cs143 编译原理
http://web.stanford.edu/class/cs143/
lab是手搓一个cool编译器
PA2词法分析 lexer
flex:https://blog.csdn.net/hczhiyue/article/details/20483209
flex定义了一系列词法规则,通过 flex example.flex编译后生成c文件lex.yy.c
flex包含用%%隔开的三个段:
- 定义段(definitions)
类似于define,给一类字符定义一个名字 - 规则段(rules)
匹配到模式(pattern)就执行后面c语句的动作(action) - 用户代码段(user code)
编译之后的main部分
没有的话编译的时候要加上 - lfl 的连接库参数
这部分会被原样放进lex.yy.c
https://blog.csdn.net/lvxiangyu11/article/details/102785259
在这一步将找出明显的语法错误,将源码分解为<Identifier, token>对和词汇表
匹配主要是靠有穷自动机(finite automation,FA),实现的,有两种:
- 确定性有穷自动机(DFA)。特点:从每一个状态只能发出一条具有某个符号的边 —— 不能出现同一个符号出现在同一状态发出的两条边上。
感觉有点像AC自动机,不过没有返回father的边(失配就要报错了) - 非确定性有穷自动机(NFA)。 特点:允许从一个状态发出多条具有相同符号的边,甚至允许发出标有ε(表示空)符号的边,即NFA可以不输入任何字符就自动沿ε边转换到下一个状态。
NFA与DFA 等价,且NFA 可以转化为 DFA - 状态表:把自动机看成有向图,状态表就是这个图的联通数组这样
/*
* The scanner definition for COOL.
*/
/*
* Stuff enclosed in %{ %} in the first section is copied verbatim to the
* output, so headers and global definitions are placed here to be visible
* to the code in the file. Don't remove anything that was here initially
*/
%{
#include <cool-parse.h>
#include <stringtab.h>
#include <utilities.h>
/* The compiler assumes these identifiers. */
#define yylval cool_yylval
#define yylex cool_yylex
/* Max size of string constants */
#define MAX_STR_CONST 1025
#define YY_NO_UNPUT /* keep g++ happy */
extern FILE *fin; /* we read from this file */
/* define YY_INPUT so we read from the FILE fin:
* This change makes it possible to use this scanner in
* the Cool compiler.
*/
#undef YY_INPUT
#define YY_INPUT(buf,result,max_size) \
if ( (result = fread( (char*)buf, sizeof(char), max_size, fin)) < 0) \
YY_FATAL_ERROR( "read() in flex scanner failed");
char string_buf[MAX_STR_CONST]; /* to assemble string constants */
char *string_buf_ptr;
extern int curr_lineno;
extern int verbose_flag;
extern YYSTYPE cool_yylval;
/*
* Add Your own definitions here
*/
/* record nested comment layer */
static int comment_layer = 0;
%}
/*
* Define names for regular expressions here.
*/
DIGIT [0-9]
%Start COMMENT
%Start INLINE_COMMENT
%Start STRING
%%
/* =================
* Nested comments
* =================
*/
/* begin a comment or nested comment */
<INITIAL,COMMENT,INLINE_COMMENT>"(*" {
comment_layer++;
BEGIN COMMENT;
}
/* if we met *) in (the outermost) comment */
<COMMENT>"*)" {
comment_layer--;
if(comment_layer == 0) {
BEGIN 0; }
}
/* any character other than '\n','(','*' is ok */
<COMMENT>[^\n(*]* { }
/* ( or ) or * that appears only once */
<COMMENT>[()*] { }
<COMMENT>\n { curr_lineno++; }
/*
* Error handling in comment
*/
"*)" {
cool_yylval.error_msg = "Unmatched *)";
return ERROR;
}
<COMMENT><<EOF>> {
cool_yylval.error_msg = "EOF in comment";
BEGIN 0;
return ERROR;
}
/* ===============
* inline comments
* ===============
*/
/* if seen "--", start inline comment */
<INITIAL>"--" { BEGIN INLINE_COMMENT; }
/* any character other than '\n' is a nop in inline comments */
<INLINE_COMMENT>[^\n]* { }
/* if seen '\n' in inline comment, the comment ends */
<INLINE_COMMENT>\n {
curr_lineno++;
BEGIN 0;
}
/* =========
* STR_CONST
* =========
* String constants (C syntax)
* Escape sequence \c is accepted for all characters c. Except for
* \n \t \b \f, the result is c.
*
*/
/* if seen '\"', start string */
<INITIAL>\" {
BEGIN STRING;
yymore();
}
/* Cannot read '\\' '\"' '\n' */
<STRING>[^\\\"\n]* { yymore(); }
/* normal escape characters, not \n */
<STRING>\\[^\n] { yymore(); }
/* seen a '\\' at the end of a line, the string continues */
<STRING>\\\n {
curr_lineno++;
yymore();
}
/* meet EOF in the middle of a string, error */
<STRING><<EOF>> {
yylval.error_msg = "EOF in string constant";
BEGIN 0;
yyrestart(yyin);
return ERROR;
}
/* meet a '\n' in the middle of a string without a '\\', error */
<STRING>\n {
yylval.error_msg = "Unterminated string constant";
BEGIN 0;
curr_lineno++;
return ERROR;
}
/* string ends, we need to deal with some escape characters */
<STRING>\" {
char* ptr = yytext;
ptr++;
string_buf_ptr = string_buf;
int string_len = 0;
while( *ptr != '"' && string_len < MAX_STR_CONST ) {
if( *ptr == '\0' ) {
cool_yylval.error_msg = "String contains null character";
BEGIN 0;
return ERROR;
}
else if( *ptr == '\\' ){
ptr++;
switch(*ptr){
case 'b':
*string_buf_ptr++ = '\b';
break;
case 't':
*string_buf_ptr++ = '\t';
break;
case 'f':
*string_buf_ptr++ = '\f';
break;
case 'n':
*string_buf_ptr++ = '\n';
break;
case '\0':
cool_yylval.error_msg = "String contains null character";
BEGIN 0;
return ERROR;
default:
*string_buf_ptr++ = *ptr;
break;
}
ptr++; string_len++;
}else{
*string_buf_ptr++ = *ptr++;
string_len++;
}
}
if( string_len >= MAX_STR_CONST ) {
cool_yylval.error_msg = "String constant too long";
BEGIN 0;
return ERROR;
}
*string_buf_ptr++ = '\0';
cool_yylval.symbol = stringtable.add_string(string_buf);
BEGIN 0;
return STR_CONST;
}
/*
* The multiple-character operators.
*/
/* =========
* operators
* =========
*/
"=>" { return (DARROW); }
"<-" { return (ASSIGN); }
"<=" { return (LE); }
/* ========
* keywords
* ========
* Keywords are case-insensitive except for the values true and false,
* which must begin with a lower-case letter.
*/
/* apply i option for case-insensitive */
(?i:class) { return CLASS; }
(?i:else) { return ELSE; }
(?i:fi) { return FI; }
(?i:if) { return IF; }
(?i:in) { return IN; }
(?i:inherits) { return INHERITS; }
(?i:let) { return LET; }
(?i:loop) { return LOOP; }
(?i:pool) { return POOL; }
(?i:then) { return THEN; }
(?i:while) { return WHILE; }
(?i:case) { return CASE; }
(?i:esac) { return ESAC; }
(?i:of) { return OF; }
(?i:new) { return NEW; }
(?i:isvoid) { return ISVOID; }
(?i:not) { return NOT; }
/* INT_CONST */
{DIGIT}+ {
cool_yylval.symbol = inttable.add_string(yytext);
return INT_CONST;
}
/* BOOL_CONST */
t(?i:rue) {
cool_yylval.boolean = 1;
return BOOL_CONST;
}
f(?i:alse) {
cool_yylval.boolean = 0;
return BOOL_CONST;
}
/* only differences between type and object id is the leading char case */
/* TYPEID */
/* Class names begin with an uppercase letter. */
[A-Z][A-Za-z0-9_]* {
cool_yylval.symbol = idtable.add_string(yytext);
return TYPEID;
}
/* OBJECTID */
[a-z][A-Za-z0-9_]* {
cool_yylval.symbol = idtable.add_string(yytext);
return OBJECTID;
}
/* ========
* others
* ========
*/
/* White Space */
[ \f\r\t\v]+ { }
/* New Line */
"\n" { curr_lineno++; }
/* all allowed single character symbols */
[:;{}().+\-*/<,~@=] { return *yytext; }
. {
cool_yylval.error_msg = yytext;
return ERROR;
}
%%
PA3语法分析 parser
把字符串转换为数据结构
可以过滤掉排列等error
最后得到一个近似语法树但忽略一些细节的AST语法树。
yacc:是Unix/Linux上一个用来生成编译器的编译器(编译器代码生成器)。 yacc生成的编译器主要是用C语言写成的语法解析器(Parser),需要与词法解析器Lex一起使用,再把两部份产生出来的C程序一并编译。
bison:https://www.cnblogs.com/pinkman/p/3179056.html
https://happyers.top/compiler/bison-parser/
bison确定性LR(1)算法在某一特定语法规则点上,不能决定这一步是归约还是移近。例如:
expr: id | id '+' id;
这样在第一个id的时候,不知道是归约还是移近'+'。这就是众所周知的reduce/rduce和shift/reduce冲突。因为语法改成LR(1)比较复杂,所以GLR分析器运用而生。它大概的原理是,当遇到冲突的时候,那么几条路都会试着走,试着走是不执行动作。如果只有一条路走通了,那么就执行动作,舍弃其它路子;如果都没有走通,那么就报语法错误;如果多余一条都走通,把相同规约合并,bison可能根据动作优先级来执行,也可能都会执行。
通常使用自下而上,左递归的bison,核心也是匹配模式串的自动机,然后处理的时候用映射表。
生成AST:递归下降,从左到右。先序遍历地生成Terminals
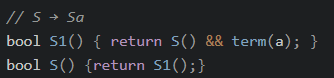
消除左递归,像下面这样的改成右递归
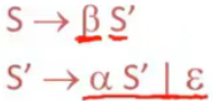
/*
* cool.y
* Parser definition for the COOL language.
*
*/
%{
#include <iostream>
#include "cool-tree.h"
#include "stringtab.h"
#include "utilities.h"
extern char *curr_filename;
/* Locations */
#define YYLTYPE int /* the type of locations */
#define cool_yylloc curr_lineno /* use the curr_lineno from the lexer
for the location of tokens */
extern int node_lineno; /* set before constructing a tree node
to whatever you want the line number
for the tree node to be */
#define YYLLOC_DEFAULT(Current, Rhs, N) \
Current = Rhs[1]; \
node_lineno = Current;
#define SET_NODELOC(Current) \
node_lineno = Current;
/* IMPORTANT NOTE ON LINE NUMBERS
*********************************
* The above definitions and macros cause every terminal in your grammar to
* have the line number supplied by the lexer. The only task you have to
* implement for line numbers to work correctly, is to use SET_NODELOC()
* before constructing any constructs from non-terminals in your grammar.
* Example: Consider you are matching on the following very restrictive
* (fictional) construct that matches a plus between two integer constants.
* (SUCH A RULE SHOULD NOT BE PART OF YOUR PARSER):
plus_consts : INT_CONST '+' INT_CONST
* where INT_CONST is a terminal for an integer constant. Now, a correct
* action for this rule that attaches the correct line number to plus_const
* would look like the following:
plus_consts : INT_CONST '+' INT_CONST
{
// Set the line number of the current non-terminal:
// ***********************************************
// You can access the line numbers of the i'th item with @i, just
// like you acess the value of the i'th exporession with $i.
//
// Here, we choose the line number of the last INT_CONST (@3) as the
// line number of the resulting expression (@$). You are free to pick
// any reasonable line as the line number of non-terminals. If you
// omit the statement @$=..., bison has default rules for deciding which
// line number to use. Check the manual for details if you are interested.
@$ = @3;
// Observe that we call SET_NODELOC(@3); this will set the global variable
// node_lineno to @3. Since the constructor call "plus" uses the value of
// this global, the plus node will now have the correct line number.
SET_NODELOC(@3);
// construct the result node:
$$ = plus(int_const($1), int_const($3));
}
*/
void yyerror(char *s); /* defined below; called for each parse error */
extern int yylex(); /* the entry point to the lexer */
/************************************************************************/
/* DONT CHANGE ANYTHING IN THIS SECTION */
Program ast_root; /* the result of the parse */
Classes parse_results; /* for use in semantic analysis */
int omerrs = 0; /* number of errors in lexing and parsing */
%}
/* A union of all the types that can be the result of parsing actions. */
%union {
Boolean boolean;
Symbol symbol;
Program program;
Class_ class_;
Classes classes;
Feature feature;
Features features;
Formal formal;
Formals formals;
Case case_;
Cases cases;
Expression expression;
Expressions expressions;
char *error_msg;
}
/*
Declare the terminals; a few have types for associated lexemes.
The token ERROR is never used in the parser; thus, it is a parse
error when the lexer returns it.
The integer following token declaration is the numeric constant used
to represent that token internally. Typically, Bison generates these
on its own, but we give explicit numbers to prevent version parity
problems (bison 1.25 and earlier start at 258, later versions -- at
257)
*/
%token CLASS 258 ELSE 259 FI 260 IF 261 IN 262
%token INHERITS 263 LET 264 LOOP 265 POOL 266 THEN 267 WHILE 268
%token CASE 269 ESAC 270 OF 271 DARROW 272 NEW 273 ISVOID 274
%token <symbol> STR_CONST 275 INT_CONST 276
%token <boolean> BOOL_CONST 277
%token <symbol> TYPEID 278 OBJECTID 279
%token ASSIGN 280 NOT 281 LE 282 ERROR 283
/* DON'T CHANGE ANYTHING ABOVE THIS LINE, OR YOUR PARSER WONT WORK */
/**************************************************************************/
/* Complete the nonterminal list below, giving a type for the semantic
value of each non terminal. (See section 3.6 in the bison
documentation for details). */
/* Declare types for the grammar's non-terminals. */
%type <program> program
%type <classes> class_list
%type <class_> class
/* You will want to change the following line. */
%type <feature> feature
%type <features> feature_list
%type <feature> method
%type <feature> attribute
%type <formal> formal
%type <formals> formal_list
%type <expression> expression
%type <expressions> expression_list
%type <expressions> expression_blocks
%type <expression> let_expr
%type <case_> branch
%type <cases> case_list
/* Precedence declarations go here. */
%right ASSIGN
%left NOT
%nonassoc LE '<' '='
%left '+' '-'
%left '*' '/'
%left ISVOID
%left '~'
%left '@'
%left '.'
%%
/*
Save the root of the abstract syntax tree in a global variable.
