Ajax技术+layer弹窗
一、Ajax技术简介
1、AJAX(Asynchronous Javascript And XML)翻译成中文就是“异步Javascript和XML”。
即使用Javascript语言与服务器进行异步交互,传输的数据为XML(当然,传输的数据不只是XML,现在更多使用json数据)。
局部刷新、一步提交
2、作用
前端技术,把前端的数据提交到后端的。Ajax技术就是局部刷新,异步提交,它不需要刷新整个页面,只需要刷新局部的,主要就是刷新的时候是无感知的
3、案例
html 前端页面:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<link href="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/twitter-bootstrap/3.3.6/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet">
<script src="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/jquery/3.6.4/jquery.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/twitter-bootstrap/3.3.6/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<input type="text" name="" id="d1">+
<input type="text" name="" id="d2">=
<input type="text" name="" id="d3">
<button class="btn btn-info">计算</button>
<script>
$(".btn").click(function() {
// 获取输入框中的内容
var d1 = $("#d1").val();
var d2 = $("#d2").val();
// 前端数据提交到后端
$.ajax({
// 1、提交到哪里
url: "",
// 2、要指定请求方式提交
type: "post",
// 3、指定要传递的数据
data: {'d1':d1,'d2':d2},
// 4、回调函数, 接收后端返回的数据
success : function(res){
{#console.log(res);#}
$("#d3").val(res)
}
})
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
注意:Ajax 提交数据到后端的4个步骤
$.ajax({
url:'/index/?a=1&b=2',
type:'post',
data:{'a':1, b:2}
success:function(res) {
