根据URL可观察请求的参数f1、f2可获取不同的数值,根据情况可删减请求的参数。
2.我学习了怎么对齐输出
3.API 返回的字段没有明确说明(如f2、f3等),一开始不知道每个字段对应的含义。通过对比网页显示的数据和 API 返回的数值,逐个验证字段映射关系(如f2除以 100 后与网页显示的 “最新价格” 一致),最终梳理出完整的字段对应表,明白了 “逆向验证” 是解析未知字段的有效方法。
作业3
爬取中国大学2021主榜(https://www.shanghairanking.cn/rankings/bcur/2021)所有院校信息,并存储在数据库中,同时将浏览器F12调试分析的过程录制Gif加入至博客中。
一、实验完整过程
上网搜索一下,可以知道爬取这个网页所需要的API url
https://www.shanghairanking.cn/api/pub/v1/bcur?bcur_type=11&year=2020

通过上面步骤在开发者工具里面寻找,却找不到,可以知道这个接口被隐藏了,不过还是可以使用

因为这个接口被隐藏了,所以这次作业不用这个方式爬取数据,虽然这个方式更简单一点
搜索我们要爬的数据,可以找到一个js文件

但是可以看见里面只有score和学校名字显式的写出来了,而其他我们需要的数据却被英文字符隐藏了。
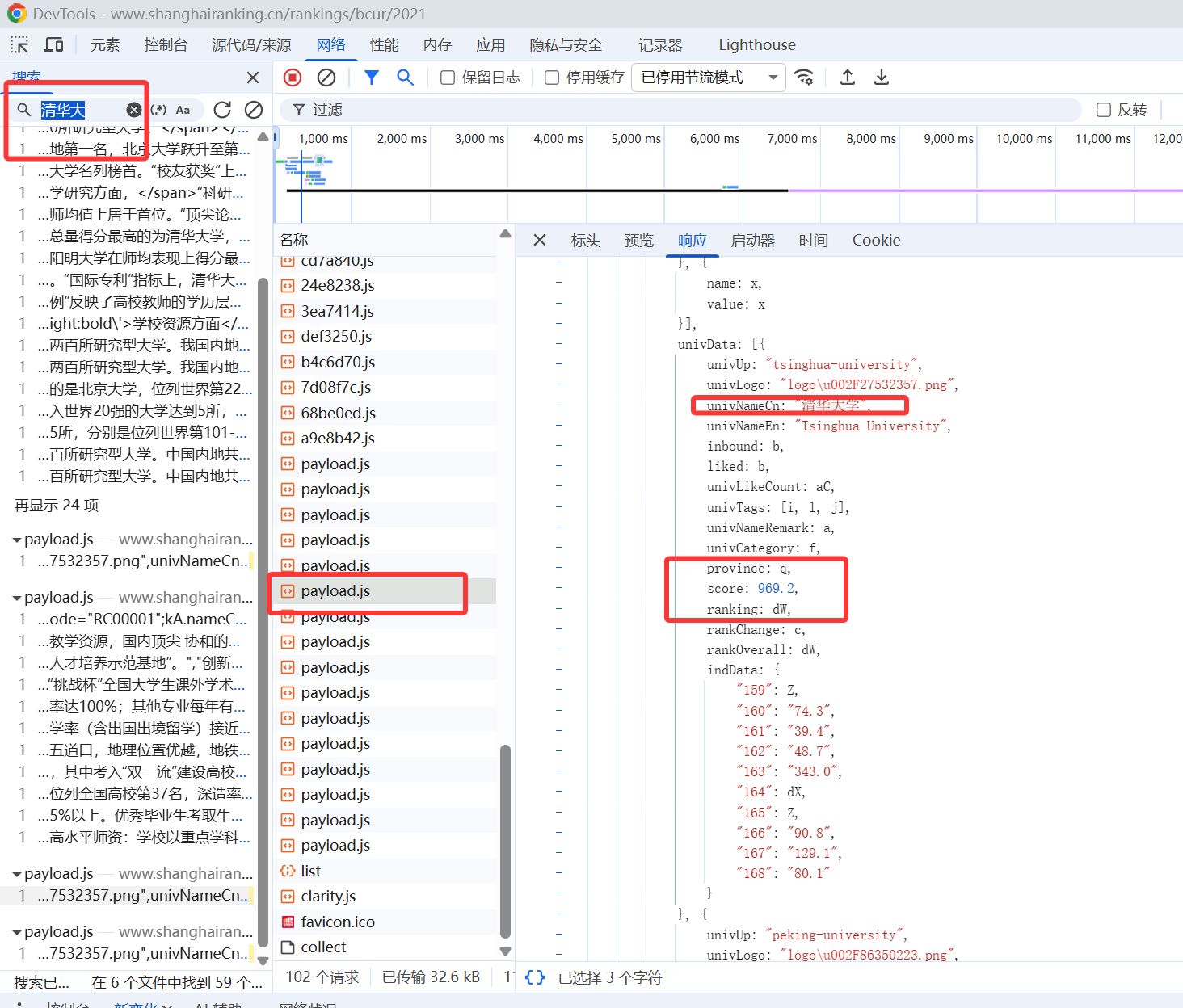
通过观察,其实可以发现里面存在一种键值映射,我们只需要找出这个映射就可以了
如下
province_mapping = {
'k': '江苏', 'n': '山东', 'o': '河南', 'p': '河北', 'q': '北京', 'r': '辽宁', 's': '陕西', 't': '四川', 'u': '广东',
'v': '湖北', 'w': '湖南', 'x': '浙江', 'y': '安徽', 'z': '江西', 'A': '黑龙江', 'B': '吉林', 'D': '上海', 'F': '福建', 'E': '山西',
'H': '云南', 'G': '广西', 'I': '贵州', 'J': '甘肃', 'K': '内蒙古', 'L': '重庆', 'N': '天津', 'O': '新疆', 'az': '宁夏','aA': '青海','aB': '西藏'
}
univ_category_mapping = {
'f': '综合', 'e': '理工', 'h': '师范', 'm': '农业', 'S': '林业',
}
按照之前的方法爬取,然后将爬取的内容在字典里寻找映射,就是我们需要的数据
二、实验完整代码
import re
import requests
import sqlite3
from datetime import datetime
province_mapping = {
'k': '江苏', 'n': '山东', 'o': '河南', 'p': '河北', 'q': '北京', 'r': '辽宁', 's': '陕西', 't': '四川', 'u': '广东',
'v': '湖北', 'w': '湖南', 'x': '浙江', 'y': '安徽', 'z': '江西', 'A': '黑龙江', 'B': '吉林', 'D': '上海', 'F': '福建', 'E': '山西',
'H': '云南', 'G': '广西', 'I': '贵州', 'J': '甘肃', 'K': '内蒙古', 'L': '重庆', 'N': '天津', 'O': '新疆', 'az': '宁夏','aA': '青海','aB': '西藏'
}
univ_category_mapping = {
'f': '综合', 'e': '理工', 'h': '师范', 'm': '农业', 'S': '林业',
}
