Java第六次上机实验(子类与继承-面向抽象编程)
目的:
本实验的目的是让学生熟悉下来知识点:子类的继承性,子类对象的创建过程。成员变量的继承与隐藏,方法的继承与重写,面向抽象编程。
要求:
1、编写抽象类Shape,Shape类中含有两个抽象方法perimeter()和graphicType(),分别用来计算周长和判断图形类型。所以类Shape只能被定义成抽象类。
2、Triangle类继承了Shape抽象类,并实现了Shape类中两个抽象方法,是一个普通类。注:Triangle类中,需要对输入的三条边进行判断,是否能构造成一个三角形。
3、再创建一个Circle普通类,Circle类也是Shape类的一个子类。
4、在main()方法中定义了两个Shape类型的引用变量shape1和shape2,他们分别指向Triangle对象和Circle对象。由于在Shape类中定义了perimeter()和 graphicType()方法,所以程序可以直接调用shape1和shape2的perimeter()和 graphicType()方法,无需强制类型转换为其子类型。
主代码入下如下:
public class E
{
public static void main(String [] args){
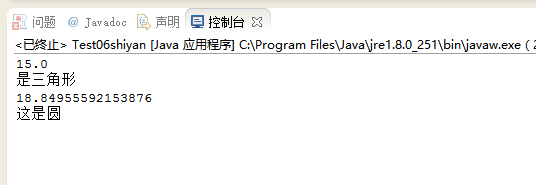
Shape shape1 = new Triangle(6,4,5);
System.out.println(shape1.perimeter());
System.out.println(shape1.graphicType());
Shape shape2 = new Circle(3);
System.out.println(shape2.perimeter());
System.out.println(shape2.graphicType());
}
}
package com.test06;
abstract class Shape{
abstract double perimeter();
abstract String graphicType();
}
class Triangle extends Shape{
int a;
int b;
int c;
Triangle(int a,int b,int c){
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
this.c = c;
}
double perimeter(){
double per;//周长
per = a+b+c;
return per;
}
String graphicType(){
if(a+b>c && a+c>b && b+c>a){
return "是三角形";
}
else{
return "不是三角形";
}
}
}
class Circle extends Shape{
int d;
Circle(int d){
this.d = d;
}
double perimeter(){
return (2*Math.PI*d);
}
String graphicType(){
return "这是圆";
}
}
public class Test06shiyan
{
public static void main(String [] args){
Shape shape1 = new Triangle(6,4,5);
System.out.println(shape1.perimeter());
System.out.println(shape1.graphicType());
Shape shape2 = new Circle(3);
System.out.println(shape2.perimeter());
System.out.println(shape2.graphicType());
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号