future和promise
要使用future和promise要先引入头文件
#include <future>
1 future
使用future时就是这个字面意思,这个类型或者变量的具体的内容,将来会给你。
所以具体使用的时候需要用get方法。
int FunctionOne(std::future<int>& f) {
int value = f.get();
std::cout << value << std::endl;
return value;
}
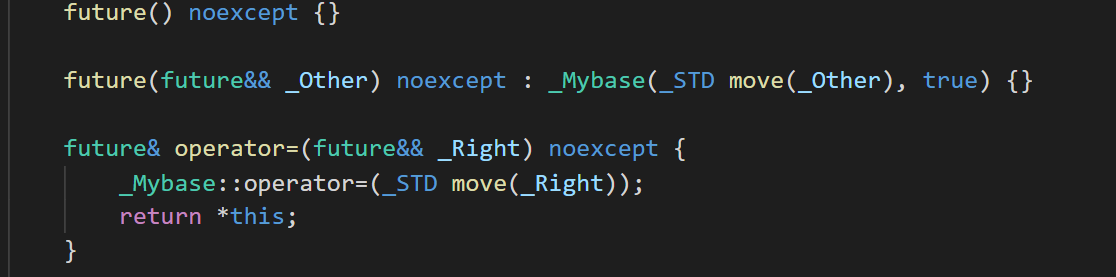
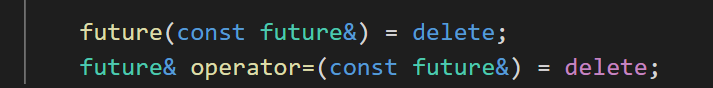
1.1 nono-copyable
从源码中我们可以看到左值复制构造和赋值运算删除的,右值复制构造和赋值运算都是采用移动语义。所以对于future变量只能进行move。

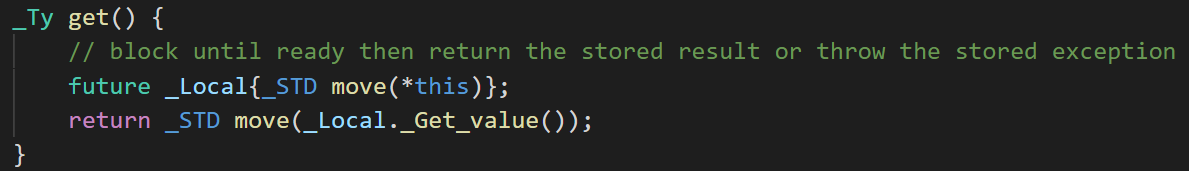
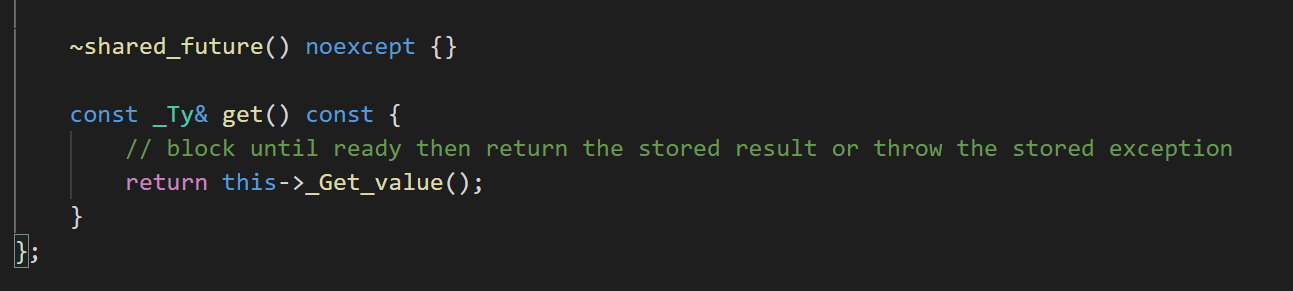
1.2 对于不带shared属性的future变量只能get一次,get操作且一直阻塞直到set_value或者抛出异常。
什么时候会报异常呢,就是整个运行过程都没有设置future类型的值。
1.3.区别shared_future
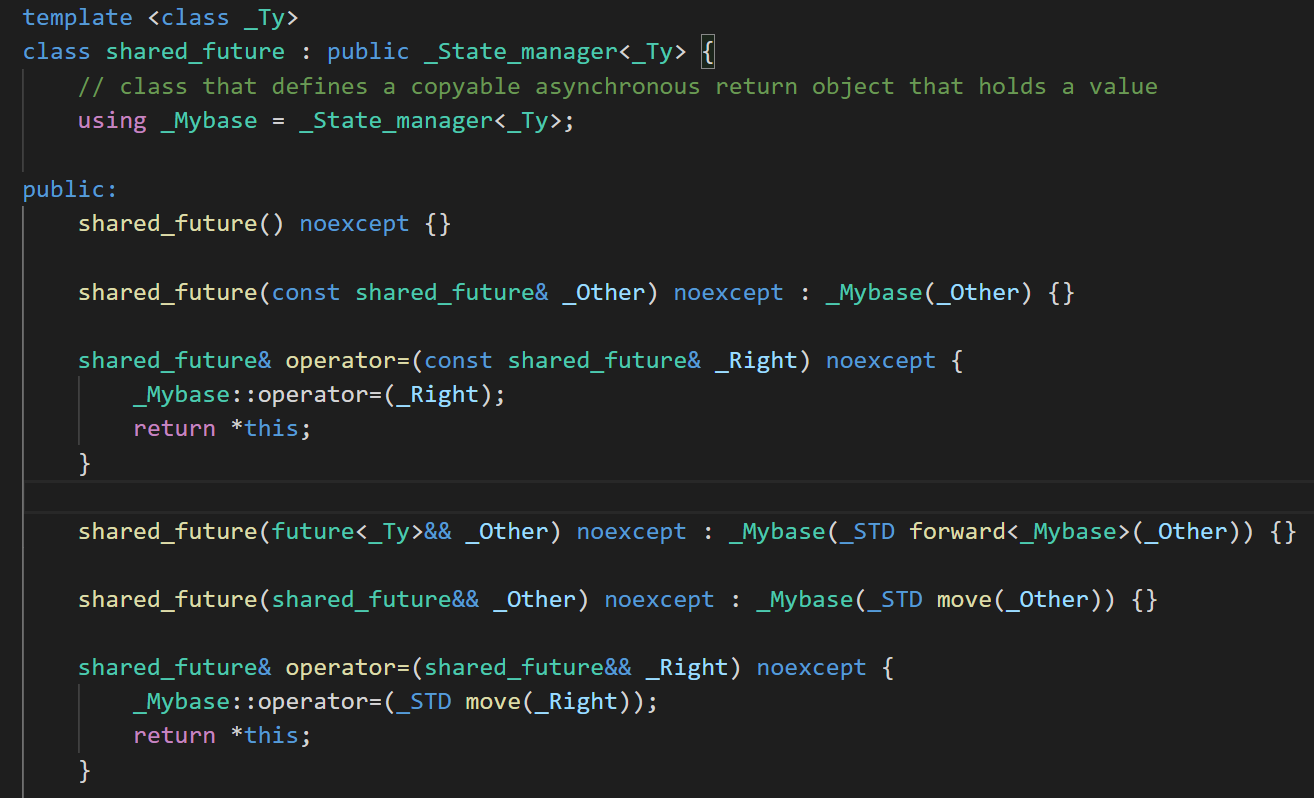
