【读书笔记】第四章、压缩列表
一、结构体
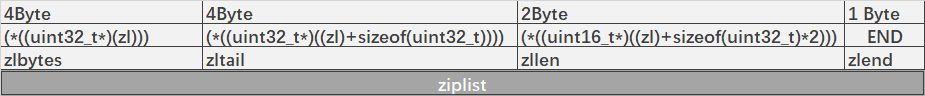
1. ziplist结构

2. entry 结构
entry 结构
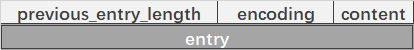
这里面 previous_entry_length 记录了上个元素的长度。
以及 encoding 编码,外加内容。
假设当前元素首地址为 p
那么 p - p->previous_entry_length 就是上一个元素。通过这样的方法可以达到从尾到头遍历的目的。
encoding,即 content 字段存储的数据类型。 为节约内存 encoding 的长度可变。
| encoding 编码 | encoding 长度 | content类型 |
|---|---|---|
| 00bbbbbb [6 bit 表长度] | 1 byte | 最大长度为 63的字节数组 |
| 01bbbbbb aaaaaaaa [14 bit 表长度] | 2 byte | 最大长度为 2^14 - 1 的字节数组 |
| 10xxxxxx aaaaaaaa cccccccc dddddddd eeeeeeee [32 bit 表长度] | 5 byte | 最大长度为 2^32 - 1的字节数组 |
| 11000000 | 1 byte | int16 整数 |
| 11010000 | 1 byte | int32 整数 |
| 11100000 | 1 byte | int64 整数 |
| 11110000 | 1 byte | 24 位整数 |
| 11111110 | 1 byte | 8 位整数 |
| 1111xxxx | 1 byte | 没有 content 字段; xxxx 表示 0 ~ 12 的整数 |
由此可见,encoding 编码的 第一个字节前两位【红色】,是解释content 是 字节数组,还是整数,
-
如果是字节数组,也同时来表达字节数组的最大长度,剩余部分位实际使用长度【10除外,貌似弃用了首字节后六位】。
-
如果是整数时候,可以根据 第 3 位,第 4 位【绿色】,表达整数的具体类型。
-
最后 当 1111xxxx 表示 0 ~ 12 的时候,可以没有 content ,相当于立即数。[这个说法是 书中说的 根据源码 我感觉不太正确]
以下源码说的是 0001 ~ 1101 是立即数。也就是 1~ 13. 除非 redis 自动做了 减一操作?大模型给出了肯定,这里需要再看源码。
也就是说 11110000 ~ 11111100 是立即数, 其中 11111110 不在其中,所以编码可用。
// 摘自 /src/ziplist
/* Different encoding/length possibilities */
#define ZIP_STR_MASK 0xc0 //11000000
#define ZIP_INT_MASK 0x30 //00110000
#define ZIP_STR_06B (0 << 6) // 00000000
#define ZIP_STR_14B (1 << 6) // 01000000
#define ZIP_STR_32B (2 << 6) // 10000000
#define ZIP_INT_16B (0xc0 | 0<<4) // 11000000
#define ZIP_INT_32B (0xc0 | 1<<4) // 00010000 | 11000000 = 11010000
#define ZIP_INT_64B (0xc0 | 2<<4) // 00100000 | 11000000 = 11100000
#define ZIP_INT_24B (0xc0 | 3<<4) // 00110000 | 11000000 = 11110000
#define ZIP_INT_8B 0xfe // 11111110
//这里说 11110001 ~ 11111101 才是立即数
/* 4 bit integer immediate encoding |1111xxxx| with xxxx between
* 0001 and 1101. */
#define ZIP_INT_IMM_MASK 0x0f /* Mask to extract the 4 bits value. To add
one is needed to reconstruct the value. */
#define ZIP_INT_IMM_MIN 0xf1 /* 11110001 */
#define ZIP_INT_IMM_MAX 0xfd /* 11111101 */
#define INT24_MAX 0x7fffff
#define INT24_MIN (-INT24_MAX - 1)
3. zlentry结构
/* We use this function to receive information about a ziplist entry.
* Note that this is not how the data is actually encoded, is just what we
* get filled by a function in order to operate more easily. */
typedef struct zlentry {
// 上个元素长度类型的长
unsigned int prevrawlensize; /* Bytes used to encode the previous entry len*/
// 上个元素长度
unsigned int prevrawlen; /* Previous entry len. */
// 本元素长度类型
unsigned int lensize; /* Bytes used to encode this entry type/len.
