字符串与STL整理
C风格表示的字符串,借助字符数组来存放,并在最后一位有'\0'标志字符串结束,因此字符数组声明时要开大一点。而string可以认为是元素为字符的容器,大小可变,并且结尾不需要以'\0'结束。
string和char数组都可以使用cin、cout。但是string不能直接使用scanf、printf、puts,需要转换形式。
char数组与string之间的转化:
//char数组转为string char p[100]; cin>>p; string str=p; //内存拷贝赋值 //string转为char数组 string str="abc"; char *p=(char *)str.data(); string str="gdfd"; char *p=str.c_str(); string str="hello"; char p[40]; str.copy(p,5,0); //这里5,代表复制几个字符,0代表复制的位置 *(p+5)='\0';
char数组字符串常见的函数操作:
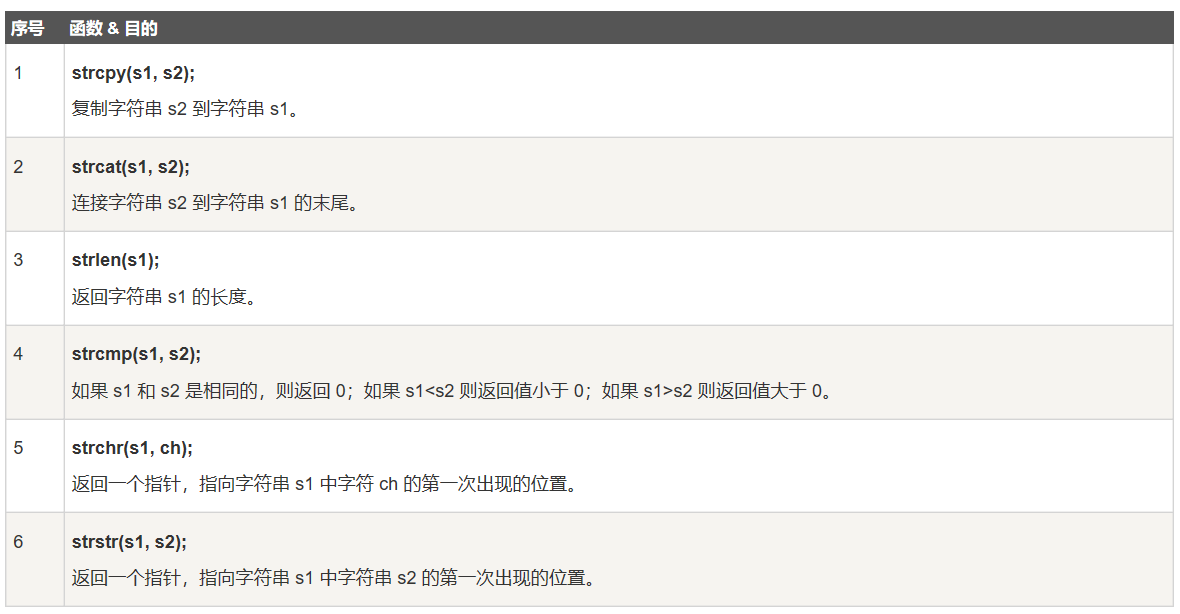
string常见操作:
+,+=,append() //添加字符和字符串 ==,<=,>=,<,> //判断大小 str.size(),s.length() //获取长度 printf("%s",str.c_str()) str.erase(10,8) //删除从str[10]开始,包括str[10]的8个元素 int pos=0; str1.find(str2,pos) //从str1中找str2第一次出现位置,找不到返回string::npos str1.insert(2,str2) //在下标为2的元素前插入str2
介绍一下STL各种容器,首先是队列
queue<int> q; priority_queue<int> q; //大顶堆 priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int>> q; //小顶堆 int a=q.front()/q.top(); q.pop(); q.push(i); q.empty(); int b=q.size(); //无符号整数,编译错误时记得将其转化为int型
对于大顶堆小顶堆可以自定义结构体和排序方式,第一中办法是在结构体中重写大于小于符号;第二种是将比较运算符外置
struct fruit { string name; double price; } f1, f2, f3; //定义三个结构体变量 struct cmp { bool operator() (fruit f1, fruit f2) // 重载括号 { return f1.price < f2.price; // 等同于less } }; priority_queue<fruit,vector<fruit> , cmp > q;
stack,操作和queue类似
s.push(x);
s.pop();
s.top();
s.empty();
lower_bound和upper_bound,利用二分方法在一个排好序的数组中进行查找
/* 从数组的begin位置到end-1位置二分查找第一个大于或等于num的数字,找到返回该数字的地 址,不存在则返回end。通过返回的地址减去起始地址begin,得到找到数字在数组中的下标。 */ int loc=lower_bound(begin,end,num)-begin //从数组的begin位置到end-1位置二分查找第一个大于num的数字 int loc=upper_bound( begin,end,num)-begin //从数组的begin位置到end-1位置二分查找第一个小于或等于num的数字 int loc=lower_bound( begin,end,num,greater<type>() )-begin //从数组的begin位置到end-1位置二分查找第一个小于num的数字 int loc=upper_bound( begin,end,num,greater<type>() )-begin
map容器,可以快速地查找与更改。
m.begin() m.end() //开始结尾的正向迭代器 m.rbegin() m.rend() //开始结尾的逆向迭代器 m.size() m.empty() m.insert(map<int, string>::value_type (1,"student_one")) //insert插入,若key值已经存在,则该语句无效 m.insert(make_pair(1,"student_one")); //可以直接以pair类型插入 m[key]=value //数组方式可以插入、查询、修改,若没有key值会自动插入 m.clear() //全部清空 m.erase(key) m.erase(m.begin(),m.end()) //erase删除部分数据,传入key值或迭代器指示范围 lower_bound(...) upper_bound(...) m.count(key) //可以用来判断key值是否存在 map<int,string>::iterator ite; ite=m.find(key) //返回指向指定键值的迭代器,没有找到返回m.end() for(ite=map.begin();ite!=map.end();ite++){ printf("%d %s\n",ite->first,ite->second.c_str()); }
set容器,内部是二叉树结构,每个元素值都唯一,根据元素的值自动排列大小,无法直接修改元素,高效的插入删除。
s.insert(1); s.erase(3); set<int>::iterator ite; ite=s.find(1); if(ite==s.end()) printf("not found"); else printf("found"); s.count(1); for(ite=s.begin();ite!=s.end();++ite){ printf("%d\n",*ite); }
vector容器
vec.push_back(a); vec[i]; vec.front(); vec.back(); vec.clear(); vec.erase(vec.begin(),vec.end()); vec.insert(p,x); //在p前插入x
list表示双向链表,不强调快速读取,而是强调快速更改。
lis.push_back(x); lis.pop_back(); lis.push_front(x); lis.pop_front(); lis.front(); lis.back(); lis.clear(); lis.erase(); lis.insert(p,x); lis.remove(x); //删除全部x,线性时间 lis.reverse(); lis.unique(); //线性时间 lis.merge(newLis) //合并后的链表在lis中,x为空;lis和newLis必须提前排好序;线性时间
merge,将两个有序序列合并为一个有序序列,可以用于vector、list
merge(a.begin(),a.end(),b.begin(),b.end(),c.begin()); //用于vector
unique,将给定去重范围内的数据去重
unqiue(vec.begin(),vec.end());
next_permutation、prev_permutation取得全排列
do{ printf("%s\n",str); }while(next_permutation(str,str+len));





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号