06 Nginx经典应用
2020年11月4日 study
2021年5月12日 review
01 Nginx全局异常兜底数据返回
任何接口都是可能出错,4xx、5xx等。如果业务没有做好统一的错误管理,直接暴露给用户,无疑是看不懂。
假如后端某个业务出错,nginx层也需要进行转换。
让前端知道Http响应是200,其实是将错误的状态码定向至200,返回了全局兜底数据。
upstream lbs {
server 47.115.23.41:8080 max_fails=2 fail_timeout=60s;
server 47.115.23.41:8081 max_fails=2 fail_timeout=60s;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name 47.115.23.41;
location / {
proxy_pass http://lbs;
proxy_redirect default;
# save the real ip of user
proxy_set_header HOST $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_next_upstream error timeout http_503 non_idempotent;
# turn on configuration of error intercept, must be turned on
proxy_intercept_errors on;
}
access_log logs/time_access.log main;
# if not add "=200", then return the original http error code;
# otherwise if there is an error status code such as 500, it will return to the user 200 status and jump to "/default_api"
error_page 404 500 502 503 504 =200 /default_api;
location = /default_api {
default_type application/json;
return 200 '{"code":"-1","msg":"invoke fail, not found"}';
}
}
注意:
- nginx.conf中最好不要复制中文进去,不然可能会出现乱码,所以注释写成英文;
- 如果正常访问,都能得到正确的结果;如果访问出错,都会返回
200 OK以及自定义Json给前端,前端可通过"code":"-1"来给用户进行提示错误信息;(这样做的目的是防止后端未定义错误状态码,或者定义不全,而给用户返回一些看不懂的信息。)
02 Nginx封禁恶意IP
- 网络攻击常见的有:TCP洪水攻击、注入攻击、DOS等,比较难防的有DDOS等;
- 数据安全,防止对手爬虫恶意爬取,封禁IP;
- 一般就是封禁IP
- linux server的层面封禁IP:iptables(推荐)
- nginx的层面封禁IP,方式多种(但request还是会进来,让nginx返回403,占用资源)
Nginx作为网关,可以有效的封禁IP:
- 单独网站屏蔽IP的方法,把
include xxx;放到网址对应的在server{}语句块(虚拟主机); - 所有网站屏蔽IP的方法,把
include xxx;放到http{}语句块。
在/usr/local/nginx/conf目录下touch blacklist.conf用于专门存放封禁的IP,格式为deny ip地址;;例如:
(先在nginx.conf中记录的access.log中找到访问的IP,把它加入黑名单进行测试)
blacklist.conf
deny 14.30.22.148;
- 然后在
nginx.conf引入
http {
......
include blacklist.conf;
server {
......
}
}

./nginx -s reload:重新加载配置,不中断服务;- 拓展:自动化封禁IP思路
- 编写shell脚本;
awk统计access.log,记录每秒访问超过60次的IP,然后配合nginx或者iptables进行封禁;crontab定时跑脚本;(Linux crontab是用来定期执行程序的命令)
03 Nginx配置浏览器跨域
跨域:浏览器同源策略1995年,同源政策由Netscape公司引入浏览器。目前,所有浏览器都实行这个政策。 最初它的含义是指,A网页设置的cookie,B网页不能打开,除非这两个网页“同源”。
所谓“同源”指的是“三个相同”:
- 协议相同:http https
- 域名相同:www.xdclass.net
- 端口相同:80 81
In a word:浏览器从一个域名的网页去请求另一个域名的资源时,域名、端口、协议任一不同,都是跨域。
浏览器控制台跨域提示:No 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' header is present on the requested resource. Origin 'null' is therefore not allowed access.
也就是用postman调试接口没问题,前端也没问题,但是数据显示不出来,这可能是跨域的问题;
解决办法:
-
JSONP(目前很少使用了)
-
HTTP响应头配置允许跨域(业界常用,有如下两种方法)
- nginx层配置
- 后端代码中处理,通过拦截器配置
-
Nginx开启跨域配置(location下配置,一般会针对特定的接口,在header头信息里面加几个字段)
server {
listen 80;
server_name 47.115.23.41;
location /api/ {
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' $http_origin;
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Credentials' 'true';
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Headers' 'DNT,web-token,app-token,Authorization,Accept,Origin,Keep-Alive,User-Agent,X-Mx-ReqToken,X-Data-Type,X-Auth-Token,X-Requested-With,If-Modified-Since,Cache-Control,Content-Type,Range';
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Methods 'GET,POST,OPTIONS';
# if request method is OPTIONS, then return 200 OK, don't need to forward to back-end codes
if ($request_method = 'OPTIONS') {
add_header 'Access-Control-Max-Age' 1728000;
add_header 'Content-Type' 'text/plain; charset=utf-8';
add_header 'Content-Length' 0;
return 200;
}
proxy_pass http://lbs;
proxy_redirect default;
# save the real ip of user
proxy_set_header HOST $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_next_upstream error timeout http_503 non_idempotent;
# turn on configuration of error intercept, must be turned on
proxy_intercept_errors on;
}
location / {
proxy_pass http://lbs;
proxy_redirect default;
}
access_log logs/time_access.log main;
# if not add "=200", then return the original http error code;
# otherwise if there is an error status code such as 500, it will return to the user 200 status and jump to "/default_api"
error_page 404 500 502 503 504 =200 /default_api;
location = /default_api {
default_type application/json;
return 200 '{"code":"-1","msg":"invoke fail, not found"}';
}
}

