1、CPU读取内存数据
计算机的内存系统通常以块为单位进行数据传输,32位系统是4字节,64位系统是8字节。
当数据存储在对齐的地址上时,数据的起始地址正好是内存块的边界,CPU可以一次性读取完整的数据。
(1)对齐数据的访问
①如果int变量存储在地址0x1000,那么CPU可以一次读取从 0x1000~0x1003 的4字节数据
②如果double变量存储在地址0x2000,那么CPU可以一次读取从 0x2000~0x2007 的8字节数据
(2)未对齐数据的访问
① 如果int变量存储在地址0x1001,那么CPU分两次读取:0x1001~0x1003 + 0x1004
② 如果double变量存储在地址0x2002,那么CPU分两次读取:0x2002~0x2007 + 0x2008~0x2009
2、内存对齐原则
(1)第一个成员偏移0,之后每个成员的起始位置是当前成员的整数倍;
(2)如果结构体A中含有结构体B,B的起始位置是B中最大元素大小整数倍;
(3)结构体总大小是内部最大成员的整数倍。
系统默认的字节对齐值:32位系统是4字节,64位系统是8字节。
3、示例代码1
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define PRINT_SIZE(intValue) printf(#intValue" is %d\n",(intValue));
#define STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(type, member) ( (char*) & ((type*)0)->member - (char*)0 )
struct employee
{
char *name;
int num;
short age;
char evaluation;
char *department;
};
int main()
{
PRINT_SIZE(sizeof(struct employee));
PRINT_SIZE(STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct employee, name));
PRINT_SIZE(STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct employee, num));
PRINT_SIZE(STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct employee, age));
PRINT_SIZE(STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct employee, evaluation));
PRINT_SIZE(STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct employee, department));
return 0;
}执行结果:
sizeof(struct employee) is 24
STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct employee, name) is 0
STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct employee, num) is 8
STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct employee, age) is 12
STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct employee, evaluation) is 14
STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct employee, department) is 16
4、示例代码2
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define PRINT_SIZE(intValue) printf(#intValue" is %d\n",(intValue));
#define STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(type, member) ( (char*) & ((type*)0)->member - (char*)0 )
struct student
{
char name[10];
int num;
char sex;
};
int main()
{
PRINT_SIZE(sizeof(struct student))
PRINT_SIZE(STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct student, name))
PRINT_SIZE(STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct student, num))
PRINT_SIZE(STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct student, sex))
return 0;
}执行结果
PS D:\Code\Data Structure> .\test.exe
sizeof(struct student) is 20
STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct student, name) is 0
STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct student, num) is 12
STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct student, sex) is 16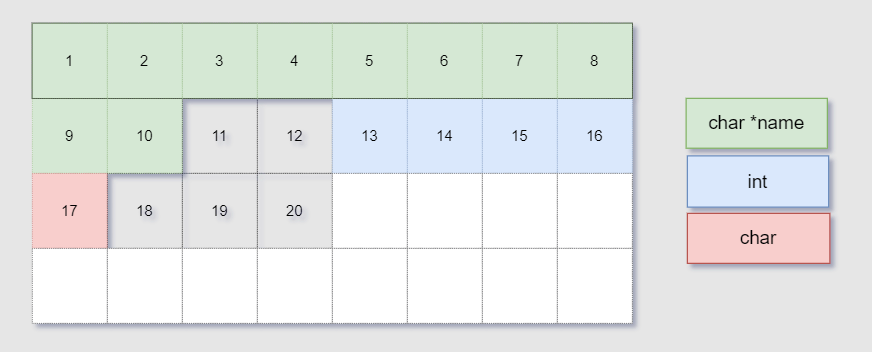
5、两种字节对齐方式
(1)#pragma pack(n)
① 指定struct或union成员的对齐边界为 n 字节
② n的取值为2的幂数,1, 2, 4, 8, 16
③ 如果没有指定#pragma pack,编译器会根据目标平台的默认对齐值4字节或者8字节;
④ 取n和默认对齐值的较小值 进行对齐
#pragma pack(1)
struct Example
{
char a; // 1字节
int b; // 4字节
short c; // 2字节
};
#pragma pack()n取1时,紧凑排列, Example结构体的大小=7
#pragma pack(2)
struct Example
{
char a; // 1字节
int b; // 4字节
short c; // 2字节
};
#pragma pack()n取2时,Example结构体的大小=8
(2)__attribute__( aligned(n) )
编译器会将让n与默认的对齐字节数进行比较,取较大值为对齐字节数
(3)__attribute__( (packed) )
取消结构在编译过程中的优化对齐, 等同于#pragma pack(1)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define PRINT_SIZE(intValue) printf(#intValue" is %ld\n",(intValue));
#define STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(type, member) ( (char*) & ((type*)0)->member - (char*)0 )
typedef struct mystruct_packed
{
int a;
double b;
char c;
}__attribute__((packed)) AP;
typedef struct mystruct2
{
int a;
double b;
char c;
}__attribute__((aligned(2))) A2;
typedef struct mystruct4
{
int a;
double b;
char c;
}__attribute__((aligned(4))) A4;
typedef struct mystruct8
{
int a;