For example strings have a 1, 2 or 5 bytes
header. Integers always use a single byte.*/
// 本元素长度
unsigned int len; /* Bytes used to represent the actual entry.
For strings this is just the string length
while for integers it is 1, 2, 3, 4, 8 or
0 (for 4 bit immediate) depending on the
number range. */
// 头大小
unsigned int headersize; /* prevrawlensize + lensize. */
// encoding字段长度
unsigned char encoding; /* Set to ZIP_STR_* or ZIP_INT_* depending on
the entry encoding. However for 4 bits
immediate integers this can assume a range
of values and must be range-checked. */
// 当前元素首地址
unsigned char *p; /* Pointer to the very start of the entry, that
is, this points to prev-entry-len field. */
} zlentry;
笔记:
注意我的 ziplist 并画里面的 entry 是 zlentry。如果直接用 zlentry ,那么当然不必要这么复杂的 zlentry。这样也不叫压缩列表了。
所以,压缩的过程是 zlentry 变为 entry 的过程。
所以,因为要压缩,就要记录 lensize 类型,len 元素长度。
解码压缩列表
// 摘自 /src/ziplist.c
/* ZIP_BIG_PREVLEN - 1 is the max number of bytes of
the previous entry, for the "prevlen" field prefixing
each entry, to be represented with just a single byte.
Otherwise it is represented as FE AA BB CC DD, where
AA BB CC DD are a 4 bytes unsigned integer
representing the previous entry len. */
#define ZIP_BIG_PREVLEN 254
/* Fills a struct with all information about an entry.
* This function is the "unsafe" alternative to the one below.
* Generally, all function that return a pointer to an element in the ziplist
* will assert that this element is valid, so it can be freely used.
* Generally functions such ziplistGet assume the input pointer is already
* validated (since it's the return value of another function). */
// p指向压缩元素, e是解压后的元素
static inline void zipEntry(unsigned char *p, zlentry *e) {
//解码上个元素长度
ZIP_DECODE_PREVLEN(p, e->prevrawlensize, e->prevrawlen);
//解码编码
ZIP_ENTRY_ENCODING(p + e->prevrawlensize, e->encoding);
//解析编码长度
ZIP_DECODE_LENGTH(p + e->prevrawlensize, e->encoding, e->lensize, e->len);
assert(e->lensize != 0); /* check that encoding was valid. */
e->headersize = e->prevrawlensize + e->lensize;
// 取出内容
e->p = p;
}
/* Return the length of the previous element, and the number of bytes that
* are used in order to encode the previous element length.
* 'ptr' must point to the prevlen prefix of an entry (that encodes the
* length of the previous entry in order to navigate the elements backward).
* The length of the previous entry is stored in 'prevlen', the number of
* bytes needed to encode the previous entry length are stored in
* 'prevlensize'. */
#define ZIP_DECODE_PREVLEN(ptr, prevlensize, prevlen) do { \
ZIP_DECODE_PREVLENSIZE(ptr, prevlensize); \
// 如果是 1 ,大小就是本身
if ((prevlensize) == 1) { \
(prevlen) = (ptr)[0]; \
//如果是5 ,第一个字节是 0xFE ,后四个字节才是真正的大小
} else { /* prevlensize == 5 */ \
// 取出头部然后获取前一个元素的大小
// 按数组取出,然后乘以对应位大小,相加
(prevlen) = ((ptr)[4] << 24) | \
((ptr)[3] << 16) | \
((ptr)[2] << 8) | \
((ptr)[1]); \
} \
} while(0)
/* Return the number of bytes used to encode the length of the previous
* entry. The length is returned by setting the var 'prevlensize'. */
//获取到上个元素长度类型
#define ZIP_DECODE_PREVLENSIZE(ptr, prevlensize) do { \
// 注意:对于 prvious_entry_length 只有 1个字节和 5 个字节。
// 如果是5个字节,则使用 0xFE 打头,所以只有四个字节表示大小
// ZIP_BIG_PREVLEN 就是 0xFE 所以,这个len 小于 254 它就是 1个字节 len 就是自身。
// 否则还要 zipStorePrevEntryLengthLarge 解析
if ((ptr)[0] < ZIP_BIG_PREVLEN) { \
(prevlensize) = 1; \
} else { \
(prevlensize) = 5; \
} \
} while(0)
/* Extract the encoding from the byte pointed by 'ptr' and set it into
* 'encoding' field of the zlentry structure. */
#define ZIP_ENTRY_ENCODING(ptr, encoding) do { \
//取出编码类型,看起来压缩的时候 将 编码类型编在 上一元素大小类型后了
(encoding) = ((ptr)[0]); \
if ((encoding) < ZIP_STR_MASK) (encoding) &= ZIP_STR_MASK; \
} while(0)
/* Decode the entry encoding type and data length (string length for strings,
* number of bytes used for the integer for integer entries) encoded in 'ptr'.