*/
program : class_list { @$ = @1; ast_root = program($1); }
;
class_list
: class /* single class */
{ $$ = single_Classes($1);
parse_results = $$; }
| class_list class /* several classes */
{ $$ = append_Classes($1,single_Classes($2));
parse_results = $$; }
;
/* If no parent is specified, the class inherits from the Object class. */
class
: CLASS TYPEID '{' feature_list '}' ';'
{ $$ = class_($2,idtable.add_string("Object"),$4,
stringtable.add_string(curr_filename)); }
| CLASS TYPEID INHERITS TYPEID '{' feature_list '}' ';'
{ $$ = class_($2,$4,$6,stringtable.add_string(curr_filename)); }
| error
;
/* Feature list may be empty, but no empty features in list. */
feature_list
: /* empty */
{ $$ = nil_Features(); }
| feature ';'
{ $$ = single_Features($1); }
| feature ';' feature_list
{ $$ = append_Features( single_Features($1), $3 ); }
;
feature
: method
{ $$ = $1; }
| attribute
{ $$ = $1; }
| error
;
method
: OBJECTID '(' formal_list ')' ':' TYPEID '{' expression '}'
{ $$ = method($1, $3, $6, $8); }
;
attribute
: OBJECTID ':' TYPEID
{ $$ = attr($1, $3, no_expr()); }
| OBJECTID ':' TYPEID ASSIGN expression
{ $$ = attr ( $1, $3, $5 ); }
;
formal_list
: /* empty */
{ $$ = nil_Formals(); }
| formal
{ $$ = single_Formals($1); }
| formal ',' formal_list
{ $$ = append_Formals( single_Formals($1), $3);}
| error
;
formal
: OBJECTID ':' TYPEID
{ $$ = formal( $1, $3 ); }
;
expression_list
: /* empty */
{ $$ = nil_Expressions(); }
| expression
{ $$ = single_Expressions( $1 ); }
| expression_list ',' expression
{ $$ = append_Expressions( $1, single_Expressions($3)); }
;
expression_blocks
: expression ';'
{ $$ = single_Expressions($1); }
| expression ';' expression_blocks
{ $$ = append_Expressions( single_Expressions($1), $3 ); }
| error
;
expression
/* assign */
: OBJECTID ASSIGN expression
{ $$ = assign( $1, $3 ); }
/* dispatch */
| expression '@' TYPEID '.' OBJECTID '(' expression_list ')'
{ $$ = static_dispatch ( $1, $3, $5, $7 ); }
| expression '.' OBJECTID '(' expression_list ')'
{ $$ = dispatch( $1, $3, $5 ); }
| OBJECTID '(' expression_list ')' /* call object to convert symbol into expression */
{ $$ = dispatch( object(idtable.add_string("self")), $1, $3 ); }
/* if then else */
| IF expression THEN expression ELSE expression FI
{ $$ = cond( $2, $4, $6 ); }
| IF error
| IF expression THEN error
| IF expression THEN expression ELSE error
/* while loop */
| WHILE expression LOOP expression POOL
{ $$ = loop( $2, $4 ); }
| WHILE error
| WHILE expression LOOP error
/* block */
| '{' expression_blocks '}'
{ $$ = block( $2 ); }
/* let */
| LET let_expr
{ $$ = $2; }
/* case */
| CASE expression OF case_list ESAC
{ $$ = typcase( $2, $4 ); }
/* new */
| NEW TYPEID
{ $$ = new_( $2 ); }
/* isvoid */
| ISVOID expression
{ $$ = isvoid( $2 );
/* + - * / ~ < <= = ! () */
| expression '+' expression
{ $$ = plus( $1, $3 ); }
| expression '-' expression
{ $$ = sub( $1, $3 ); }
| expression '*' expression
{ $$ = mul( $1, $3 ); }
| expression '/' expression
{ $$ = divide( $1, $3 ); }
| '~' expression
{ $$ = neg( $2 ); }
| expression '<' expression
{ $$ = lt( $1, $3 ); }
| expression LE expression
{ $$ = leq( $1, $3 ); }
| expression '=' expression
{ $$ = eq( $1, $3 ); }
| NOT expression
{ $$ = comp( $2 ); }
| '(' expression ')'
{ $$ = $2; }
/* object, constant */
| OBJECTID
{ $$ = object( $1 ); }
| INT_CONST
{ $$ = int_const( $1 ); }
| STR_CONST
{ $$ = string_const( $1 ); }
| BOOL_CONST
{ $$ = bool_const( $1 ); }
/* error */
| error
;
let_expr
: OBJECTID ':' TYPEID IN expression
{ $$ = let( $1, $3, no_expr(), $5 ); }
| OBJECTID ':' TYPEID ASSIGN expression IN expression
{ $$ = let( $1, $3, $5, $7 ); }
| OBJECTID ':' TYPEID ',' let_expr
{ $$ = let( $1, $3, no_expr(), $5 ); }
| OBJECTID ':' TYPEID ASSIGN expression ',' let_expr
{ $$ = let( $1, $3, $5, $7 ); }
;
branch
: OBJECTID ':' TYPEID DARROW expression ';'
{ $$ = branch( $1, $3, $5 ); }
;
case_list
: branch
{ $$ = single_Cases( $1 ); }
| branch case_list
{ $$ = append_Cases( single_Cases( $1 ), $2 ); }
;
/* end of grammar */
%%
/* This function is called automatically when Bison detects a parse error. */
void yyerror(char *s)
{
extern int curr_lineno;
cerr << "\"" << curr_filename << "\", line " << curr_lineno << ": " \
<< s << " at or near ";
print_cool_token(yychar);
cerr << endl;
omerrs++;
if(omerrs>50) {fprintf(stdout, "More than 50 errors\n"); exit(1);}
}
PA4语义分析 semant
要求你进行语义分析,对AST进行遍历来标注各个表达式的类型,解决剩余的所有错误
https://www.cnblogs.com/Theffth-blog/p/13338386.html
Cool Reference Manual:参考相关类型规则,标识符作用域规则,Cool语言的相关限制
A Tour of Cool Support Code:结合project中的源码理解已有的架构
对于每一个类:
1.遍历AST,把所有可视化的声明加入到符号表中
需要遍历树,管理从AST中收集到的信息,并由此加强语义分析,同时需要利用SymbolTable确定变量的有效作用域
2.检查每一个表达式的类型正确性
包括检查是否在有需要时声明有效类型,以及根据类型规则验证每个表达式是否具有有效类型
3.用类型注释符号表
4.给出恰当的错误报告
除了类继承关系的错误之外,语义分析需要为其他错误给出完整且信息丰富的错误
步骤:
- 安装基本类,Basic Class中只有Object 和 IO 类可以被继承,其余类均不可被继承
- 安装用户自定义类,会检查是否与基本类和已install的用户定义类重复
- 简单检查不正确的继承关系,会检查是否继承自未定义或者不可被继承的父类
- 建立继承树,建立父子继承关系,从继承树的根部自顶向下标记reachable
- 判断继承图是否成环,为每一个类继承节点设置父子节点关系。
由于Cool中的继承是单继承的,每个没有继承父类的节点都设置为继承自父类,因此如果出现成环的情况,该环一定独立于以Object为根的AST。
从抽象语法树的根Object出发,递归遍历AST树,为每一个子类标记为Reachable,再次遍历所有的类继承节点,若出现没有被标记过的类,则说明该继承图中存在环,退出。 - 建立feature_table,添加每一个类的attr和method
- 检查main函数
- 从Root自顶向下检查每一个类的features:对类中的每一个attr和method进行类型检查
semant.h
#ifndef SEMANT_H_
#define SEMANT_H_
#include "cool-tree.h"
#include "list.h"
#include "stringtab.h"
#include "symtab.h"
#include <assert.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
#include <map>
#include <vector>
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
class ClassTable;
typedef ClassTable *ClassTableP;
// This is a structure that may be used to contain the semantic
// information such as the inheritance graph. You may use it or not as
// you like: it is only here to provide a container for the supplied
// methods.
class ClassTable
{
private:
int semant_errors;
void install_basic_classes();
ostream &error_stream;
// add my own map
std::map<Symbol, Class_> mp_class;
std::map<Symbol, std::list<Symbol>> edges;
void DFS(Class_ cur, Classes classes, std::map<Class_, int> &mp, bool &err,
bool &cycle);
public:
Class_ getClassByName(Symbol classname)
{
if (mp_class.find(classname) == mp_class.end())
return NULL;
return mp_class[classname];
}
std::list<Symbol> getChildClasses(Symbol classname)
{
return edges[classname];
}
bool isBasicClass(Symbol);
bool isSubtype(Symbol, Symbol);
Symbol CommonAncestor(Symbol, Symbol);
Symbol findMethodInAncestor(Symbol, Symbol);
ClassTable(Classes);
int errors()
{
return semant_errors;
}
ostream &semant_error();
ostream &semant_error(Class_ c);
ostream &semant_error(Symbol filename, tree_node *t);
};
#endif
semant.cc
// This file implements the semantic checks for Cool. There are three
// passes:
//
// Pass 1: This is not a true pass, as only the classes are inspected.
// The inheritance graph is built and checked for errors. There are
// two "sub"-passes: check that classes are not redefined and inherit
// only from defined classes, and check for cycles in the inheritance
// graph. Compilation is halted if an error is detected between the
// sub-passes.
//
// Pass 2: Symbol tables are built for each class. This step is done
// separately because methods and attributes have global
// scope---therefore, bindings for all methods and attributes must be
// known before type checking can be done.
//
// Pass 3: The inheritance graph---which is known to be a tree if
// there are no cycles---is traversed again, starting from the root
// class Object. For each class, each attribute and method is
// typechecked. Simultaneously, identifiers are checked for correct
// definition/use and for multiple definitions. An invariant is
// maintained that all parents of a class are checked before a class
// is checked.
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdarg.h>
#include "semant.h"
#include "utilities.h"
extern int semant_debug;
extern char *curr_filename;
extern int node_lineno;
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// Symbols
//
// For convenience, a large number of symbols are predefined here.
// These symbols include the primitive type and method names, as well
// as fixed names used by the runtime system.
//
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
static Symbol
arg,
arg2,
Bool,
concat,
cool_abort,
copy,
Int,
in_int,
in_string,
IO,
isProto,
length,
Main,
main_meth,
No_class,
No_type,
Object,
out_int,
out_string,
prim_slot,
self,
SELF_TYPE,
Str,
str_field,
substr,
type_name,
val;
//
// Initializing the predefined symbols.
//
static void initialize_constants(void)
{
arg = idtable.add_string("arg");
arg2 = idtable.add_string("arg2");
Bool = idtable.add_string("Bool");
concat = idtable.add_string("concat");
cool_abort = idtable.add_string("abort");
copy = idtable.add_string("copy");
Int = idtable.add_string("Int");
in_int = idtable.add_string("in_int");
in_string = idtable.add_string("in_string");
IO = idtable.add_string("IO");
isProto = idtable.add_string("isProto");
length = idtable.add_string("length");
Main = idtable.add_string("Main");
main_meth = idtable.add_string("main");
// _no_class is a symbol that can't be the name of any
// user-defined class.
No_class = idtable.add_string("_no_class");
No_type = idtable.add_string("_no_type");
Object = idtable.add_string("Object");
out_int = idtable.add_string("out_int");
out_string = idtable.add_string("out_string");
prim_slot = idtable.add_string("_prim_slot");
self = idtable.add_string("self");
SELF_TYPE = idtable.add_string("SELF_TYPE");
Str = idtable.add_string("String");
str_field = idtable.add_string("_str_field");
substr = idtable.add_string("substr");
type_name = idtable.add_string("type_name");
val = idtable.add_string("_val");
}
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// Enviroment functions.
//
// The Cool type checking rules require four structures to typecheck a
// class X. These four items are encapsulated in an Environment:
//
// a) a mapping from method names to method definitions for X
// b) a mapping from variable (local and attribute) names to
// definitions in X
// c) a mapping from method names and class names to defintions
// for methods of classes other than X
// d) the self class (X)
//
// c) is realized using a class_table, which contains a mapping
// from class names to InheritanceNodes (and thereby to Environments)
// for all classes.
//
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
Environment::Environment(ClassTableP ct, InheritanceNodeP sc):
method_table(*(new SymbolTable<Symbol, method_class>())),
var_table(*(new SymbolTable<Symbol, Entry>())),
class_table(ct),
self_class(sc)
{
method_table.enterscope();
var_table.enterscope();
var_table.addid(self,SELF_TYPE); // self : SELF_TYPE in all environments
}
Environment::Environment(SymbolTable<Symbol, method_class> mt,
SymbolTable<Symbol, Entry> vt,
ClassTableP ct,
InheritanceNodeP sc):
method_table(mt), // copies the method_table
var_table(vt), // copies the var_table
class_table(ct),
self_class(sc)
{
// push a new scope for each of the method/variable tables,
// so that new methods/variables will not conflict with existing ones.
method_table.enterscope();
var_table.enterscope();
}
//
// Most "new" environments are duplicates of a parent class environment
// with the self class replaced. An small but important point is that
// the method table and var table structures are copied, so that
// additions to the new environment have no effect on the original.
//
EnvironmentP Environment::clone_Environment(InheritanceNodeP n)
{
return new Environment(method_table,var_table,class_table,n);
}
ostream& Environment::semant_error()
{
return class_table->semant_error();
}
ostream& Environment::semant_error(tree_node *t)
{
return class_table->semant_error(self_class->get_filename(),t);
}
InheritanceNodeP Environment::lookup_class(Symbol s)
{
return class_table->probe(s);
}
void Environment::method_add(Symbol s, method_class *m)
{
method_table.addid(s,m);
}
method_class *Environment::method_lookup(Symbol s)
{
return method_table.lookup(s);
}
method_class *Environment::method_probe(Symbol s)
{
return method_table.probe(s);
}
void Environment::method_enterscope()
{
method_table.enterscope();
}
void Environment::method_exitscope()
{
method_table.exitscope();
}
void Environment::var_add(Symbol s, Symbol v)
{
var_table.addid(s,v);
}
Symbol Environment::var_lookup(Symbol s)
{
return var_table.lookup(s);
}
Symbol Environment::var_probe(Symbol s)
{
return var_table.probe(s);
}
void Environment::var_enterscope()
{
var_table.enterscope();
}
void Environment::var_exitscope()
{
var_table.exitscope();
}
Symbol Environment::get_self_type()
{
return self_class->get_name();
}
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// semant_error is an overloaded function for reporting errors
// during semantic analysis. There are three versions:
//
// ostream& ClassTable::semant_error()
//
// ostream& ClassTable::semant_error(Class_ c)
// print line number and filename for `c'
//
// ostream& ClassTable::semant_error(Symbol filename, tree_node *t)
// print a line number and filename
// (line number is extracted from tree_node)
//
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
ostream& ClassTable::semant_error(Class_ c)
{
return semant_error(c->get_filename(),c);
}
ostream& ClassTable::semant_error(Symbol filename, tree_node *t)
{
error_stream << filename << ":" << t->get_line_number() << ": ";
return semant_error();
}
ostream& ClassTable::semant_error()
{
semant_errors++;
return error_stream;
}
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// The inheritance graph.
//
// The following functions allow nodes of the inheritance graph to
// be created, and parent nodes to be set/retrieved from nodes.
//
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
InheritanceNode::InheritanceNode(Class_ nd,
Inheritable istatus,
Basicness bstatus):
// Use of the copy constructor is important
// here.
class__class((const class__class &) *nd),
parentnd(NULL),
children(NULL),
inherit_status(istatus),
basic_status(bstatus),
reach_status(UnReachable),
env(NULL)
{ }
void InheritanceNode::set_parentnd(InheritanceNodeP p)
{
assert(parentnd == NULL);
assert(p != NULL);
parentnd = p;
}
InheritanceNodeP InheritanceNode::get_parentnd()
{
return parentnd;
}
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// ClassTable::ClassTable
//
// The ClassTable constructor initializes a symbol table mapping
// class names to inheritance graph nodes. The constructor also
// installs the basic classes.