double b;
char c;
}__attribute__((aligned(8))) A8;
typedef struct mystruct16
{
int a;
double b;
char c;
}__attribute__((aligned(16))) A16;
typedef struct mystruct32
{
int a;
double b;
char c;
}__attribute__((aligned(32))) A32;
int main()
{
PRINT_SIZE(sizeof(struct mystruct_packed))
PRINT_SIZE(STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct mystruct_packed, a))
PRINT_SIZE(STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct mystruct_packed, b))
PRINT_SIZE(STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct mystruct_packed, c))
printf("\n");
PRINT_SIZE(sizeof(struct mystruct2))
PRINT_SIZE(STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct mystruct2, a))
PRINT_SIZE(STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct mystruct2, b))
PRINT_SIZE(STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct mystruct2, c))
printf("\n");
PRINT_SIZE(sizeof(struct mystruct4))
PRINT_SIZE(STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct mystruct4, a))
PRINT_SIZE(STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct mystruct4, b))
PRINT_SIZE(STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct mystruct4, c))
printf("\n");
PRINT_SIZE(sizeof(struct mystruct8))
PRINT_SIZE(STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct mystruct8, a))
PRINT_SIZE(STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct mystruct8, b))
PRINT_SIZE(STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct mystruct8, c))
printf("\n");
PRINT_SIZE(sizeof(struct mystruct16))
PRINT_SIZE(STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct mystruct16, a))
PRINT_SIZE(STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct mystruct16, b))
PRINT_SIZE(STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct mystruct16, c))
printf("\n");
PRINT_SIZE(sizeof(struct mystruct32))
PRINT_SIZE(STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct mystruct32, a))
PRINT_SIZE(STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct mystruct32, b))
PRINT_SIZE(STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct mystruct32, c))
return 0;
}
执行结果:
xuanmiao@linux:~/Test$ ./test
sizeof(struct mystruct_packed) is 13
STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct mystruct_packed, a) is 0
STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct mystruct_packed, b) is 4
STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct mystruct_packed, c) is 12
sizeof(struct mystruct2) is 24
STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct mystruct2, a) is 0
STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct mystruct2, b) is 8
STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct mystruct2, c) is 16
sizeof(struct mystruct4) is 24
STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct mystruct4, a) is 0
STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct mystruct4, b) is 8
STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct mystruct4, c) is 16
sizeof(struct mystruct8) is 24
STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct mystruct8, a) is 0
STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct mystruct8, b) is 8
STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct mystruct8, c) is 16
sizeof(struct mystruct16) is 32
STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct mystruct16, a) is 0
STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct mystruct16, b) is 8
STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct mystruct16, c) is 16
sizeof(struct mystruct32) is 32
STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct mystruct32, a) is 0
STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct mystruct32, b) is 8
STRUCT_MEMBER_OFFSET(struct mystruct32, c) is 16
 计算机的内存系统通常以块为单位进行数据传输
计算机的内存系统通常以块为单位进行数据传输

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号