【读书笔记】第三章、跳跃表
一、跃表节点与结构
/*
* 摘自 /src/server.h
*/
//节点结构
/* ZSETs use a specialized version of Skiplists */
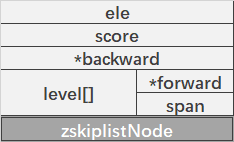
typedef struct zskiplistNode {
// sds 很明显是字符串类型
sds ele;
// 用于存储排序的分值
double score;
// 指向上一个指针
struct zskiplistNode *backward;
// level,为柔性数组。每个节点的数组长度不一样,在生成条约表节点是,随机生成 1 ~ 64的值,值越大出现的概率越低。
struct zskiplistLevel {
//指向本层的下一个节点
struct zskiplistNode *forward;
// forward 指向的节点,与本节点之间的元素个数
unsigned long span;
} level[];
} zskiplistNode;
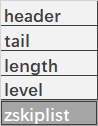
typedef struct zskiplist {
// 表头尾节点
struct zskiplistNode *header, *tail;
// 表长度
unsigned long length;
// 表高度
int level;
} zskiplist;
二、基本操作
1. 创建跳跃表
# 摘自 /src/zset.c
/* Create a new skiplist. */
zskiplist *zslCreate(void) {
int j;
zskiplist *zsl;
zsl = zmalloc(sizeof(*zsl));
zsl->level = 1;
zsl->length = 0;
zsl->header = zslCreateNode(ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL,0,NULL);
// 将头节点全部搞出来
// header 是一个记录下全部层数的 zskiplistNode,其中 ele 信息为 NULL
for (j = 0; j < ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL; j++) {
//必然没有下一个节点,等待插入
zsl->header->level[j].forward = NULL;
// 下一个节点之间的也为0
zsl->header->level[j].span = 0;
}
zsl->header->backward = NULL;
zsl->tail = NULL;
return zsl;
}
/* Create a skiplist node with the specified number of levels.
* The SDS string 'ele' is referenced by the node after the call. */
zskiplistNode *zslCreateNode(int level, double score, sds ele) {
zskiplistNode *zn = zmalloc(sizeof(*zn)+level*sizeof(struct zskiplistLevel));
zn->score = score;
zn->ele = ele;
return zn;
}
// 摘自 /src/serve.h
// 书上说定义为64,我这里是 32 .不知道是不是代码改了。
#define ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL 32 /* Should be enough for 2^64 elements */
#define ZSKIPLIST_P 0.25 /* Skiplist P = 1/4 */
2. 拆入节点
/* Insert a new node in the skiplist. Assumes the element does not already
* exist (up to the caller to enforce that). The skiplist takes ownership
* of the passed SDS string 'ele'. */
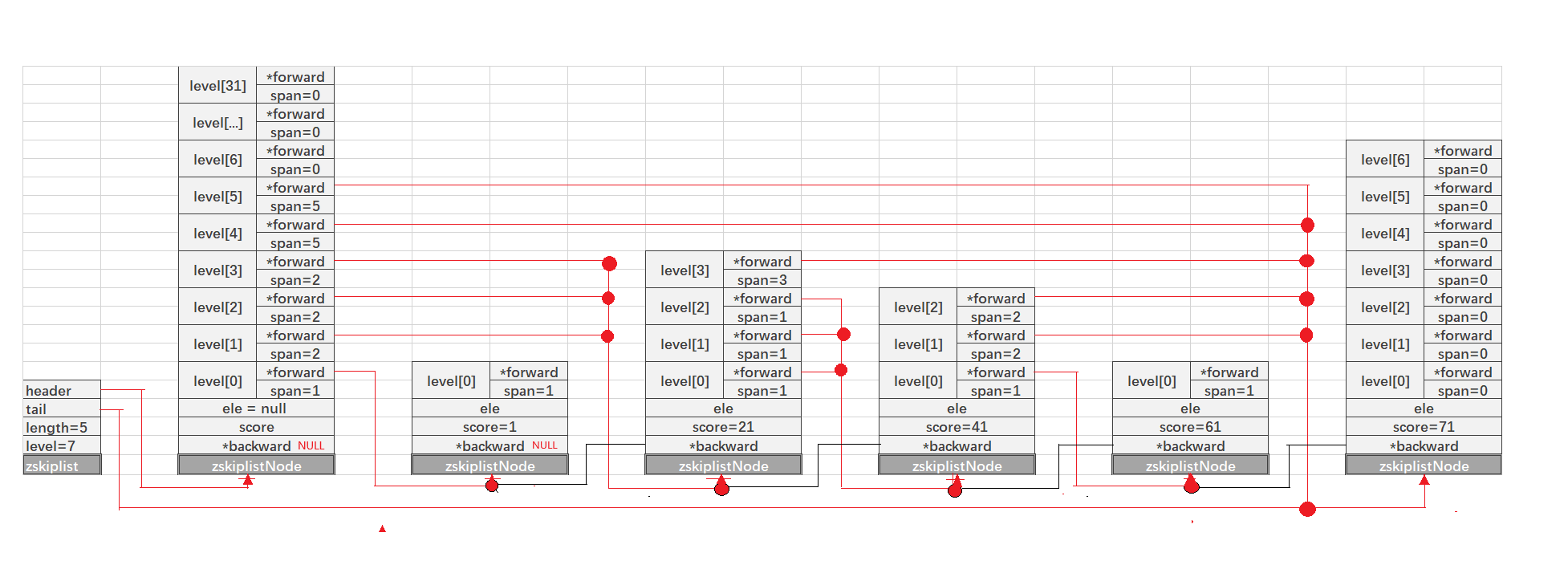
zskiplistNode *zslInsert(zskiplist *zsl, double score, sds ele) {
// update[n] 第 n 层 需要更新的节点
zskiplistNode *update[ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL], *x;
// rank[n] 第 n 层 从 update[n] 到 header 的步长
unsigned long rank[ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL];
int i, level;
serverAssert(!isnan(score));
x = zsl->header;
//先不老驴插入节点,先考虑插入该节点后,各个元素之间的位置
//从拥有最高层的元素开始分析 所以是 zsl->level -1
for (i = zsl->level-1; i >= 0; i--) {
/* store rank that is crossed to reach the insert position */
//如果 i层 为最高层,则赋值 0. 否则为 rank[i + 1]
rank[i] = i == (zsl->level-1) ? 0 : rank[i+1];
// 当前元素存在下一个节点 且 下个节点分数小于当前分数,或该层下一个节点分数和当前分数相等 且 字符串小于当前字符串。
// 这时候需要继续判断
while (x->level[i].forward &&
(x->level[i].forward->score < score ||
(x->level[i].forward->score == score &&
sdscmp(x->level[i].forward->ele,ele) < 0)))
{
//当前rank值 硬加上 该层 span
rank[i] += x->level[i].span;
// x 指向下一个节点
x = x->level[i].forward;
}
// 最后计算得出 该层插入位置节点为 x 之后, 记录下 x
update[i] = x;
}
/* we assume the element is not already inside, since we allow duplicated