# res:什么时候反序列化,什么时候不反序列化
console.log(res.username)
console.log(res.data.password)
}
})
$.ajax({ }) ajax的调用,
后端返回的数据给res,大多数情况下,后端返回的数据直接就是json格式,如果是json格式的,就不用反序列化了
如果返回的是JSON格式的字符串,就需要反序列化
后端视图函数:
def index(request):
if request.method == 'POST':
# 接收参数
d1 = request.POST.get('d1')
d2 = request.POST.get('d2')
# 做运算
d3 = int(d1) + int(d2)
return HttpResponse(d3) # 返回给res
return render(request, 'index.html')
注意⚠️后端返回数据的多种情况:
第一种:
当后端返回的值 res为string类型时,即 return HttpResponse(d3)。前端html页面可以直接使用。
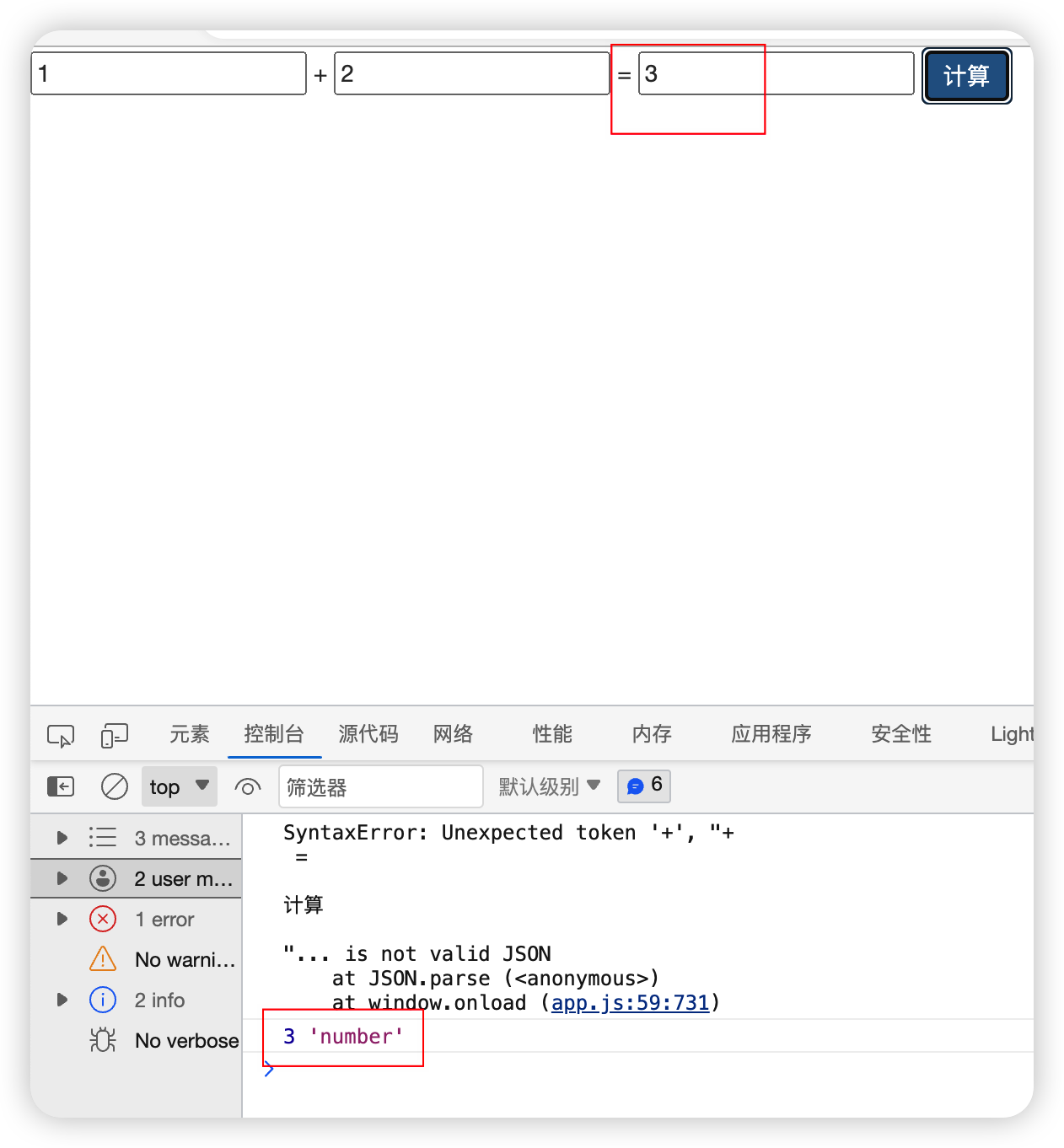
前端自行反序列化 JSON.parse()后可以改变类型,比如前端传来的d3是一个string,JSON.parse()后是number。
success : function(res){
res = JSON.parse(res);
console.log(res);
console.log(res.code);
{#$("#d3").val(res)#}
}
没有反序列化:前端能直接使用后端传来的string数据
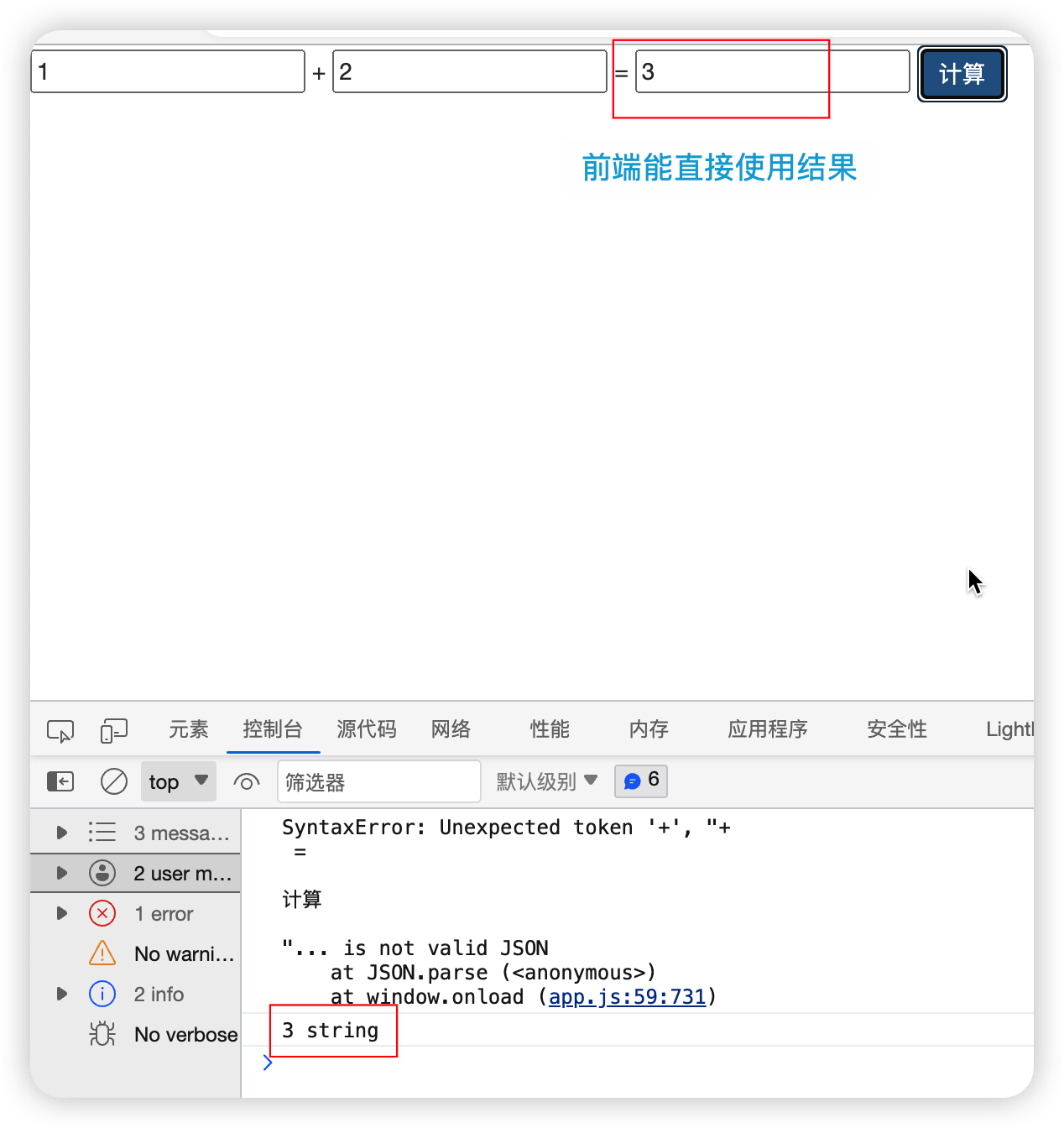
反序列化以后:反序列化之后依旧可以直接使用,数据类型变为number
第二种:
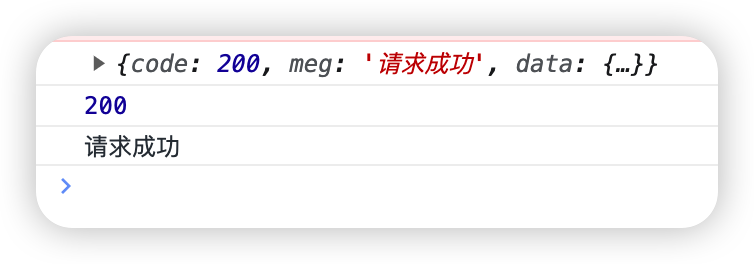
后端直接返回 JsonResponse()数据,前端不需要在反序列化,可以直接取值。
JsonResponse()返回的数据就是json数据
# 后端
from django.http import JsonResponse
def index(request):
if request.method == 'POST':
d = {'code': 200, 'meg': '请求成功', 'data': {'username': 'jingzhi'}}
return JsonResponse(d)
return render(request, 'index.html')
# 前端
$.ajax({
// 1、提交到哪里
url: "",
// 2、要指定请求方式提交
type: "post",
// 3、指定要传递的数据
data: {'d1':d1,'d2':d2},
// 4、回调函数, 接收后端返回的数据
success : function(res){
console.log(res);
