Java并发编程-------Executor的子接口ExecutorService和ScheduledExecutorService
Executor子接口之ExecutorService
ExecutorService接口-----相比Executor接口,ExecutorService更像一个线程池,因为其提供了对线程池的更多的操作方法,如关闭线程池,而Executor只提供了execute方法。
下面结合API文档对其功能进行分析:
- execute()------提交任务并运行
void execute(Runnable command)方法是ExecutorService从其父接口Executor接口继承来的,接收Runnable类型的参数,没有任何返回值
- submit方法----提交任务并运行
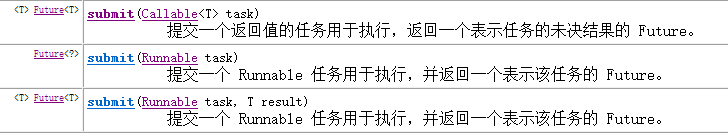
这三个方法都会返回一个表示任务结果的Future接口的实例化对象,该Future的get方法在任务完成之前会一直被阻塞,直至任务完成。
<T> Future<T> sumit(Runnable task,T result)--------参数result是返回的结果;这个result是做什么用的?
Future<?> sumit(Runnable task)-----------返回一个表示该任务的Future,当该任务直接结束之后,该Future的get方法会返回null。
execute方法和submit方法的异同:
1、接收的参数不一样 submit()可以接受runnable和callable ;execute()接受runnable 无返回值
2、sumit有返回值,execute没有返回值
3、submit更加方便异常处理,如果在需要执行的任务里执行编译时异常或者运行时异常,希望任务执行的调用者能够获得这些异常并做出及时的处理,那么就需要用到submit,通过Future.get获得抛出的异常。
这主要是因为submit能够接收Callable类型的对象,Callable能够返回任务结果并抛出异常,而execute方法只能接收Runnable接口的实例对象,Runnable接口不会返回结果,也无法抛出异常。
- 关闭线程池
1.void shutDown()
在终止线程池之前允许执行以前提交的任务,拒绝接收新任务。
2.List<Runnable> shutDownNow()
试图停止所有正在执行的活动任务,暂停处理正在等待的任务,并返回等待执行的任务列表。在终止时,执行程序没有任务在执行,也没有任务在等待执行,并且无法提交新任务。
- 判断
1. boolean isShutdown()----------如果此执行程序已关闭,则返回 true。
2. boolean isTerminated()----------如果关闭后所有任务都已完成,则返回 true。注意,除非首先调用 shutdown 或 shutdownNow,否则 isTerminated 永不为 true。
- 执行任务并返回结果
1.<T> List<Future<T>> invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks) throws InterruptedException
执行列表中给定的任务,任务列表中的任务必须实现了Callable接口,当所有任务完成时,返回保持任务状态和结果的Future列表。状态:返回列表中Future元素的Future.isDone()都为true。注意:如果正在进行此操作时修改了给定的collection,则此方法的结果是不确定的。
返回值是表示任务的Future列表,列表顺序与给定任务列表的迭代器所生成的顺序相同,每个任务都已完成。
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import java.util.Random; import java.util.concurrent.*; public class CachedThreadPool { public static void main(String[] args) { ExecutorService cachedThreadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); List<Task> taskList = new ArrayList<Task>(); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { taskList.add(new Task()); } List<Future<Integer>> futureList = new ArrayList<>(); try { futureList = cachedThreadPool.invokeAll(taskList); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { for (int i = 0; i < futureList.size(); i++) { System.out.println("isDone---" + futureList.get(i).isDone()+"---"+i); System.out.println("result---" + futureList.get(i).get()); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ExecutionException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } class Task implements Callable<Integer> { @Override public Integer call() throws Exception { return new Random().nextInt(100); } }
输出:
isDone---true---0
result---91
isDone---true---1
result---57
isDone---true---2
result---32
isDone---true---3
result---5
isDone---true---4
result---74
isDone---true---5
result---94
isDone---true---6
result---10
isDone---true---7
result---48
isDone---true---8
result---34
isDone---true---9
result---13
2.<T> List<Future<T>> invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException
- 执行给定的任务,当所有任务完成或超时期满时(无论哪个首先发生),返回保持任务状态和结果的 Future 列表。返回列表的所有元素的
Future.isDone()为 true。一旦返回后,即取消尚未完成的任务。注意,可以正常地或通过抛出异常来终止已完成 任务。如果此操作正在进行时修改了给定的 collection,则此方法的结果是不确定的。 - 参数:
tasks- 任务 collectiontimeout- 最长等待时间unit- timeout 参数的时间单位- 返回:
- 表示任务的 Future 列表,列表顺序与给定任务列表的迭代器所生成的顺序相同。如果操作未超时,则已完成所有任务。如果确实超时了,则某些任务尚未完成。
- 抛出:
InterruptedException- 如果等待时发生中断,在这种情况下取消尚未完成的任务NullPointerException- 如果任务或其任意元素或 unit 为 nullRejectedExecutionException- 如果所有任务都无法安排执行
