Trie 系列 208, 211, 212, 421, 386, 1233, 588, 745
208. Implement Trie (Prefix Tree)
A trie (pronounced as "try") or prefix tree is a tree data structure used to efficiently store and retrieve keys in a dataset of strings. There are various applications of this data structure, such as autocomplete and spellchecker.
Implement the Trie class:
Trie()Initializes the trie object.void insert(String word)Inserts the stringwordinto the trie.boolean search(String word)Returnstrueif the stringwordis in the trie (i.e., was inserted before), andfalseotherwise.boolean startsWith(String prefix)Returnstrueif there is a previously inserted stringwordthat has the prefixprefix, andfalseotherwise.
Example 1:
Input
["Trie", "insert", "search", "search", "startsWith", "insert", "search"]
[[], ["apple"], ["apple"], ["app"], ["app"], ["app"], ["app"]]
Output
[null, null, true, false, true, null, true]
Explanation
Trie trie = new Trie();
trie.insert("apple");
trie.search("apple"); // return True
trie.search("app"); // return False
trie.startsWith("app"); // return True
trie.insert("app");
trie.search("app"); // return True
Constraints:
1 <= word.length, prefix.length <= 2000wordandprefixconsist only of lowercase English letters.- At most
3 * 104calls in total will be made toinsert,search, andstartsWith.
class Trie { class TrieNode{ TrieNode[] children = new TrieNode[26]; boolean isWord; } private TrieNode root=null; public Trie() { root = new TrieNode(); } public void insert(String word) { TrieNode curr = root; for(char c:word.toCharArray()){
//之前犯过低级错误,谨防,将instance赋给了临时引用,并没有赋给curr.children[c-'a']
//curr = curr.children[c-'a'];
//if(curr == null) curr = new TrieNode();
if(curr.children[c-'a']==null) curr.children[c-'a']=new TrieNode(); curr = curr.children[c-'a']; } curr.isWord=true; } public boolean search(String word) { TrieNode curr = root; for(char c:word.toCharArray()){ if(curr.children[c-'a']==null) return false;; curr = curr.children[c-'a']; } return curr.isWord; } public boolean startsWith(String prefix) { TrieNode curr = root; for(char c:prefix.toCharArray()){ if(curr.children[c-'a']==null) return false;; curr = curr.children[c-'a']; } return true; } }
时间复杂度:O(Len)
211. Design Add and Search Words Data Structure
Design a data structure that supports adding new words and finding if a string matches any previously added string.
Implement the WordDictionary class:
WordDictionary()Initializes the object.void addWord(word)Addswordto the data structure, it can be matched later.bool search(word)Returnstrueif there is any string in the data structure that matcheswordorfalseotherwise.wordmay contain dots'.'where dots can be matched with any letter.
Example:
Input
["WordDictionary","addWord","addWord","addWord","search","search","search","search"]
[[],["bad"],["dad"],["mad"],["pad"],["bad"],[".ad"],["b.."]]
Output
[null,null,null,null,false,true,true,true]
Explanation
WordDictionary wordDictionary = new WordDictionary();
wordDictionary.addWord("bad");
wordDictionary.addWord("dad");
wordDictionary.addWord("mad");
wordDictionary.search("pad"); // return False
wordDictionary.search("bad"); // return True
wordDictionary.search(".ad"); // return True
wordDictionary.search("b.."); // return True
Constraints:
1 <= word.length <= 500wordinaddWordconsists lower-case English letters.wordinsearchconsist of'.'or lower-case English letters.- At most
50000calls will be made toaddWordandsearch.