//
// Cool has five basic classes:
// Object: The root of the hierarchy; all objects are Objects.
// IO: A class for simple string and integer input/output.
// Int: Integers
// Bool: Booleans
// String: Strings
//
// User-defined classes may inherit from Object and IO, but the
// Int, Bool, and String classes cannot be inherited.
//
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
ClassTable::ClassTable(Classes classes) : nds(NULL),
semant_errors(0),
error_stream(cerr)
{
enterscope(); // initially the symbol table is empty
install_basic_classes(); // predefined basic classes
if (semant_debug) cerr << "Installed basic classes." << endl;
install_classes(classes); // user defined classes
if (semant_debug)
{
cerr << "Installed user-defined classes" << endl;
dump();
}
check_improper_inheritance(); // check for simple inheritance mistakes
if (semant_debug)
{
cerr << "Checked for simple inheritance errors." << endl;
}
if (errors()) return;
build_inheritance_tree(); // build the full inheritance tree
if (semant_debug)
{
cerr << "Built inheritance tree." << endl;
}
root()->mark_reachable(); // find all classes reachable from root class
if (semant_debug)
{
cerr << "Marked reachable classes." << endl;
}
check_for_cycles(); // check that it really is a tree
if (semant_debug)
{
cerr << "Checked for cycles." << endl;
}
if (errors()) return;
build_feature_tables(); // build symbol tables of features for each class
if (semant_debug)
{
cerr << "Built feature tables." << endl;
}
check_main(); // check for Main class and main method
if (semant_debug)
{
cerr << "Checked Main class and method." << endl;
}
root()->type_check_features(); // type check all expressions
}
void ClassTable::install_basic_classes()
{
// The tree package uses these globals to annotate the classes built below.
node_lineno = 0;
Symbol filename = stringtable.add_string("<basic class>");
//
// A few special class names are installed in the lookup table but not
// the class list. Thus, these classes exist, but are not part of the
// inheritance hierarchy.
// No_class serves as the parent of Object and the other special classes.
// SELF_TYPE is the self class; it cannot be redefined or inherited.
// prim_slot is a class known to the code generator.
//
addid(No_class,
new InheritanceNode(class_(No_class,No_class,nil_Features(),filename),
CanInherit,
Basic));
addid(SELF_TYPE,
new InheritanceNode(class_(SELF_TYPE,No_class,nil_Features(),filename),
CantInherit,
Basic));
addid(prim_slot,
new InheritanceNode(class_(prim_slot,No_class,nil_Features(),filename),
CantInherit,
Basic));
//
// The Object class has no parent class. Its methods are
// cool_abort() : Object aborts the program
// type_name() : Str returns a string representation of class name
// copy() : SELF_TYPE returns a copy of the object
//
// There is no need for method bodies in the basic classes---these
// are already built in to the runtime system.
//
Class_ Object_class =
class_(Object,
No_class,
append_Features(
append_Features(
single_Features(method(cool_abort, nil_Formals(), Object, no_expr())),
single_Features(method(type_name, nil_Formals(), Str, no_expr()))),
single_Features(method(copy, nil_Formals(), SELF_TYPE, no_expr()))),
filename);
install_class(new InheritanceNode(Object_class, CanInherit, Basic));
//
// The IO class inherits from Object. Its methods are
// out_string(Str) : SELF_TYPE writes a string to the output
// out_int(Int) : SELF_TYPE " an int " " "
// in_string() : Str reads a string from the input
// in_int() : Int " an int " " "
//
Class_ IO_class =
class_(IO,
Object,
append_Features(
append_Features(
append_Features(
single_Features(method(out_string, single_Formals(formal(arg, Str)),
SELF_TYPE, no_expr())),
single_Features(method(out_int, single_Formals(formal(arg, Int)),
SELF_TYPE, no_expr()))),
single_Features(method(in_string, nil_Formals(), Str, no_expr()))),
single_Features(method(in_int, nil_Formals(), Int, no_expr()))),
filename);
install_class(new InheritanceNode(IO_class, CanInherit, Basic));
//
// The Int class has no methods and only a single attribute, the
// "val" for the integer.
//
Class_ Int_class =
class_(Int,
Object,
single_Features(attr(val, prim_slot, no_expr())),
filename);
install_class(new InheritanceNode(Int_class, CantInherit, Basic));
//
// Bool also has only the "val" slot.
//
Class_ Bool_class =
class_(Bool, Object, single_Features(attr(val, prim_slot, no_expr())),filename);
install_class(new InheritanceNode(Bool_class, CantInherit, Basic));
//
// The class Str has a number of slots and operations:
// val the length of the string
// str_field the string itself
// length() : Int returns length of the string
// concat(arg: Str) : Str performs string concatenation
// substr(arg: Int, arg2: Int): Str substring selection
//
Class_ Str_class =
class_(Str,
Object,
append_Features(
append_Features(
append_Features(
append_Features(
single_Features(attr(val, Int, no_expr())),
single_Features(attr(str_field, prim_slot, no_expr()))),
single_Features(method(length, nil_Formals(), Int, no_expr()))),
single_Features(method(concat,
single_Formals(formal(arg, Str)),
Str,
no_expr()))),
single_Features(method(substr,
append_Formals(single_Formals(formal(arg, Int)),
single_Formals(formal(arg2, Int))),
Str,
no_expr()))),
filename);
install_class(new InheritanceNode(Str_class, CantInherit, Basic));
// Some debugging
// Object_class->dump_with_types(cerr, 0);
// IO_class->dump_with_types(cerr, 0);
// Int_class->dump_with_types(cerr, 0);
// Bool_class->dump_with_types(cerr, 0);
// Str_class->dump_with_types(cerr, 0);
}
// ClassTable::install_class
// ClassTable::install_classes
//
// install_classes enters a list of classes in the symbol table.
// The following possible errors are checked:
// - a class called SELF_TYPE
// - redefinition of a basic class
// - redefinition of another previously defined class
//
void ClassTable::install_class(InheritanceNodeP nd)
{
Symbol name = nd->get_name();
if (probe(name))
{
InheritanceNodeP old = probe(name);
if (old->basic())
semant_error(nd) << "Redefinition of basic class " << name << "."<< endl;
else
semant_error(nd) << "Class " << name << " was previously defined."
<< endl;
return;
}
// The class name is legal, so add it to the list of classes
// and the symbol table.
nds = new List<InheritanceNode>(nd,nds);
addid(name,nd);
}
//
// Install all user-defined classes; all of these classes can
// be inherited and are not basic classes.
//
void ClassTable::install_classes(Classes cs)
{
for(int i = cs->first(); cs->more(i); i = cs->next(i))
install_class(new InheritanceNode(cs->nth(i),CanInherit,NotBasic));
}
//
// ClassTable::check_improper_inheritance
//
// This function checks whether the classes in a ClassTable illegally inherit
// from
// - a CantInherit class
// - SELF_TYPE
// - an undefined class
//
// All of these checks are local (do not require traversing the inheritance
// graph).
//
void ClassTable::check_improper_inheritance()
{
for(List<InheritanceNode> *l = nds; l; l = l->tl())
{
InheritanceNodeP c = l->hd();
Symbol parent = c->get_parent();
InheritanceNode *node = probe(parent);
if (!node)
{
semant_error(c) << "Class " << c->get_name() <<
" inherits from an undefined class " << parent << "." << endl;
continue;
}
if (!node->inherit())
semant_error(c) << "Class " << c->get_name() <<
" cannot inherit class " << parent << "." << endl;
}
}
//
// ClassTable::build_inheritance_tree
//
// For each class node in the inheritance graph, set its parent,
// and add the node to the parent's list of child nodes.
//
void ClassTable::build_inheritance_tree()
{
for(List<InheritanceNode> *l = nds; l; l = l->tl())
set_relations(l->hd());
}
//
// ClassTable::set_relations
//
// Takes a InheritanceNode and locates its, and its parent's, inheritance nodes
// via the class table. Parent and child pointers are added as appropriate.
//
void ClassTable::set_relations(InheritanceNodeP nd)
{
InheritanceNode *parent_node = probe(nd->get_parent());
nd->set_parentnd(parent_node);
parent_node->add_child(nd);
}
//
// This method should be run only after mark_reachable has executed.
// If there are any unreachable classes in the inheritance graph and
// all of the local checks of check_improper_inheritance succeeded,
// then there is a cycle in the inheritance graph.
//
void ClassTable::check_for_cycles()
{
for(List<InheritanceNode> *l = nds; l; l = l->tl())
if(!(l->hd()->reachable()))
semant_error(l->hd()) << "Class " << l->hd()->get_name() <<
", or an ancestor of " << l->hd()->get_name() <<
", is involved in an inheritance cycle." << endl;
}
void InheritanceNode::add_child(InheritanceNodeP n)
{
children = new List<InheritanceNode>(n,children);
}
//
// InheritanceNode::mark_reachable()
// Recursively mark all nodes reachable from the argument as Reachable.
// Initally called with Object.
//
// This function is guaranteed to terminate because the subgraph of the
// inheritance hierarchy reachable from Object cannot contain a cycle
// if no local errors are discovered by check_improper_inheritance.
//
void InheritanceNode::mark_reachable()
{
reach_status = Reachable; // mark the current node as reachable
// process the children
for(List<InheritanceNode> *kids = children; kids; kids = kids->tl())
kids->hd()->mark_reachable();
}
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// Feature Symbol Tables
//
// The following group of functions recursively walk each feature
// of each class, adding information to the environment for the classes
// about the features. Errors such as redefining method/attribute names
// within a class are caught here.
//
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
void InheritanceNode::build_feature_tables()
{
// add each feature of the class to the class symbol table
for(int i = features->first(); features->more(i); i = features->next(i))
features->nth(i)->add_to_table(env);
for(List<InheritanceNode> *l = children; l; l = l->tl())
{
// for each child of the current class, we
l->hd()->copy_env(env); // copy the parent's environment,
// thus inheriting the parent's features;
l->hd()->build_feature_tables(); // add the child's features
}
}
void InheritanceNode::type_check_features()
{
if (semant_debug)
{
cerr << "Type checking class " << name << endl;
}
for(int i = features->first(); features->more(i); i = features->next(i))
features->nth(i)->tc(env);
for(List<InheritanceNode> *l = children; l; l = l->tl())
l->hd()->type_check_features();
}
//
// Allocate new Environment structure. Presently used only for the
// root (Object) class; all other classes make a copy of their parent's
// Environment.
//
void InheritanceNode::init_env(ClassTableP ct)
{
env = new Environment(ct,this);
}
void ClassTable::build_feature_tables()
{
root()->init_env(this); // create symbol tables for the root class
root()->build_feature_tables(); // recursively build feature tables for
// the root class and all descendants.
}
InheritanceNodeP ClassTable::root()
{
return probe(Object);
}
void method_class::add_to_table(EnvironmentP env)
{
// 查找cool当前类中是否有重名函数
if (env->method_probe(name))
{
env->semant_error(this) << "Method " << name << " is multiply defined."
<< endl;
return;
}
// 查找继承类中是否有同名方法(即函数重写)
method_class *old = env->method_lookup(name);
if(old)
{
if (old->get_return_type() != return_type)
{
env->semant_error(this) << "In redefined method " << name <<
", return type " << return_type <<
" is different from original return type " <<
old->get_return_type() << "." << endl;
return;
}
if (old->num_formals() != num_formals())
{
env->semant_error(this) <<
"Incompatible number of formal parameters in redefined method " <<
name << "." << endl;
return;
}
Formals old_formals = old->get_formals();
for(int i = formals->first(); formals->more(i); i = formals->next(i))
if (old_formals->nth(i)->get_type_decl() != formals->nth(i)->get_type_decl())
{
env->semant_error(this) << "In redefined method " << name <<
", parameter type " << formals->nth(i)->get_type_decl() <<
" is different from original type " <<
old_formals->nth(i)->get_type_decl() << endl;
return;
}
}
env->method_add(name,this);
}
void attr_class::add_to_table(EnvironmentP env)
{
if (name == self)
{
env->semant_error(this) << "'self' cannot be the name of an attribute."
<< endl;
return;
}
// 查找当前类中是否有重名变量
if (env->var_probe(name))
{
env->semant_error(this) << "Attribute " << name <<
" is multiply defined in class." << endl;
return;
}
// 查找祖先类中是否有重名变量
if (env->var_lookup(name))
{
env->semant_error(this) << "Attribute " << name <<
" is an attribute of an inherited class." << endl;
return;
}
env->var_add(name,type_decl);
}
//
// Checks for the existence of the Main class, and that it has access to a
// method main in its inheritance hierarchy.
//
void ClassTable::check_main()
{
InheritanceNodeP mainclass = probe(Main);
if(!mainclass)
semant_error() << "Class Main is not defined." << endl;
else
mainclass->check_main_method();
}
//
// Checks that the class has a main method that takes no arguments.
// The method must be defied *in*, not inherited into, the Main class.
//
void InheritanceNode::check_main_method()
{
if (!env->method_probe(main_meth))
{
env->semant_error(this) << "No 'main' method in class Main." << endl;
return;
}
if (env->method_lookup(main_meth)->num_formals() != 0)
env->semant_error(this) <<
"'main' method in class Main should have no arguments." << endl;
}
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// Type Operations
//
// type_leq Is type X <= type Y?
// type_lub What is the most specific type greater than both X and Y?
//
// These functions are complicated slightly by the handling of SELF_TYPE
// and by taking care to avoid generating multiple error messages for
// undefined classes (which have already been reported by the time
// these functions are used).
//
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
int Environment::type_leq(Symbol subtype, Symbol supertype)
{
// If one of the classes doesn't exist, return TRUE to cut down on the
// the number of spurious error messages. Also provides
// No_type < t for any t.
//
if(!(lookup_class(supertype) && lookup_class(subtype)))
return TRUE;
// SELF_TYPE <= SELF_TYPE
if (subtype == SELF_TYPE && supertype == SELF_TYPE) return TRUE;
// X is not <= SELF_TYPE if X is not SELF_TYPE
if (supertype == SELF_TYPE) return FALSE;
// if the lhs is SELF_TYPE, it is promoted here to the self_type of the class.
if (subtype == SELF_TYPE) subtype = get_self_type();
// X <= Y if Y is an ancestor of X in the inheritance hierarchy.
InheritanceNodeP y = lookup_class(supertype);
for(InheritanceNodeP x = lookup_class(subtype); x; x = x->get_parentnd())
if(x == y) return TRUE;
return FALSE;
}
// 返回type1和type2共同的祖先
Symbol Environment::type_lub(Symbol type1, Symbol type2)
{
//
// The order of tests in the this procedure is important.
//
// 1. If one type is undefined (i.e., No_class), return the other
// 2. If both types are SELF_TYPE, return SELF_TYPE
// 3. If either is SELF_TYPE, convert it to the type of the class
// 4. Find the least common ancestor in the inheritance graph.