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import java.util.Random; import java.util.concurrent.*; public class CachedThreadPool { public static void main(String[] args) { ExecutorService cachedThreadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); List<Task> taskList = new ArrayList<Task>(); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { taskList.add(new Task()); } List<Future<Integer>> futureList = new ArrayList<>(); try { futureList = cachedThreadPool.invokeAll(taskList,2,TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { for (int i = 0; i < futureList.size(); i++) { System.out.println("isDone---" + futureList.get(i).isDone()+"---"+i); System.out.println("result---" + futureList.get(i).get()); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ExecutionException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } class Task implements Callable<Integer> { @Override public Integer call() throws Exception { return new Random().nextInt(100); } }
输出:
isDone---true---0
result---11
Exception in thread "main" java.util.concurrent.CancellationException
isDone---true---1
at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.report(FutureTask.java:121)
result---88
at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.get(FutureTask.java:192)
isDone---true---2
at CachedThreadPool.main(CachedThreadPool.java:24)
result---83
isDone---true---3
result---20
isDone---true---4
3.<T> T invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException
执行给定的任务,如果某个任务已成功完成(也就是未抛出异常),则返回其结果。一旦正常或异常返回后,则取消尚未完成的任务。如果此操作正在进行时修改了给定的 collection,则此方法的结果是不确定的。
参数:
tasks- 任务 collection- 返回:
- 某个任务返回的结果
- 抛出:
InterruptedException- 如果等待时发生中断NullPointerException- 如果任务或其任意元素为 nullIllegalArgumentException- 如果任务为空ExecutionException- 如果没有任务成功完成RejectedExecutionException- 如果任务无法安排执行
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import java.util.Random; import java.util.concurrent.*; public class CachedThreadPool { public static void main(String[] args) { ExecutorService cachedThreadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); List<Task> taskList = new ArrayList<Task>(); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { taskList.add(new Task()); } Integer result=new Integer(100); try { result = cachedThreadPool.invokeAny(taskList); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ExecutionException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("result---" +result); } } class Task implements Callable<Integer> { @Override public Integer call() throws Exception { return new Random().nextInt(100); } }
输出:
result---14
4. <T> T invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException
执行给定的任务,如果在给定的超时期满前某个任务已成功完成(也就是未抛出异常),则返回其结果。一旦正常或异常返回后,则取消尚未完成的任务。如果此操作正在进行时修改了给定的 collection,则此方法的结果是不确定的。
- 参数:
tasks- 任务 collectiontimeout- 最长等待时间unit- timeout 参数的时间单位- 返回:
- 某个任务返回的结果
- 抛出:
InterruptedException- 如果等待时发生中断NullPointerException- 如果任务或其任意元素或 unit 为 nullTimeoutException- 如果在所有任务成功完成之前给定的超时期满ExecutionException- 如果没有任务成功完成RejectedExecutionException- 如果任务无法安排执行
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import java.util.Random; import java.util.concurrent.*; public class CachedThreadPool { public static void main(String[] args) { ExecutorService cachedThreadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); List<Task> taskList = new ArrayList<Task>(); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { taskList.add(new Task()); } Integer result=new Integer(100); try { result = cachedThreadPool.invokeAny(taskList,1,TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ExecutionException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (TimeoutException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("result---" +result); } } class Task implements Callable<Integer> { @Override public Integer call() throws Exception { return new Random().nextInt(100); } }
