Mybatis
项目中常用
对于日期
java中日期属性使用String类型也可以插入Msyql (Mybatis做了转换)
插入和更新操作的返回值
大概吧,忘记了
insert: 插入n条记录,返回影响行数n。(要么成功,要么失败抛出异常)
update:更新n条记录,返回影响行数n。(n>=0)
delete: 删除n条记录,返回影响行数n。(n>=0)
打印sql语句插件
mybatis log free
需开启设置
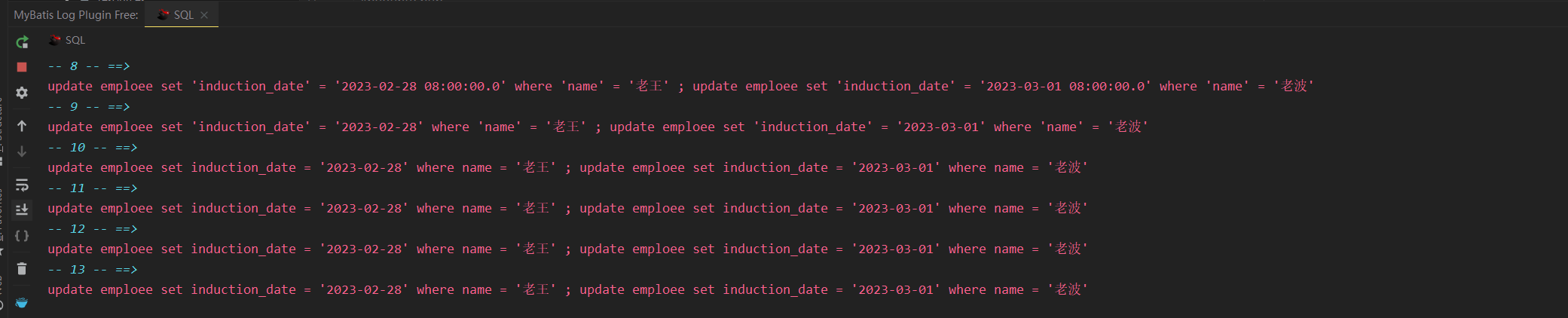
插入
单条插入
<insert id="createEmployee"> insert into emploee values ( null, #{employee.name}, #{employee.age}, #{employee.inductionDate}, #{employee.quitDate}, #{employee.identityDesc}, #{employee.statusFlag}) </insert>
批量插入
方式一:原生sql方式
xml使用原生sql结合mybatis动态sql
int batchCreateEmployee(@Param("empList") List<Employee> employees);
<!-- 批量插入--> <insert id="batchCreateEmployee"> insert into emploee values <foreach collection="empList" item="emp" separator=","> (null, #{emp.name}, #{emp.age}, #{emp.inductionDate}, #{emp.quitDate}, #{emp.identityDesc}, #{emp.statusFlag}) </foreach>
sql语句过长会报错(项目中一般不超过100条),这个由数据库决定,过长时可以对list集合进行拆分,再循环调用批量插入
方式二:使用JDBC批处理
参考:https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1825993
@Autowired private SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory; //批处理 @Transactional public void add(List<Item> itemList) { SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(ExecutorType.BATCH,false); ItemMapper mapper = session.getMapper(ItemMapper.class); for (int i = ; i < itemList.size(); i++) { mapper.insertSelective(itemList.get(i)); if(i%1000==0){//每1000条提交一次防止内存溢出 session.commit(); session.clearCache(); } } session.commit(); session.clearCache(); }
插入操作设置返回主键
<!--<insert id="addTeacher" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="teacherId" parameterType="Teacher"> INSERT INTO teacher(teacherId, teacherName) VALUES(teacherId,#{teacherName}) </insert>-->
INSERT INTO teacher(teacherName) VALUES(#{teacherName})
<insert id="addTeacher" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="teacherId" parameterType="Teacher" keyColumn="teacherId"> INSERT INTO teacher(teacherName) VALUES(#{teacherName}) </insert>
测试
@Test public void addTeacher() { SqlSession sqlSession=null; try { sqlSession= MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); TeacherMapper teacherMapper=sqlSession.getMapper(TeacherMapper.class); Teacher teacher=new Teacher().builder() .teacherName("隔壁老王") .build(); System.out.println("之前:"+teacher); teacherMapper.addTeacher(teacher); System.out.println("之后:"+teacher); }catch(Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ MybatisUtils.closeSqlSession(); } }