对于shared_future是可以copy的,且值可以get多次(阻塞直到set_value)。
2 promise
刚才说了future变量,那么既然有说将来这个值会设定,那你得许下承诺。
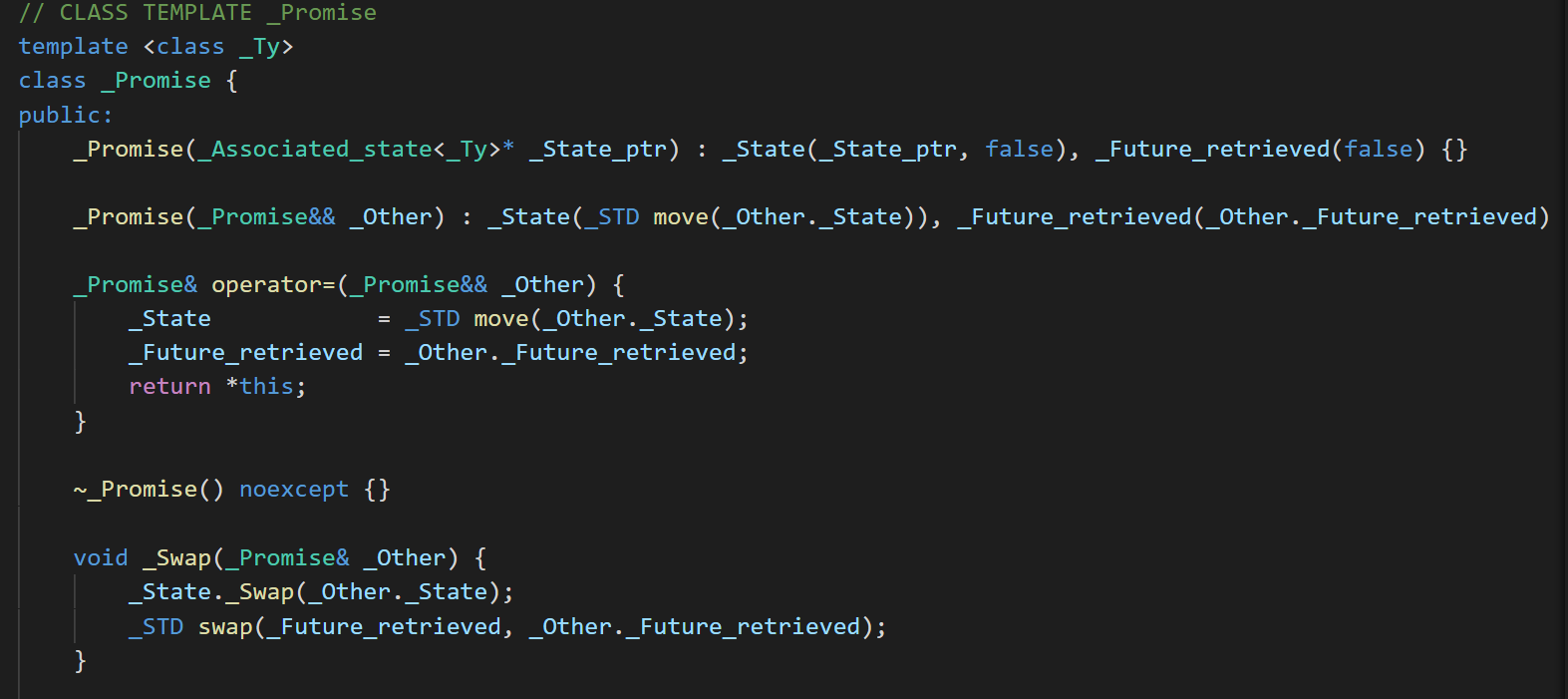
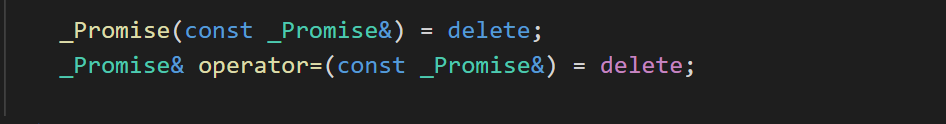
这里我们看到只能使用移动语义
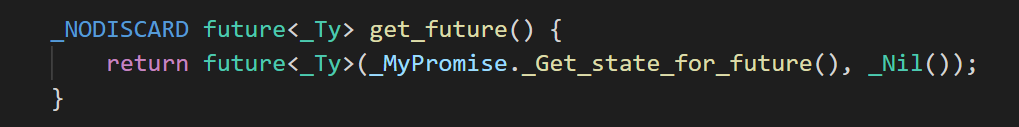
常用的是这个方法,给future变量初始化
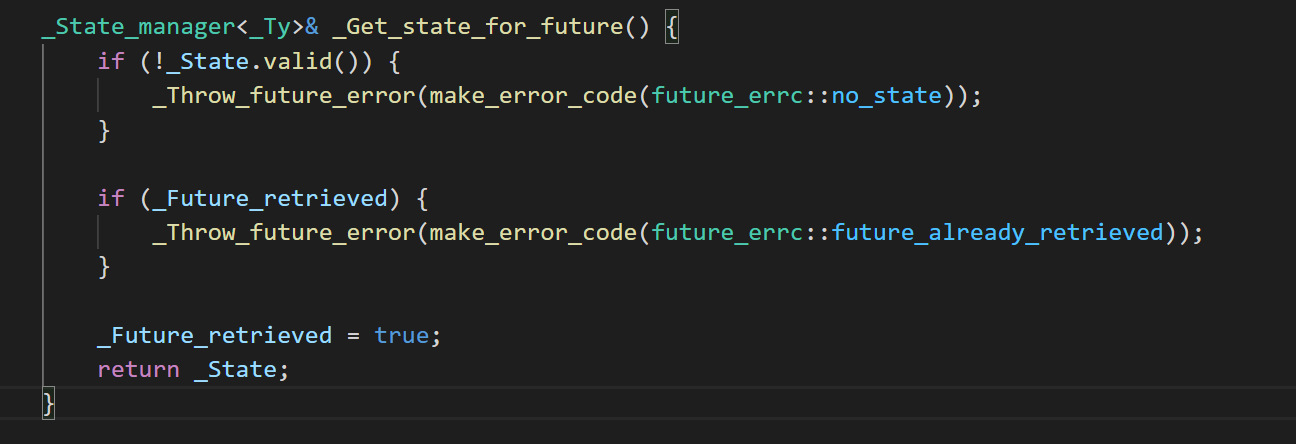
2.1 set方法
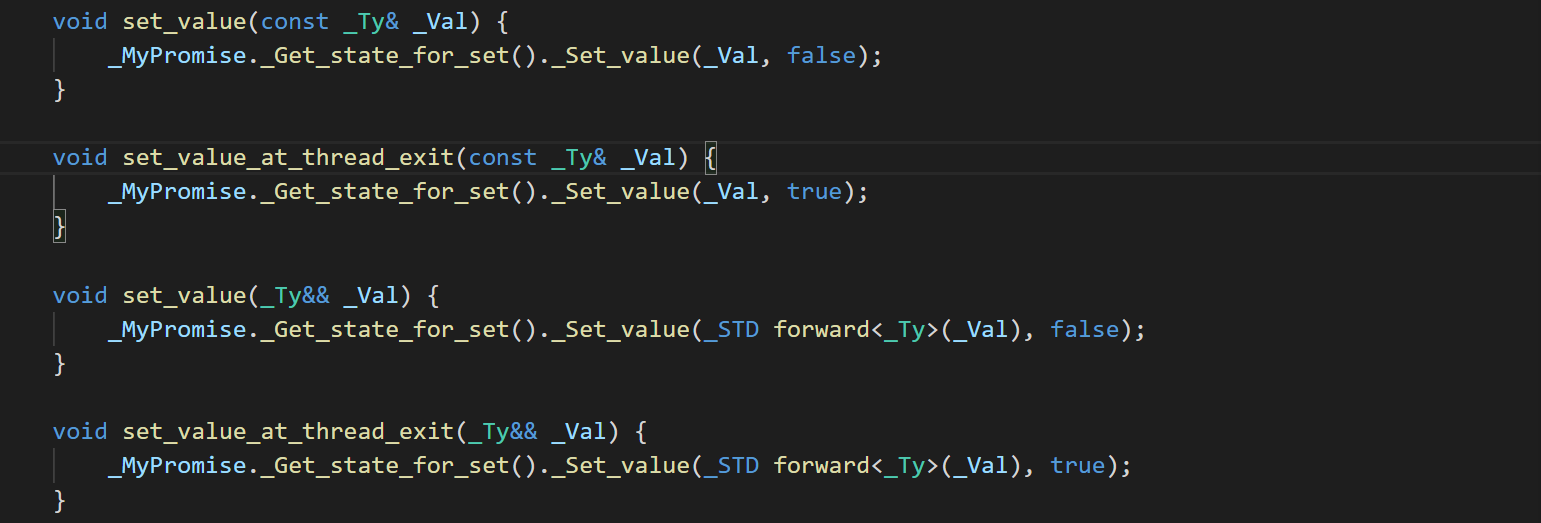
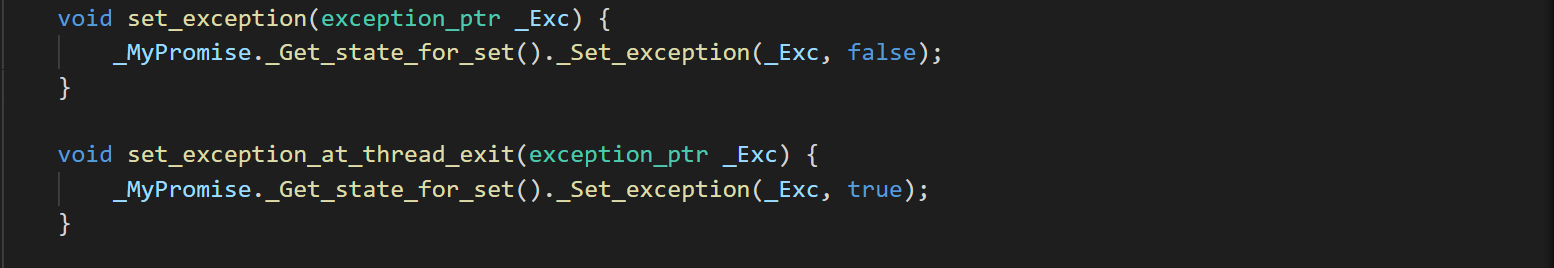
可以直接设置值或者设置异常设置线程退出时调用方法
简单的使用方法
#include <future>
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
int FunctionOne(std::future<int>& f) {
int value = f.get();
std::cout << value << std::endl;
return value;
}
int main(){
std::promise<int> pms;