//
if (!lookup_class(type1)) return type2; // if either type is undefined,
if (!lookup_class(type2)) return type1; // return the other.
if (type1 == type2) return type1; // SELF_TYPE u SELF_TYPE = SELF_TYPE
if (type1 == SELF_TYPE) type1 = get_self_type();
if (type2 == SELF_TYPE) type2 = get_self_type();
InheritanceNodeP nd;
for(nd = lookup_class(type1);
!type_leq(type2,nd->get_name());
nd = nd->get_parentnd())
;
return nd->get_name();
}
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// Type Checking Features
//
// For each class of expression, there is a tc method to typecheck it.
// The tc methods make use of the environments previously constructred
// for each class. This code parallels the structure of the type
// inference rules in the CoolAid very closely.
//
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
void attr_class::tc(EnvironmentP env)
{
if (! env->lookup_class(type_decl))
env->semant_error(this) << "Class " << type_decl << " of attribute " << name
<< " is undefined." << endl;
if (! env->type_leq(init->tc(env), type_decl))
env->semant_error(this) << "Inferred type " << init->get_type() <<
" of initialization of attribute " << name <<
" does not conform to declared type " << type_decl << "." << endl;
}
void method_class::tc(EnvironmentP env)
{
env->var_enterscope();
for(int i = formals->first(); formals->more(i); i = formals->next(i))
formals->nth(i)->install_formal(env);
if (! env->lookup_class(return_type))
env->semant_error(this) << "Undefined return type " << return_type <<
" in method " << name << "." << endl;
if(! env->type_leq(expr->tc(env), return_type))
env->semant_error(this) << "Inferred return type " << expr->get_type() <<
" of method " << name << " does not conform to declared return type " <<
return_type << "." << endl;
env->var_exitscope();
}
void formal_class::install_formal(EnvironmentP env)
{
if (type_decl == SELF_TYPE)
env->semant_error(this) << "Formal parameter " << name <<
" cannot have type SELF_TYPE." << endl;
else
{
if (! env->lookup_class(type_decl))
env->semant_error(this) << "Class " << type_decl <<
" of formal parameter " << name << " is undefined." << endl;
};
if (name == self)
{
env->semant_error(this) <<
"'self' cannot be the name of a formal parameter." << endl;
return;
}
if(env->var_probe(name))
{
env->semant_error(this) << "Formal parameter " << name <<
" is multiply defined." << endl;
return;
}
env->var_add(name,type_decl);
}
Symbol int_const_class::tc(EnvironmentP)
{
type = Int;
return Int;
}
Symbol bool_const_class::tc(EnvironmentP)
{
type = Bool;
return Bool;
}
Symbol string_const_class::tc(EnvironmentP)
{
type = Str;
return Str;
}
Symbol plus_class::tc(EnvironmentP env)
{
e1->tc(env);
e2->tc(env);
if ((e1->get_type() != Int) || (e2->get_type() != Int))
env->semant_error(this) << "non-Int arguments: " << e1->get_type() << " + "
<< e2->get_type() << endl;
type = Int;
return Int;
}
Symbol sub_class::tc(EnvironmentP env)
{
e1->tc(env);
e2->tc(env);
if ((e1->get_type() != Int) || (e2->get_type() != Int))
env->semant_error(this) << "non-Int arguments: " << e1->get_type() << " - "
<< e2->get_type() << endl;
type = Int;
return Int;
}
Symbol mul_class::tc(EnvironmentP env)
{
e1->tc(env);
e2->tc(env);
if ((e1->get_type() != Int) || (e2->get_type() != Int))
env->semant_error(this) << "non-Int arguments: " << e1->get_type() << " * "
<< e2->get_type() << endl;
type = Int;
return Int;
}
Symbol divide_class::tc(EnvironmentP env)
{
e1->tc(env);
e2->tc(env);
if ((e1->get_type() != Int) || (e2->get_type() != Int))
env->semant_error(this) << "non-Int arguments: " << e1->get_type() << " / "
<< e2->get_type() << endl;
type = Int;
return Int;
}
Symbol neg_class::tc(EnvironmentP env)
{
e1->tc(env);
if(e1->get_type() != Int)
env->semant_error(this) << "Argument of '~' has type " << e1->get_type()
<< " instead of Int." << endl;
type = Int;
return Int;
}
Symbol lt_class::tc(EnvironmentP env)
{
e1->tc(env);
e2->tc(env);
if ((e1->get_type() != Int) || (e2->get_type() != Int))
env->semant_error(this) << "non-Int arguments: " << e1->get_type() << " < "
<< e2->get_type() << endl;
type = Bool;
return Bool;
}
Symbol leq_class::tc(EnvironmentP env)
{
e1->tc(env);
e2->tc(env);
if ((e1->get_type() != Int) || (e2->get_type() != Int))
env->semant_error(this) << "non-Int arguments: " << e1->get_type() << " <= "
<< e2->get_type() << endl;
type = Bool;
return Bool;
}
Symbol comp_class::tc(EnvironmentP env)
{
e1->tc(env);
if(e1->get_type() != Bool)
env->semant_error(this) << "Argument of 'not' has type " << e1->get_type()
<< " instead of Bool." << endl;
type = Bool;
return Bool;
}
Symbol object_class::tc(EnvironmentP env)
{
if (env->var_lookup(name))
type = env->var_lookup(name);
else
{
env->semant_error(this) << "Undeclared identifier " << name << "." << endl;
type = Object;
}
return type;
}
Symbol no_expr_class::tc(EnvironmentP)
{
type = No_type;
return No_type;
}
Symbol new__class::tc(EnvironmentP env)
{
if(env->lookup_class(type_name))
type = type_name;
else
{
env->semant_error(this) << "'new' used with undefined class " <<
type_name << "." << endl;
type = Object;
}
return type;
}
Symbol isvoid_class::tc(EnvironmentP env)
{
e1->tc(env);
type = Bool;
return Bool;
}
Symbol eq_class::tc(EnvironmentP env)
{
Symbol t1 = e1->tc(env);
Symbol t2 = e2->tc(env);
if ((t1 != t2) &&
((t1 == Int) || (t2 == Int) ||
(t1 == Bool) || (t2 == Bool) ||
(t1 == Str) || (t2 == Str)))
env->semant_error(this) << "Illegal comparison with a basic type." << endl;
type = Bool;
return Bool;
}
Symbol let_class::tc(EnvironmentP env)
{
if (! env->lookup_class(type_decl))
env->semant_error(this) << "Class " << type_decl <<
" of let-bound identifier " << identifier << " is undefined." << endl;
if (! env->type_leq(init->tc(env), type_decl))
env->semant_error(this) << "Inferred type " << init->get_type() <<
" of initialization of " << identifier <<
" does not conform to identifier's declared type " << type_decl << "." <<
endl;
env->var_enterscope();
if(identifier == self)
env->semant_error(this) << "'self' cannot be bound in a 'let' expression."
<< endl;
else
env->var_add(identifier,type_decl);
type = body->tc(env);
env->var_exitscope();
return type;
}
Symbol block_class::tc(EnvironmentP env)
{
for(int i = body->first(); body->more(i); i = body->next(i))
type = body->nth(i)->tc(env);
return type;
}
Symbol assign_class::tc(EnvironmentP env)
{
if (name == self)
env->semant_error(this) << "Cannot assign to 'self'." << endl;
if (! env->var_lookup(name))
env->semant_error(this) << "Assignment to undeclared variable " << name
<< "." << endl;
type = expr->tc(env);
if(! env->type_leq(type, env->var_lookup(name)))
env->semant_error(this) << "Type " << type <<
" of assigned expression does not conform to declared type " <<
env->var_lookup(name) << " of identifier " << name << "." << endl;
return type;
}
Symbol dispatch_class::tc(EnvironmentP env)
{
// Type check the subexpressions first.
Symbol expr_type = expr->tc(env);
if (expr_type == SELF_TYPE) expr_type = env->get_self_type();
for(int i = actual->first(); actual->more(i); i = actual->next(i))
actual->nth(i)->tc(env);
InheritanceNode *nd = env->lookup_class(expr_type);
if (!nd)
{
env->semant_error(this) << "Dispatch on undefined class " << expr_type <<
"." << endl;
type = Object;
return Object;
}
method_class *meth = nd->method_lookup(name);
if(! meth)
{
env->semant_error(this) << "Dispatch to undefined method " << name << "."
<< endl;
type = Object;
return Object;
}
if(actual->len() != meth->num_formals())
env->semant_error(this) << "Method " << name <<
" called with wrong number of arguments." << endl;
else
for(int i = actual->first(); actual->more(i); i = actual->next(i))
if (! env->type_leq(actual->nth(i)->get_type(),
meth->sel_formal(i)->get_type_decl()))
env->semant_error(this) << "In call of method " << name <<
", type " << actual->nth(i)->get_type() <<
" of parameter " << meth->sel_formal(i)->get_name() <<
" does not conform to declared type " <<
meth->sel_formal(i)->get_type_decl() << "." << endl;
type = (meth->get_return_type() == SELF_TYPE) ? expr->get_type() :
meth->get_return_type();
return type;
}
Symbol static_dispatch_class::tc(EnvironmentP env)
{
Symbol expr_type = expr->tc(env);
for(int i = actual->first(); actual->more(i); i = actual->next(i))
actual->nth(i)->tc(env);
if(type_name == SELF_TYPE)
{
env->semant_error(this) << "Static dispatch to SELF_TYPE." << endl;
type = Object;
return Object;
}
InheritanceNode *nd = env->lookup_class(type_name);
if(!nd)
{
env->semant_error(this) << "Static dispatch to undefined class " <<
type_name << "." << endl;
type = Object;
return Object;
}
if(! env->type_leq(expr_type, type_name))
{
env->semant_error(this) << "Expression type " << expr_type <<
" does not conform to declared static dispatch type " << type_name <<
"." << endl;
type = Object;
return Object;
}
method_class *meth = nd->method_lookup(name);
if(! meth)
{
env->semant_error(this) << "Static dispatch to undefined method " << name
<< "." << endl;
type = Object;
return Object;
}
if(actual->len() != meth->num_formals())
env->semant_error(this) << "Method " << name
<< " invoked with wrong number of arguments." << endl;
else
for(int i = actual->first(); actual->more(i); i = actual->next(i))
if (! env->type_leq(actual->nth(i)->get_type(),
meth->sel_formal(i)->get_type_decl()))
env->semant_error(this) << "In call of method " << name <<
", type " << actual->nth(i)->get_type() <<
" of parameter " << meth->sel_formal(i)->get_name() <<
" does not conform to declared type " <<
meth->sel_formal(i)->get_type_decl() << "." << endl;
type = (meth->get_return_type() == SELF_TYPE) ? expr_type :
meth->get_return_type();
return type;
}
Symbol cond_class::tc(EnvironmentP env)
{
if(pred->tc(env) != Bool)
env->semant_error(this) << "Predicate of 'if' does not have type Bool.\n";
Symbol then_type = then_exp->tc(env);
Symbol else_type = else_exp->tc(env);
type = env->type_lub(then_type, else_type);
return type;
}
Symbol loop_class::tc(EnvironmentP env)
{
if(pred->tc(env) != Bool)
env->semant_error(this) << "Loop condition does not have type Bool." << endl;
body->tc(env);
type = Object;
return Object;
}
Symbol typcase_class::tc(EnvironmentP env)
{
type = No_type;
expr->tc(env);
// 判断是否有重复声明
for (int i=cases->first(); cases->more(i); i = cases->next(i))
{
Case c = cases->nth(i);
for(int j=cases->first(); j<i; j = cases->next(j))
{
if(cases->nth(j)->get_type_decl() == c->get_type_decl())
{
env->semant_error(c) << "Duplicate branch " << c->get_type_decl() <<
" in case statement." << endl;
break;
}
}
env->var_enterscope();
if (! env->lookup_class(c->get_type_decl()))
env->semant_error(c) << "Class " << c->get_type_decl() <<
" of case branch is undefined." << endl;
if (c->get_name() == self)
env->semant_error(c) << "'self' bound in 'case'." << endl;
if (c->get_type_decl() == SELF_TYPE)
env->semant_error(c) << "Identifier " << c->get_name() <<
" declared with type SELF_TYPE in case branch." << endl;
env->var_add(c->get_name(), c->get_type_decl());
type = env->type_lub(type, c->tc(env));
env->var_exitscope();
}
return type;
}
// The function which runs the semantic analyser.
InheritanceNodeP program_class::semant()
{
initialize_constants();
ClassTableP classtable = new ClassTable(classes);
if (classtable->errors())
{
cerr << "Compilation halted due to static semantic errors." << endl;
exit(1);
}
return classtable->root();
}
PA5 cgen目标代码生成
要求将代码翻译成MIPS代码
MIPS:https://www.cnblogs.com/thoupin/p/4018455.html
执行流程:
1.首先执行__start
2.在__start中,初始化垃圾回收器GC
3.设置_exception_handler异常处理程序
4.复制一份Main类,并将其保存至栈上
5.调用Main.init进行初始化
6.执行Main.main
7.待函数返回后恢复栈
8.输出终止信息并调用exit退出
- 寄存器:有32个通用寄存器,寄存器标志由$符开头。
乘法寄存器$lo除法寄存器$hi,不存在直接寻址,栈走向从高到低 - 程序结构:数据声明+普通文本+程序编码(文件后缀为.s,或者.asm)
- 数据声明:数据段以 .data为开始标志,声明变量后,即在主存中分配空间。
name: storage_type value(s)
变量名: 数据类型 变量值
- 代码:代码段以 .text为开始标志,程序入口为main标志
- 读写:只能用load或者store指令访问内存,其他都是寄存器操作
lw register_destination, RAM_source
//从内存中 复制 RAM_source 的内容到对应的寄存器中
lb register_destination, RAM_source
sw register_source, RAM_destination
//将指定寄存器中的数据 写入 到指定的内存中
sb register_source, RAM_destination
//store byte (low-order) in source register into RAM destination
li register_destination, value
//load immediate value into destination register
- 算术指令:最多三个操作数
sub $t2,$t3,$t4 # $t2 = $t3 Ð $t4
addi $t2,$t3, 5 # $t2 = $t3 + 5; "add immediate" (no sub immediate)
addu $t1,$t6,$t7 # $t1 = $t6 + $t7; add as unsigned integers
subu $t1,$t6,$t7 # $t1 = $t6 + $t7; subtract as unsigned integers
mult $t3,$t4 # multiply 32-bit quantities in $t3 and $t4, and store 64-bit
# result in special registers Lo and Hi: (Hi,Lo) = $t3 * $t4
运算结果存储在hi,lo(hi高位数据, lo地位数据)
div $t5,$t6 # Lo = $t5 / $t6 (integer quotient)
# Hi = $t5 mod $t6 (remainder)
商数存放在 lo, 余数存放在 hi
mfhi $t0 # move quantity in special register Hi to $t0: $t0 = Hi
不能直接获取 hi 或 lo中的值, 需要mfhi, mflo指令传值给寄存器
mflo $t1 # move quantity in special register Lo to $t1: $t1 = Lo
# used to get at result of product or quotient
move $t2,$t3 # $t2 = $t3
- 分支:
b target # unconditional branch to program label target
beq $t0,$t1,target # branch to target if $t0 = $t1
blt $t0,$t1,target # branch to target if $t0 < $t1
ble $t0,$t1,target # branch to target if $t0 <= $t1
bgt $t0,$t1,target # branch to target if $t0 > $t1
bge $t0,$t1,target # branch to target if $t0 >= $t1
bne $t0,$t1,target # branch to target if $t0 <> $t1
- 跳转:
j target # unconditional jump to program label target
看到就跳, 不用考虑任何条件
jr $t3 # jump to address contained in $t3 ("jump register")
类似相对寻址,跳到该寄存器给出的地址处
- 子程序调用:
jal sub_label # "jump and link"
jr $ra # "jump register"
代码生成
1.声明全局变量
2.生成GC器
3.输出常量
4.输出所有类的名称
5.输出所有类中的object table
6.输出每个类所含的方法
7.输出每个类的类型信息
8.声明全局代码段的相关信息
9.输出每个类的初始化函数的代码
10.输出每个类中的函数代码
注意:
- 翻译一个函数的时候,先约定好堆栈的次序
- 调用函数前,将可能被调用的函数改变的寄存器里面的内容保存起来,可以压栈或者保存在别的不用的寄存器里,调用返回之后要记得恢复
- 用寄存器比较快
GC垃圾回收
- 当cgen_Memmgr == GC_GENGC时,_GenGC_Assign函数只AttributeBinding::code_update中被调用,以记录成员变量的赋值操作至assignment table(用于分代垃圾回收)。
- 当cgen_Memmgr_Debug == GC_DEBUG时,_gc_check函数会被频繁调用,以检测对象的eye catcher是否存在,防止heap chunk的 重叠/被覆盖。
cgen.h
#include "cool-tree.h"
#include "emit.h"
#include "symtab.h"
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <map>
#include <stack>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
enum Basicness { Basic, NotBasic };
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
class CgenClassTable;
typedef CgenClassTable *CgenClassTableP;
class CgenNode;
typedef CgenNode *CgenNodeP;
class CgenClassTable : public SymbolTable<Symbol, CgenNode>
{
private:
List<CgenNode> *nds;
ostream &str;
int stringclasstag;
int intclasstag;
int boolclasstag;
// The following methods emit code for
// constants and global declarations.