结果

更新
批量更新
注意:
1.列名不加单引号,若要区分敏感字符可以加反撇号,不然会导致语法错误
2.数据库连接要增加参数设置allowMultiQueries=true
jdbc:mysql://localhost/java_base?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&characterEncoding=utf8&useUnicode=true&allowMultiQueries=true
int batchUpdateEmployee(@Param("empList") List<Employee> employees);
<!-- 批量更新--> <update id="batchUpdateEmployee"> <foreach collection="empList" item="emp" separator=";"> update emploee set induction_date = #{emp.inductionDate} where name = #{emp.name} </foreach> </update>

Mybatis参数传递的几种方式
匿名参数 顺序传递
xml中按照参数传递顺序,使用#{arg0} , #{arg1} 或者#{param1},#{param2}来获取传递参数
List result= employeeMapper.selectByGenderAndAge(gender,age)
xml中
<select id="selectByGenderAndAge" resultMap="BaseResultMap" > select * from employee where gender = #{param1} and age = #{param2} </select>
@param注解 (一般用这种)
一般该方式结合javaBean和List集合
UserInfo selectByUserIdAndStatus(@Param("userId") String userId, @Param("status") Integer status);
xml中
<select id="selectByUserIdAndStatus" resultType="cn.cb.demo.domain.UserInfo"> select * from user_info where user_id=#{userId} and status=#{status} </select>
一般用对象封装参数也是结合@param注解
Map对象封装
List result= employeeMapper.selectByMapParams(params);
按照key名称来取
<select id="selectByMapParams" resultMap="BaseResultMap" parameterType="map"> select * from employee where gender = #{gender} and age = #{age} </select>
JSON对象封装
@ApiOperation(value = "多个参数查询_通过JSON传递多个参数") @PostMapping("findByJSONObject") public ResultMsg findByJSONObject(@RequestBody JSONObject params) { List result= employeeMapper.findByJSONObject(params); return ResultMsg.getMsg(result); }
parameterType为JSONObject
按键名来取
<select id="findByJSONObject" resultMap="BaseResultMap" parameterType="com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject"> select * from employee where gender = #{gender} and age = #{age} </select>
SQL可以放在哪?
- 常见的xml里放sql
- Mapper接口上使用注解方式放sql
引用:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44411569/article/details/93468943
Mybatis缓存机制
用来减少对数据库查询操作的次数。性能会有提升
MyBatis缓存
- 一级缓存(默认)
- 二级缓存
一级缓存
一级缓存的概念
- 一级缓存基于SqlSession级别 (存储的数据只在sqlsession内有效)
- 只有SqlSession关闭、提交、或flush,一级缓存消失( 否则重复同一条sql只会输出一次sql) (commit方法带有刷新)
- 干预一级缓存(强制将对象从一级缓存中移除)(sqlsession.clearCache清空缓存后再查会再次输出sql)
- 只要执行了增删改操作,一级缓存消失 (缓存替代 查-改-查会输出两次select的sql)
- 内容相同,但是执行sql的id不同,不算同一条语句 会输出两次sql (缓存的Map和namespace、id值(方法名)有关)