add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' $http_origin;:允许的源,$http_origin表示任何一个源都可以传过去;add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Credentials' 'true';:请求的时候可以根据cookie来进行配置;add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Headers':常见的header有没有加进去;add_header Access-Control-Allow-Methods 'GET,POST,OPTIONS';:哪些请求需要进行跨域;if ($request_method = 'OPTIONS') {:预检请求,H5新规范,一般都会发一个OPTIONS请求,预检一下接口是否畅通;如果后端没有写好,即使配置了跨域,也会出现跨域问题;
04 路径匹配-Nginx的locatioin规则
- 语法规则:
location [ = | ~ | ~* | ^~ ] uri { ... }
location @name { ... }
语法规则很简单,一个location关键字,后面跟着可选的修饰符,后面是要匹配的字符,花括号中是要执行的操作。
修饰符:
=:表示精确匹配。只有请求的url路径与后面的字符串完全相等时,才会命中。~:表示该规则是使用正则定义的,区分大小写。~*:表示该规则是使用正则定义的,不区分大小写。^~:表示如果该符号后面的字符是最佳匹配,采用该规则,不再进行后续的查找。
location有两种表示形式,一种是使用前缀字符,一种是使用正则。如果是正则的话,前面有~或~*修饰符。
具体的匹配过程如下:
首先先检查使用前缀字符定义的location,选择最长匹配的项并记录下来。如果找到了精确匹配的location,也就是使用了=修饰符的location,结束查找,使用它的配置。然后按顺序查找使用正则定义的location,如果匹配则停止查找,使用它定义的配置。如果没有匹配的正则location,则使用前面记录的最长匹配前缀字符location。
基于以上的匹配过程,我们可以得到以下两点启示:
- 使用正则定义的location在配置文件中出现的顺序很重要。因为找到第一个匹配的正则后,查找就停止了,后面定义的正则就是再匹配也没有机会了。
- 使用精确匹配可以提高查找的速度。例如经常请求/的话,可以使用=来定义location。
总结:精准匹配 > 字符串匹配(若有多个匹配项匹配成功,那么选择匹配长的并记录) > 正则匹配
- 示例:
location = / {
return 1;
}
location / {
return 2;
}
location /user/ {
return 3;
}
location ^~ /images/ {
return 4;
}
location ~* \.(gif|jpg|jpeg)$ {
return 5;
}
请求/精准匹配1,不再往下查找。
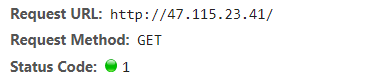
请求/index.html匹配2。首先查找匹配的前缀字符,找到最长匹配是配置2,接着又按照顺序查找匹配的正则。结果没有找到,因此使用先前标记的最长匹配,即配置2。
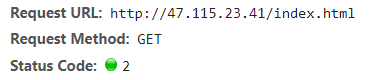
请求/user/index.html匹配3。首先找到最长匹配3,由于后面没有匹配的正则,所以使用最长匹配3。