* The 'encoding' variable is input, extracted by the caller, the 'lensize'
* variable will hold the number of bytes required to encode the entry
* length, and the 'len' variable will hold the entry length.
* On invalid encoding error, lensize is set to 0. */
#define ZIP_DECODE_LENGTH(ptr, encoding, lensize, len) do { \
//ZIP_STR_MASK 0xc0 //11000000
if ((encoding) < ZIP_STR_MASK) { \
//小于该值,则是字符串
if ((encoding) == ZIP_STR_06B) { \
(lensize) = 1; \
// 0x3f = 00111111
// 掩码取出真实使用长度
(len) = (ptr)[0] & 0x3f; \
} else if ((encoding) == ZIP_STR_14B) { \
(lensize) = 2; \
(len) = (((ptr)[0] & 0x3f) << 8) | (ptr)[1]; \
} else if ((encoding) == ZIP_STR_32B) { \
(lensize) = 5; \
(len) = ((uint32_t)(ptr)[1] << 24) | \
((uint32_t)(ptr)[2] << 16) | \
((uint32_t)(ptr)[3] << 8) | \
((uint32_t)(ptr)[4]); \
} else { \
(lensize) = 0; /* bad encoding, should be covered by a previous */ \
(len) = 0; /* ZIP_ASSERT_ENCODING / zipEncodingLenSize, or */ \
/* match the lensize after this macro with 0. */ \
} \
} else { \
(lensize) = 1; \
if ((encoding) == ZIP_INT_8B) (len) = 1; \
else if ((encoding) == ZIP_INT_16B) (len) = 2; \
else if ((encoding) == ZIP_INT_24B) (len) = 3; \
else if ((encoding) == ZIP_INT_32B) (len) = 4; \
else if ((encoding) == ZIP_INT_64B) (len) = 8; \
// 立即数,它的content 大小为 0
else if (encoding >= ZIP_INT_IMM_MIN && encoding <= ZIP_INT_IMM_MAX) \
(len) = 0; /* 4 bit immediate */ \
else \
(lensize) = (len) = 0; /* bad encoding */ \
} \
} while(0)
笔记:
宏定义为什么用 do{}while(0)?
这里宏定义用了 do {} while(0) ,明显只运行一次,为什么用 do while ?
- 确保宏展开为单一语句块
注意这里的 else 会错误地绑定到内层的 if,导致语法错误或逻辑错误。#define ZIP_DECODE_PREVLENSIZE(ptr, prevlensize) \ if ((ptr)[0] < ZIP_BIG_PREVLEN) { \ (prevlensize) = 1; \ } else { \ (prevlensize) = 5; \ } if (condition) ZIP_DECODE_PREVLENSIZE(ptr, prevlensize); else do_something(); //展开后 if (condition) if (ptr[0] < ZIP_BIG_PREVLEN) { prevlensize = 1; } else { prevlensize = 5; }; else do_something(); - 避免空宏问题
如果宏定义为空(比如某些条件编译中宏可能不包含任何代码),直接写 {} 可能导致空语句块引发编译器警告或错误。而 do { } while(0) 是一个合法的空语句块,不会被编译器优化掉,也不会引发警告。 - 一致性与可维护性
使用 do { ... } while(0) 是C语言宏定义的惯例,开发者看到这种形式会立刻明白这是一个多语句宏,方便阅读和维护。
即使宏当前只有一条语句,未来可能扩展为多条语句,使用 do { ... } while(0) 能保持向前兼容,减少修改时的风险。 - 避免意外的分号问题
#define BAD_MACRO(x) x = 1; x = 2 if (condition) BAD_MACRO(x); if (condition) x = 1; x = 2; //此时 x = 2 在外面
二、基本操作
1.创建压缩列表
// 摘自 /src/ziplist.c
/* Create a new empty ziplist. */
/* Return total bytes a ziplist is composed of. */
#define ZIPLIST_BYTES(zl) (*((uint32_t*)(zl)))
/* Return the offset of the last item inside the ziplist. */
#define ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) (*((uint32_t*)((zl)+sizeof(uint32_t))))
/* Return the length of a ziplist, or UINT16_MAX if the length cannot be
* determined without scanning the whole ziplist. */
#define ZIPLIST_LENGTH(zl) (*((uint16_t*)((zl)+sizeof(uint32_t)*2)))
#define ZIPLIST_HEADER_SIZE (sizeof(uint32_t)*2+sizeof(uint16_t)) //10
#define ZIPLIST_END_SIZE (sizeof(uint8_t)) //1
#define ZIP_END 255 /* Special "end of ziplist" entry. */
unsigned char *ziplistNew(void) {
unsigned int bytes = ZIPLIST_HEADER_SIZE + ZIPLIST_END_SIZE; // 11
// 直接申请内存
