Trie树
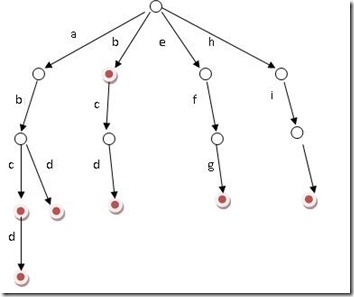
上图表示一个trie树,有abc,abcd,abd,b,bcd,efg,hii七个字符串,红色点代表为一个字符串的最后一个字符。
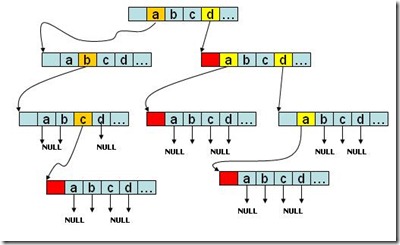
上图同样表示一个trie树,有abc,d,da,dda四个字符串,字符串尾部同样进行了标记。
已知n个由小写字母构成的平均长度为10的字符串,判断其中是否存在某个串为另一个串的前缀子串,有三种方法:
1、遍历字符串集合,对于遍历的每两个字符串,判断其中一个是否为另一个的前缀子串,时间复杂度为O(n^2)。
2、使用hash,对于每一个字符串的所有前缀子串,进行hash,对于完整的字符串进行标记,然后再进行查询。其中建立hash的时间复杂度为O(n*len),而查询的时间复杂度为O(n)。
3、使用trie树,很自然的一个数据结构,可以建立的同时进行查询,其中建立trie树的时间复杂度为O(n*len),实际查询的复杂度为O(len)。
Trie树的实现代码,数据结构是上述第二幅图
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int BranchNum=26;
struct Trie_Node
{
bool isStr;//标记是否为完整字符串
Trie_Node* next[BranchNum];
Trie_Node()
{
isStr=false;
for(int i=0;i<BranchNum;++i)
next[i]=NULL;
}
};
class Trie
{
public:
Trie();
void insert(const char* word);
bool search(const char* word);
void deleteTrie(Trie_Node* root);
private:
Trie_Node* root;
};
Trie::Trie()
{
root=new Trie_Node;
}
void Trie::insert(const char* word)
{
Trie_Node* current=root;
while(*word)
{
if(current->next[*word-'a']==NULL)
{
current->next[*word-'a']=new Trie_Node;
}
current=current->next[*word-'a'];
word++;
}
current->isStr=true;
}
bool Trie::search(const char* word)
{
Trie_Node* current=root;
while(*word && current)
{
current=current->next[*word-'a'];
++word;
}
return (current!=NULL && current->isStr);
}
void Trie::deleteTrie(Trie_Node* root)
{
for(int i=0;i<BranchNum;++i)
if(root->next[i])
deleteTrie(root->next[i]);
delete root;
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号