SQL 学习笔记(二)
本次主要内容如下:
1, 视图
视图是虚表,不会真实存储数据,需要通过在创建视图的时候用 SELECT 语句创建。
视图的好处:数据安全性,只开放必要的数据字段;提高数据使用效率,减少频率使用 SELECT 语句查询,直接通过视图可以查询;
视图的创建: CREATE VIEW AS SELECT XXXX FROM TABLE;
视图的修改: ALTER VIEW XXXX AS SELECT XXXX FROM TABLE;
视图的更新: 视图可以更新,但是必须是与原始数据一直的数据行会被更新,被聚合的,计算的字段不会更新;一般视图只开发查询权限,不可以更新;
视图的删除: DROP VIEW XXXX;
2, 子查询:指一个查询语句嵌套在另一个查询语句内部的查询。
1),嵌套子查询,顾名思义,子查询中再嵌套一层子查询,为嵌套子查询
2),关联子查询:查询与子查询之间存在着联系
3),标量子查询:标量子查询可以返回一个值了
3, 函数
SQL 中常见的函数操作有 算术,字符,日期,转换
算术:
abs:求绝对值
mod:求余数
round : 四舍五入
字符串:
concat:拼接
length:字符串长度
lower:小写
upper:大写
replace:字符串替换
substring():字符串截取
substring_index():字符串按照索引截取
repeat(string,number) :字符串按需重复多次
日期函数:
current_date()
current_time()
current_timestamp() 当前日期和时间
extract:截取日期元素
转换函数:
CAST
COALESCE,使用较多,将null值转为其他值
4, 谓词
常见谓词: LIKE, BETWEEN, ISNULL, IS NOT NULL, IN , EXISTS
5, case 表达式,常用于条件多组条件分支的情况
语法如下:
CASE WHEN <求值表达式> THEN <表达式>
WHEN <求值表达式> THEN <表达式>
WHEN <求值表达式> THEN <表达式>
.
.
.
ELSE <表达式>
END
练习题:
3.1
创建出满足下述三个条件的视图(视图名称为 ViewPractice5_1)。使用 product(商品)表作为参照表,假设表中包含初始状态的 8 行数据。
- 条件 1:销售单价大于等于 1000 日元。
- 条件 2:登记日期是 2009 年 9 月 20 日。
- 条件 3:包含商品名称、销售单价和登记日期三列。
create view ViewPractice5_1 as
select
product_name, sale_price, regist_date
from product
where sale_price >= 1000
and regist_date = '2009-09-20';
select *
from ViewPractice5_1;

3.2
向习题一中创建的视图 ViewPractice5_1 中插入如下数据,会得到什么样的结果?为什么?
INSERT INTO ViewPractice5_1 VALUES (' 刀子 ', 300, '2009-11-02');
报错消息如下:
Error Code: 1423. Field of view 'shop.viewpractice5_1' underlying table doesn't have a default value
数据无法插入, product_id, product_type 非空,插入的数据未提供值,视图中不包含这两个字段,所以报错。
3.3
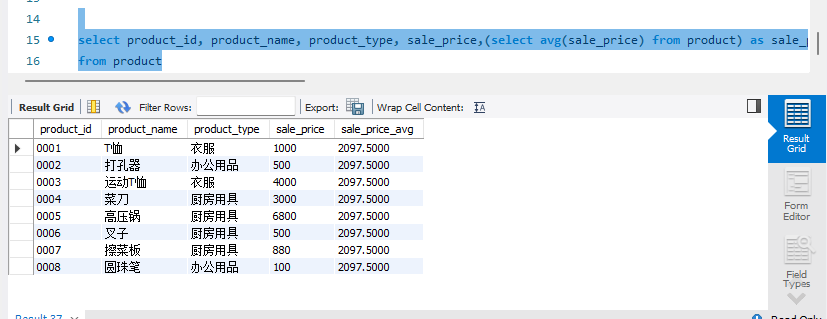
请根据如下结果编写 SELECT 语句,其中 sale_price_avg 列为全部商品的平均销售单价。
