1、虚函数
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
/* 定义基类CBase */
class CBase
{
public:
virtual void print()
{
cout << "CBase print" << endl;
}
};
/* 定义派生类CDerived */
class CDerived : public CBase
{
public:
/* 此处的override关键字显示声明子类覆盖基类print函数,
基类函数名发生改变时,会有编译错误提醒检查 */
void print() override
{
cout << "CDerived print" << endl;
}
};
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
CBase* basePtr = new CDerived();
basePtr->print();
delete basePtr;
return 0;
}| xuanmiao@linux:~/Test/C++$ ./test38 CDerived print |
2、虚继承
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class CAnimal
{
public:
CAnimal()
{
cout << "CAnimal is constructed!"<< endl;
}
~CAnimal()
{
cout << "CAnimal is deconstructed!"<< endl;
}
void move()
{
cout << " animal can move " << endl;
}
};
class CBird : virtual public CAnimal //此处CBird虚继承CAnimal
{
public:
void fly()
{
cout << "bird can fly" << endl;
}
void breath()
{
cout << "bird can breath" << endl;
}
};
class CFish : virtual public CAnimal //此处CFish虚继承CAnimal
{
public:
void swim()
{
cout << "fish can swim" << endl;
}
void breath()
{
cout << "fish can breath" << endl;
}
};
class CWaterBird: public CBird, public CFish
{
public:
void action()
{
cout << "waterbird can fly and swim"<< endl;
}
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
cout << endl <<"调用父类各自的成员函数:" << endl;
CWaterBird waterbird;
waterbird.fly();
waterbird.swim();
waterbird.action();
cout << endl <<"调用父类重复的成员函数:" << endl;
waterbird.CBird::breath(); // 调用bird类的Breatha成员函数
waterbird.CFish::breath(); // 调用fish类的Breatha成员函数
cout << endl;
return 0;
}|
xuanmiao@linux:~/Test/C++$ ./test39 调用父类各自的成员函数: 调用父类重复的成员函数: CAnimal is deconstructed! |
此处如果去掉 class CBird : virtual public CAnimal 和 class CFish : virtual public CAnimal 中的virtual关键字,那么CAnimal类中的构造函数和析构函数会被执行两遍
|
xuanmiao@linux:~/Test/C++$ ./test39 调用父类各自的成员函数: 调用父类重复的成员函数: CAnimal is deconstructed! |
3、虚函数表
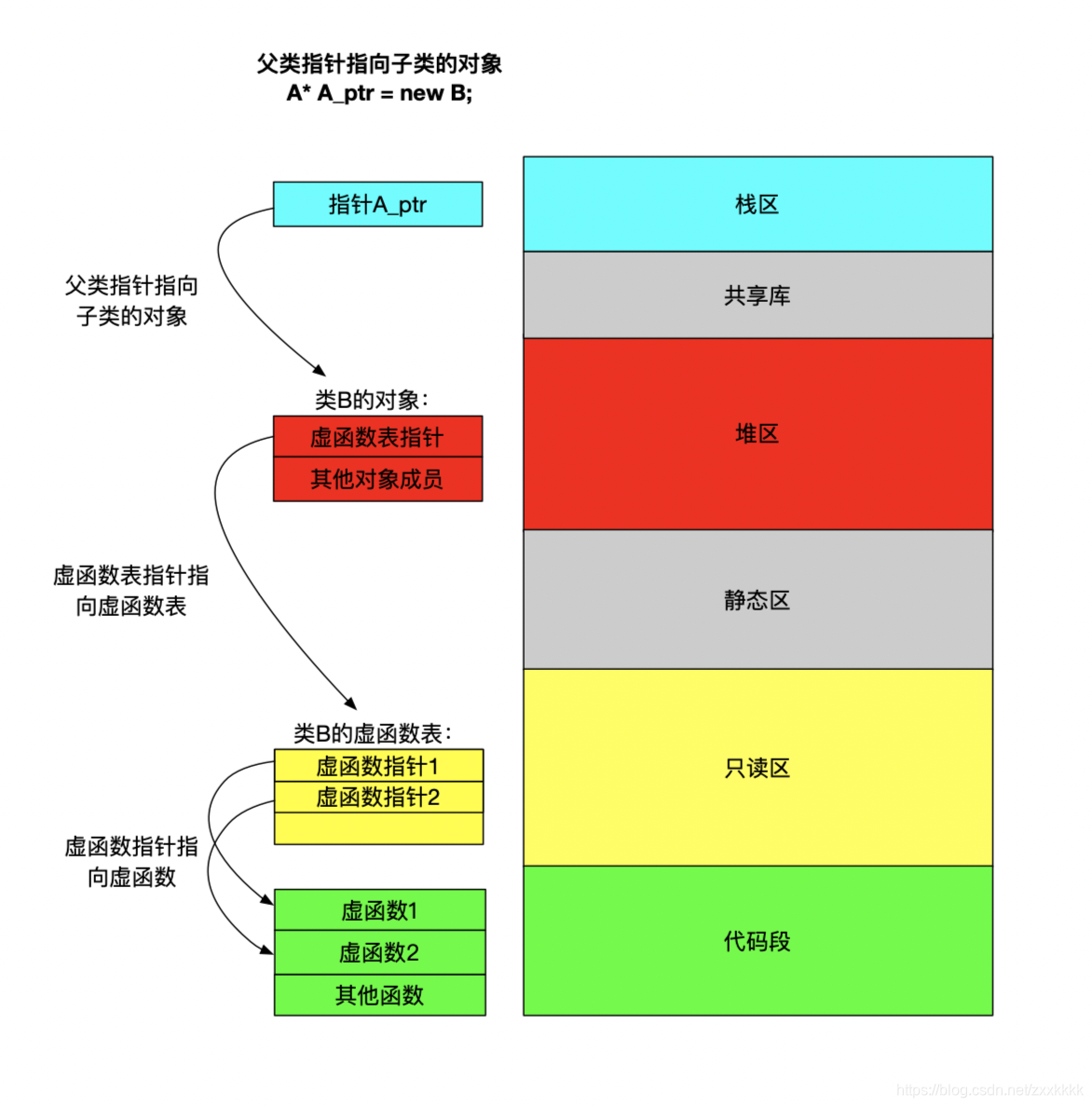
(1)打印虚函数表
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
class Base
{
public:
virtual void a() { cout << "Base a()" << endl; }
virtual void b() { cout << "Base b()" << endl; }
virtual void c() { cout << "Base c()" << endl; }
