顺序表与链表
顺序表
线性表的本质就是数组
手动实现线性表
先定义一下需要实现功能的接口
package List;
public interface IList {
// 新增元素,默认在数组最后新增
void add(int data);
// 在 pos 位置新增元素
void add(int pos, int data);
// 判定是否包含某个元素
boolean contains(int toFind);
// 查找某个元素对应的位置
int indexOf(int toFind);
// 获取 pos 位置的元素
int get(int pos);
// 给 pos 位置的元素设为 value
void set(int pos, int value);
//删除第⼀次出现的关键字key
void remove(int toRemove);
// 获取顺序表⻓度
int size();
// 清空顺序表
void clear();
// 打印顺序表,注意:该⽅法并不是顺序表中的⽅法,为了⽅便看测试结果给出的
void display();
}
方法实现
package List;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class MyArrayList implements IList {
public int[] elem;
public int usedSize;
public static final int DEAFULT_CAPACITY = 10;
public MyArrayList() {
elem = new int[DEAFULT_CAPACITY];
}
public MyArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
elem = new int[initialCapacity];
}
//把数据存放到数据表当中(最后一个位置)
@Override
public void add(int data) {
if (ifFull()) {
//扩容-》2倍扩容
grow();
}
elem[usedSize] = data;
usedSize++;
}
private void grow() {
elem = Arrays.copyOf(elem, 2 * elem.length);
}
boolean ifFull() {
return usedSize == elem.length;
}
@Override
public void add(int pos, int data) {
checkPos(pos);
if (ifFull()) {
//扩容-》2倍扩容
grow();
}
//1.移动元素
for (int i = usedSize - 1; i >= pos; i--) {
elem[i + 1] = elem[i];
}
elem[pos] = data;
usedSize++;
}
private void checkPos(int pos) {