class WordDictionary { TrieNode root; class TrieNode{ TrieNode[] children = new TrieNode[26]; boolean isWord; } public WordDictionary() { root = new TrieNode(); } public void addWord(String word) { TrieNode curr = root; for(char c:word.toCharArray()){ if(curr.children[c-'a']==null) curr.children[c-'a'] = new TrieNode(); curr = curr.children[c-'a']; } curr.isWord=true; } public boolean search(String word){ return search(word,root); } private boolean search(String word,TrieNode start) { if(word.length()==0) return start.isWord; TrieNode curr = start; for(int i=0;i<word.length();i++){ char c = word.charAt(i); if(c=='.'){ for(int j=0;j<26;j++){ if(curr.children[j]!=null && search(word.substring(i+1),curr.children[j])) return true; } return false; } if(curr.children[c-'a']==null) return false; curr = curr.children[c-'a']; } return curr.isWord; } }
时间复杂度:所有字符串长度和为totalLen, 时间复杂度O(totalLen) , 查找单个len长度的字符串时间复杂度 O(len)
class WordDictionary { private TrieNode root; public WordDictionary() { root = new TrieNode(); } public void addWord(String word) { TrieNode curr = root; for(char c : word.toCharArray()) { if(curr.children[c - 'a'] == null) { curr.children[c - 'a'] = new TrieNode(); } curr = curr.children[c - 'a']; } curr.isEnd = true; } public boolean search(String word) { return search(word, 0, root); } private boolean search(String word, int ind, TrieNode curr) { if(ind == word.length()) return curr.isEnd; char c = word.charAt(ind); if(c == '.') { for(int j = 0; j < 26; j++){ if(curr.children[j] != null && search(word, ind + 1, curr.children[j])) return true; } } else { if(curr.children[c - 'a'] != null && search(word, ind + 1, curr.children[c - 'a'])) return true; } return false; } } class TrieNode{ TrieNode[] children = new TrieNode[26]; boolean isEnd; }
212. Word Search II
Given an m x n board of characters and a list of strings words, return all words on the board.
Each word must be constructed from letters of sequentially adjacent cells, where adjacent cells are horizontally or vertically neighboring. The same letter cell may not be used more than once in a word.
Example 1:
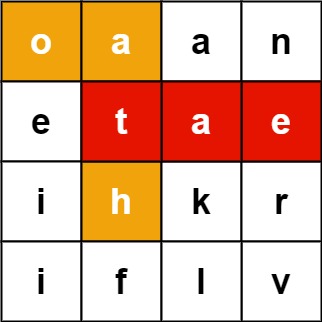
Input: board = [["o","a","a","n"],["e","t","a","e"],["i","h","k","r"],["i","f","l","v"]], words = ["oath","pea","eat","rain"] Output: ["eat","oath"]
Example 2:
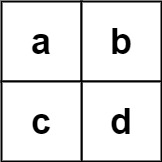
Input: board = [["a","b"],["c","d"]], words = ["abcb"] Output: []
Constraints:
m == board.lengthn == board[i].length1 <= m, n <= 12board[i][j]is a lowercase English letter.1 <= words.length <= 3 * 1041 <= words[i].length <= 10words[i]consists of lowercase English letters.- All the strings of
wordsare unique.
解法1 : dfs backtracking
class Solution { public List<String> findWords(char[][] board, String[] words) { int m = board.length, n = board[0].length; //define result list List<String> list = new ArrayList(); //for loop all the word in words, get result for(String word : words){ boolean flag = false; for(int i = 0; i < m && !flag; i++) { for(int j = 0; j < n && !flag; j++){ boolean[][] visited = new boolean[m][n]; if(find(board, word, i, j, 0, visited)) { list.add(word); flag = true; } } } } return list; } int[][] directions = new int[][]{{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}}; //define bfs or dfs to search one word private boolean find(char[][] board, String word, int x, int y, int ind, boolean[][] visited) { if(ind == word.length()) return true; int m = board.length, n = board[0].length; if(x < 0 || x >= m || y < 0 || y >= n || visited[x][y] || word.charAt(ind) != board[x][y]) return false; visited[x][y] = true; for(int[] direct : directions) { int xx = x + direct[0], yy = y + direct[1]; if(find(board, word, xx, yy, ind + 1, visited)) return true; } visited[x][y] = false; return false; } }
解法2 : Trie