console.log(res.code);
console.log(res.meg);
}
})
第三种:
后端序列化后使用HttpResponse()方式,前端需要指定数据类型dataType: "json",
# 后端
def index(request):
if request.method == 'POST':
d = {'code': 200, 'meg': '请求成功', 'data': {'username': 'jingzhi'}}
import json
res = json.dumps(d, ensure_ascii=False) # res序列化为字符串
return HttpResponse(res) # 返回给res
return render(request, 'index.html')
# 前端
$.ajax({
// 1、提交到哪里
url: "",
// 2、要指定请求方式提交
type: "post",
// 3、指定要传递的数据
data: {'d1':d1,'d2':d2},
dataType: "json",
// 4、回调函数, 接收后端返回的数据
success : function(res){
console.log(res);
console.log(res.code);
console.log(res.meg);
}
})
二、
要满足的两个条件
1. 你传的数据一定要是json格式的
2. 一定要把ajax默认提交的urlencode改为'application/json'
1、html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<link href="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/twitter-bootstrap/3.3.6/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet">
<script src="https://cdn.staticfile.org/jquery/2.1.1/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/twitter-bootstrap/3.3.6/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<button class="btn btn-info">按钮</button>
<script>
$(".btn").click(function () {
$.ajax({
url: '/index/',
type: 'post',
data: JSON.stringify({a1: 1, a2: 2}),
contentType : 'application/json',
success: function (res) {
console.log(res)
}
})