if (pos < 0 || pos > usedSize) {
throw new RuntimeException("pos位置不合法:" + pos);
}
}
private boolean isEmpty(){
return usedSize == 0;
}
@Override
public boolean contains(int toFind) {
for (int i = 0; i < usedSize; i++) {
if (elem[i] == toFind) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
@Override
public int indexOf(int toFind) {
for (int i = 0; i < usedSize; i++) {
if (elem[i] == toFind) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
@Override
public int get(int pos) {
if(isEmpty()){
throw new ListEmployeeException("获取元素为空");
}
checkPos(pos);
return elem[pos];
}
@Override
public void set(int pos, int value) {
checkPos(pos);
elem[pos] = value;
}
@Override
public void remove(int toRemove) {
int index = indexOf(toRemove);
if (index == -1) {
throw new ListEmployeeException("没有这个元素");
}
for (int i = index; i < usedSize - 1; i++) {
elem[i] = elem[i + 1];
usedSize--;
}
}
@Override
public int size() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public void clear() {
usedSize = 0;
}
@Override
public void display() {
for (int i = 0; i < usedSize; i++) {
System.out.print(elem[i]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
package List;
public class ListEmployeeException extends RuntimeException {
public ListEmployeeException() {
super();
}
public ListEmployeeException(String message) {
super(message);