unsigned char *zl = zmalloc(bytes);
// (*((uint32_t*)(zl))) 强转为 uint32_t* 指针,并指向地址对应值
ZIPLIST_BYTES(zl) = intrev32ifbe(bytes);
// (*((uint32_t*)((zl)+sizeof(uint32_t)))) 强转为 uint32_t* 指针,并指向 4 字节后对应值 然后赋值 10
ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) = intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_HEADER_SIZE);
// (*((uint16_t*)((zl)+sizeof(uint32_t)*2))) 强转为 uint16_t* 指针,并指向 8 字节后对应值 然后赋值 0
ZIPLIST_LENGTH(zl) = 0;
//结尾标注 0xFF
zl[bytes-1] = ZIP_END;
return zl;
}
什么是小端序
以下是 intrev32ifbe 相关。
// 摘自 /src/endianconv.h
/* variants of the function doing the actual conversion only if the target
* host is big endian */
// 小端序(Little Endian)是指低位字节存储在低地址,高位字节存储在高地址(常见于 x86 架构)。
#if (BYTE_ORDER == LITTLE_ENDIAN)
#define memrev16ifbe(p) ((void)(0))
#define memrev32ifbe(p) ((void)(0))
#define memrev64ifbe(p) ((void)(0))
#define intrev16ifbe(v) (v)
#define intrev32ifbe(v) (v)
#define intrev64ifbe(v) (v)
#else
#define memrev16ifbe(p) memrev16(p)
#define memrev32ifbe(p) memrev32(p)
#define memrev64ifbe(p) memrev64(p)
#define intrev16ifbe(v) intrev16(v)
#define intrev32ifbe(v) intrev32(v)
#define intrev64ifbe(v) intrev64(v)
#endif
笔记:
LITTLE_ENDIAN 是小端序,小端序是 你存储的值 高位在高位地址,低位在低位地址。
我也是今天才听说这个词,很疑惑之前不都是正常的吗?什么高位地位?
仔细想想其实地址的高低位抽象出来确实应该是 从左到右越从上到下来越高。
正常情况加我们学编程其实不怎么考虑这个问题。当我们尝试看一个二进制编码就明白了。
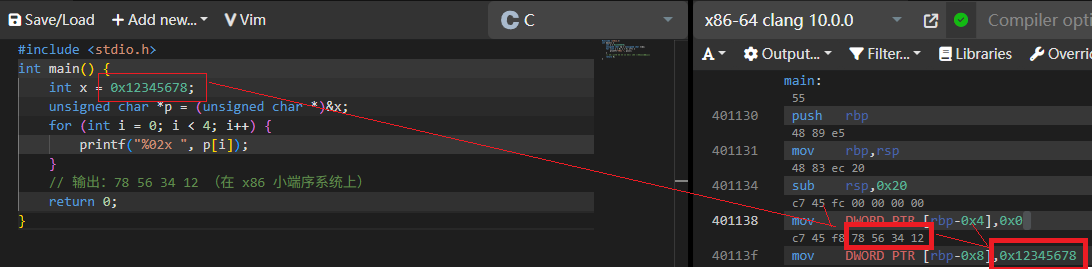
这里很明显,先储存地位,再储存高位。这就是 x86 cpu。
然后大端序当然是相反了。但是注意,手机 arm 处理器是支持双端序的,就是说看配置。
我暂时没有找到纯 大端序 的编译器。不能给出例子。
2.插入元素
// 摘自 /src/ziplist.c
/* Return the pointer to the last entry of a ziplist, using the
* last entry offset inside the ziplist header. */
//指针移动到结尾 //defined ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) (*((uint32_t*)((zl)+sizeof(uint32_t))))
#define ZIPLIST_ENTRY_TAIL(zl) ((zl)+intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl)))
/* Insert an entry at "p". */
unsigned char *ziplistInsert(unsigned char *zl, unsigned char *p, unsigned char *s, unsigned int slen) {
return __ziplistInsert(zl,p,s,slen);
}
/* Insert item at "p". */
unsigned char *__ziplistInsert(unsigned char *zl, unsigned char *p, unsigned char *s, unsigned int slen) {
// 取出 当前长度,定义 要求长度,和新长度
// ziplist 第一个元素为压缩表长度
size_t curlen = intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_BYTES(zl)), reqlen, newlen;
unsigned int prevlensize, prevlen = 0;
size_t offset;
int nextdiff = 0;
unsigned char encoding = 0;
long long value = 123456789; /* initialized to avoid warning. Using a value
that is easy to see if for some reason
we use it uninitialized. */
zlentry tail;
/* Find out prevlen for the entry that is inserted. */
// 如果p 不指向终点
if (p[0] != ZIP_END) {
//解析出上个元素的信息
ZIP_DECODE_PREVLEN(p, prevlensize, prevlen);
} else {
// ptail 指回开头,开始判断是否有元素
unsigned char *ptail = ZIPLIST_ENTRY_TAIL(zl);
//ZIPLIST_ENTRY_TAIL 之后 *ptail 如果并没有指向尾部,说明有元素
if (ptail[0] != ZIP_END) {
//获取上个元素大小
prevlen = zipRawEntryLengthSafe(zl, curlen, ptail);
}
}
/* See if the entry can be encoded */
//开始对插入的字节进行编码
//返回 1 则是整数类型,0则是字符串类型
if (zipTryEncoding(s,slen,&value,&encoding)) {
/* 'encoding' is set to the appropriate integer encoding */
// 当前 encoding 其实只有一个头元素,所以可以通过这个方法判断 size 大小