void code_global_data();
void code_global_text();
void code_bools(int);
void code_select_gc();
void code_constants();
void code_class_nameTab();
void code_class_objTab();
void code_class_dispTab();
void code_class_protObj();
void code_class_init();
void code_methods();
// The following creates an inheritance graph from
// a list of classes. The graph is implemented as
// a tree of `CgenNode', and class names are placed
// in the base class symbol table.
void install_basic_classes();
void install_class(CgenNodeP nd);
void install_classes(Classes cs);
void build_inheritance_tree();
void set_relations(CgenNodeP nd);
public:
CgenClassTable(Classes, ostream &str);
void code();
void execute();
CgenNodeP root();
};
class CgenNode : public class__class
{
private:
CgenNodeP parentnd; // Parent of class
List<CgenNode> *children; // Children of class
Basicness basic_status; // `Basic' if class is basic
// `NotBasic' otherwise
public:
int tag;
std::map<Symbol, int> attr_index;
std::map<Symbol, int> method_index;
void code_nameTab(int &, ostream &);
void code_objTab(ostream &);
void code_protObj(std::vector<Symbol>, ostream &);
void code_dispTab(std::vector<std::pair<Symbol, Symbol>>, ostream &);
void code_init(ostream &);
method_class *find_method(Symbol);
void install_args(Symbol);
CgenNode(Class_ c, Basicness bstatus, CgenClassTableP class_table);
void add_child(CgenNodeP child);
List<CgenNode> *get_children()
{
return children;
}
void set_parentnd(CgenNodeP p);
CgenNodeP get_parentnd()
{
return parentnd;
}
int basic()
{
return (basic_status == Basic);
}
};
class BoolConst
{
private:
int val;
public:
BoolConst(int);
void code_def(ostream &, int boolclasstag);
void code_ref(ostream &) const;
};
class Environment
{
public:
int args_size = 0, var_scopes = 0;
std::map<Symbol, int> attr_index;
SymbolTable<Symbol, int> args_index;
SymbolTable<Symbol, int> var_index;
Environment()
{
args_index.enterscope();
var_index.enterscope();
}
void add_Attribute(CgenNodeP p)
{
attr_index = p->attr_index;
}
void add_Argument(Symbol s)
{
// args_index.insert(std::make_pair(s, args_index.size()));
args_index.addid(s, new int(args_size));
args_size++;
}
void add_Variable(Symbol s, int id)
{
var_index.addid(s, new int(id));
}
//-----------------------------------------
int get_Attribute(Symbol s)
{
if (attr_index.find(s) == attr_index.end())
return -1;
return attr_index[s];
}
int get_Argument(Symbol s)
{
if (args_index.probe(s) == NULL)
return -1;
return args_size - *args_index.probe(s) - 1;
}
int get_Var(Symbol s)
{
if (var_index.lookup(s) == NULL)
return -1;
return *var_index.lookup(s);
}
void args_enter()
{
args_index.enterscope();
}
void vars_enter()
{
var_index.enterscope();
var_scopes++;
}
void args_exit()
{
args_index.exitscope();
args_size = 0;
}
void vars_exit()
{
var_index.exitscope();
}
void vars_dump()
{
while (var_scopes > 1)
{
vars_exit();
var_scopes--;
}
}
};
cgen.cc
//**************************************************************
//
// Code generator SKELETON
//
// Read the comments carefully. Make sure to
// initialize the base class tags in
// `CgenClassTable::CgenClassTable'
//
// Add the label for the dispatch tables to
// `IntEntry::code_def'
// `StringEntry::code_def'
// `BoolConst::code_def'
//
// Add code to emit everyting else that is needed
// in `CgenClassTable::code'
//
//
// The files as provided will produce code to begin the code
// segments, declare globals, and emit constants. You must
// fill in the rest.
//
//**************************************************************
#include "cgen.h"
#include "cgen_gc.h"
extern void emit_string_constant(ostream &str, char *s);
extern int cgen_debug;
int label_num = 0, nodesize = 0;
int temp_size, used_temp = 0;
std::map<Symbol, int> class_tags;
Symbol current_class;
Environment env;
CgenClassTable *codegen_classtable = nullptr;
//
// Three symbols from the semantic analyzer (semant.cc) are used.
// If e : No_type, then no code is generated for e.
// Special code is generated for new SELF_TYPE.
// The name "self" also generates code different from other references.
//
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// Symbols
//
// For convenience, a large number of symbols are predefined here.
// These symbols include the primitive type and method names, as well
// as fixed names used by the runtime system.
//
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
Symbol arg, arg2, Bool, concat, cool_abort, copy, Int, in_int, in_string, IO,
length, Main, main_meth, No_class, No_type, Object, out_int, out_string,
prim_slot, self, SELF_TYPE, Str, str_field, substr, type_name, val;
//
// Initializing the predefined symbols.
//
static void initialize_constants(void)
{
arg = idtable.add_string("arg");
arg2 = idtable.add_string("arg2");
Bool = idtable.add_string("Bool");
concat = idtable.add_string("concat");
cool_abort = idtable.add_string("abort");
copy = idtable.add_string("copy");
Int = idtable.add_string("Int");
in_int = idtable.add_string("in_int");
in_string = idtable.add_string("in_string");
IO = idtable.add_string("IO");
length = idtable.add_string("length");
Main = idtable.add_string("Main");
main_meth = idtable.add_string("main");
// _no_class is a symbol that can't be the name of any
// user-defined class.
No_class = idtable.add_string("_no_class");
No_type = idtable.add_string("_no_type");
Object = idtable.add_string("Object");
out_int = idtable.add_string("out_int");
out_string = idtable.add_string("out_string");
prim_slot = idtable.add_string("_prim_slot");
self = idtable.add_string("self");
SELF_TYPE = idtable.add_string("SELF_TYPE");
Str = idtable.add_string("String");
str_field = idtable.add_string("_str_field");
substr = idtable.add_string("substr");
type_name = idtable.add_string("type_name");
val = idtable.add_string("_val");
}
static char *gc_init_names[] = {"_NoGC_Init", "_GenGC_Init", "_ScnGC_Init"};
static char *gc_collect_names[] = {"_NoGC_Collect", "_GenGC_Collect",
"_ScnGC_Collect"
};
// BoolConst is a class that implements code generation for operations
// on the two booleans, which are given global names here.
BoolConst falsebool(FALSE);
BoolConst truebool(TRUE);
//*********************************************************
//
// Define method for code generation
//
// This is the method called by the compiler driver
// `cgtest.cc'. cgen takes an `ostream' to which the assembly will be
// emmitted, and it passes this and the class list of the
// code generator tree to the constructor for `CgenClassTable'.
// That constructor performs all of the work of the code
// generator.
//
//*********************************************************
void program_class::cgen(ostream &os)
{
// spim wants comments to start with '#'
os << "# start of generated code\n";
cgen_debug = 0;
initialize_constants();
codegen_classtable = new CgenClassTable(classes, os);
codegen_classtable->execute();
os << "\n# end of generated code\n";
}
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// emit_* procedures
//
// emit_X writes code for operation "X" to the output stream.
// There is an emit_X for each opcode X, as well as emit_ functions
// for generating names according to the naming conventions (see emit.h)
// and calls to support functions defined in the trap handler.
//
// Register names and addresses are passed as strings. See `emit.h'
// for symbolic names you can use to refer to the strings.
//
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
static void emit_load(char *dest_reg, int offset, char *source_reg,
ostream &s)
{
s << LW << dest_reg << " " << offset * WORD_SIZE << "(" << source_reg << ")"
<< endl;
}
static void emit_store(char *source_reg, int offset, char *dest_reg,
ostream &s)
{
s << SW << source_reg << " " << offset * WORD_SIZE << "(" << dest_reg << ")"
<< endl;
}
static void emit_load_imm(char *dest_reg, int val, ostream &s)
{
s << LI << dest_reg << " " << val << endl;
}
static void emit_load_address(char *dest_reg, char *address, ostream &s)
{
s << LA << dest_reg << " " << address << endl;
}
static void emit_partial_load_address(char *dest_reg, ostream &s)
{
s << LA << dest_reg << " ";
}
static void emit_load_bool(char *dest, const BoolConst &b, ostream &s)
{
emit_partial_load_address(dest, s);
b.code_ref(s);
s << endl;
}
static void emit_load_string(char *dest, StringEntry *str, ostream &s)
{
emit_partial_load_address(dest, s);
str->code_ref(s);
s << endl;
}
static void emit_load_int(char *dest, IntEntry *i, ostream &s)
{
emit_partial_load_address(dest, s);
i->code_ref(s);
s << endl;
}
static void emit_move(char *dest_reg, char *source_reg, ostream &s)
{
s << MOVE << dest_reg << " " << source_reg << endl;
}
static void emit_neg(char *dest, char *src1, ostream &s)
{
s << NEG << dest << " " << src1 << endl;
}
static void emit_add(char *dest, char *src1, char *src2, ostream &s)
{
s << ADD << dest << " " << src1 << " " << src2 << endl;
}
static void emit_addu(char *dest, char *src1, char *src2, ostream &s)
{
s << ADDU << dest << " " << src1 << " " << src2 << endl;
}
static void emit_addiu(char *dest, char *src1, int imm, ostream &s)
{
s << ADDIU << dest << " " << src1 << " " << imm << endl;
}
static void emit_div(char *dest, char *src1, char *src2, ostream &s)
{
s << DIV << dest << " " << src1 << " " << src2 << endl;
}
static void emit_mul(char *dest, char *src1, char *src2, ostream &s)
{
s << MUL << dest << " " << src1 << " " << src2 << endl;
}
static void emit_sub(char *dest, char *src1, char *src2, ostream &s)
{
s << SUB << dest << " " << src1 << " " << src2 << endl;
}
static void emit_sll(char *dest, char *src1, int num, ostream &s)
{
s << SLL << dest << " " << src1 << " " << num << endl;
}
static void emit_jalr(char *dest, ostream &s)
{
s << JALR << "\t" << dest << endl;
}
static void emit_jal(char *address, ostream &s)
{
s << JAL << address << endl;
}
static void emit_return(ostream &s)
{
s << RET << endl;
}
static void emit_gc_assign(ostream &s)
{
s << JAL << "_GenGC_Assign" << endl;
}
static void emit_disptable_ref(Symbol sym, ostream &s)
{
s << sym << DISPTAB_SUFFIX;
}
static void emit_init_ref(Symbol sym, ostream &s)
{
s << sym << CLASSINIT_SUFFIX;
}
static void emit_label_ref(int l, ostream &s)
{
s << "label" << l;
}
static void emit_protobj_ref(Symbol sym, ostream &s)
{
s << sym << PROTOBJ_SUFFIX;
}
static void emit_method_ref(Symbol classname, Symbol methodname, ostream &s)
{
s << classname << METHOD_SEP << methodname;
}
static void emit_label_def(int l, ostream &s)
{
emit_label_ref(l, s);
s << ":" << endl;
}
static void emit_beqz(char *source, int label, ostream &s)
{
s << BEQZ << source << " ";
emit_label_ref(label, s);
s << endl;
}
static void emit_beq(char *src1, char *src2, int label, ostream &s)
{
s << BEQ << src1 << " " << src2 << " ";
emit_label_ref(label, s);
s << endl;
}
static void emit_bne(char *src1, char *src2, int label, ostream &s)
{
s << BNE << src1 << " " << src2 << " ";
emit_label_ref(label, s);
s << endl;
}
static void emit_bleq(char *src1, char *src2, int label, ostream &s)
{
s << BLEQ << src1 << " " << src2 << " ";
emit_label_ref(label, s);
s << endl;
}
static void emit_blt(char *src1, char *src2, int label, ostream &s)
{
s << BLT << src1 << " " << src2 << " ";
emit_label_ref(label, s);
s << endl;
}
static void emit_blti(char *src1, int imm, int label, ostream &s)
{
s << BLT << src1 << " " << imm << " ";
emit_label_ref(label, s);
s << endl;
}
static void emit_bgti(char *src1, int imm, int label, ostream &s)
{
s << BGT << src1 << " " << imm << " ";
emit_label_ref(label, s);
s << endl;
}
static void emit_branch(int l, ostream &s)
{
s << BRANCH;
emit_label_ref(l, s);
s << endl;
}
//
// Push a register on the stack. The stack grows towards smaller addresses.
//
static void emit_push(char *reg, ostream &str)
{
emit_store(reg, 0, SP, str);
emit_addiu(SP, SP, -4, str);
}
static void emit_pop(char *reg, ostream &str)
{
emit_load(reg, 1, SP, str);
emit_addiu(SP, SP, 4, str);
}
//
// Fetch the integer value in an Int object.
// Emits code to fetch the integer value of the Integer object pointed
// to by register source into the register dest
//
static void emit_fetch_int(char *dest, char *source, ostream &s)
{
emit_load(dest, DEFAULT_OBJFIELDS, source, s);
}
//
// Emits code to store the integer value contained in register source
// into the Integer object pointed to by dest.
