Java中创建线程的几种方式
盘点一下Java中创建线程的几种方式
一、继承Thread类,重写run()方法
public class MyThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("my thread start " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("main thread start "+Thread.currentThread().getName());
MyThread myThread = new MyThread();
myThread.start();
}
}
二、实现Runnable接口,并重写run()方法
public class MyThreadRunnable implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("my thread start " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("main thread start " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
MyThreadRunnable myThreadRunnable = new MyThreadRunnable();
Thread thread = new Thread(myThreadRunnable);
thread.start();
}
}
三、实现Callable接口,并重写call()方法
public class MyThreadCallable implements Callable<Integer> {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("my thread start " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
Integer ret = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
ret += i;
}
return ret;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
MyThreadCallable myThreadCallable = new MyThreadCallable();
FutureTask<Integer> futureTask = new FutureTask<>(myThreadCallable);
Thread thread = new Thread(futureTask, "A");
thread.start();
int ret = futureTask.get();
System.out.println("main thread ret = " + ret + " " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
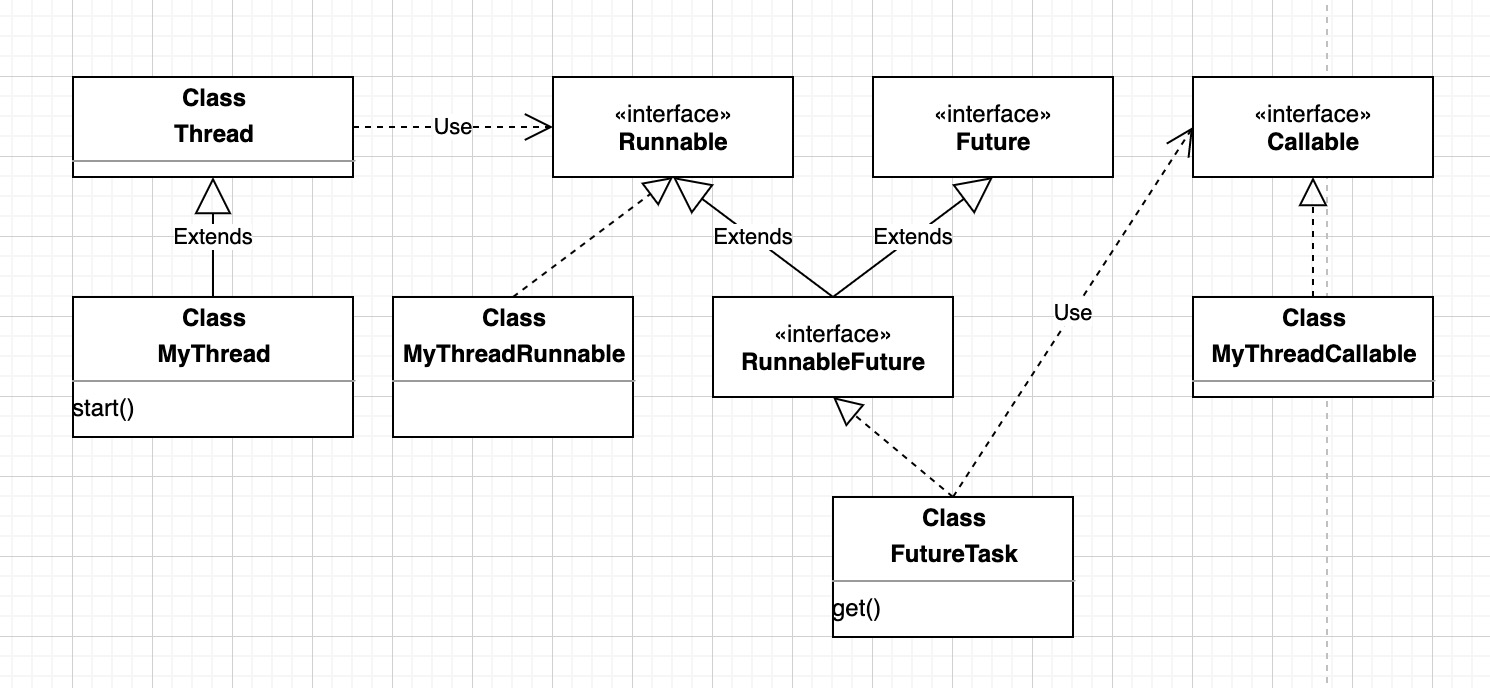
综上,类图关系如下:
四、CompletableFuture
public class CompletableFutureDemo {
private static ExecutorService threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
2,
5,
1L,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(3),
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy()
);
public static void main(String[] args) {
CompletableFuture future1 = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("执行没有返回值的任务");
});
CompletableFuture<String> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("执行有返回值的任务");
return "abc";
});
CompletableFuture<String> future3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("线程池执行有返回值的任务");
return "123";
}, threadPool);
future1.join();
System.out.println(future2.join());
System.out.println(future3);
threadPool.shutdown();
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号