// 放入 reqlen 中
reqlen = zipIntSize(encoding);
} else {
/* 'encoding' is untouched, however zipStoreEntryEncoding will use the
* string length to figure out how to encode it. */
// 长度大于 32 或者等于 0 或者 或者无法转换为 允许的数字类型 则表示为 string
reqlen = slen;
}
/* We need space for both the length of the previous entry and
* the length of the payload. */
//计算头 entry 第一个元素大小,首先是 prevlen
reqlen += zipStorePrevEntryLength(NULL,prevlen);
//然后是 encoding 大小
reqlen += zipStoreEntryEncoding(NULL,encoding,slen);
/* When the insert position is not equal to the tail, we need to
* make sure that the next entry can hold this entry's length in
* its prevlen field. */
int forcelarge = 0;
// 如果不是 ziplist 末尾,计算一下 当前元素大小,和 p 记录的前一个元素大小差距
// 这里主要是为了算 ziplist 大小变化,对于 插入位置后面的节点, previous_entry_length 完全可以拿过来继续用,
// 但是后面元素的 previous_entry_length 却要修改。简单说就是 让后一个元素,把 previous_entry_length 留下,让它滚后面去
// 但是滚后面要滚多少?要取决于新元素的头大小 + 新元素大小
nextdiff = (p[0] != ZIP_END) ? zipPrevLenByteDiff(p,reqlen) : 0;
// 因为每个元素都有上一个元素的头,然而这种插入可能导致每个元素的头大小都会变化,进而导致连锁更新,导致性能下降。
// 一般来说,如果元素头缩小。且元素长度小于4 就是插入元素长度不是太长的话,我们就强制这个要去后面的元素继续使用大头,这样对它后面的元素影响不大,
// 这样它的大小对于后一个元素连说不变,避免了连锁更新。
// 但是,reqlen >= 4 的时候依然可能触发连锁更新 ,这时候 放入 __ziplistCascadeUpdate 解决
if (nextdiff == -4 && reqlen < 4) {
nextdiff = 0;
forcelarge = 1;
}
/* Store offset because a realloc may change the address of zl. */
offset = p-zl;
newlen = curlen+reqlen+nextdiff;
// 重新申请内存 注意 ziplistResize 即使申请到新位置的内存,也会把内存中的数据移动过去
zl = ziplistResize(zl,newlen);
// 将 p 指向 新的内存位置
p = zl+offset;
/* Apply memory move when necessary and update tail offset. */
if (p[0] != ZIP_END) {
/* Subtract one because of the ZIP_END bytes */
//内存移动
//拷贝下个数据到新位置
//目标位置 p+reqlen ,起始位置 p-nextdiff, 赋值内存长度 当前长度
memmove(p+reqlen,p-nextdiff,curlen-offset-1+nextdiff);
/* Encode this entry's raw length in the next entry. */
//为让出位置的元素 生成新的头
if (forcelarge)
zipStorePrevEntryLengthLarge(p+reqlen,reqlen);
else
zipStorePrevEntryLength(p+reqlen,reqlen);
/* Update offset for tail */
ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) =
intrev32ifbe(intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl))+reqlen);
/* When the tail contains more than one entry, we need to take
* "nextdiff" in account as well. Otherwise, a change in the
* size of prevlen doesn't have an effect on the *tail* offset. */
assert(zipEntrySafe(zl, newlen, p+reqlen, &tail, 1));
if (p[reqlen+tail.headersize+tail.len] != ZIP_END) {
ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) =
intrev32ifbe(intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl))+nextdiff);
}
} else {
/* This element will be the new tail. */
ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) = intrev32ifbe(p-zl);
}
/* When nextdiff != 0, the raw length of the next entry has changed, so
* we need to cascade the update throughout the ziplist */
if (nextdiff != 0) {
offset = p-zl;
//有空如何解决连锁更新吧
zl = __ziplistCascadeUpdate(zl,p+reqlen);
p = zl+offset;
}
/* Write the entry */
p += zipStorePrevEntryLength(p,prevlen);
p += zipStoreEntryEncoding(p,encoding,slen);
if (ZIP_IS_STR(encoding)) {
memcpy(p,s,slen);
} else {
zipSaveInteger(p,value,encoding);