请求/user/1.jpg匹配5。首先进行前缀字符的查找,找到最长匹配项3,继续进行正则查找,找到匹配项5。因此使用5。

请求/images/1.jpg匹配4。首先进行前缀字符的查找,找到最长匹配4。但是,特殊的是它使用了^~修饰符,不再进行接下来的正则的匹配查找,因此使用4。这里,如果没有前面的修饰符,其实最终的匹配是5。

请求/documents/index.html匹配2。因为2表示任何以/开头的URL都匹配。在上面的配置中,只有2能满足,所以匹配2。

location @name的用法
@用来定义一个命名location。主要用于内部重定向,不能用来处理正常的请求。其用法如下:
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ @custom
}
location @custom {
# ...do something
}
上例中,当尝试访问url找不到对应的文件就重定向到我们自定义的命名location(此处为custom)。
值得注意的是,命名location中不能再嵌套其它的命名location。
URL尾部的
/需不需要
关于URL尾部的/有三点也需要说明一下。第一点与location配置有关,其他两点无关。
- location中的字符有没有/都没有影响。也就是说/user/和/user是一样的。
- 如果URL结构是https://domain.
com/的形式,尾部有没有/都不会造成重定向。因为浏览器在发起请求的时候,默认加上了/。虽然很多浏览器在地址栏里也不会显示/。这一点,可以访问baidu验证一下。 - 如果URL的结构是https://domain.com/
some-dir/。尾部如果缺少/将导致重定向。因为根据约定,URL尾部的/表示目录,没有/表示文件。所以访问/some-dir/时,服务器会自动去该目录下找对应的默认文件。如果访问/some-dir的话,服务器会先去找some-dir文件,找不到的话会将some-dir当成目录,重定向到/some-dir/,去该目录下找默认文件。可以去测试一下你的网站是不是这样的。
05 地址重定向-Nginx的rewrite规则
https://www.cnblogs.com/tugenhua0707/p/10798762.html
rewrite功能就是,使用nginx提供的全局变量或自己设置的变量,结合正则表达式和标志位实现url重写以及重定向。
语法:
一:理解“地址重写”与“地址转发”的含义。(地址重写与地址转发是两个不同的概念)
地址重写:是为了实现地址的标准化,比如我们可以在地址栏中中输入www.baidu.com我们也可以输入www.baidu.cn最后都会被重写到www.baidu.com上。浏览器的地址栏也会显示www.baidu.com。
地址转发:它是指在网络数据传输过程中数据分组到达路由器或桥接器后,该设备通过检查分组地址并将数据转发到最近的局域网的过程。
因此地址重写和地址转发有以下不同点:
- 地址重写会改变浏览器中的地址,使之变成重写成浏览器最新的地址。而地址转发是不会改变浏览器的地址的。
- 地址重写会产生两次请求,而地址转发只会有一次请求。
- 地址转发一般发生在同一站点项目内部,而地址重写不受限制。
- 地址转发的速度比地址重定向快。(地址重写即是重定向)
二:理解rewrite指令使用
该指令是通过正则表达式的使用来改变URI。可以同时存在一个或多个指令。需要按照顺序依次对URL进行匹配和处理。
rewrite只能放在server{}、location{}、if{}中,并且只能对域名后边的除去传递的参数外的字符串起作用,例如:
http://seanlook.com/a/we/index.php?id=1&u=str 只对 /a/we/index.php 重写
其基本语法结构如下:
rewrite regex replacement [flag];
- rewrite的含义:该指令是实现URL重写的指令。
- regex的含义:用于匹配URI的正则表达式。
- replacement:将regex正则匹配到的内容替换成replacement。
- flag: flag标记。
flag有如下值:
last: 本条规则匹配完成后,继续向下匹配新的location URI 规则。(不常用)break: 本条规则匹配完成即终止,不再匹配后面的任何规则(不常用)。redirect: 返回302临时重定向,浏览器地址会显示跳转新的URL地址。permanent: 返回301永久重定向。浏览器地址会显示跳转新的URL地址。