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
2、views
from django.shortcuts import render
import json
# Create your views here.
def index(request):
print(request.body) # b'{"a1":1,"a2":2}'
json_str = json.loads(request.body) # json.loads 能够自动进行二进制解码,然后再反序列化
print(json_str.get('a1'))
return render(request, 'index.html')
注意:
1. 针对ajax提交的json格式的数据,django后端不在把数据封装到request.POST中了。
2. 前端发送json数据的前提:数据进行序列化、指定内容类型
data: JSON.stringify({a1: 1, a2: 2}),
contentType : 'application/json',
3、后端拿到数据是纯原生的,发送过来的数据是二进制形式的,后端需要解码、反序列化
三、
1、html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<link href="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/twitter-bootstrap/3.3.6/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet">
<script src="https://cdn.staticfile.org/jquery/2.1.1/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/twitter-bootstrap/3.3.6/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<form action="">
username: <input type="text" id="username">
password: <input type="password" id="password">
文件: <input type="file" id="my_file">
<button class="btn btn-primary">提交</button>
{# 两次提交,提交按钮可以放到form表单外#}
</form>
{#<button class="btn btn-info">按钮</button>#}
<script>
$(".btn").click(function (event) {
// 拿普通数据
var username = $("#username").val();
var password = $("#password").val();
// 拿文件数据
{#var my_file = $("#my_file"); {#产生一个jq对象,在浏览器控制台可以查看#}
{#console.log(my_file);#}
var myfile = $("#my_file")[0].files[0];
{#console.log(myfile);#}
// 发送文件数据到后端需要借助于FormData对象
var myFormDataObj = new FormData();
myFormDataObj.append('username', username);
myFormDataObj.append('password', password);
myFormDataObj.append('myfile', myfile);
$.ajax({
url: '/index/',
type: 'post',
data: myFormDataObj,
contentType:false, // 告诉浏览器不要做任何的编码格式处理,django自己来做处理
processData:false, // 告诉浏览器不要对我处理的数据做任何的处理
success: function (res) {
{#console.log(res)#}
}
});
event.preventDefault(); {#阻止后续提交第一种方式#}
{#return false #} {#阻止后续提交第二种方式#}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
关于 var myfile = $("#my_file")[0].files[0]; 的补充
$("#my_file") 返回一个包含匹配元素的数组。由于我们只对一个元素感兴趣,通过 [0] 来获取这个元素。
.files[0]: 一旦我们有了文件输入字段元素,我们可以通过 .files 属性访问用户选择的文件列表。因为文件输入字段允许用户一次选择多个文件,这是一个文件列表。在这里,我们使用 [0] 来获取列表中的第一个文件。因此,$("#my_file")[0].files[0] 返回用户选择的第一个文件。