}
ZIPLIST_INCR_LENGTH(zl,1);
return zl;
}
/* Return the total number of bytes used by the entry pointed to by 'p'. */
static inline unsigned int zipRawEntryLengthSafe(unsigned char* zl, size_t zlbytes, unsigned char *p) {
zlentry e;
assert(zipEntrySafe(zl, zlbytes, p, &e, 0));
return e.headersize + e.len;
}
/* Fills a struct with all information about an entry.
* This function is safe to use on untrusted pointers, it'll make sure not to
* try to access memory outside the ziplist payload.
* Returns 1 if the entry is valid, and 0 otherwise. */
//validate_prevlen 是检测上个元素是否越界。这里调用方法给了 0 ,也就是说无需检查直接. 也许给 1 的时候有其他用途?
static inline int zipEntrySafe(unsigned char* zl, size_t zlbytes, unsigned char *p, zlentry *e, int validate_prevlen) {
//取出第一第二个元素
unsigned char *zlfirst = zl + ZIPLIST_HEADER_SIZE;
unsigned char *zllast = zl + zlbytes - ZIPLIST_END_SIZE;
#define OUT_OF_RANGE(p) (unlikely((p) < zlfirst || (p) > zllast))
/* If there's no possibility for the header to reach outside the ziplist,
* take the fast path. (max lensize and prevrawlensize are both 5 bytes) */
// 10 是头部,p + 10 后依然小于最后元素地址,说明可以插
if (p >= zlfirst && p + 10 < zllast) {
//解析出该有的数据
ZIP_DECODE_PREVLEN(p, e->prevrawlensize, e->prevrawlen);
ZIP_ENTRY_ENCODING(p + e->prevrawlensize, e->encoding);
ZIP_DECODE_LENGTH(p + e->prevrawlensize, e->encoding, e->lensize, e->len);
e->headersize = e->prevrawlensize + e->lensize;
//数据指针
e->p = p;
/* We didn't call ZIP_ASSERT_ENCODING, so we check lensize was set to 0. */
//e lensize == 0
if (unlikely(e->lensize == 0))
return 0;
/* Make sure the entry doesn't reach outside the edge of the ziplist */
// 插入位置 + e的头部 + e的长度 不超过 ziplist 最大长度
if (OUT_OF_RANGE(p + e->headersize + e->len))
return 0;
//确保上个元素不超界
/* Make sure prevlen doesn't reach outside the edge of the ziplist */
if (validate_prevlen && OUT_OF_RANGE(p - e->prevrawlen))
return 0;
return 1;
}
//判断是否越界
/* Make sure the pointer doesn't reach outside the edge of the ziplist */
if (OUT_OF_RANGE(p))
return 0;
//确保 描述上个头 没有越界
/* Make sure the encoded prevlen header doesn't reach outside the allocation */
ZIP_DECODE_PREVLENSIZE(p, e->prevrawlensize);
if (OUT_OF_RANGE(p + e->prevrawlensize))
return 0;
/* Make sure encoded entry header is valid. */
ZIP_ENTRY_ENCODING(p + e->prevrawlensize, e->encoding);
// 获取头大小
e->lensize = zipEncodingLenSize(e->encoding);
//#define ZIP_ENCODING_SIZE_INVALID 0xff
//头无效值
if (unlikely(e->lensize == ZIP_ENCODING_SIZE_INVALID))
return 0;
/* Make sure the encoded entry header doesn't reach outside the allocation */
// 确保自己没有头不越界
if (OUT_OF_RANGE(p + e->prevrawlensize + e->lensize))
return 0;
/* Decode the prevlen and entry len headers. */
// 获取实际上个元素大小
ZIP_DECODE_PREVLEN(p, e->prevrawlensize, e->prevrawlen);
// 获取本元素实际大小
ZIP_DECODE_LENGTH(p + e->prevrawlensize, e->encoding, e->lensize, e->len);
//赋值 headersize
e->headersize = e->prevrawlensize + e->lensize;
/* Make sure the entry doesn't reach outside the edge of the ziplist */
//越界测试
if (OUT_OF_RANGE(p + e->headersize + e->len))
return 0;
// 上个元素越界测试
/* Make sure prevlen doesn't reach outside the edge of the ziplist */
