24.11.19
实验6:原型模式
本次实验属于模仿型实验,通过本次实验学生将掌握以下内容:
1、理解原型模式的动机,掌握该模式的结构;
2、能够利用原型模式解决实际问题。
[实验任务一]:向量的原型
用C++完成数学中向量的封装,其中,用指针和动态申请支持向量长度的改变,使用浅克隆和深克隆复制向量类,比较这两种克隆方式的异同。
实验要求:
1.画出对应的类图;
2.提交源代码(用C++完成);
3.注意编程规范。
- 类图:
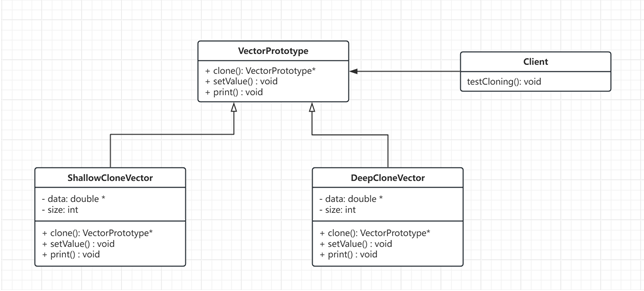
- 源代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring> // 使用memcpy进行浅拷贝
// 抽象原型类
class VectorPrototype {
public:
virtual ~VectorPrototype() = default;
// 克隆方法
virtual VectorPrototype* clone() const = 0;
// 设置和打印向量数据
virtual void setValue(int index, double value) = 0;
virtual void print() const = 0;
};
// 浅克隆向量类
class ShallowCloneVector : public VectorPrototype {
private:
double* data;
int size;
public:
// 构造函数
ShallowCloneVector(int s) : size(s) {
data = new double[size];
std::fill(data, data + size, 0.0); // 初始化为0
}
// 浅拷贝构造函数
ShallowCloneVector(const ShallowCloneVector& other) : size(other.size), data(other.data) {}
// 浅克隆方法
VectorPrototype* clone() const override {
return new ShallowCloneVector(*this); // 调用浅拷贝构造函数
}
// 设置向量的值
void setValue(int index, double value) override {
if (index >= 0 && index < size) {
data[index] = value;
}
}
// 打印向量
void print() const override {
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
std::cout << data[i] << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
// 析构函数
~ShallowCloneVector() override {
// 浅拷贝不释放data,因为多个对象共享data指针
}
};
// 深克隆向量类
class DeepCloneVector : public VectorPrototype {
private:
double* data;
int size;
public:
// 构造函数
DeepCloneVector(int s) : size(s) {
data = new double[size];
std::fill(data, data + size, 0.0); // 初始化为0
}
// 深拷贝构造函数
DeepCloneVector(const DeepCloneVector& other) : size(other.size) {
data = new double[size];
std::memcpy(data, other.data, sizeof(double) * size); // 深拷贝数据
}
// 深克隆方法
VectorPrototype* clone() const override {
return new DeepCloneVector(*this); // 调用深拷贝构造函数
}
// 设置向量的值
void setValue(int index, double value) override {
if (index >= 0 && index < size) {
data[index] = value;
}
}
// 打印向量
void print() const override {
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
std::cout << data[i] << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
// 析构函数
~DeepCloneVector() override {
delete[] data; // 深拷贝需要独立释放data
}
};
// 客户端类
class Client {
public:
static void testCloning(VectorPrototype* prototype) {
// 原始对象
prototype->setValue(0, 1.1);
prototype->setValue(1, 2.2);
prototype->print();
// 克隆对象
VectorPrototype* clonedVector = prototype->clone();
clonedVector->print();
// 修改克隆对象,观察是否会影响原始对象
clonedVector->setValue(0, 9.9);
std::cout << "After modifying cloned vector:" << std::endl;
std::cout << "Original vector: ";
prototype->print();
std::cout << "Cloned vector: ";
clonedVector->print();
// 释放克隆的向量
delete clonedVector;
}
};
// 测试
int main() {
std::cout << "Testing Shallow Clone:" << std::endl;
ShallowCloneVector shallowVector(3);
Client::testCloning(&shallowVector);
std::cout << "\nTesting Deep Clone:" << std::endl;
DeepCloneVector deepVector(3);
Client::testCloning(&deepVector);
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号