2、views
from django.shortcuts import render
# Create your views here.
def index(request):
# print(request.body) # b'{"a1":1,"a2":2}'
# json_str = json.loads(request.body) # json.loads 能够自动进行二进制解码,然后再反序列化
# print(json_str.get('a1'))
if request.method == 'POST':
print(request.POST.get('username')) # <QueryDict: {'username': ['DSAD'], 'password': ['DSADAS']}>
print(request.FILES.get('myfile')) # <MultiValueDict: {'myfile': [<InMemoryUploadedFile: 462_001_afm_3600_5400.jpg (image/jpeg)>]}>
file_obj = request.FILES.get('myfile')
with open(file_obj.name, 'wb') as f:
for line in file_obj:
f.write(line)
return render(request, 'index.html')
四、
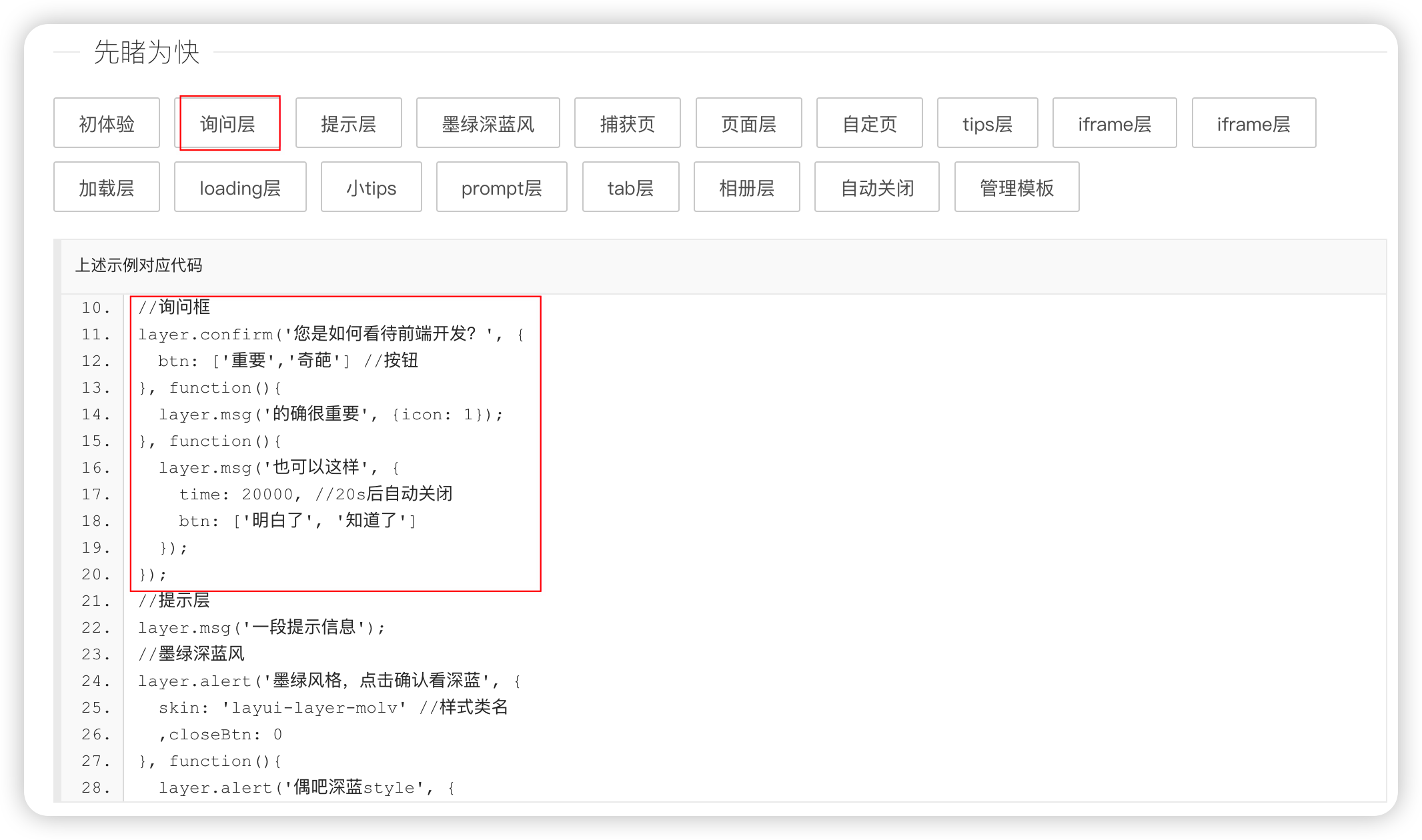
1、
引入static文件
<script src="/static/layer/layer.js"></script>
引用效果
2、html
{% extends 'home.html' %}
{% block content %}
<h1 class="text-center">图书列表展示</h1>
<a href="/book_add/" class="btn btn-info">添加图书</a>
<table class="table table-striped table-hover">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>标题</th>
<th>价格</th>
<th>出版日期</th>
<th>出版社</th>
<th>作者</th>
<th>操作</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{% for foo in book_queryset %}
<tr class="tr_{{ foo.pk }}">
<td>{{ foo.title }}</td>
<td>{{ foo.price }}</td>
<td>{{ foo.publish_date|date:'Y-m-d' }}</td>
<td>{{ foo.publish.name }}</td>
{#书查出版社,正向查询,外键字段跳表#}
<td>
{% for author in foo.authors.all %}
{% if forloop.last %}
{{ author.name }}
{% else %}
{{ author.name }} |
{% endif %}
{% endfor %}
</td>
<td>
{# <a href="/book/edit/{{ foo.pk }}" class="btn btn-success">修改</a>#}
<a href="/book_edit/?id={{ foo.pk }}" class="btn btn-success">修改</a>
<a href="#" class="del btn btn-danger" delete_id="{{ foo.pk }}">删除</a>
{#这里不能使用id标签,因为在for循环中,id不能重复 自定义一个id,a标签自动跳转也相当于有二次提交#}
</td>
</tr>
{% endfor %}
</tbody>