}
public ListEmployeeException(String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
}
public ListEmployeeException(Throwable cause) {
super(cause);
}
}
线性表的直接调用
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>();
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3};
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
int x = arr[i];
list1.add(x);
}
System.out.println(list1);
System.out.println("========");
list1.add(1, 6); // 插入元素到指定位置
System.out.println(list1);
// 删除指定位置的元素
if (list1.size() > 2) {
Integer removedElement = list1.remove(2);
System.out.println("Removed element: " + removedElement);
System.out.println("After removal: " + list1);
}
// 修改指定位置的元素
if (list1.size() > 1) {
list1.set(1, 10); // 将索引1处的元素替换为10
System.out.println("After update: " + list1);
}
// 查找元素是否存在
boolean containsSix = list1.contains(6);
System.out.println("List contains 6? " + containsSix);
// 获取指定元素的索引
int indexOfTen = list1.indexOf(10);
System.out.println("Index of 10: " + indexOfTen);
}
}
单链表
单链表是由一个一个节点组成的
节点的构成
- 单链表的节点由两部分构成
- 数值域
- 指针域
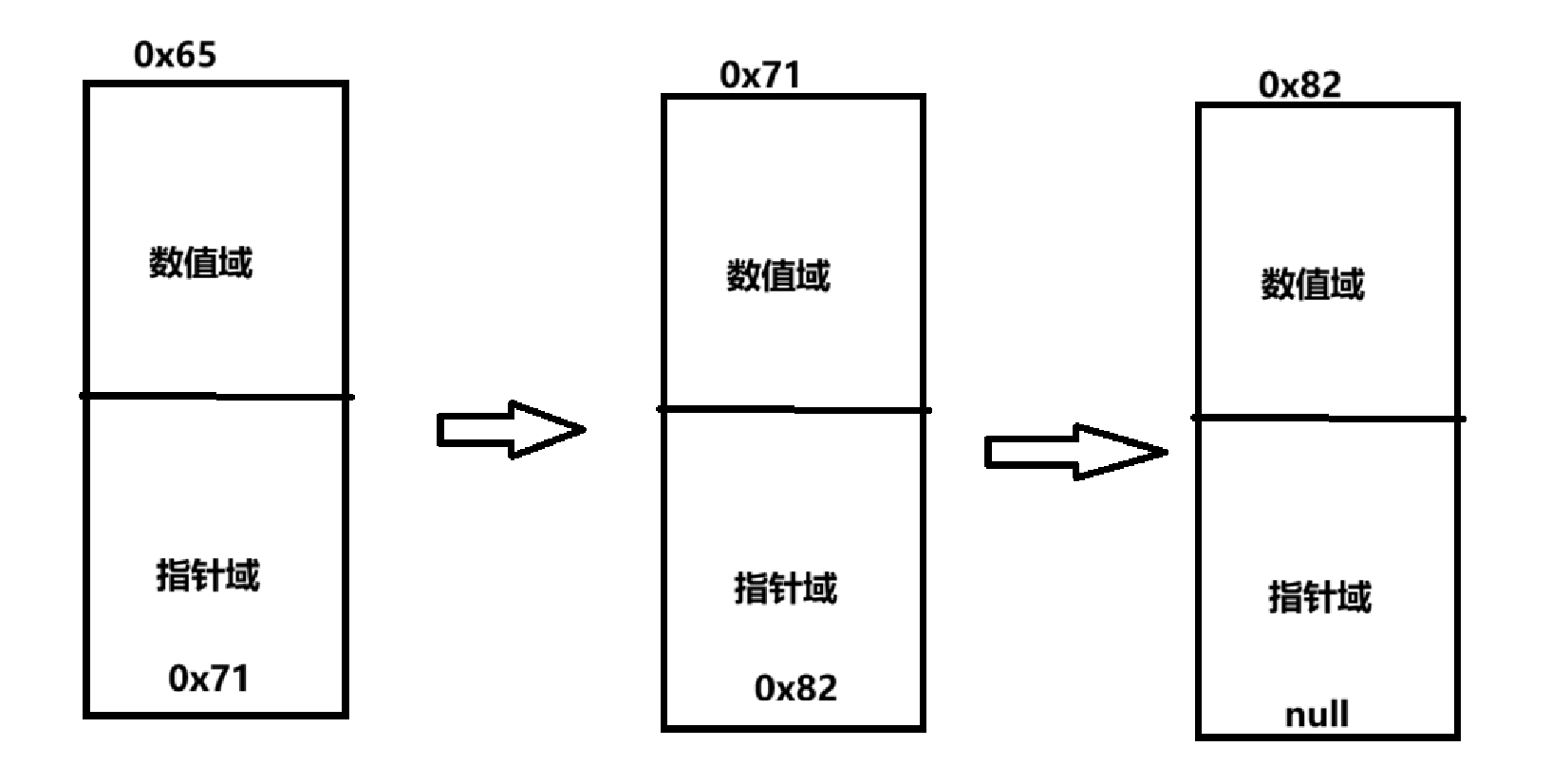
指针域是用来存放下一个节点的地址的
单链表内部类构建
类似于c/c++的结构体创建链表
public class MySingleList {
static class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
ListNode next;
}
}
ListNode head;
头插尾差法
public class MySingleList {
static class ListNode{
int val;