if (validate_prevlen && OUT_OF_RANGE(p - e->prevrawlen))
return 0;
//指向内容
e->p = p;
return 1;
#undef OUT_OF_RANGE
}
#define ZIP_ENCODING_SIZE_INVALID 0xff
/* Return the number of bytes required to encode the entry type + length.
* On error, return ZIP_ENCODING_SIZE_INVALID */
static inline unsigned int zipEncodingLenSize(unsigned char encoding) {
if (encoding == ZIP_INT_16B || encoding == ZIP_INT_32B ||
encoding == ZIP_INT_24B || encoding == ZIP_INT_64B ||
encoding == ZIP_INT_8B)
return 1;
if (encoding >= ZIP_INT_IMM_MIN && encoding <= ZIP_INT_IMM_MAX)
return 1;
if (encoding == ZIP_STR_06B)
return 1;
if (encoding == ZIP_STR_14B)
return 2;
if (encoding == ZIP_STR_32B)
return 5;
return ZIP_ENCODING_SIZE_INVALID;
}
/* Return bytes needed to store integer encoded by 'encoding' */
static inline unsigned int zipIntSize(unsigned char encoding) {
switch(encoding) {
case ZIP_INT_8B: return 1;
case ZIP_INT_16B: return 2;
case ZIP_INT_24B: return 3;
case ZIP_INT_32B: return 4;
case ZIP_INT_64B: return 8;
}
if (encoding >= ZIP_INT_IMM_MIN && encoding <= ZIP_INT_IMM_MAX)
return 0; /* 4 bit immediate */
/* bad encoding, covered by a previous call to ZIP_ASSERT_ENCODING */
redis_unreachable();
return 0;
}
/* Given a pointer 'p' to the prevlen info that prefixes an entry, this
* function returns the difference in number of bytes needed to encode
* the prevlen if the previous entry changes of size.
*
* So if A is the number of bytes used right now to encode the 'prevlen'
* field.
*
* And B is the number of bytes that are needed in order to encode the
* 'prevlen' if the previous element will be updated to one of size 'len'.
*
* Then the function returns B - A
*
* So the function returns a positive number if more space is needed,
* a negative number if less space is needed, or zero if the same space
* is needed. */
int zipPrevLenByteDiff(unsigned char *p, unsigned int len) {
unsigned int prevlensize;
ZIP_DECODE_PREVLENSIZE(p, prevlensize);
return zipStorePrevEntryLength(NULL, len) - prevlensize;
}
/* Encode the length of the previous entry and write it to "p". Return the
* number of bytes needed to encode this length if "p" is NULL. */
unsigned int zipStorePrevEntryLength(unsigned char *p, unsigned int len) {
if (p == NULL) {
return (len < ZIP_BIG_PREVLEN) ? 1 : sizeof(uint32_t) + 1;
} else {
if (len < ZIP_BIG_PREVLEN) {
p[0] = len;
return 1;
} else {
return zipStorePrevEntryLengthLarge(p,len);
}
}
}
/* Encode the length of the previous entry and write it to "p". This only
* uses the larger encoding (required in __ziplistCascadeUpdate). */
int zipStorePrevEntryLengthLarge(unsigned char *p, unsigned int len) {
uint32_t u32;
if (p != NULL) {
p[0] = ZIP_BIG_PREVLEN;
u32 = len;
memcpy(p+1,&u32,sizeof(u32));
memrev32ifbe(p+1);
}
return 1 + sizeof(uint32_t);
}
/* Write the encoding header of the entry in 'p'. If p is NULL it just returns
* the amount of bytes required to encode such a length. Arguments:
*
* 'encoding' is the encoding we are using for the entry. It could be
* ZIP_INT_* or ZIP_STR_* or between ZIP_INT_IMM_MIN and ZIP_INT_IMM_MAX
* for single-byte small immediate integers.
