day31--ArrayList、Vector、LinkedList
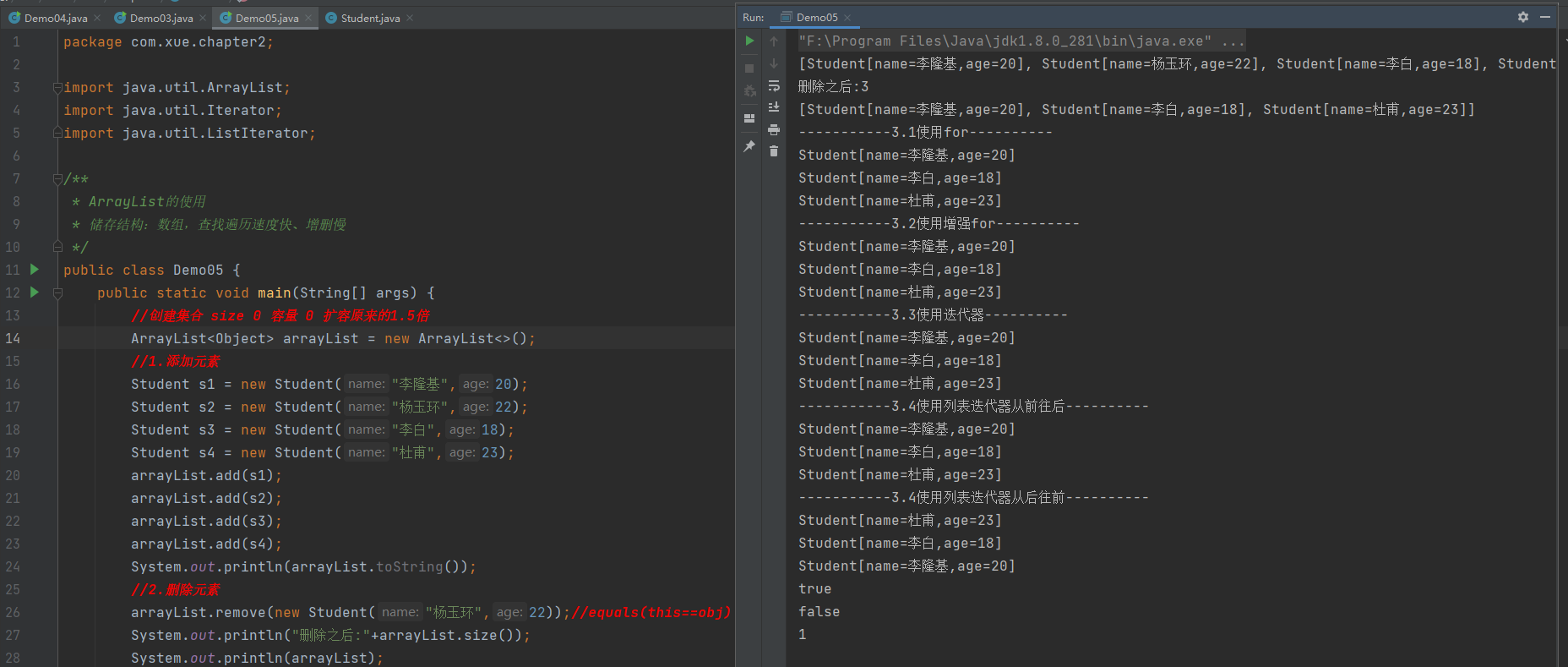
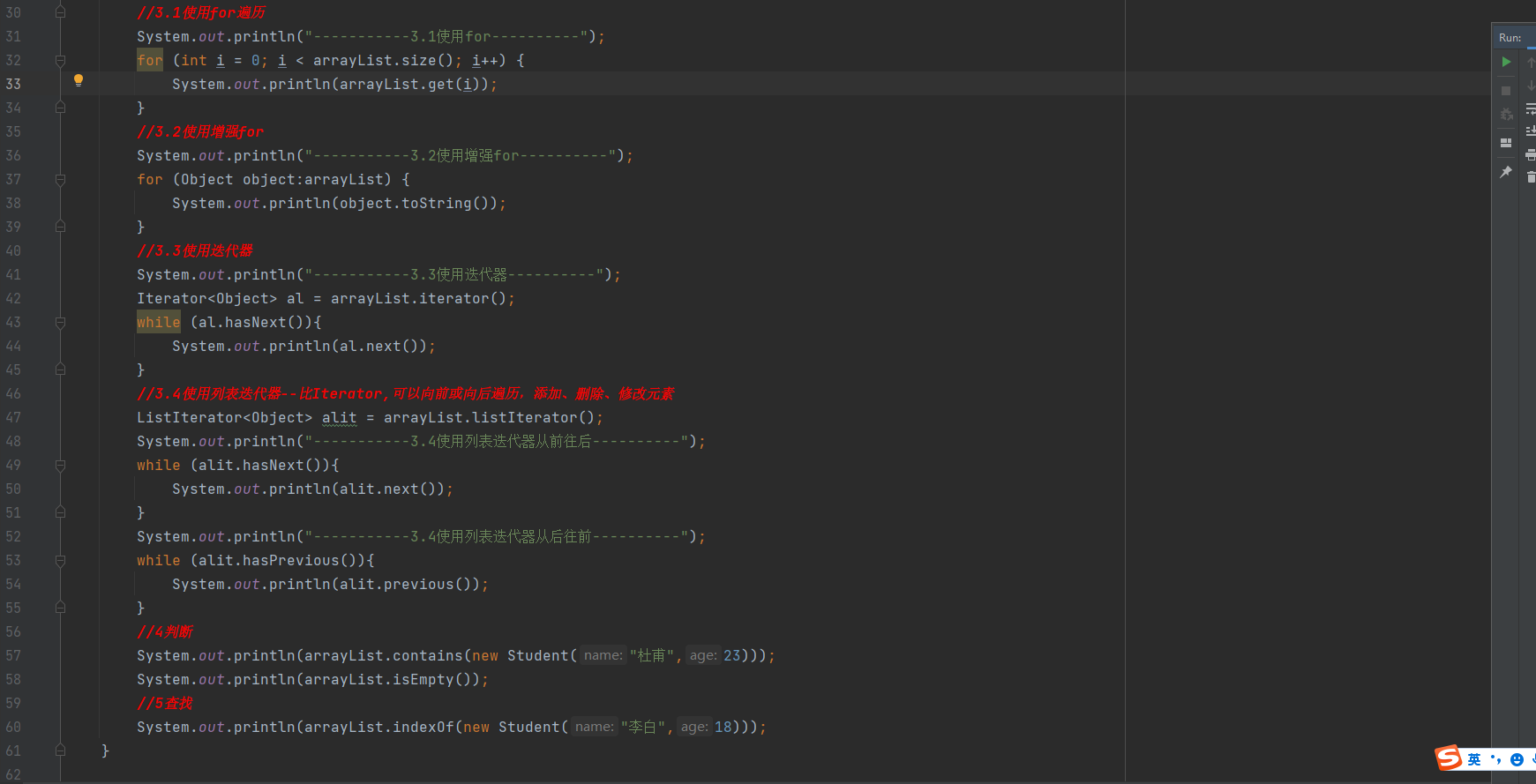
如何实现?
arrayList.remove(new Student("杨玉环",22));
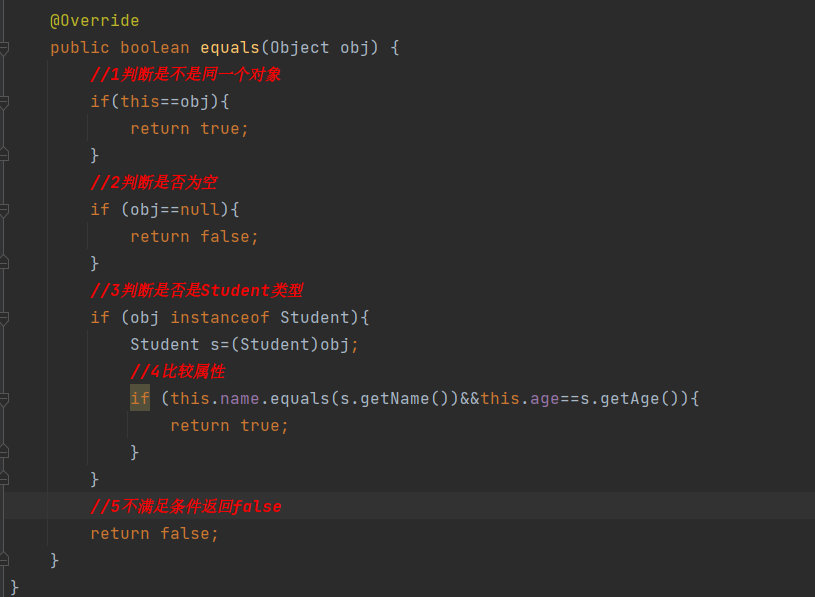
源码分析:
-
ArrayList
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
DEFAULT_CAPACITY:默认容量。
注意:如果没有向集合中添加任何元素,默认容量为0。添加任意一个元素后,容量为10。