ListNode next;
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
ListNode head;
void addFirst(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);//创建出来新的节点
node.next=head;
head = node;
}
void addEnd(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if(head == null){
head=node;
return;
}
ListNode cur=head;
while(cur.next != null){
cur=cur.next;
}
cur.next=node;
}
void show() {
ListNode cur=head;
while(cur != null){
System.out.print(cur.val+" ");
cur=cur.next;
}
}
}
在任意位置插入元素
//在任意位置插入元素
void addIndex(int index,int data) {
int len=size();
if(index < 0 || index > len){
System.out.println("插入位置不合法");
return;
}
if(index==0){
addFirst(data);
return;
}
if(index==len){
addEnd(data);
return;
}
ListNode node=new ListNode(data);
ListNode cur=searchIndex(index-1);
node.next=cur.next;
cur.next=node;
}
private ListNode searchIndex(int index) {
ListNode cur=head;
int count=0;
while(count<index){
count++;
cur=cur.next;
}
return cur;
}
//计算链表长度
private int size() {
ListNode cur = head;
int count = 0;
while(cur.next!=null){
count++;
cur=cur.next;
}
return count;
}
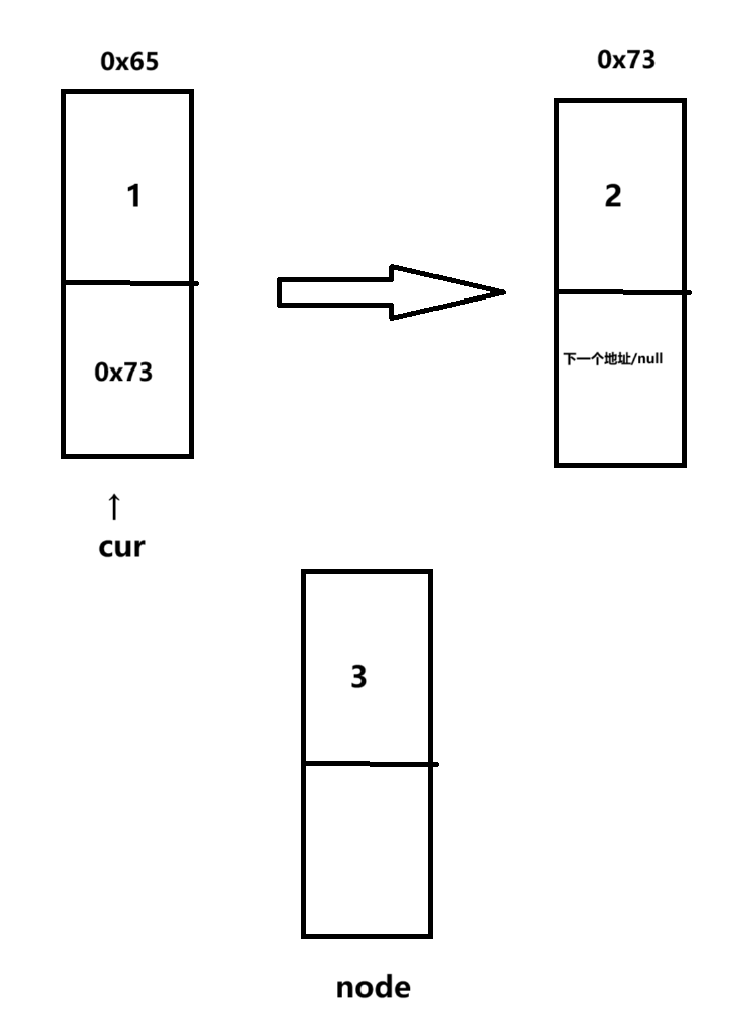
插入步骤详解
核心的两行代码:
node.next=cur.next;
cur.next=node;
cur指针移动到了index的位置,注意计数器从count计数,所以真实的位置是index-1。
如果我们想插在指定位置的前面就是这样:
- 初始状态:
![在这里插入图片描述]()
- 注意此时cur指向的是index-1的位置,因为我们想让新节点插入在index之前,让新节点插入到index之后后面解释。
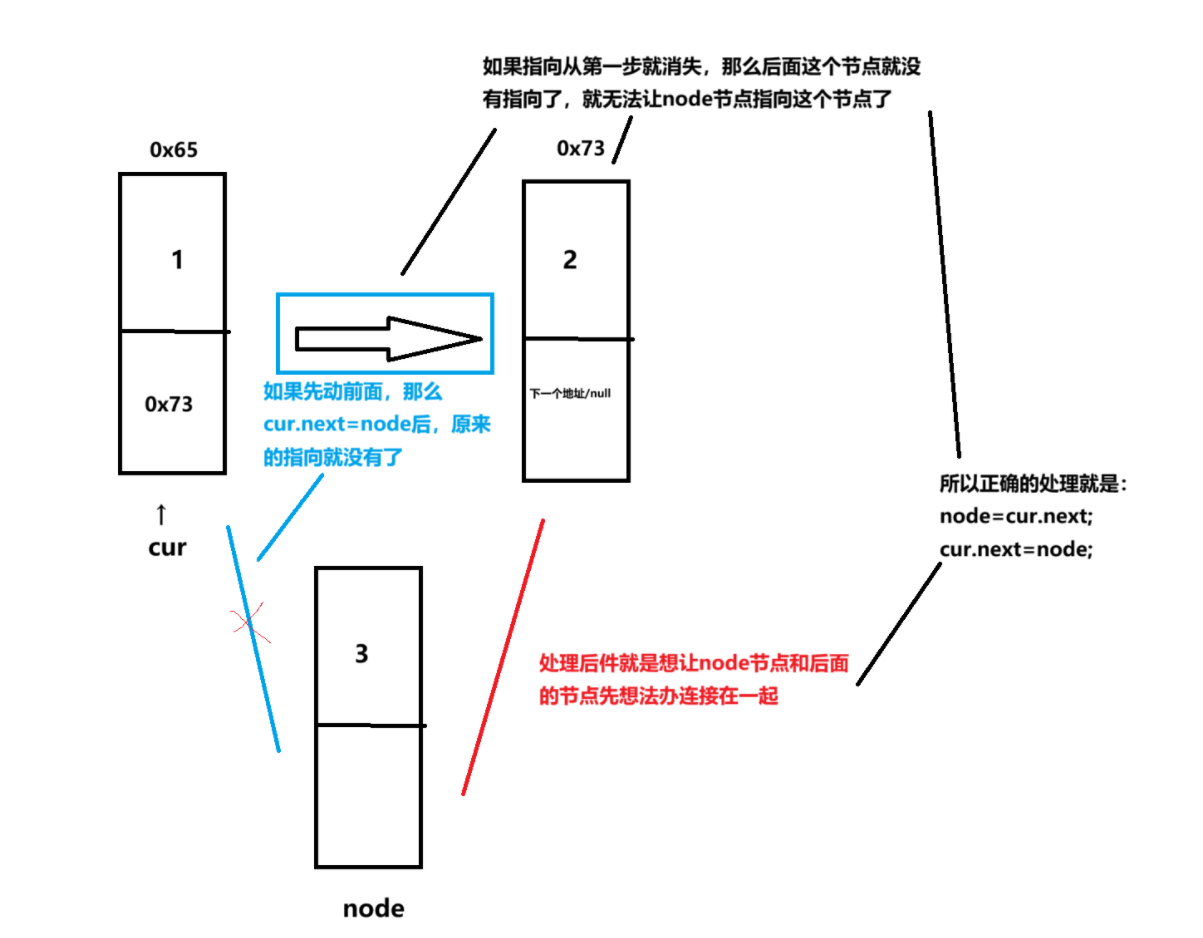