select product_id, product_name, product_type, sale_price,(select avg(sale_price) from product) as sale_price_avg
from product;
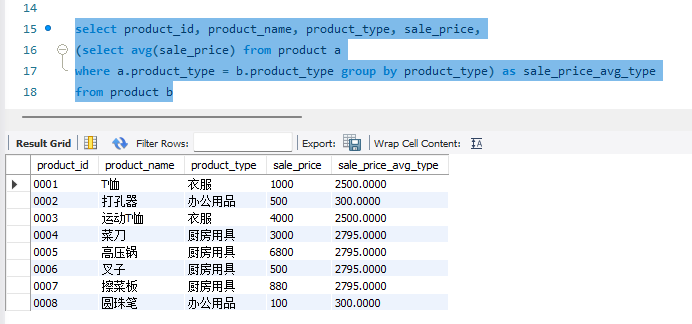
3.4 请根据习题一中的条件编写一条 SQL 语句,创建一幅包含如下数据的视图(名称为AvgPriceByType)
select product_id, product_name, product_type, sale_price,
(select avg(sale_price) from product a
where a.product_type = b.product_type group by product_type) as sale_price_avg_type
from product b
3.5 判断题
四则运算中含有 NULL 时(不进行特殊处理的情况下),运算结果是否必然会变为NULL ? 答案是对的
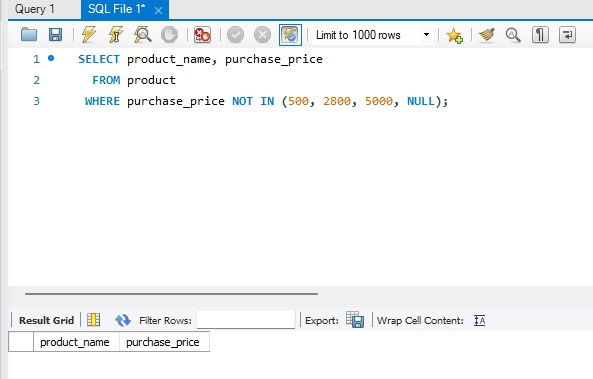
3.6 对本章中使用的 product(商品)表执行如下 2 条 SELECT 语句,能够得到什么样的结果呢?
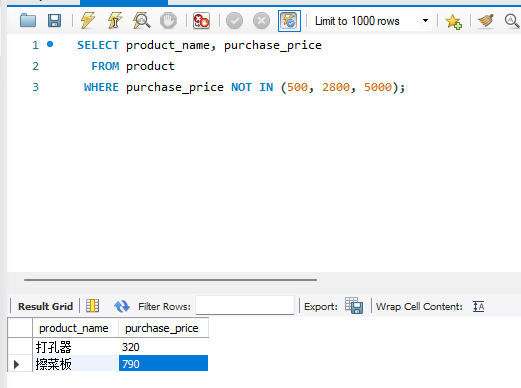
过滤 NULL 值时需要对 NULL 值做特殊处理。
3.7,
按照销售单价( sale_price )对练习 3.6 中的 product(商品)表中的商品进行如下分类。
- 低档商品:销售单价在1000日元以下(T恤衫、办公用品、叉子、擦菜板、 圆珠笔)
- 中档商品:销售单价在1001日元以上3000日元以下(菜刀)
- 高档商品:销售单价在3001日元以上(运动T恤、高压锅)
请编写出统计上述商品种类中所包含的商品数量的 SELECT 语句,结果如下所示。
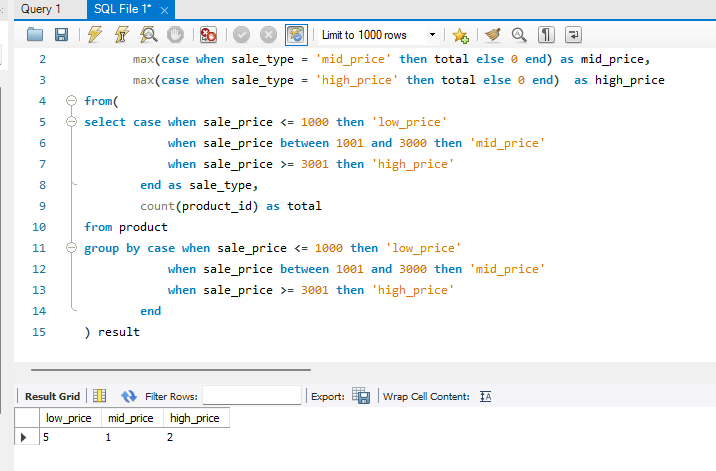
执行结果
low_price | mid_price | high_price
----------+-----------+------------
5 | 1 | 2
脚本如下:
select max(case when sale_type = 'low_price' then total else 0 end) as low_price,
max(case when sale_type = 'mid_price' then total else 0 end) as mid_price,
max(case when sale_type = 'high_price' then total else 0 end) as high_price
from(
select case when sale_price <= 1000 then 'low_price'
when sale_price between 1001 and 3000 then 'mid_price'
when sale_price >= 3001 then 'high_price'
end as sale_type,
count(product_id) as total
from product
group by case when sale_price <= 1000 then 'low_price'
when sale_price between 1001 and 3000 then 'mid_price'
when sale_price >= 3001 then 'high_price'
end
) result;



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号