</table>
{% endblock %}
{% block js %}
<script>
$(".del").click(function () {
// 删除的逻辑:当我们点击删除按钮的时候,应该获取点击行的id值,然后,把这个id传到后端,后端接收这个id值
// 做删除逻辑
var id = $(this).attr('delete_id'); {#这里的this代表的是$(".btn")对象#}
var _this = $(this);
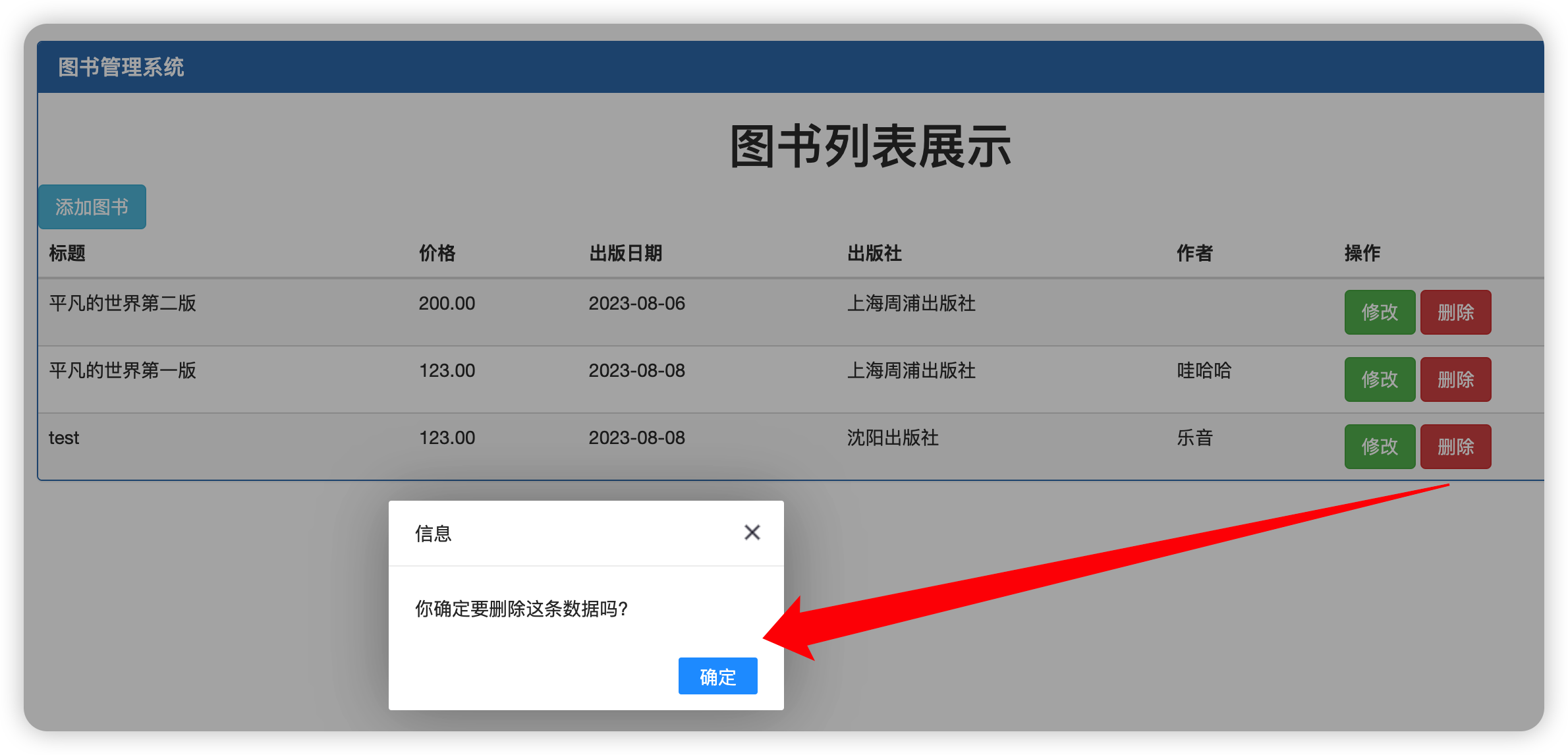
// 紧接着要发送ajax请求,最好做一个二次确认
layer.confirm('你确定要删除这条数据吗?', {
btn: ['确定'] //按钮
}, function () {
// 发送ajax请求
$.ajax({
url: '/book_del/', // {# 把请求提交到del视图函数中去#}
type: 'post',
data: {id: id},
success: function (res) {
if (res.code == 200) {
{#layer.msg(res.msg, {icon:2}, function () {#}
{# location.reload();} {# ajax不会自动刷新页面 #}
layer.msg(res.msg); {# 接收后端返回的信息 #}
_this.parent().parent().remove(); {# this 指的是function (res) _this引用变量 #}
{#$(".tr_" + id).remove(); 删除dom的tr行来实现不展示#}
}
}
});
});
})
</script>
{% endblock %}
3、views
def book_del(request):
del_id = request.POST.get('id') # 这个id是 ajx传的 id = $(this).attr('delete_id');
print(del_id)
models.Book.objects.filter(pk=del_id).delete()
# return redirect('/authors_list/') ajax发过来的数据,不需要页面跳转
return JsonResponse({'code': 200, 'msg': '删除成功!'}) # 如果需要给前端返回数据+'data':{}
4、效果
五、Ajax 实操
简易图书管理系统,前端通过Ajax传数据到后端
html
{% extends 'home.html' %}
{% block content %}
<h1 class="text-center">修改作者</h1>
<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="form-group">
<input type="hidden" id="hidden_id" value="{{ author_obj.pk }}" name="hidden_id">
<div class="form-group">
作者名:<input type="text" id="name" class="form-control" name="name" value="{{ author_obj.name }}">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
年龄:<input type="text" id="age" class="form-control" name="age" value="{{ author_obj.age }}">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
phone:<input type="text" id="phone" class="form-control" name="phone"