//
static void emit_store_int(char *source, char *dest, ostream &s)
{
emit_store(source, DEFAULT_OBJFIELDS, dest, s);
}
static void emit_test_collector(ostream &s)
{
emit_push(ACC, s);
emit_move(ACC, SP, s); // stack end
emit_move(A1, ZERO, s); // allocate nothing
s << JAL << gc_collect_names[cgen_Memmgr] << endl;
emit_addiu(SP, SP, 4, s);
emit_load(ACC, 0, SP, s);
}
static void emit_gc_check(char *source, ostream &s)
{
if (source != (char *)A1)
emit_move(A1, source, s);
s << JAL << "_gc_check" << endl;
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------
static void emit_push_stack(int args, ostream &s)
{
emit_addiu(SP, SP, -12 - 4 * temp_size, s);
s << "\t# push fp,s0,ra" << endl;
emit_store(FP, 3 + temp_size, SP, s);
emit_store(SELF, 2 + temp_size, SP, s);
emit_store(RA, 1 + temp_size, SP, s);
s << "\t# fp point to return addr" << endl;
emit_addiu(FP, SP, 4, s);
s << "\t# a0 has the current self" << endl;
emit_move(SELF, ACC, s);
}
static void emit_pop_stack(int args, ostream &s)
{
emit_load(FP, 3 + temp_size, SP, s);
emit_load(SELF, 2 + temp_size, SP, s);
emit_load(RA, 1 + temp_size, SP, s);
emit_addiu(SP, SP, 12 + 4 * args, s);
emit_return(s);
}
static void emit_push_temp(char *source_reg, ostream &s)
{
emit_store(source_reg, used_temp++, FP, s);
if (cgen_debug)
if (used_temp > temp_size)
{
cout << "Stack overflow!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!" << endl;
s << "# stack overflow !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!\n";
}
}
static void emit_pop_temp(char *dest_reg, ostream &s)
{
emit_load(dest_reg, --used_temp, FP, s);
if (cgen_debug)
if (used_temp < 0)
cout << "Stack emmmm flow!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!" << endl;
}
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// coding strings, ints, and booleans
//
// Cool has three kinds of constants: strings, ints, and booleans.
// This section defines code generation for each type.
//
// All string constants are listed in the global "stringtable" and have
// type StringEntry. StringEntry methods are defined both for String
// constant definitions and references.
//
// All integer constants are listed in the global "inttable" and have
// type IntEntry. IntEntry methods are defined for Int
// constant definitions and references.
//
// Since there are only two Bool values, there is no need for a table.
// The two booleans are represented by instances of the class BoolConst,
// which defines the definition and reference methods for Bools.
//
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// Strings
//
void StringEntry::code_ref(ostream &s)
{
s << STRCONST_PREFIX << index;
}
//
// Emit code for a constant String.
// You should fill in the code naming the dispatch table.
//
void StringEntry::code_def(ostream &s, int stringclasstag)
{
IntEntryP lensym = inttable.add_int(len);
// Add -1 eye catcher
s << WORD << "-1" << endl;
code_ref(s);
s << LABEL // label
<< WORD << stringclasstag << endl // tag
<< WORD << (DEFAULT_OBJFIELDS + STRING_SLOTS + (len + 4) / 4)
<< endl // size
<< WORD;
/***** Add dispatch information for class String ******/
emit_disptable_ref(Str, s);
s << endl; // dispatch table
s << WORD;
lensym->code_ref(s);
s << endl; // string length
emit_string_constant(s, str); // ascii string
s << ALIGN; // align to word
}
//
// StrTable::code_string
// Generate a string object definition for every string constant in the
// stringtable.
//
void StrTable::code_string_table(ostream &s, int stringclasstag)
{
for (List<StringEntry> *l = tbl; l; l = l->tl())
l->hd()->code_def(s, stringclasstag);
}
//
// Ints
//
void IntEntry::code_ref(ostream &s)
{
s << INTCONST_PREFIX << index;
}
//
// Emit code for a constant Integer.
// You should fill in the code naming the dispatch table.
//
void IntEntry::code_def(ostream &s, int intclasstag)
{
// Add -1 eye catcher
s << WORD << "-1" << endl;
code_ref(s);
s << LABEL // label
<< WORD << intclasstag << endl // class tag
<< WORD << (DEFAULT_OBJFIELDS + INT_SLOTS) << endl // object size
<< WORD;
/***** Add dispatch information for class Int ******/
emit_disptable_ref(Int, s);
s << endl; // dispatch table
s << WORD << str << endl; // integer value
}
//
// IntTable::code_string_table
// Generate an Int object definition for every Int constant in the
// inttable.
//
void IntTable::code_string_table(ostream &s, int intclasstag)
{
for (List<IntEntry> *l = tbl; l; l = l->tl())
l->hd()->code_def(s, intclasstag);
}
//
// Bools
//
BoolConst::BoolConst(int i) : val(i)
{
assert(i == 0 || i == 1);
}
void BoolConst::code_ref(ostream &s) const
{
s << BOOLCONST_PREFIX << val;
}
//
// Emit code for a constant Bool.
// You should fill in the code naming the dispatch table.
//
void BoolConst::code_def(ostream &s, int boolclasstag)
{
// Add -1 eye catcher
s << WORD << "-1" << endl;
code_ref(s);
s << LABEL // label
<< WORD << boolclasstag << endl // class tag
<< WORD << (DEFAULT_OBJFIELDS + BOOL_SLOTS) << endl // object size
<< WORD;
/***** Add dispatch information for class Bool ******/
emit_disptable_ref(Bool, s);
s << endl; // dispatch table
s << WORD << val << endl; // value (0 or 1)
}
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// CgenClassTable methods
//
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//***************************************************
//
// Emit code to start the .data segment and to
// declare the global names.
//
//***************************************************
void CgenClassTable::code_global_data()
{
Symbol main = idtable.lookup_string(MAINNAME);
Symbol string = idtable.lookup_string(STRINGNAME);
Symbol integer = idtable.lookup_string(INTNAME);
Symbol boolc = idtable.lookup_string(BOOLNAME);
str << "\t.data\n" << ALIGN;
//
// The following global names must be defined first.
//
str << GLOBAL << CLASSNAMETAB << endl;
str << GLOBAL;
emit_protobj_ref(main, str);
str << endl;
str << GLOBAL;
emit_protobj_ref(integer, str);
str << endl;
str << GLOBAL;
emit_protobj_ref(string, str);
str << endl;
str << GLOBAL;
falsebool.code_ref(str);
str << endl;
str << GLOBAL;
truebool.code_ref(str);
str << endl;
str << GLOBAL << INTTAG << endl;
str << GLOBAL << BOOLTAG << endl;
str << GLOBAL << STRINGTAG << endl;
//
// We also need to know the tag of the Int, String, and Bool classes
// during code generation.
//
str << INTTAG << LABEL << WORD << intclasstag << endl;
str << BOOLTAG << LABEL << WORD << boolclasstag << endl;
str << STRINGTAG << LABEL << WORD << stringclasstag << endl;
}
//***************************************************
//
// Emit code to start the .text segment and to
// declare the global names.
//
//***************************************************
void CgenClassTable::code_global_text()
{
str << GLOBAL << HEAP_START << endl
<< HEAP_START << LABEL << WORD << 0 << endl
<< "\t.text" << endl
<< GLOBAL;
emit_init_ref(idtable.add_string("Main"), str);
str << endl << GLOBAL;
emit_init_ref(idtable.add_string("Int"), str);
str << endl << GLOBAL;
emit_init_ref(idtable.add_string("String"), str);
str << endl << GLOBAL;
emit_init_ref(idtable.add_string("Bool"), str);
str << endl << GLOBAL;
emit_method_ref(idtable.add_string("Main"), idtable.add_string("main"), str);
str << endl;
}
void CgenClassTable::code_bools(int boolclasstag)
{
falsebool.code_def(str, boolclasstag);
truebool.code_def(str, boolclasstag);
}
void CgenClassTable::code_select_gc()
{
//
// Generate GC choice constants (pointers to GC functions)
//
str << GLOBAL << "_MemMgr_INITIALIZER" << endl;
str << "_MemMgr_INITIALIZER:" << endl;
str << WORD << gc_init_names[cgen_Memmgr] << endl;
str << GLOBAL << "_MemMgr_COLLECTOR" << endl;
str << "_MemMgr_COLLECTOR:" << endl;
str << WORD << gc_collect_names[cgen_Memmgr] << endl;
str << GLOBAL << "_MemMgr_TEST" << endl;
str << "_MemMgr_TEST:" << endl;
str << WORD << (cgen_Memmgr_Test == GC_TEST) << endl;
}
//********************************************************
//
// Emit code to reserve space for and initialize all of
// the constants. Class names should have been added to
// the string table (in the supplied code, is is done
// during the construction of the inheritance graph), and
// code for emitting string constants as a side effect adds
// the string's length to the integer table. The constants
// are emmitted by running through the stringtable and inttable
// and producing code for each entry.
//
//********************************************************
void CgenClassTable::code_constants()
{
//
// Add constants that are required by the code generator.
//
stringtable.add_string("");
inttable.add_string("0");
stringtable.code_string_table(str, stringclasstag);
inttable.code_string_table(str, intclasstag);
code_bools(boolclasstag);
}
void CgenNode::code_nameTab(int &nodesize, ostream &s)
{
class_tags.insert(std::make_pair(name, nodesize));
tag = nodesize++;
s << WORD;
stringtable.lookup_string(name->get_string())->code_ref(s);
s << endl;
for (List<CgenNode> *l = children; l; l = l->tl())
l->hd()->code_nameTab(nodesize, s);
}
void CgenClassTable::code_class_nameTab()
{
str << CLASSNAMETAB << LABEL;
int nodesize = 0;
root()->code_nameTab(nodesize, str);
}
void CgenNode::code_objTab(ostream &s)
{
StringEntry *e = stringtable.lookup_string(name->get_string());
s << WORD;
emit_protobj_ref(e, s);
s << endl << WORD;
emit_init_ref(e, s);
s << endl;
for (List<CgenNode> *l = children; l; l = l->tl())
l->hd()->code_objTab(s);
}
void CgenClassTable::code_class_objTab()
{
str << CLASSOBJTAB << LABEL;
root()->code_objTab(str);
}
void CgenNode::code_protObj(std::vector<Symbol> mp, ostream &s)
{
attr_index = get_parentnd()->attr_index;
int a_size = attr_index.size();
for (int i = features->first(); features->more(i); i = features->next(i))
{
if (!features->nth(i)->is_attr())
continue;
attr_class *a = (attr_class *)features->nth(i);
attr_index.insert(std::make_pair(a->name, a_size++));
mp.push_back(a->type_decl);
}
s << WORD << "-1" << endl;
emit_protobj_ref(name, s);
s << LABEL;
s << WORD << tag << endl << WORD << (DEFAULT_OBJFIELDS + a_size) << endl;
s << WORD;
emit_disptable_ref(name, s);
s << endl;
if (name == Int || name == Bool)
{
s << WORD << "0" << endl;
}
else if (name == Str)
{
s << WORD;
inttable.lookup_string("0")->code_ref(s);
s << endl << WORD << "0" << endl;
}
else
{
for (int i = 0; i < (int)mp.size(); ++i)
{
Symbol type = mp[i];
if (type == Int)
{
s << WORD;
inttable.lookup_string("0")->code_ref(s);
s << "\t# int(0)" << endl;
}
else if (type == Bool)
{
s << WORD;
falsebool.code_ref(s);
s << "\t# bool(0)" << endl;
}
else if (type == Str)
{
s << WORD;
stringtable.lookup_string("")->code_ref(s);
s << "\t# s(\"\")" << endl;
}
else
{
s << WORD << "0\t# void" << endl;
}
}
}
for (List<CgenNode> *l = children; l; l = l->tl())
l->hd()->code_protObj(mp, s);
}
void CgenClassTable::code_class_protObj()
{
std::vector<Symbol> mp;
root()->code_protObj(mp, str);
}
//----------------
void CgenNode::code_dispTab(std::vector<std::pair<Symbol, Symbol>> mp,
ostream &s)
{
emit_disptable_ref(name, s);
s << LABEL;
method_index = get_parentnd()->method_index;
int m_size = method_index.size();
for (int i = features->first(); features->more(i); i = features->next(i))
{
if (!features->nth(i)->is_method())
continue;
method_class *m = (method_class *)features->nth(i);
Symbol method_name = m->name;
if (method_index.find(method_name) == method_index.end())
{
method_index.insert(std::make_pair(method_name, m_size++));
mp.push_back(std::make_pair(method_name, name));
}
else
{
// override
int index = method_index[method_name];
mp[index].second = name;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < (int)mp.size(); ++i)
{
s << WORD;
emit_method_ref(mp[i].second, mp[i].first, s);
s << endl;
}
for (List<CgenNode> *l = children; l; l = l->tl())
l->hd()->code_dispTab(mp, s);
}
void CgenClassTable::code_class_dispTab()
{
std::vector<std::pair<Symbol, Symbol>> mp;
root()->code_dispTab(mp, str);
}
// init-----------
void CgenNode::code_init(ostream &s)
{
current_class = name;
env.add_Attribute(this);
if (cgen_debug)
cout << "current class is " << name << endl;
temp_size = 0;
for (int i = features->first(); features->more(i); i = features->next(i))
{
if (!features->nth(i)->is_attr())
continue;
attr_class *a = (attr_class *)features->nth(i);
temp_size = std::max(temp_size, a->tmp_Num());
}
if (cgen_debug)
cout << "temp size " << temp_size << endl;
used_temp = 0;
emit_init_ref(name, s);
s << LABEL;
emit_push_stack(temp_size, s);
Symbol parent_name = parentnd->name;
if (parent_name != No_class)
{
s << JAL;
emit_init_ref(parent_name, s);
}
for (int i = features->first(); features->more(i); i = features->next(i))
{
if (!features->nth(i)->is_attr())
continue;
attr_class *a = (attr_class *)features->nth(i);
if (a->init->isempty())
{
}
else
{
s << "\t# initialize argument " << a->name << endl;
a->init->code(s);
int indx = attr_index[a->name];
emit_store(ACC, DEFAULT_OBJFIELDS + indx, SELF, s);
if (cgen_Memmgr == 1)
{
emit_addiu(A1, SELF, 4 * (indx + DEFAULT_OBJFIELDS), s);
emit_gc_assign(s);
}
}
}
s << "\t# return self" << endl;
emit_move(ACC, SELF, s);
emit_pop_stack(temp_size, s);
for (List<CgenNode> *l = children; l; l = l->tl())
l->hd()->code_init(s);
}
void CgenClassTable::code_class_init()
{
root()->code_init(str);
}
// methods-----------------------
void CgenClassTable::code_methods()
{
for (List<CgenNode> *l = nds; l; l = l->tl())
{
CgenNodeP cur = l->hd();
env.add_Attribute(cur);
current_class = cur->name;
if (cgen_debug)
cout << "current class is " << current_class << endl;
if (cur->basic() == true)
continue;
Features f = cur->features;
for (int i = f->first(); f->more(i); i = f->next(i))
if (f->nth(i)->is_method())
{
str << cur->name << METHOD_SEP;
f->nth(i)->code(str);
}
}
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
CgenClassTable::CgenClassTable(Classes classes, ostream &s)
: nds(NULL), str(s)
{
stringclasstag = 3 /* Change to your String class tag here */;
intclasstag = 1 /* Change to your Int class tag here */;
boolclasstag = 2 /* Change to your Bool class tag here */;
enterscope();
if (cgen_debug)
cout << "Building CgenClassTable" << endl;
install_basic_classes();
install_classes(classes);
build_inheritance_tree();
code();
}
void CgenClassTable::install_basic_classes()
{
// The tree package uses these globals to annotate the classes built below.