输出:
result---14
疑问:
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import java.util.Random; import java.util.concurrent.*; public class CachedThreadPool { public static void main(String[] args) { ExecutorService cachedThreadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); List<Task> taskList = new ArrayList<Task>(); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { taskList.add(new Task()); } List<Future<Integer>> futureList = new ArrayList<>(); try { futureList = cachedThreadPool.invokeAll(taskList); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { for (int i = 0; i < futureList.size(); i++) { System.out.println("isDone---" + futureList.get(i).isDone()+"---"+i); System.out.println("result---" + futureList.get(i).get()); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ExecutionException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { cachedThreadPool.shutdownNow(); System.out.println("isShutDown---"+cachedThreadPool.isShutdown()); System.out.println("isTerminated---"+cachedThreadPool.isTerminated()); } } } class Task implements Callable<Integer> { @Override public Integer call() throws Exception { return new Random().nextInt(100); } }
输出为:
isDone---true---0
result---67
isDone---true---1
result---8
isDone---true---2
result---42
isDone---true---3
result---15
isDone---true---4
result---43
isDone---true---5
result---9
isDone---true---6
result---7
isDone---true---7
result---94
isDone---true---8
result---23
isDone---true---9
result---82
isShutDown---true
isTerminated---false
为什么isTerminated输出为false
二、ScheduledExecutorService接口
ScheduledExecutorSerice是ExecutorService的子接口,它可以执行固定延迟或者需要定期执行的任务。
所有的schedule方法都接受相对延迟和周期作为参数,而不是绝对的时间或者日期。
将Date所表示的绝对时间转换成符合方法参数的形式很容易。例如,要安排在某个Date以后运行可以使用:
schedule(task,date.getTime()-System.currentTimeMillis(),TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)。
主要方法:
1.ScheduledFuture<?> schedule(Runnable command, long delay, TimeUnit unit)
创建并执行一个在固定延迟之后的任务
参数:
command-----要执行的任务;
delay----------从现在开始延迟执行的时间
unit------------延迟参数的时间单位
返回:
返回任务的ScheduledFuture对象,因为传入的参数是Runnable类型,所以在该任务完成之后get()方法将返回null。
抛出:
RejectedExecutionException - 如果无法安排执行该任务;
NullPointerException - 如果 command 为 null
2. <V> ScheduledFuture<V> schedule(Callable<V> callable, long delay, TimeUnit unit)
同上一个方法相同,但是返回的结果ScheduledFuture可以用于结果提取
3. ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long period, TimeUnit unit)
在固定的延迟后以一定的周期循环运行。如果任务的任何一个执行遇到异常,则后续的执行都会被取消。否则,只能通过执行程序的取消或终止方法来终止该任务。
如果此任务的任何一个执行要花费比起周期更长的时间,则将推迟后续任务的执行,但不会同时执行。
- 参数:
command- 要执行的任务initialDelay- 首次执行的延迟时间period- 连续执行之间的周期 period=(下一次任务开始执行的时间-上一次任务开始执行的时间)unit- initialDelay 和 period 参数的时间单位- 返回:
- 表示挂起任务完成的 ScheduledFuture,并且其 get() 方法在取消后将抛出异常
- 抛出:
RejectedExecutionException- 如果无法安排执行该任务NullPointerException- 如果 command 为 nullIllegalArgumentException- 如果 period 小于等于 0
示例:
package Test; import java.util.Date; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; public class ScheduledExecutorServiceTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { ScheduledExecutorService scheduledThreadPool = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5); //schedule to run after sometime System.out.println("Current Time = "+new Date()); WorkerThread worker = new WorkerThread("do heavy processing"); scheduledThreadPool.scheduleAtFixedRate(worker, 1, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);//add some delay to let some threads spawn by scheduler Thread.sleep(30000); scheduledThreadPool.shutdown(); while(!scheduledThreadPool.isTerminated()){ //wait for all tasks to finish } System.out.println("Finished all threads"); } } class WorkerThread implements Runnable{ private String command; public WorkerThread(String s){ this.command=s; } @Override public void run() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" Start. Time = "+new Date()); processCommand(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" End. Time = "+new Date()); } private void processCommand() { try { Thread.sleep(5000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @Override public String toString(){ return this.command; } }
输出为:
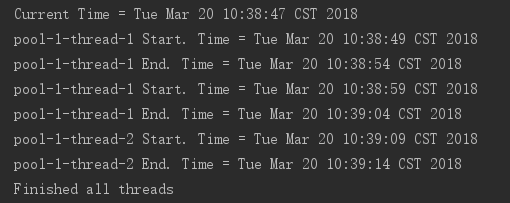
period=10s,可以看到每次Thread-1开始的时间相隔为10秒
当线程的运行时长大于周期时间时,下一次任务的启动时间将会顺延
package Test; import java.util.Date; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; public class ScheduledExecutorServiceTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { ScheduledExecutorService scheduledThreadPool = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5); //schedule to run after sometime System.out.println("Current Time = "+new Date()); WorkerThread worker = new WorkerThread("do heavy processing"); scheduledThreadPool.scheduleAtFixedRate(worker, 1, 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS); //add some delay to let some threads spawn by scheduler Thread.sleep(30000); scheduledThreadPool.shutdown(); while(!scheduledThreadPool.isTerminated()){ //wait for all tasks to finish } System.out.println("Finished all threads"); } } class WorkerThread implements Runnable{ private String command; public WorkerThread(String s){ this.command=s; } @Override public void run() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" Start. Time = "+new Date()); processCommand(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" End. Time = "+new Date()); } private void processCommand() { try { Thread.sleep(8000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @Override public String toString(){ return this.command; } }
输出为:
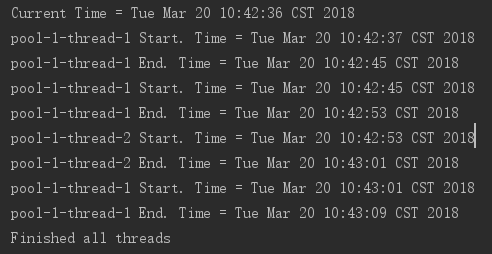
运行时间为8秒,每次的间隔为5秒,可以看到这时每次的开始运行时间发生了顺延。
4. ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long delay, TimeUnit unit)
此方法与上一个方法的不同之处在于 delay=下一次任务开始的时间-上一次任务结束的时间
示例:
package Test; import java.util.Date; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; public class ScheduledExecutorServiceTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { ScheduledExecutorService scheduledThreadPool = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5); //schedule to run after sometime System.out.println("Current Time = "+new Date()); WorkerThread worker = new WorkerThread("do heavy processing"); scheduledThreadPool.scheduleWithFixedDelay(worker, 1, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS); //add some delay to let some threads spawn by scheduler Thread.sleep(30000); scheduledThreadPool.shutdown(); while(!scheduledThreadPool.isTerminated()){ //wait for all tasks to finish } System.out.println("Finished all threads"); } } class WorkerThread implements Runnable{ private String command; public WorkerThread(String s){ this.command=s; } @Override public void run() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" Start. Time = "+new Date()); processCommand(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" End. Time = "+new Date()); } private void processCommand() { try { Thread.sleep(5000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @Override public String toString(){ return this.command; } }
输出为:
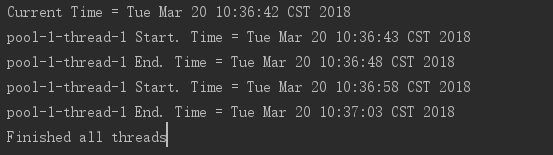
delay=10s,
可以看到Thread-1下一次开始的时间与上一次结束运行的时间相差10秒。





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号