大语言模型量化方法对比:GPTQ、GGUF、AWQ
在过去的一年里,大型语言模型(llm)有了飞速的发展,在本文中,我们将探讨几种(量化)的方式,除此以外,还会介绍分片及不同的保存和压缩策略。
说明:每次加载LLM示例后,建议清除缓存,以防止出现OutOfMemory错误。
del model, tokenizer, pipeimport torchtorch.cuda.empty_cache()
如果在jupyter中无法释放显存,请重启这个jupyter notebook。
模型加载
加载LLM的最直接、最普通的方式是通过🤗Transformers。HuggingFace已经创建了一个套件,我们能够直接使用
pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.gitpip install accelerate bitsandbytes xformers
安装完成后,我们可以使用以下管道轻松加载LLM:
from torch import bfloat16from transformers import pipeline# Load in your LLM without any compression trickspipe = pipeline("text-generation",model="HuggingFaceH4/zephyr-7b-beta",torch_dtype=bfloat16,device_map="auto")
我们这里使用zephyr-7b-beta作为示例
这种加载LLM的方法通常不会执行任何压缩技巧。我们来做个使用的示例
messages = [{"role": "system","content": "You are a friendly chatbot.",},{"role": "user","content": "Tell me a funny joke about Large Language Models."},]prompt = pipe.tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages,tokenize=False,add_generation_prompt=True)
使用内部提示模板生成的提示是这样构造的:
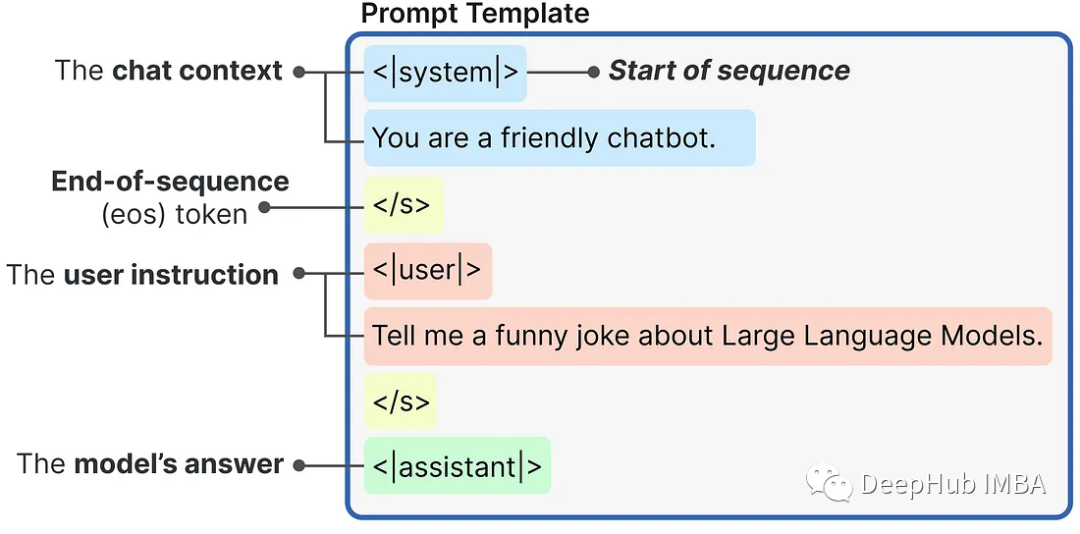
然后,我们可将提示传递给LLM来生成答案:
https://avoid.overfit.cn/post/47f8871b7144405795301aa0a6bd9a24


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号