例子:
rewrite ^/(.*) http://www.baidu.com/$1 permanent;
说明:
- rewrite为固定关键字,表示开始进行rewrite匹配规则。
- regex为
^/(.*),这是一个正则表达式,匹配完整的域名和后面的路径地址。 - replacement就是http://www.baidu.com/$1这块了,其中$1是取regex部分
()里面的内容。如果匹配成功后跳转到的URL。 - flag就是permanent,代表永久重定向的含义,即跳转到http://www.baidu.com/$1地址上。
server {
listen 80;
server_name 47.115.23.41;
location /api {
rewrite ^/(.*) https://www.baidu.com permanent;
}
error_page 404 500 502 503 504 =200 /default_api;
location = /default_api {
default_type application/json;
return 200 '{"code":"-1","msg":"invoke fail, not found"}';
}
- 访问
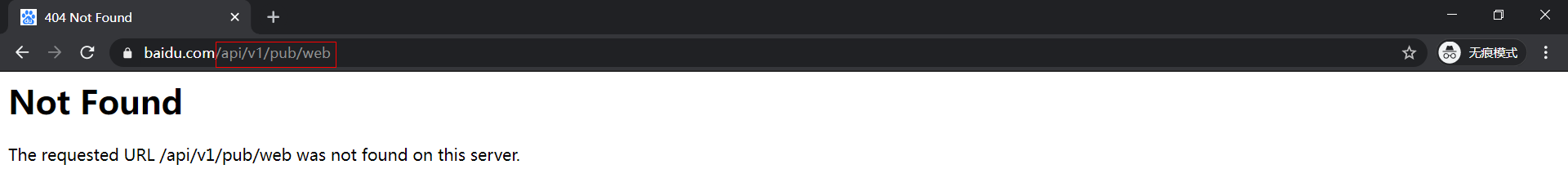
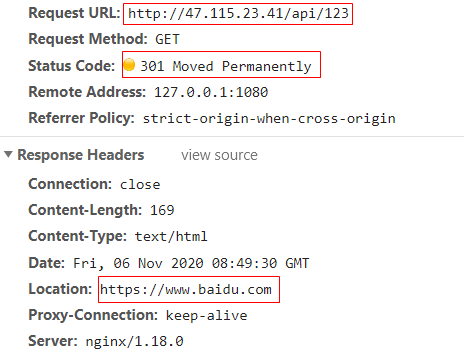
47.115.23.41/api/v1/pub/web会跳转到https://www.baidu.com/api/v1/pub/web从而报错Not Found;(47.115.23.41/api/v1/pub/web,这个地址是java jar包启动的接口地址) - 访问
47.115.23.41/aa/xx/xx/xx...;如果aa=api,则会直接跳转到https://www.baidu.com,否则会跳到自定义返回Json的错误页面; - 访问
47.115.23.41或者47.115.23.41/会直接跳转到https://www.baidu.com; rewrite ^/(.*) https://www.baidu.com/$1 permanent;;除了47.115.23.41/会直接跳转到https://www.baidu.com,其它都不行;

常用正则表达式:
| 字符 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| ^ | 匹配输入字符串的起始位置 |
| $ | 匹配输入字符串的结束位置 |
- | 匹配前面的字符串0次或者多次
- | 匹配前面的字符串1次或者多次
? | 匹配前面的字符串0次或者1次
. | 匹配除“\n”之外的所有单个字符
(pattern) | 匹配括号内的pattern
应用场景:
- 非法访问跳转,防盗链
- 网站更换新域名
- http跳转https
- 不同地址访问同一个虚拟主机的资源
06 Nginx配置Websocket反向代理
配置:
server {
listen 80;
server_name xdclass.net;
location / {
proxy_pass http://lbs;
proxy_read_timeout 300s; # websocket 空闲保持时长
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection $connection_upgrade;
}
}
核心是下面的配置,其他和普通反向代理没区别, 表示请求服务器升级协议为WebSocket:
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection $connection_upgrade;
服务器处理完请求后,响应如下报文(状态码为101)
HTTP/1.1 101 Switching Protocols
Upgrade: websocket
Connection: upgrade


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号