value="{{ author_obj.author.phone }}">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
addr:<input type="text" id="addr" class="form-control" name="addr"
value="{{ author_obj.author.addr }}">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<input type="button" id="submitButton" class="btn btn-success btn-block" value="Submit">
</div>
<script>
$("#submitButton").click(function () {
let id = $("#hidden_id").val();
let name = $("#name").val();
let age = $("#age").val();
let phone = $("#phone").val();
let addr = $("#addr").val();
console.log(id)
console.log(name)
$.ajax({
url: '/authors_edit/',
type: 'post',
data: {'id':id,'name': name, 'age': age, 'phone': phone, 'addr': addr},
success: function (res) {
// 这里可以添加一些成功后的处理逻辑
alert(res.msg);
window.location.href=res.url;
},
error: function (err) {
// 这里可以添加一些错误处理逻辑
alert("提交失败,请重试");
}
})
})
</script>
</div>
</div>
{% endblock %}
views
# 修改作者
def authors_edit(request):
author_edit_id = request.GET.get('id') # 先获取GET传参的id
author_obj = models.Author.objects.filter(pk=author_edit_id).first() # 获取一个publish_obj对象
author_detail_obj = models.Author.objects.filter(pk=author_edit_id).first() # 获取一个publish_obj对象
if request.method == 'POST':
new_id = request.POST.get('id')
new_name = request.POST.get('name')
new_age = request.POST.get('age')
new_phone = request.POST.get('phone')
new_addr = request.POST.get('addr')
# 写入数据库
models.Author.objects.filter(pk=new_id).update(name=new_name, age=new_age)
models.Authordetail.objects.filter(author__pk=author_edit_id).update(phone=new_phone, addr=new_addr)
res = {'url': '/authors_list/', 'code': 200, 'msg': '后端拿到数据!', 'data': {'username': new_name}}
return JsonResponse(res)
return render(request, 'authors_edit.html', locals())


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号