};
class Derive : public Base
{
public:
virtual void b() { cout << "Derive b()" << endl; }
};
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
cout << "-----------Base------------" << endl;
Base* q = new Base;
long* tmp1 = (long*)q;
long* vptr1 = (long*)(*tmp1);
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
printf("vptr[%d] : %p\n", i, (void*)vptr1[i]);
}
cout << endl << "---------Derive------------" << endl;
Derive* p = new Derive;
long* tmp = (long*)p;
long* vptr = (long*)(*tmp);
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
printf("vptr[%d] : %p\n", i, (void*)vptr[i]);
}
return 0;
}|
xuanmiao@linux:~/Test/C++$ ./test43 ---------Derive------------ |
(2)通过虚函数表中的指针调用函数
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
class Base
{
public:
virtual void a() { cout << "Base a()" << endl; }
virtual void b() { cout << "Base b()" << endl; }
virtual void c() { cout << "Base c()" << endl; }
};
class Derive : public Base
{
public:
virtual void b() { cout << "Derive b()" << endl; }
};
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
typedef void (*Func)();
cout << "-----------Base------------" << endl;
Base* q = new Base;
long* tmp1 = (long*)q;
long* vptr1 = (long*)(*tmp1);
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
printf("vptr[%d] : %p\n", i, (void*)vptr1[i]);
}
Func a = (Func)vptr1[0];
Func b = (Func)vptr1[1];
Func c = (Func)vptr1[2];
a();
b();
c();
Derive* p = new Derive;
long* tmp = (long*)p;
long* vptr = (long*)(*tmp);
cout << "---------Derive------------" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
printf("vptr[%d] : %p\n", i, (void*)vptr[i]);
}
Func d = (Func)vptr[0];
Func e = (Func)vptr[1];
Func f = (Func)vptr[2];
d();
e();
f();
return 0;
}| xuanmiao@linux:~/Test/C++$ ./test44 -----------Base------------ vptr[0] : 0x56451b1e740c vptr[1] : 0x56451b1e7448 vptr[2] : 0x56451b1e7484 Base a() Base b() Base c() ---------Derive------------ vptr[0] : 0x56451b1e740c vptr[1] : 0x56451b1e74c0 vptr[2] : 0x56451b1e7484 Base a() Derive b() Base c() |
参考博客:https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1599283

 虚函数和虚继承
虚函数和虚继承

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号