url = 'https://www.shanghairanking.cn/_nuxt/static/1762223212/rankings/bcur/2021/payload.js'
header = {
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/120.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
}
#数据库初始化函数
def init_database():
conn = sqlite3.connect('university_rankings_2021.db')
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 排名、学校、省市、类型、总分、爬取时间
create_table_sql = '''
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS bcur_2021_main (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,
ranking INTEGER NOT NULL,
university_name TEXT NOT NULL,
province TEXT NOT NULL,
category TEXT NOT NULL,
total_score FLOAT NOT NULL,
crawl_time DATETIME NOT NULL
)
'''
cursor.execute(create_table_sql)
conn.commit()
conn.close()
print("数据库初始化完成!")
#数据存入数据库函数
def save_to_database(results):
conn = sqlite3.connect('university_rankings_2021.db')
cursor = conn.cursor()
crawl_time = datetime.now().strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S') # 记录爬取时间
data_list = []
for idx, data in enumerate(results, start=1):
school, province, category, score = data
data_list.append((idx, school, province, category, score, crawl_time))
insert_sql = '''
INSERT INTO bcur_2021_main (ranking, university_name, province, category, total_score, crawl_time)
VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)
'''
cursor.executemany(insert_sql, data_list)
conn.commit()
conn.close()
#爬虫函数
def crawl_and_process():
resp = requests.get(url, headers=header)
resp.raise_for_status()
resp.encoding = resp.apparent_encoding
obj = re.compile(
r'univNameCn:"(?P<univNameCn>[^"]+)",'
r'.*?'
r'univCategory:(?P<univCategory>[^,]+),'
r'.*?'
r'province:(?P<province>[^,]+),'
r'.*?'