一级缓存内存结构
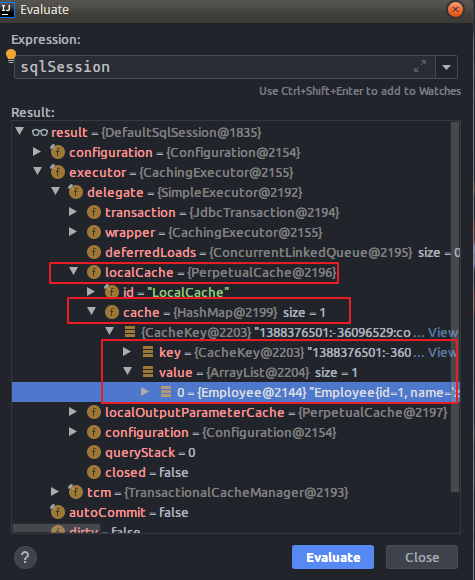
从上面的内存图得知:一级缓存实际缓存的是HashMap。这个Map中的Key主要的组成部分是映射文件中namepace属性值与<select>标签中的id值和具体sql语句拼接而成,valuse则是一个Arraylist,存放查询出来的对象

二级缓存
二级缓存是mapper映射级别的缓存,多个SqlSession去操作同一个Mapper映射的sql语句,多个SqlSession可以共享二级缓存,二级缓存是跨SqlSession的
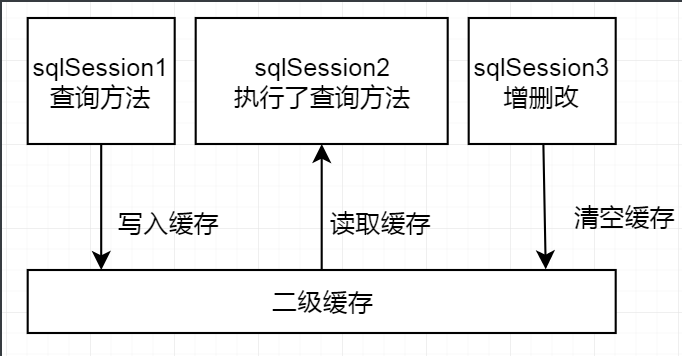
映射语句文件中的所有 select 语句的结果将会被缓存。
映射语句文件中的所有 insert、update 和 delete 语句会刷新缓存。
缓存会使用最近最少使用算法(LRU, Least Recently Used)算法来清除不需要的缓存。
缓存不会定时进行刷新(也就是说,没有刷新间隔)。
缓存会保存列表或对象(无论查询方法返回哪种)的 1024 个引用。
缓存会被视为读/写缓存,这意味着获取到的对象并不是共享的,可以安全地被调用者修改,而不干扰其他调用者或线程所做的潜在修改。作者:AC编程
链接:https://www.jianshu.com/p/003a449cd8e2
来源:简书
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
先配置文件中开启总开关
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
再Mapper中或者Mapper接口上添加也行
<mapper namespace="com.bjlemon.mybatis.mapper.EmployeeMapper"> <!--开启二级缓存的支持--> <cache type=""/> </mapper>
在接口上添加
@CacheNamespace 后面可以带参数指定加载自定义的缓存实现类 @CacheNamespace(implementation = RedisCache.class)//开启二级缓存
使用
<select id="findAll" resultMap="EmployeeResultMap" useCache="true"> select * from mybatis_employee </select>
自定义缓存
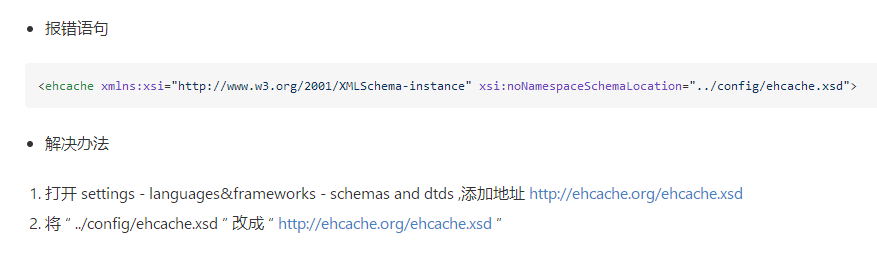
1.与Ecache整合
映射语句文件中的所有 select 语句的结果将会被缓存。
使用Ehcache
两个依赖
org.ehcache
ehcache
3.8.1
org.mybatis
mybatis-ehcache
1.0.0
将ehcache核心库中一个ehcache-xxx.xml文件拷贝一份到类路径下,一般修改为ehcache.xml
- 修改配置(一般使用默认)
- 开启二级缓存
1.config.xml里面开启二级缓存
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
2.mapper.xml里面开启Ehcache
<cache type="org.mybatis.caches.ehcache.EhcacheCache"/>
3.mapper.xml方法上开启
<select id="selectByID" resultType="user" useCache="true">
分页
1.直接sql中limit分页 物理分页
2.RowBounds 一次性加载所有服务查询条件的目标数据 根据分页参数的值再去内存中实现分页 滚动加载数据 不适合数据量较大场景 频繁访问数据库 内存级分页
3.拦截器实现 拦截需要分页的select语句 然后动态拼接分页关键字 PageHelper Mybatis-Plus 已经实现
$与#占位符传参的区别
在预编译之前#{}解析为JDBC的预编译语句(preperd statement)的参数标记符 "?"
${} 在sql解析阶段会进行变量替换,不能实现预编译,${xxx} 这样格式的参数会直接参与sql编译导致可能出现sql注入
-》使用${} 不会进行预编译,传参会参与编译过程,可能导致sql注入
使用#{}会进行预编译,而且预编译能够防止sql注入
什么是预编译
数据库接收到sql之后需要进行词法和语义解析、优化sql、指定执行计划等会花费时间,但是很多时候一条sql语句可能会反复执行,或者只是个别参数不同,为了减少编译,就有了预编译。
预编译就是使用占位符替代将sql语句模板化,一次编译多次运行,省去了解析优化等过程
缓存预编译
预编译语句被DB的编译器编译后的执行代码被缓存起来,name下次调用时只要是相同的预编译语句就不需要编译,只要将参数直接传入编译过的语句的执行代码中,相当于函数,就会执行
预编译实现
基于preperdStatement和占位符来实现
作者: deity-night
出处: https://www.cnblogs.com/deity-night/
关于作者:码农
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出, 原文链接 如有问题, 可邮件(***@163.com)咨询.




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号