- 插入节点的核心——先处理“后件”
![在这里插入图片描述]()
- node.next=cur.next;
- cur.next=node;
- 这样前一个式子的末尾是下一个式子的开头,在链表中操作的cur节点一定是指向需要插入节点的前面的。假如cur在需要插入节点的后面,那单链表就不好操作了,后面双向链表就很很容易解决这样的问题
- 刚才的问题,如果需要插入的指定位置的后面呢?我们这里就只需要改变ListNode cur=searchIndex(index) 的传入参数的位置就可以了
查找key的前驱节点
//查找key的前驱节点
public ListNode findNodes(int key){
ListNode prev=head;
while(prev.next!=null){
if(prev.next.val==key){
return prev;
}
prev=prev.next;
}
return null;
}
删除指定节点
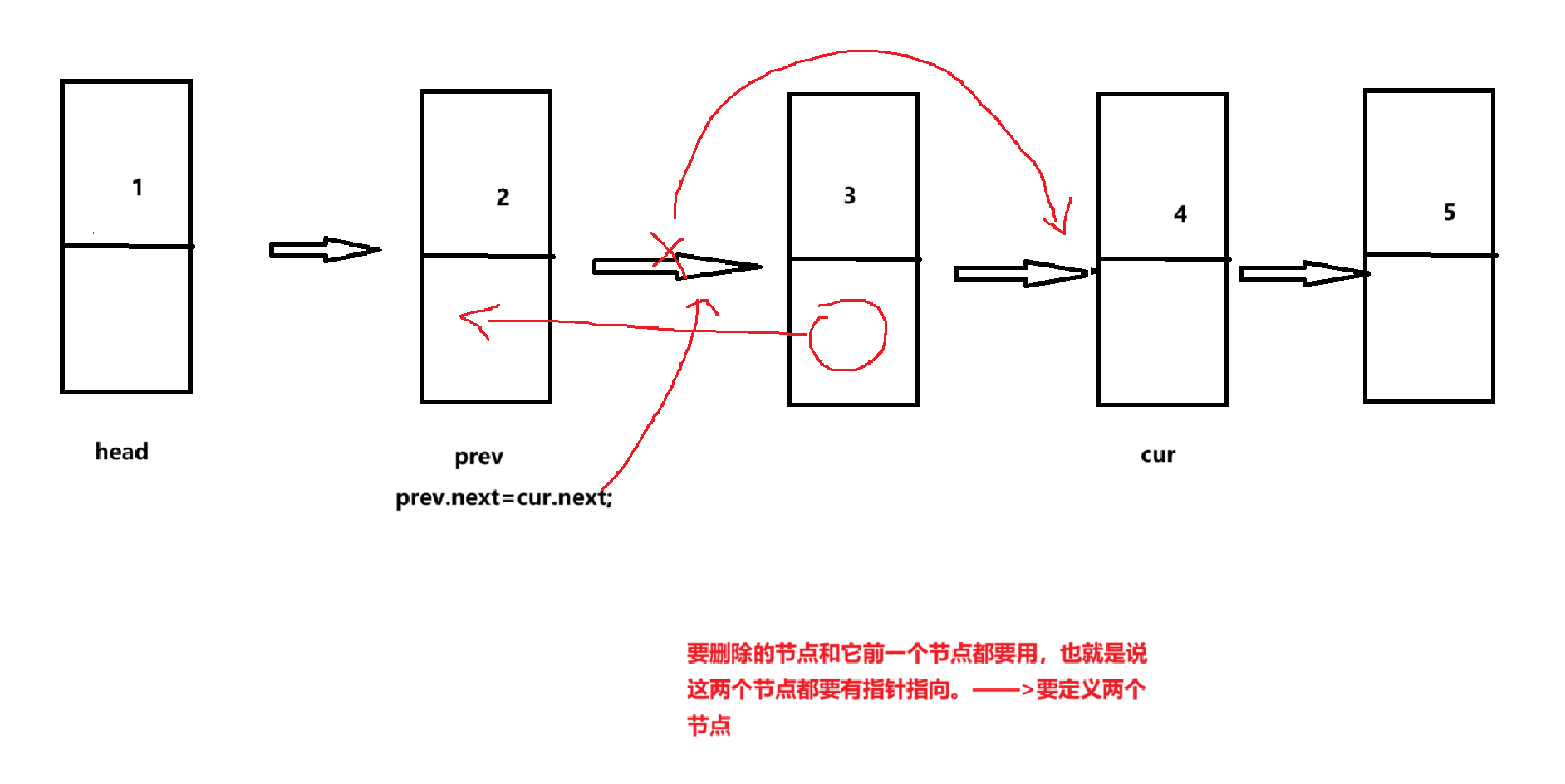
//删除元素
public void removeAllKeys(int key) {
if(head==null) return;
ListNode prev=head;
ListNode cur = head.next;
while(cur.next != null){
if(cur.val==key){
prev.next=cur.next;
cur=cur.next;
}else{
prev=cur;
cur=cur.next;
}
}
//单独处理一下开头的节点
if(head.val==key){
head=head.next;
}
}
返回中间节点
- 代码一
//返回中间节点
public ListNode middleNode() {
if(head==null) return null;
if(head.next==null) return head;
int len=size();
ListNode cur=head;
for(int i=0;i<len/2;i++){
cur=cur.next;
}
return cur;
}
- 代码二
//返回中间节点
public ListNode middleNode() {
if(head==null){
return head;
}
if(head.next==null){
return head;
}
ListNode fast=head;
ListNode slow=head;
//不能互换前后的顺序
while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){
fast=fast.next.next;
slow=slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
-
fast != null && fast.next != null,奇数和偶数的判断条件为什么能放到一起去判断?