* scores, reinserting the same element should never happen since the
* caller of zslInsert() should test in the hash table if the element is
* already inside or not. */
// 随机出当前元素的层数
level = zslRandomLevel();
if (level > zsl->level) {
// 先将自己高出的节点处理了,从以前的最高点 zsl->level 到 level 之间。
for (i = zsl->level; i < level; i++) {
// 因为自己最高,不存在 forward 元素,所以 rank 都是 0
rank[i] = 0;
// 因为自己最高,所以更新header 的 level 信息指向自己就可以了
update[i] = zsl->header;
// ?
update[i]->level[i].span = zsl->length;
}
//更新层级
zsl->level = level;
}
//创建节点
x = zslCreateNode(level,score,ele);
for (i = 0; i < level; i++) {
// 因为 x 节点在 update 节点后,所以像链表一样交换指针就可以了
x->level[i].forward = update[i]->level[i].forward;
update[i]->level[i].forward = x;
//其实 rank[0] 就是 元素应该的排序位置【因为 第 1 层 span 都为1】,减去该层 rank 的位置。
// 这时候距离下个元素就是 当前更新元素 和它的差值
/* update span covered by update[i] as x is inserted here */
x->level[i].span = update[i]->level[i].span - (rank[0] - rank[i]);
// update 的 rank 值就是 (rank[0] - rank[i]) + 1
update[i]->level[i].span = (rank[0] - rank[i]) + 1;
}
// 如果最终获取的层级低,则需要更新 上层元素。因为他们之间加了一个元素
/* increment span for untouched levels */
for (i = level; i < zsl->level; i++) {
update[i]->level[i].span++;
}
// 设定好 backward
x->backward = (update[0] == zsl->header) ? NULL : update[0];
if (x->level[0].forward)
x->level[0].forward->backward = x;
else
zsl->tail = x;
zsl->length++;
return x;
}
/* Returns a random level for the new skiplist node we are going to create.
* The return value of this function is between 1 and ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL
* (both inclusive), with a powerlaw-alike distribution where higher
* levels are less likely to be returned. */
//该方法,书本上在 创建阶段就已经介绍了。但是我没有在源码里发现。只在 insert 方法里看到了。
int zslRandomLevel(void) {
// 每次随机数循环,层级概率为 1/4
static const int threshold = ZSKIPLIST_P*RAND_MAX;
int level = 1;
while (random() < threshold)
level += 1;
return (level<ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL) ? level : ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL;
}
3. 删除跳跃表
// 摘自 /src/t_zset.c
/* Free a whole skiplist. */
void zslFree(zskiplist *zsl) {
zskiplistNode *node = zsl->header->level[0].forward, *next;
zfree(zsl->header);
while(node) {
next = node->level[0].forward;
zslFreeNode(node);
node = next;
}
zfree(zsl);
}
/* Free the specified skiplist node. The referenced SDS string representation
* of the element is freed too, unless node->ele is set to NULL before calling
* this function. */
void zslFreeNode(zskiplistNode *node) {
sdsfree(node->ele);
zfree(node);
}
三、跃表节点应用
在redis 中,跳跃表主要应用于有序集合的底层实现。有序集合有两种状态,另一种状态时 压缩列表。
主要看以下配置
zset-max-ziplist-entries 128: //采用压缩列表时候,元素个数最大值 默认 128
zset-max-ziplist-value 64 //采用压缩列表时候,每个元素长度的最大值 默认64
1.zset创建时候的底层实现
zset 插入元素的时候会判断下面两种条件
- zset-max-ziplist-entries 的值是否等于0
- zset-max-ziplist-value 小于要插入元素的字符串长度
满足两者之一就会使用调表实现,否则使用压缩列表。
1.zset插入过程中的底层实现
插入过程中,则判断
- zset中元素个数是否大于 zset-max-ziplist-entries
- 插入元素的字符串长度是否大于 zset-max-ziplist-value
满足任意条件,zset 就会从压缩列表转换为 跳表



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号