// curr_lineno = 0;
Symbol filename = stringtable.add_string("<basic class>");
//
// A few special class names are installed in the lookup table but not
// the class list. Thus, these classes exist, but are not part of the
// inheritance hierarchy.
// No_class serves as the parent of Object and the other special classes.
// SELF_TYPE is the self class; it cannot be redefined or inherited.
// prim_slot is a class known to the code generator.
//
addid(No_class,
new CgenNode(class_(No_class, No_class, nil_Features(), filename),
Basic, this));
addid(SELF_TYPE,
new CgenNode(class_(SELF_TYPE, No_class, nil_Features(), filename),
Basic, this));
addid(prim_slot,
new CgenNode(class_(prim_slot, No_class, nil_Features(), filename),
Basic, this));
//
// The Object class has no parent class. Its methods are
// cool_abort() : Object aborts the program
// type_name() : Str returns a string representation of class
// name copy() : SELF_TYPE returns a copy of the object
//
// There is no need for method bodies in the basic classes---these
// are already built in to the runtime system.
//
//
install_class(new CgenNode(
class_(
Object, No_class,
append_Features(
append_Features(single_Features(method(cool_abort, nil_Formals(),
Object, no_expr())),
single_Features(method(type_name, nil_Formals(),
Str, no_expr()))),
single_Features(
method(copy, nil_Formals(), SELF_TYPE, no_expr()))),
filename),
Basic, this));
//
// The Int class has no methods and only a single attribute, the
// "val" for the integer.
//
install_class(new CgenNode(
class_(Int, Object, single_Features(attr(val, prim_slot, no_expr())),
filename),
Basic, this));
//
// Bool also has only the "val" slot.
//
install_class(new CgenNode(
class_(Bool, Object, single_Features(attr(val, prim_slot, no_expr())),
filename),
Basic, this));
//
// The class Str has a number of slots and operations:
// val ???
// str_field the string itself
// length() : Int length of the string
// concat(arg: Str) : Str string concatenation
// substr(arg: Int, arg2: Int): Str substring
//
install_class(new CgenNode(
class_(Str, Object,
append_Features(
append_Features(
append_Features(
append_Features(
single_Features(attr(val, Int, no_expr())),
single_Features(
attr(str_field, prim_slot, no_expr()))),
single_Features(
method(length, nil_Formals(), Int, no_expr()))),
single_Features(method(concat,
single_Formals(formal(arg, Str)),
Str, no_expr()))),
single_Features(
method(substr,
append_Formals(single_Formals(formal(arg, Int)),
single_Formals(formal(arg2, Int))),
Str, no_expr()))),
filename),
Basic, this));
// The IO class inherits from Object. Its methods are
// out_string(Str) : SELF_TYPE writes a string to the output
// out_int(Int) : SELF_TYPE " an int " " "
// in_string() : Str reads a string from the input
// in_int() : Int " an int " " "
//
install_class(new CgenNode(
class_(
IO, Object,
append_Features(
append_Features(
append_Features(
single_Features(method(out_string,
single_Formals(formal(arg, Str)),
SELF_TYPE, no_expr())),
single_Features(method(out_int,
single_Formals(formal(arg, Int)),
SELF_TYPE, no_expr()))),
single_Features(
method(in_string, nil_Formals(), Str, no_expr()))),
single_Features(method(in_int, nil_Formals(), Int, no_expr()))),
filename),
Basic, this));
//
}
// CgenClassTable::install_class
// CgenClassTable::install_classes
//
// install_classes enters a list of classes in the symbol table.
//
void CgenClassTable::install_class(CgenNodeP nd)
{
Symbol name = nd->get_name();
if (probe(name))
{
return;
}
// The class name is legal, so add it to the list of classes
// and the symbol table.
nds = new List<CgenNode>(nd, nds);
addid(name, nd);
}
void CgenClassTable::install_classes(Classes cs)
{
for (int i = cs->first(); cs->more(i); i = cs->next(i))
install_class(new CgenNode(cs->nth(i), NotBasic, this));
}
//
// CgenClassTable::build_inheritance_tree
//
void CgenClassTable::build_inheritance_tree()
{
for (List<CgenNode> *l = nds; l; l = l->tl())
{
set_relations(l->hd());
// class_tags.insert(std::make_pair(l->hd()->name, nodesize++));
}
}
//
// CgenClassTable::set_relations
//
// Takes a CgenNode and locates its, and its parent's, inheritance nodes
// via the class table. Parent and child pointers are added as appropriate.
//
void CgenClassTable::set_relations(CgenNodeP nd)
{
// nd->tag = nodesize;
CgenNode *parent_node = probe(nd->get_parent());
nd->set_parentnd(parent_node);
parent_node->add_child(nd);
}
void CgenNode::add_child(CgenNodeP n)
{
children = new List<CgenNode>(n, children);
}
void CgenNode::set_parentnd(CgenNodeP p)
{
assert(parentnd == NULL);
assert(p != NULL);
parentnd = p;
}
void CgenClassTable::code()
{
str << "# coding global data" << endl;
code_global_data();
str << "# choosing gc" << endl;
code_select_gc();
str << "# coding constants" << endl;
code_constants();
// Add your code to emit
// - prototype objects
// - class_nameTab
// - dispatch tables
//
str << "# coding class name table" << endl;
code_class_nameTab();
str << "# coding class obj table" << endl;
code_class_objTab();
str << "# coding dispatch tables" << endl;
code_class_dispTab();
str << "# coding prototype object" << endl;
code_class_protObj();
str << "# coding global text" << endl;
code_global_text();
}
void CgenClassTable::execute()
{
// Add your code to emit
// - object initializer
// - the class methods
// - etc...
str << "# coding init" << endl;
code_class_init();
str << "# code method" << endl;
code_methods();
exitscope();
}
CgenNodeP CgenClassTable::root()
{
return probe(Object);
}
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// CgenNode methods
//
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
CgenNode::CgenNode(Class_ nd, Basicness bstatus, CgenClassTableP ct)
: class__class((const class__class &)*nd), parentnd(NULL), children(NULL),
basic_status(bstatus)
{
stringtable.add_string(name->get_string()); // Add class name to string table
}
method_class *CgenNode::find_method(Symbol method_name)
{
if (name == No_class)
return NULL;
for (int i = features->first(); features->more(i); i = features->next(i))
{
if (!features->nth(i)->is_method())
continue;
method_class *tmp = (method_class *)features->nth(i);
if (tmp->name == method_name)
return tmp;
}
return parentnd->find_method(method_name);
}
void method_class::install_args()
{
for (int i = formals->first(); formals->more(i); i = formals->next(i))
{
formal_class *f = (formal_class *)formals->nth(i);
env.add_Argument(f->name);
if (cgen_debug)
cout << "\tinstall arg " << f->name << endl;
}
}
//******************************************************************
//
// Fill in the following methods to produce code for the
// appropriate expression. You may add or remove parameters
// as you wish, but if you do, remember to change the parameters
// of the declarations in `cool-tree.h' Sample code for
// constant integers, strings, and booleans are provided.
//
//*****************************************************************
void method_class::code(ostream &s)
{
if (cgen_debug)
cout << "start method " << name << endl;
used_temp = 0;
temp_size = tmp_Num();
if (cgen_debug)
cout << "temps: " << temp_size << endl << endl;
s << name << LABEL;
emit_push_stack(temp_size, s);
if (cgen_debug)
cout << "args enter scope\n";
env.args_enter();
install_args();
expr->code(s);
env.args_exit();
if (cgen_debug)
cout << "args exit scope\n";
int formal_size = formals->len();
emit_pop_stack(formal_size + temp_size, s);
}
void attr_class::code(ostream &s) {}
void assign_class::code(ostream &s)
{
s << "# assign expr\n";
expr->code(s);
s << "\t# look up lval addr\n";
int indx;
if ((indx = env.get_Var(name)) != -1)
{
s << "\t# find in " << indx << " position in let variables\n";
emit_store(ACC, indx, FP, s);
if (cgen_Memmgr == 1)
{
emit_addiu(A1, FP, 4 * indx, s);
emit_gc_assign(s);
}
}
else if ((indx = env.get_Argument(name)) != -1)
{
s << "\t# find in " << indx << " position in argument\n";
emit_store(ACC, DEFAULT_FPFIELDS + temp_size + indx, FP, s);
if (cgen_Memmgr == 1)
{
emit_addiu(A1, FP, 4 * (DEFAULT_FPFIELDS + temp_size + indx), s);
emit_gc_assign(s);
}
}
else if ((indx = env.get_Attribute(name)) != -1)
{
s << "\t# find in " << indx << " position in attribute\n";
emit_store(ACC, DEFAULT_OBJFIELDS + indx, SELF, s);
if (cgen_Memmgr == 1)
{
emit_addiu(A1, SELF, 4 * (DEFAULT_OBJFIELDS + indx), s);
emit_gc_assign(s);
}
}
else
{
s << "\t#bad assign! ERRORRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRR\n";
if (cgen_debug)
cout << "\t#bad assign! ERRORRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRR\n";
}
}
void static_dispatch_class::code(ostream &s)
{
s << "# static dispatch exp " << name << endl;
for (int i = actual->first(); actual->more(i); i = actual->next(i))
{
actual->nth(i)->code(s);
s << "\t# push arg on stack\n";
emit_push(ACC, s);
}
s << "\t# then eval e0 and save in a0\n";
expr->code(s);
s << "\t# if e0 is void \n";
int e0_not_zero = label_num++;
emit_bne(ACC, ZERO, e0_not_zero, s);
s << "\t# abort\n\t#loading filename to a0 and linenumber to t1\n";
s << LA << ACC << " str_const0" << endl;
emit_load_imm(T1, 1, s);
emit_jal("_dispatch_abort", s);
s << "\t# continue dispatching\n";
emit_label_def(e0_not_zero, s);
Symbol old_class = current_class;
current_class = type_name;
// get static dispatch class
CgenNodeP c = codegen_classtable->probe(current_class);
int indx = c->method_index[name];
s << "\t# locate method " << name << " of class " << type_name << endl;
s << "\t# get " << type_name << "''s dispatch table\n";
s << LA << T1 << " " << type_name << DISPTAB_SUFFIX << endl;
s << "\t# find method in index " << indx << endl;
emit_load(T1, indx, T1, s);
current_class = old_class;
s << "\t# jump to method " << name << endl;
emit_jalr(T1, s);
}
void dispatch_class::code(ostream &s)
{
s << "# dispatch exp " << name << "\n";
for (int i = actual->first(); actual->more(i); i = actual->next(i))
{
actual->nth(i)->code(s);
s << "\t# push arg on stack\n";
emit_push(ACC, s);
}
s << "\t# then eval e0 and save in a0\n";
expr->code(s);
s << "\t# if e0 is void \n";
int e0_not_zero = label_num++;
emit_bne(ACC, ZERO, e0_not_zero, s);
s << "\t# abort\n\t#loading filename to a0 and linenumber to t1\n";
s << LA << ACC << " str_const0" << endl;
emit_load_imm(T1, 1, s);
emit_jal("_dispatch_abort", s);
s << "\t# continue dispatching\n";
emit_label_def(e0_not_zero, s);
//------------------------
Symbol old_class = current_class;
if (expr->get_type() != SELF_TYPE)
current_class = expr->get_type();
CgenNodeP c = codegen_classtable->probe(current_class);
if (cgen_debug)
cout << "dispatch class " << current_class << endl;
int indx = c->method_index[name];
s << "\t# locate method " << name << " of class " << current_class << endl;
s << "\t# get self's dispatch table\n";
emit_load(T1, 2, ACC, s);
s << "\t# find method in index " << indx << endl;
emit_load(T1, indx, T1, s);
current_class = old_class;
s << "\t# jump to method " << name << endl;
emit_jalr(T1, s);
}
void cond_class::code(ostream &s)
{
s << "# if_else exp\n";
s << "\t# eval predicate\n";
pred->code(s);
s << "\t# extract bool value of predicate to T1\n";
emit_fetch_int(T1, ACC, s);
int false_label = label_num++;
int finish_label = label_num++;
s << "\t# if false, goto else\n";
emit_beq(T1, ZERO, false_label, s);
s << "\t# coding then exp\n";
then_exp->code(s);
s << "\t# jump to finish label\n";
emit_branch(finish_label, s);
s << "\t# coding else exp\n";
emit_label_def(false_label, s);
else_exp->code(s);
s << "\t# finish\n";
emit_label_def(finish_label, s);
}
void loop_class::code(ostream &s)
{
int start_label = label_num++;
int finish_label = label_num++;
s << "# while exp\n";
emit_label_def(start_label, s);
s << "\t# eval predicate\n";
pred->code(s);
s << "\t# fetch predicate result\n";
emit_fetch_int(T1, ACC, s);
s << "\t# if false => finish\n";
emit_beqz(T1, finish_label, s);
s << "\t# eval body\n";
body->code(s);
s << "\t# jump to pred\n";
emit_branch(start_label, s);
s << "\t# while finish\n";
emit_label_def(finish_label, s);
s << "\t# while result is void\n";
emit_move(ACC, ZERO, s);
}
int branch_class::get_child_tag()
{
int tag = class_tags[type_decl];
CgenNodeP c = codegen_classtable->probe(type_decl);
while (c->get_children() != NULL)
{
for (List<CgenNode> *l = c->get_children(); l; l = l->tl())
{
c = l->hd();
tag = std::max(tag, class_tags[c->name]);
}
}
return tag;
}
void typcase_class::code(ostream &s)
{
s << "# typcase expr\n";
int finish_label = label_num++;
s << "\t# eval e0\n";
expr->code(s);
s << "\t# save expr on temp\n";
emit_push_temp(ACC, s);
s << "\t# abort if void\n";
emit_bne(ACC, ZERO, label_num, s);
emit_load_address(ACC, "str_const0", s);
emit_load_imm(T1, 1, s);
emit_jal("_case_abort2", s);
emit_label_def(label_num++, s);
s << "\t# T2 = class tag of e0\n";
emit_load(T2, 0, ACC, s);
//-------------------------------
//计算所有case 的tag
//计算所有case的孩子最大tag
//按照大到小的顺序排序,输出
std::vector<std::pair<int, int>> case_tag;
std::map<int, Expression> mp;
env.vars_enter();
for (int i = cases->first(); cases->more(i); i = cases->next(i))
{
branch_class *b = (branch_class *)cases->nth(i);
//局部变量,let覆盖?