这段代码中
fast != null && fast.next != null是循环继续的条件,它的作用是确保快指针fast能够安全地向后移动两步,同时巧妙地处理了链表长度为奇数和偶数的两种情况。条件解释:
fast != null:防止快指针已经到达链表末尾时,执行fast.next.next出现空指针异常fast.next != null:确保快指针有下一个节点,这样fast.next.next才是有效的
为什么能同时处理奇数和偶数长度:
-
当链表长度为奇数时:
- 快指针最终会停在最后一个节点(
fast != null但fast.next == null) - 此时慢指针恰好指向正中间的节点
- 快指针最终会停在最后一个节点(
-
当链表长度为偶数时:
- 快指针最终会停在倒数第二个节点的
next(即fast == null) - 此时慢指针指向中间两个节点中的第二个节点
- 快指针最终会停在倒数第二个节点的
这种处理方式的巧妙之处在于:无论链表长度是奇数还是偶数,循环都会在合适的时机终止,不需要分开处理两种情况。通过一次遍历就能找到中间节点,时间复杂度为 O(n),空间复杂度为 O(1),是寻找链表中间节点的最优解法。
-
while中的两个判断条件是否可以交换?
不行,这两个条件的顺序不能交换,否则可能会导致空指针异常(NullPointerException)。
原因在于逻辑与(
&&)运算的短路特性:- 当判断
fast != null && fast.next != null时,会先检查fast != null- 如果
fast已经是null,则直接跳过第二个条件,不会执行fast.next的判断 - 只有当
fast不为null时,才会去检查fast.next != null
- 如果
如果交换顺序写成
fast.next != null && fast != null:- 当
fast已经是null时,会先执行fast.next != null的判断 - 此时访问
null.next就会直接抛出空指针异常
举个具体例子(偶数长度链表的最后一步):
- 当
fast已经指向D(最后一个节点),此时fast.next是null - 原条件:
fast != null为真,继续判断fast.next != null为假,循环终止(安全) - 交换后:先判断
