httpPost的两种方式
1,post-Body流和post参数,以下客户端代码和服务端代码可共用
客户端代码
/**
* post 方法
* 抛送给EDI
* @param url http://127.0.0.1:9003/api/edi/csm/csmReturnSubConBody?customerId=Fotile_CSM&api=csmreturnsub_confirm&id=6006
* @param jsonParam xml报文结构
* @return
*/
String httpPost45(String url, String jsonParam) {
//url?后面的即为post parmas 参数,bodu 放在数据流中进行传输
CloseableHttpClient httpclient = HttpClients.createDefault()
// HttpGet httpGet = new HttpGet(url)
HttpPost post=new HttpPost(url)
//httpClient 4.5版本的超时参数配置
RequestConfig requestConfig = RequestConfig.custom()
.setConnectTimeout(50000).setConnectionRequestTimeout(50000)
.setSocketTimeout(50000).build()
post.setConfig(requestConfig)
//往BODY里填充数据主体
StringEntity entitys=new StringEntity(jsonParam.toString(), "utf-8")
entitys.setContentEncoding("UTF-8")
entitys.setContentType("application/xml")
post.setEntity(entitys)
HttpResponse response = httpclient.execute(post)
// System.out.println("得到的结果:" + response.getStatusLine())//得到请求结果
String str = EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity())//得到请求回来的数据
return str
}
客户端代码二=========================================
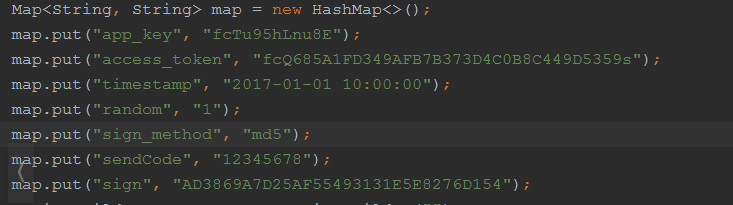
如果只是简单拼接进url是行不通的,因为我们都知道URLEncoder,对url字符集编码设置,所以需要对所有的值进行字符集编码设置,最终我们封装成了如下post方法支持url拼接入相应的请求参数:
POST_URL:请求url
urlParam:如上需要封装进url的参数
body:普通需要传递的参数
public static String httpURLConnectionPOST (String POST_URL,Map<String, String> urlParam,String body) {
CloseableHttpResponse response = null;
try {
RequestConfig defaultRequestConfig = RequestConfig.custom()
.setSocketTimeout(6000)
.setConnectTimeout(6000)
.setConnectionRequestTimeout(6000)
.build();
//httpclient
CloseableHttpClient httpclient = HttpClients.custom().setDefaultRequestConfig(defaultRequestConfig).build();
// HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost(POST_URL);
StringBuilder param=new StringBuilder("");
//将要拼接的参数urlencode
for (String key:urlParam.keySet()){
param.append(key + "=" + URLEncoder.encode(urlParam.get(key), "UTF-8") + "&");
}
//pingjie
HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost(POST_URL+param.toString());
//请求参数设置
if(com.sf.ccsp.common.util.StringUtils.isNotEmpty(body)){
StringEntity entity=new StringEntity(body, ContentType.APPLICATION_JSON);
httpPost.setEntity(entity);
}
response = httpclient.execute(httpPost);
HttpEntity entity = response.getEntity();
return EntityUtils.toString(entity, "UTF-8");
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
logger.error(e.getMessage(), e);
} catch (ClientProtocolException e) {
logger.error(e.getMessage(), e);
} catch (IOException e) {
logger.error(e.getMessage(), e);
} catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(e);
}finally {
if (response != null) {
try {
response.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
logger.error(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
}
return null;
}
服务端代码
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping(value = "csmReturnSubConBody", method = RequestMethod.POST, produces = "application/xml")
ResponseMessage csmReturnSubConBody(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
@RequestParam Map<String, String> params) {
//params为客户端URL?后面的参数集,同理,也可以将bodu放到参数集里,进行传输
CustomerInfo customerInfo = erpSetting.getCustomerInfo(params.customerId as String)
if (!customerInfo) return
ApiInfo apiInfo = erpSetting.getApiInfo(customerInfo, params.api as String)
if (!apiInfo) return
String body = readBody(request)//这里去解析post流里的body数据
ResponseMessage rsp = csmSvc.convertBodyAndSendErpRetu(apiInfo, customerInfo, body, "xml", params.id as Object, null)
return rsp
}
对于post参数流,服务端,可以这样取值
String body = params.keySet()[0] + "=" + params[params.keySet()[0]].toString()
params.keySet()[0]得到key
params[params.keySet()[0]].toString()得到第一个key的value
OLY电子标签项目


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号