每次扩容大小是原来的1.5倍。
transient Object[] elementData;
elementDate:存放元素的数组。
private int size;
size:实际元素的个数。
-
Add()
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity));
}
private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) {
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
return minCapacity;
}
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
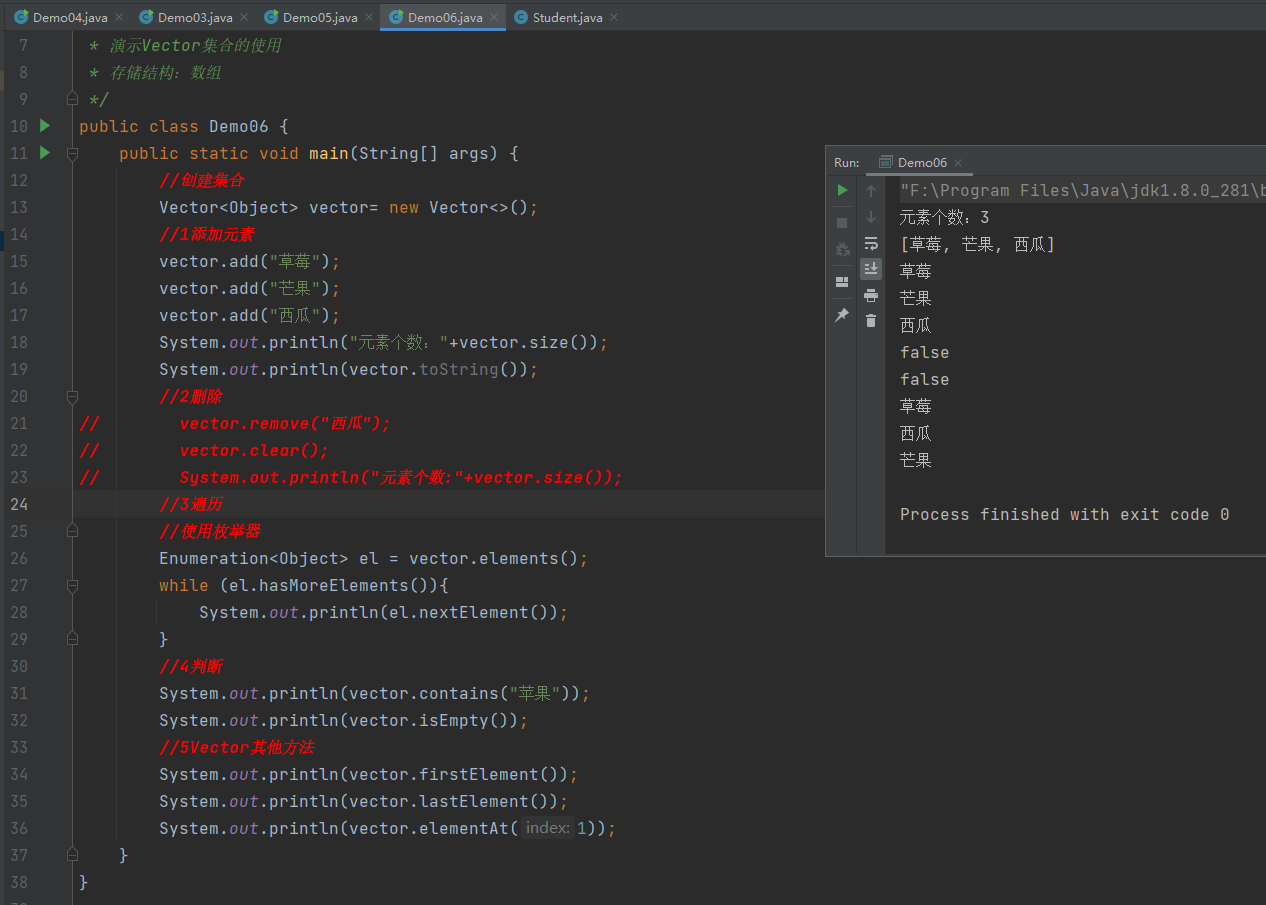
Vector
LinkedList
LinkedList源码分析
int size:集合的大小
Node first:链表的头节点
Node lase:链表的尾节点
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
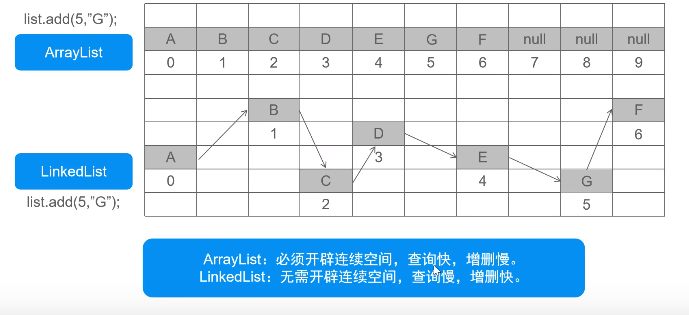
ArrayList和LinkedList的区别
-
不同结构实现方式


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号