*
* 'rawlen' is only used for ZIP_STR_* encodings and is the length of the
* string that this entry represents.
*
* The function returns the number of bytes used by the encoding/length
* header stored in 'p'. */
unsigned int zipStoreEntryEncoding(unsigned char *p, unsigned char encoding, unsigned int rawlen) {
unsigned char len = 1, buf[5];
if (ZIP_IS_STR(encoding)) {
/* Although encoding is given it may not be set for strings,
* so we determine it here using the raw length. */
//表达字节数组只有三种, 1个字节,2个字节,5个字节。
//其中 00 开头表示 encoding 长度只有 1个字节 后面 6位表示长度
// 00111111
if (rawlen <= 0x3f) {
if (!p) return len;
buf[0] = ZIP_STR_06B | rawlen;
// 00111111 11111111 这里既然它不是 1个字节的 那么 小于该值就是 2个字节的。
} else if (rawlen <= 0x3fff) {
len += 1;
if (!p) return len;
buf[0] = ZIP_STR_14B | ((rawlen >> 8) & 0x3f);
buf[1] = rawlen & 0xff;
// 前两种都不是,剩下的是五个字节的
} else {
len += 4;
if (!p) return len;
buf[0] = ZIP_STR_32B;
buf[1] = (rawlen >> 24) & 0xff;
buf[2] = (rawlen >> 16) & 0xff;
buf[3] = (rawlen >> 8) & 0xff;
buf[4] = rawlen & 0xff;
}
} else {
/* Implies integer encoding, so length is always 1. */
// 数字只有一个字节的 encoding
if (!p) return len;
buf[0] = encoding;
}
/* Store this length at p. */
memcpy(p,buf,len);
return len;
}
压缩元素
/* Check if string pointed to by 'entry' can be encoded as an integer.
* Stores the integer value in 'v' and its encoding in 'encoding'. */
// 返回 0 代表 解析为字符串, 1 代表数字
int zipTryEncoding(unsigned char *entry, unsigned int entrylen, long long *v, unsigned char *encoding) {
long long value;
// 过长的数字 redis 即转换数字意义不大,长度为0 也没必要转换。
if (entrylen >= 32 || entrylen == 0) return 0;
// string2ll 尝试将 string数字 转换为 longlong
// int string2ll(const char *s, size_t slen, long long *value)
if (string2ll((char*)entry, entrylen,&value)) {
/* Great, the string can be encoded. Check what's the smallest
* of our encoding types that can hold this value. */
if (value >= 0 && value <= 12) {
// 这里解答了之前的困惑,使用 ZIP_INT_IMM_MIN 加上当前值,解码的时候 减去 ZIP_INT_IMM_MIN 即可。所以和 1 ~ 13 无关
*encoding = ZIP_INT_IMM_MIN+value;
} else if (value >= INT8_MIN && value <= INT8_MAX) {
*encoding = ZIP_INT_8B;
} else if (value >= INT16_MIN && value <= INT16_MAX) {
*encoding = ZIP_INT_16B;
} else if (value >= INT24_MIN && value <= INT24_MAX) {
*encoding = ZIP_INT_24B;
} else if (value >= INT32_MIN && value <= INT32_MAX) {
*encoding = ZIP_INT_32B;
} else {
*encoding = ZIP_INT_64B;
}
*v = value;
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
笔记:
// 摘自 /src/config.h
// __builtin_expect 是 linux 内含有的方法。所以这里需要宏定义
#if __GNUC__ >= 3
#define likely(x) __builtin_expect(!!(x), 1)
#define unlikely(x) __builtin_expect(!!(x), 0)
#else
#define likely(x) (x)
#define unlikely(x) (x)
#endif


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号