env.add_Variable(b->name, used_temp - 1);
int fs = class_tags[b->type_decl];
int se = b->get_child_tag();
if (cgen_debug)
cout << "[ " << fs << " , " << se << " ]\n";
case_tag.push_back(std::make_pair(fs, se));
mp.insert(std::make_pair(fs, b->expr));
}
auto sortbysec = [&](const std::pair<int, int> &a,
const std::pair<int, int> &b)
{
return (a.first > b.first);
};
std::sort(case_tag.begin(), case_tag.end(), sortbysec);
for (int i = 0; i < (int)case_tag.size(); ++i)
{
int fs = case_tag[i].first, se = case_tag[i].second;
int next_case = label_num++;
emit_blti(T2, fs, next_case, s);
emit_bgti(T2, se, next_case, s);
mp[fs]->code(s);
emit_branch(finish_label, s);
emit_label_def(next_case, s);
}
emit_jal("_case_abort", s);
used_temp--;
env.vars_exit();
emit_label_def(finish_label, s);
}
void block_class::code(ostream &s)
{
s << "# block exp\n";
for (int i = body->first(); body->more(i); i = body->next(i))
{
body->nth(i)->code(s);
}
}
void let_class::code(ostream &s)
{
s << "# let exp\n";
s << "\t# first eval init exps\n";
init->code(s);
if (init->isempty())
{
// We still need to deal with basic types.
if (type_decl == Str)
{
emit_load_string(ACC, stringtable.lookup_string(""), s);
}
else if (type_decl == Int)
{
emit_load_int(ACC, inttable.lookup_string("0"), s);
}
else if (type_decl == Bool)
{
emit_load_bool(ACC, BoolConst(0), s);
}
}
s << "\t# push let var " << identifier << " onto temp\n";
// emit_push(ACC, s);
emit_push_temp(ACC, s);
env.vars_enter();
env.add_Variable(identifier, used_temp - 1);
if (cgen_debug)
cout << "var enter scope\n";
s << "\t# eval let body\n";
body->code(s);
env.vars_exit();
if (cgen_debug)
cout << "var exit scope\n";
s << "\t# pop let var " << endl;
s << "\t# used_temp--;" << endl;
// emit_addiu(SP, SP, 4, s);
used_temp--;
}
void plus_class::code(ostream &s)
{
s << "# Plus\n";
s << "\t# start eval e1" << endl;
e1->code(s);
s << "\t# e1 save to temp var" << endl;
emit_push_temp(ACC, s);
s << "\t# start eval e2 and copy" << endl;
e2->code(s);
emit_jal("Object.copy", s);
s << "\t# pop e1 to t1, move e2 to t2\n"
<< "\t# a0 has true and a1 has false to call equality_test\n";
emit_pop_temp(T1, s);
// emit_move(T2, ACC, s);
s << "\t# extract int value inside the object\n";
emit_load(T1, 3, T1, s);
emit_load(T2, 3, ACC, s);
s << "\t# modify int into t1\n";
emit_add(T1, T1, T2, s);
emit_store(T1, 3, ACC, s);
}
void sub_class::code(ostream &s)
{
s << "# Subtract\n";
s << "\t# start eval e1" << endl;
e1->code(s);
s << "\t# e1 save to temp var" << endl;
emit_push_temp(ACC, s);
s << "\t# start eval e2 and copy" << endl;
e2->code(s);
emit_jal("Object.copy", s);
s << "\t# pop e1 to t1, move e2 to t2\n"
<< "\t# a0 has true and a1 has false to call equality_test\n";
emit_pop_temp(T1, s);
// emit_move(T2, ACC, s);
s << "\t# extract int value inside the object\n";
emit_load(T1, 3, T1, s);
emit_load(T2, 3, ACC, s);
s << "\t# modify int into t1\n";
emit_sub(T1, T1, T2, s);
emit_store(T1, 3, ACC, s);
}
void mul_class::code(ostream &s)
{
s << "# Multiplication\n";
s << "\t# start eval e1" << endl;
e1->code(s);
s << "\t# e1 save to temp var" << endl;
emit_push_temp(ACC, s);
s << "\t# start eval e2 and copy" << endl;
e2->code(s);
emit_jal("Object.copy", s);
s << "\t# pop e1 to t1, move e2 to t2\n"
<< "\t# a0 has true and a1 has false to call equality_test\n";
emit_pop_temp(T1, s);
// emit_move(T2, ACC, s);
s << "\t# extract int value inside the object\n";
emit_load(T1, 3, T1, s);
emit_load(T2, 3, ACC, s);
s << "\t# modify int into t1\n";
emit_mul(T1, T1, T2, s);
emit_store(T1, 3, ACC, s);
}
void divide_class::code(ostream &s)
{
s << "# Divide \n";
s << "\t# start eval e1" << endl;
e1->code(s);
s << "\t# e1 save to temp var" << endl;
emit_push_temp(ACC, s);
s << "\t# start eval e2 and copy" << endl;
e2->code(s);
emit_jal("Object.copy", s);
s << "\t# pop e1 to t1, move e2 to t2\n"
<< "\t# a0 has true and a1 has false to call equality_test\n";
emit_pop_temp(T1, s);
// emit_move(T2, ACC, s);
s << "\t# extract int value inside the object\n";
emit_load(T1, 3, T1, s);
emit_load(T2, 3, ACC, s);
s << "\t# modify int into t2\n";
emit_div(T1, T1, T2, s);
emit_store(T1, 3, ACC, s);
}
void neg_class::code(ostream &s)
{
s << "\t# negative exp\n";
s << "\t# eval e1 and copy\n";
e1->code(s);
emit_jal("Object.copy", s);
s << "\t# eval neg to a0\n";
emit_load(T1, 3, ACC, s);
emit_neg(T1, T1, s);
emit_store(T1, 3, ACC, s);
}
void lt_class::code(ostream &s)
{
s << "# Int operation: less than\n";
s << "\t# start eval e1" << endl;
e1->code(s);
s << "\t# e1 save to temp var" << endl;
emit_push_temp(ACC, s);
s << "\t# start eval e2" << endl;
e2->code(s);
s << "\t# pop e1 to t1, move e2 to t2\n"
<< "\t# a0 has true and a1 has false to call equality_test\n";
emit_pop_temp(T1, s);
// emit_move(T2, ACC, s);
s << "\t# extract int value inside the object\n";
emit_load(T1, 3, T1, s);
emit_load(T2, 3, ACC, s);
s << "\t# pretend t1 < t2\n";
emit_load_bool(ACC, BoolConst(1), s);
s << "\t# if t1 < t2 return true and finish\n";
emit_blt(T1, T2, label_num, s);
emit_load_bool(ACC, BoolConst(0), s);
emit_label_def(label_num++, s);
}
void eq_class::code(ostream &s)
{
s << "# equality_test exp" << endl;
s << "\t# start eval e1" << endl;
e1->code(s);
s << "\t# e1 save to temp var" << endl;
// emit_push(ACC, s);
emit_push_temp(ACC, s);
s << "\t# start eval e2" << endl;
e2->code(s);
s << "\t# pop e1 to t1, move e2 to t2\n"
<< "\t# a0 has true and a1 has false to call equality_test\n";
// emit_pop(T1, s);
emit_pop_temp(T1, s);
emit_move(T2, ACC, s);
if (e1->type == Int || e1->type == Str || e1->type == Bool)
if (e2->type == Int || e2->type == Str || e2->type == Bool)
{
emit_load_bool(ACC, BoolConst(1), s);
emit_load_bool(A1, BoolConst(0), s);
emit_jal("equality_test", s);
return;
}
s << "\t# Pretend that t1 = t2" << endl;
emit_load_bool(ACC, BoolConst(1), s);
s << "\t# Compare the two pointers." << endl;
emit_beq(T1, T2, label_num, s);
emit_load_bool(ACC, BoolConst(0), s);
emit_label_def(label_num++, s);
}
void leq_class::code(ostream &s)
{
s << "# Int operation: less and euqal\n";
s << "\t# start eval e1" << endl;
e1->code(s);
s << "\t# e1 save to temp var" << endl;
emit_push_temp(ACC, s);
s << "\t# start eval e2" << endl;
e2->code(s);
s << "\t# pop e1 to t1, move e2 to t2\n"
<< "\t# a0 has true and a1 has false to call equality_test\n";
emit_pop_temp(T1, s);
// emit_move(T2, ACC, s);
s << "\t# extract int value inside the object\n";
emit_load(T1, 3, T1, s);
emit_load(T2, 3, ACC, s);
s << "\t# pretend t1 <= t2\n";
emit_load_bool(ACC, BoolConst(1), s);
s << "\t# if t1 <= t2 return true and finish\n";
emit_bleq(T1, T2, label_num, s);
emit_load_bool(ACC, BoolConst(0), s);
emit_label_def(label_num++, s);
}
void comp_class::code(ostream &s)
{
s << "\t# not expr" << endl;
s << "\t# First eval the bool" << endl;
e1->code(s);
emit_load(T1, 3, ACC, s);
s << "\t# Pretend ACC = false, then we need to construct true" << endl;
emit_load_bool(ACC, BoolConst(1), s);
s << "\t# If ACC = false, jumpto finish" << endl;
emit_beq(T1, ZERO, label_num, s);
s << "\t# Load false" << endl;
emit_load_bool(ACC, BoolConst(0), s);
s << "\t# finish:" << endl;
emit_label_def(label_num, s);
++label_num;
}
void int_const_class::code(ostream &s)
{
//
// Need to be sure we have an IntEntry *, not an arbitrary Symbol
//
emit_load_int(ACC, inttable.lookup_string(token->get_string()), s);
}
void string_const_class::code(ostream &s)
{
emit_load_string(ACC, stringtable.lookup_string(token->get_string()), s);
}
void bool_const_class::code(ostream &s)
{
emit_load_bool(ACC, BoolConst(val), s);
}
void new__class::code(ostream &s)
{
s << "# new exp\n";
if (type_name == SELF_TYPE)
{
s << "\t# new selftype, find it out\n";
emit_load_address(T1, "class_objTab", s);
s << "\t# get class by tag\n";
emit_load(T2, 0, SELF, s);
emit_sll(T2, T2, 3, s);
s << "\t# get self prototype addr\n";
emit_addu(T1, T1, T2, s);
s << "\t# push addr on temp\n";
emit_push_temp(T1, s);
emit_load(ACC, 0, T1, s);
emit_jal("Object.copy", s);
s << "\t# pop addr from temp\n";
emit_pop_temp(T1, s);
s << "\t# get self init addr\n";
emit_load(T1, 1, T1, s);
s << "\t# goto init\n";
emit_jalr(T1, s);
return;
}
s << LA << ACC << " " << type_name << PROTOBJ_SUFFIX << endl;
emit_jal("Object.copy", s);
s << JAL << type_name << CLASSINIT_SUFFIX << endl;
}
void isvoid_class::code(ostream &s)
{
s << "# isvoid expr\n";
e1->code(s);
emit_move(T1, ACC, s);
emit_load_bool(ACC, BoolConst(1), s);
emit_beqz(T1, label_num, s);
emit_load_bool(ACC, BoolConst(0), s);
emit_label_def(label_num++, s);
}
void no_expr_class::code(ostream &s)
{
emit_move(ACC, ZERO, s);
}
void object_class::code(ostream &s)
{
s << "\t# It's Object " << name << endl;
int indx;
if ((indx = env.get_Var(name)) != -1)
{
s << "\t# find in " << indx << " position in let variables\n";
emit_load(ACC, indx, FP, s);
if (cgen_Memmgr == 1)
{
emit_addiu(A1, FP, 4 * indx, s);
emit_gc_assign(s);
}
}
else if ((indx = env.get_Argument(name)) != -1)
{
s << "\t# find in " << indx << " position in argument\n";
emit_load(ACC, DEFAULT_FPFIELDS + temp_size + indx, FP, s);
if (cgen_Memmgr == 1)
{
emit_addiu(A1, FP, 4 * (DEFAULT_FPFIELDS + temp_size + indx), s);
emit_gc_assign(s);
}
}
else if ((indx = env.get_Attribute(name)) != -1)
{
s << "\t# find in " << indx << " position in attribute\n";
emit_load(ACC, DEFAULT_OBJFIELDS + indx, SELF, s);
if (cgen_Memmgr == 1)
{
emit_addiu(A1, SELF, 4 * (DEFAULT_OBJFIELDS + indx), s);
emit_gc_assign(s);
}
}
else if (name == self)
{
s << "\t# It is self." << endl;
emit_move(ACC, SELF, s);
}
else
{
s << "\t#obj not found! ERRORRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRR\n";
if (cgen_debug)
cout << "\t#obj not found! " << name << " ERRORRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRR\n";
}
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
int method_class::tmp_Num()
{
return expr->tmp_Num();
}
int attr_class::tmp_Num()
{
return init->tmp_Num();
}
int assign_class::tmp_Num()
{
return expr->tmp_Num();
}
int static_dispatch_class::tmp_Num()
{
int mx = expr->tmp_Num();
for (int i = actual->first(); actual->more(i); i = actual->next(i))
mx = std::max(mx, actual->nth(i)->tmp_Num());
return mx;
}
int dispatch_class::tmp_Num()
{
int mx = expr->tmp_Num();
for (int i = actual->first(); actual->more(i); i = actual->next(i))
mx = std::max(mx, actual->nth(i)->tmp_Num());
return mx;
}
int cond_class::tmp_Num()
{
return std::max(pred->tmp_Num(),
std::max(then_exp->tmp_Num(), else_exp->tmp_Num()));
}
int loop_class::tmp_Num()
{
return std::max(pred->tmp_Num(), body->tmp_Num());
}
int typcase_class::tmp_Num()
{
int mx = expr->tmp_Num();
for (int i = cases->first(); cases->more(i); i = cases->next(i))
{
mx = std::max(mx, 1 + cases->nth(i)->tmp_Num());
}
return mx;
}
int branch_class::tmp_Num()
{
return expr->tmp_Num();
}
int block_class::tmp_Num()
{
int mx = 0;
for (int i = body->first(); body->more(i); i = body->next(i))
{
mx = std::max(mx, body->nth(i)->tmp_Num());
}
return mx;
}
int let_class::tmp_Num()
{
return std::max(init->tmp_Num(), body->tmp_Num() + 1);
}
int plus_class::tmp_Num()
{
return std::max(e1->tmp_Num(), e2->tmp_Num() + 1);
}
int sub_class::tmp_Num()
{
return std::max(e1->tmp_Num(), e2->tmp_Num() + 1);
}
int mul_class::tmp_Num()
{
return std::max(e1->tmp_Num(), e2->tmp_Num() + 1);
}
int divide_class::tmp_Num()
{
return std::max(e1->tmp_Num(), e2->tmp_Num() + 1);
}
int lt_class::tmp_Num()
{
return std::max(e1->tmp_Num(), e2->tmp_Num() + 1);
}
int eq_class::tmp_Num()
{
return std::max(e1->tmp_Num(), e2->tmp_Num() + 1);
}
int leq_class::tmp_Num()
{
return std::max(e1->tmp_Num(), e2->tmp_Num() + 1);
}
int neg_class::tmp_Num()
{
return e1->tmp_Num();
}
int comp_class::tmp_Num()
{
return e1->tmp_Num();
}
int int_const_class::tmp_Num()
{
return 0;
}
int bool_const_class::tmp_Num()
{
return 0;
}
int string_const_class::tmp_Num()
{
return 0;
}
int new__class::tmp_Num()
{
if (type_name == SELF_TYPE)
return 1;
return 0;
}
int object_class::tmp_Num()
{
return 0;
}
int no_expr_class::tmp_Num()
{
return 0;
}
int isvoid_class::tmp_Num()
{
return e1->tmp_Num();
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号