fast.next != null为假,直接终止(看似安全)
但再看另一种情况(
fast已经是null时):- 原条件:先判断
fast != null为假,直接终止(安全) - 交换后:先判断
fast.next != null,此时fast是null,直接抛出异常(危险)
因此,这两个条件的顺序是经过精心设计的,必须先判断
fast != null,再判断fast.next != null,才能保证代码的安全性。这种处理方式的巧妙之处在于:无论链表长度是奇数还是偶数,循环都会在合适的时机终止,不需要分开处理两种情况。通过一次遍历就能找到中间节点,时间复杂度为 O (n),空间复杂度为 O (1),是寻找链表中间节点的最优解法。
- 当判断
双向链表
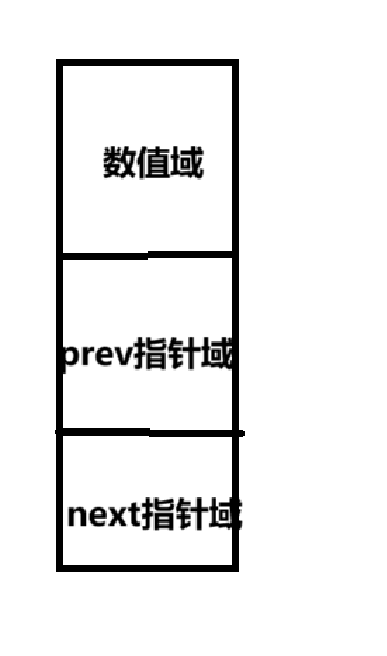
头插尾插
static class ListNode{
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode prev;
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
ListNode head;
//头插法
public void addFirst(int data){
ListNode node=new ListNode(data);
node.next=head;
head.prev=node;
head=node;
}
//尾插法
public void addLast(int data){
ListNode node=new ListNode(data);
if(head==null){
head=node;
}else{
ListNode cur=head;
while(cur.next!=null){
cur=cur.next;
}
cur.next=node;
node.prev=cur;
}
}
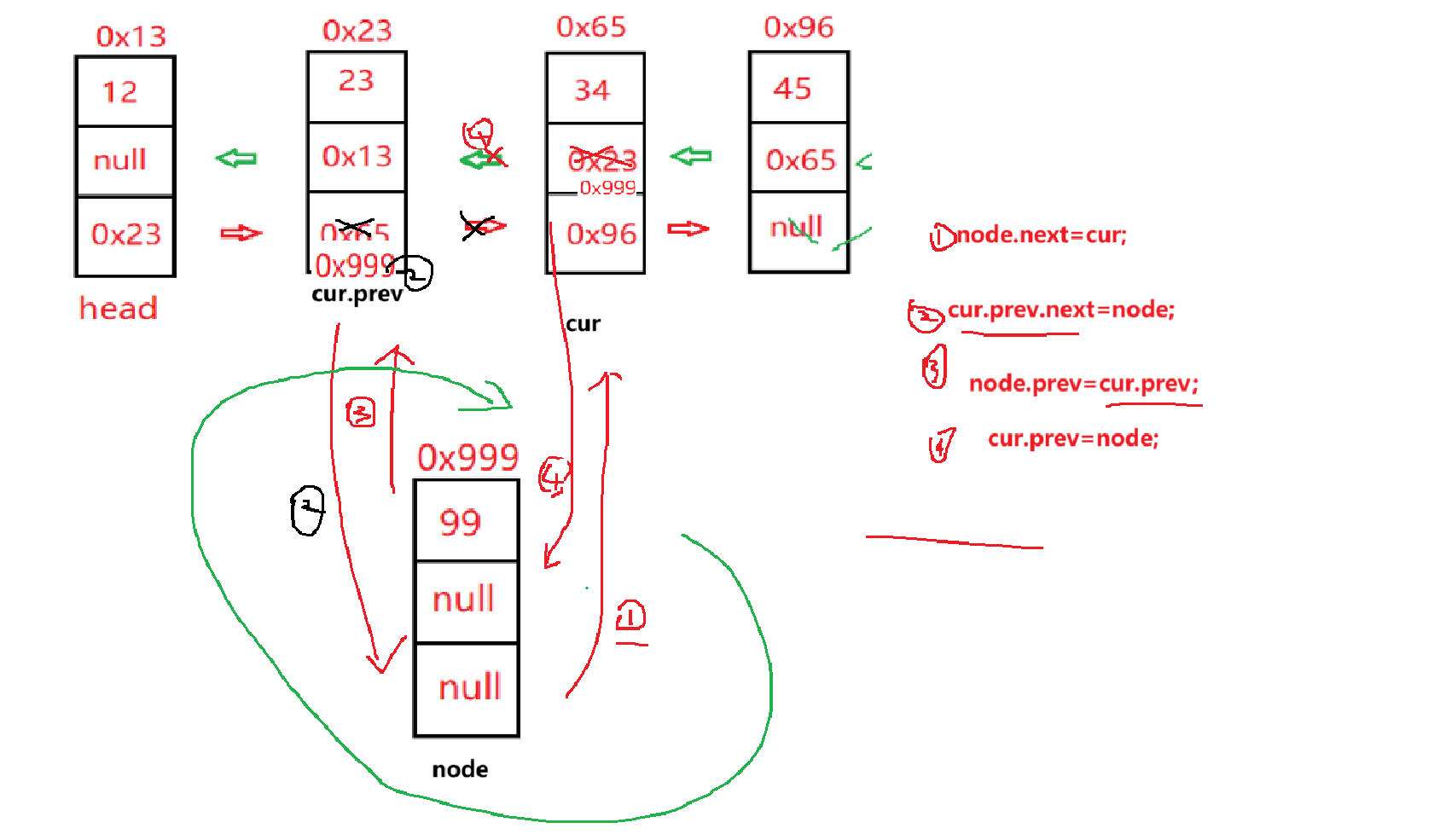
双向链表的插入元素



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号