pytorch中构建模型
pytorch构建层的方法和tensorflow基本一致。
1 简单的模型构建
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import functional as F
class NewModule(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.hidden = nn.Linear(20, 256)
self.output = nn.Linear(256, 5)
def forward(self, X):
return self.output(F.relu(self.hidden(X)))
net = NewModule()
input = torch.rand(2, 20)
out = net(input)
标准三板斧:
(1)继承nn.Module
class NewModule(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):#如果没有额外参数,就默认只写入一个self
super().__init__()
(2)确认自己网络中有哪些层
self.hidden = nn.Linear(20, 256)
self.output = nn.Linear(256, 5)
(3) 确定前向传播的过程,重写forward方法
2 构建一个简单的Sequential模块
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import functional as F
# 构建自己的Sequential
class MySequential(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, *args):
super().__init__()
for block in args:
self._modules[block] = block
def forward(self, X):
for block in self._modules.values():
X = block(X)
return X
input = torch.rand(10,20)
new_net = MySequential(nn.Linear(20, 256), nn.ReLU(), nn.Linear(256, 10))
new_out = new_net(input)
print(new_out)
三板斧
(1)继承nn.Module
(2)确认模型包含的层
初始化使用*args作为参数列表,使用for循环取出参数。
_modules是nn.Module内部的变量,放入的数据可当成ordered dict。
(3)确认前向传播的过程。
这里可以使用for循环将刚才放入_modules中的数据取出来。
3 加入自定义操作
可在init函数或者forward函数中加入自己的操作。
4 参看某些层
net0 = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(20, 256), nn.ReLU(), nn.Linear(256, 10))
val = torch.rand(10,20)
network = net0(val)
print(net0[2].state_dict())
print(type(net0[2].bias))
print(net0[2].bias.data)
print(net0[2].weight.data)
print(net0[2].weight.grad)
对于这里构建的Sequential,net0[2]代表其中的nn.Linear(256,10),对于线性层包含weight和bias两部分,每部分包括data和grad。
5 参看网络中的参数
print([(name, param.shape) for name, param in net0[2].named_parameters()])
print([(name, param.shape) for name, param in net0.named_parameters()])
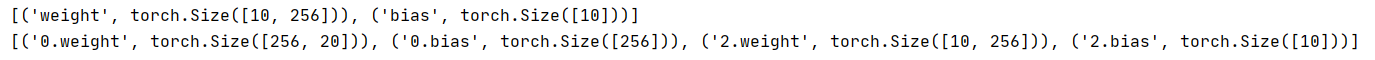





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号