std::future<int> fu = pms.get_future();
std::future<int> res = std::async(std::launch::async|std::launch::deferred, FunctionOne, std::ref(fu));
pms.set_value(10);
pms.set_exception(std::make_exception_ptr(std::runtime_error("Not set future value")));
std::cout << res.get() << std::endl;;
return 0;
}
如果没有设置set_exception,当没有set_value,程序是不会正常退出的。async会等待子线程结束才结束,而子线程中get方法(没有进行set_value)会一直阻塞。
整个程序不会正常退出,如果加上set_exception就不会阻塞。
注意
- 通常而言这种非Loop的function,一般是不会单独起线程的,而是使用async,这种时候系统执行的时候可能时异步任务或者线程。
通常使用thread需要加锁,条件变量,还有就是创建也需要消耗资源。
2.std::launch::deferred就是直到调用future::get方法时才去执行相应的函数,具体函数时另起一个线程还是就在当前线程中调用该函数
取决于是否设置std::launch::async。
std::async第一个默认参数就是std::launch::async|std::launch::deferred, 就是让系统自行决定。
3 测试
3.1 只设置std::launch::deferred时候
#include <future>
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
int FunctionOne(std::future<int>& f) {
int value = f.get();
std::cout << std::this_thread::get_id() << std::endl;
return value;
}
int main(){
std::cout << std::this_thread::get_id() << std::endl;
std::promise<int> pms;
std::future<int> fu = pms.get_future();
std::future<int> res = std::async(std::launch::deferred, FunctionOne, std::ref(fu));
pms.set_value(10);
int x = res.get();
return 0;
}

发现async的function就是在主线程中执行,如果设置程std::launch::deferred模式时,如果不掉用get方法是不会执行async中的内容的。
3.2 只设置std::launch::async
#include <future>
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
int FunctionOne(std::future<int>& f) {
int value = f.get();
std::cout << std::this_thread::get_id() << std::endl;
return value;
}
int main(){
std::cout << std::this_thread::get_id() << std::endl;
std::promise<int> pms;
std::future<int> fu = pms.get_future();
std::future<int> res = std::async(std::launch::async, FunctionOne, std::ref(fu));
pms.set_value(10);
int x = res.get();
return 0;
}

这里我们发现时起了另一个线程
3.3 使用默认参数时 std::launch::async | std::launch::deferred
照理说应该async或者deferred模式都可能。
但是我实验的时候通常时是单独起了线程





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号