r'score:(?P<score>[^,]+),'
, re.S)
results = []
for it in obj.finditer(resp.text):
univNameCn = it.group('univNameCn').strip().strip('"')
univCategory = it.group('univCategory').strip().strip('"')
province_code = it.group('province').strip().strip('"')
score_str = it.group('score').strip().strip('"')
mapped_province = province_mapping.get(province_code, '其他')
mapped_category = univ_category_mapping.get(univCategory, '其他')
if univNameCn and score_str.replace('.', '').isdigit():
results.append((univNameCn, mapped_province, mapped_category, float(score_str)))
results.sort(key=lambda x: x[3], reverse=True)
return results
def main():
init_database()
results = crawl_and_process()
print("\n{:<4} {:<20} {:<8} {:<6} {:<8}".format('排名', '学校', '省市', '类型', '总分'))
print("-" * 56)
for idx, data in enumerate(results, start=1):
school, province, category, score = data
print("{:<4} {:<20} {:<8} {:<6} {:<8.1f}".format(
idx, school, province, category, score
))
save_to_database(results)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
三、结果
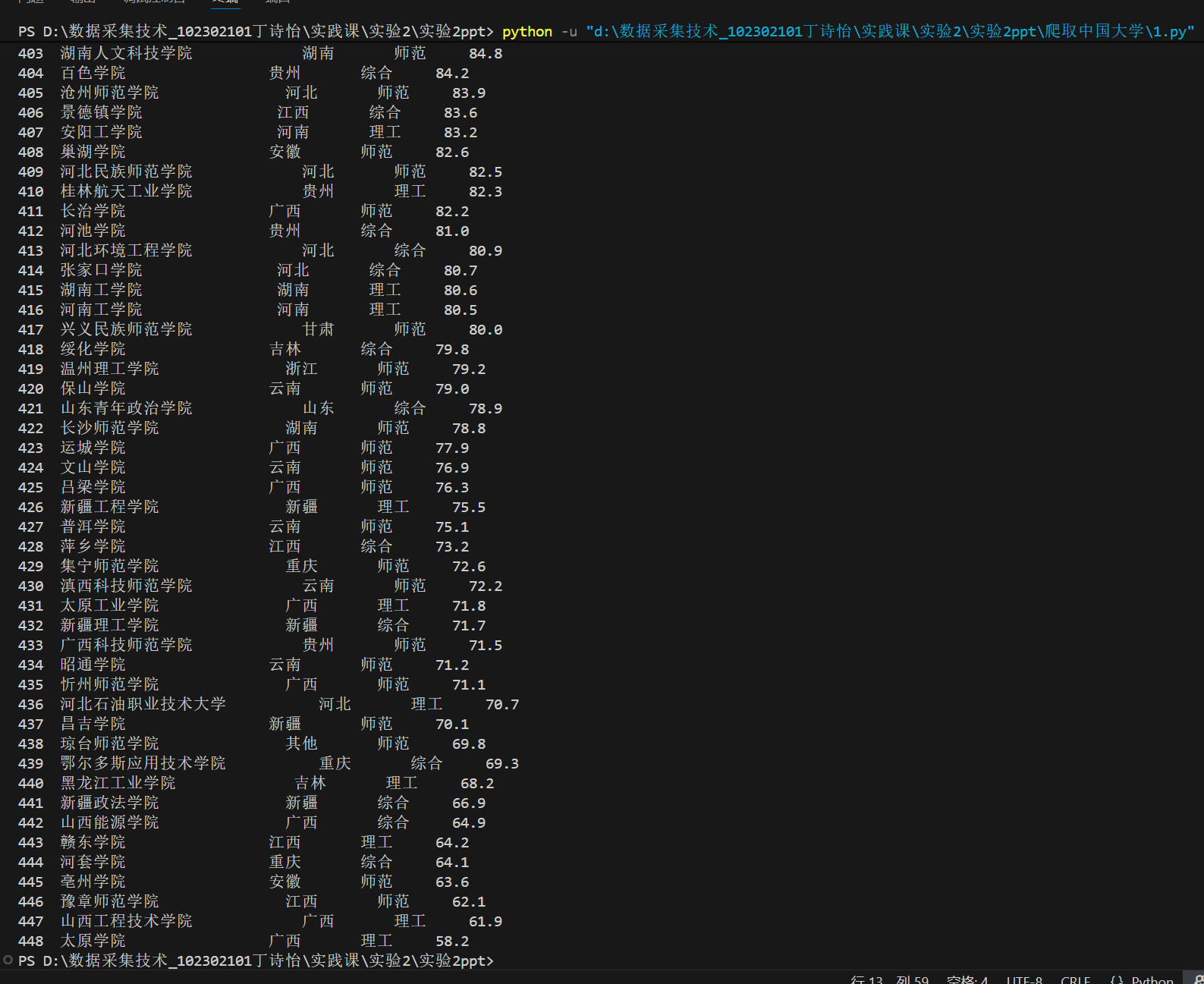
四、实验心得
JS 文件中省市和类型以短字符编码存储,没有任何说明文档,这是本次实验最大的困难。我通过 “抽样对比” 的方法 —— 先在页面上找到已知信息的学校(如 “北京大学” 属于北京、综合类),再在 JS 中查找该学校对应的编码(province:"q"、univCategory:"f"),逐步积累编码与中文的对应关系,最终整理出完整的映射字典。这个过程让我明白,面对无文档的隐藏数据,逆向对比是有效的破解方法。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号