class Solution { private TrieNode root=null; public List<String> findWords(char[][] board, String[] words) { //trie build root = new TrieNode(); for(String str:words) insert(str); int m = board.length,n=board[0].length; //set 为了去重 Set<String> result = new HashSet(); boolean[][] visited = new boolean[m][n]; //循环遍历每个元素,dfs进行trie搜索 for(int i=0;i<m;i++){ for(int j=0;j<n;j++){ helper(visited,result,i,j,root,"",board); } } return new ArrayList(result); } private void helper(boolean[][] visited,Set<String> result,int i,int j,TrieNode root,String curr,char[][] board){ if(i<0||j<0||i>=visited.length||j>=visited[0].length) return; if(visited[i][j]) return; visited[i][j]=true; char c = board[i][j]; if(root.children[c-'a']!=null){ if(root.children[c-'a'].isWord) result.add(curr+c); helper(visited,result,i-1,j,root.children[c-'a'],curr+c,board); helper(visited,result,i+1,j,root.children[c-'a'],curr+c,board); helper(visited,result,i,j-1,root.children[c-'a'],curr+c,board); helper(visited,result,i,j+1,root.children[c-'a'],curr+c,board); } visited[i][j]=false;//记得这是一个backtracking的过程,访问结束还原变量,这个是坑点 } //Trie数据结构 class TrieNode{ TrieNode[] children = new TrieNode[26]; boolean isWord; } private void insert(String word) { TrieNode curr = root; for(char c:word.toCharArray()){ if(curr.children[c-'a']==null) curr.children[c-'a']=new TrieNode(); curr = curr.children[c-'a']; } curr.isWord=true; } }
时间复杂度:O(M(4⋅3L-1)) M为格子总数, L为word长度
421. Maximum XOR of Two Numbers in an Array
Given an integer array nums, return the maximum result of nums[i] XOR nums[j], where 0 <= i <= j < n.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [3,10,5,25,2,8] Output: 28 Explanation: The maximum result is 5 XOR 25 = 28.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [0] Output: 0
Example 3:
Input: nums = [2,4] Output: 6
Example 4:
Input: nums = [8,10,2] Output: 10
Example 5:
Input: nums = [14,70,53,83,49,91,36,80,92,51,66,70] Output: 127
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 2 * 1050 <= nums[i] <= 231 - 1
class Solution { public int findMaximumXOR(int[] nums) { //建立Trie Trie root = new Trie(); for( int num:nums ) build(num,root); int max = 0; //循环遍历所有元素,求出最优解 for(int num:nums){ max = Math.max(max,xor(num,root)); } return max; } //Trie 数据结构 class Trie{ Trie[] children = new Trie[2]; } //建立 Trie private void build(int num,Trie root){ for(int i=31;i>=0;i--){ int res = (num>>i)&1; if(root.children[res]==null) root.children[res]=new Trie(); root = root.children[res]; } } //从trie中取出当前num xor的最优解 private int xor(int num,Trie root){ int sum = 0; for(int i=31;i>=0;i--){ int res = (num>>i)&1; int resMax = res==1 ? 0 : 1; if(root.children[resMax]!=null){ sum+=1<<i; root = root.children[resMax]; } else root = root.children[res]; } return sum; } }
386. Lexicographical Numbers
Given an integer n, return all the numbers in the range [1, n] sorted in lexicographical order.
You must write an algorithm that runs in O(n) time and uses O(1) extra space.
Example 1:
Input: n = 13 Output: [1,10,11,12,13,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]
Example 2:
Input: n = 2 Output: [1,2]
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 5 * 104
class Solution { public List<Integer> lexicalOrder(int n) { Trie root = new Trie(); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) buildTrie(i,root); List<Integer> result = new ArrayList(); traversalTrie(root,result,0); return result; } private void traversalTrie(Trie trie,List<Integer> list,int sum){ if(trie.isNumber) list.add(sum); for(int i=0;i<10;i++){ Trie child= trie.children[i]; if(child==null) continue; traversalTrie(child,list,sum*10+i); } } class Trie{ Trie[] children= new Trie[10]; boolean isNumber; } private void buildTrie(int num,Trie root){ Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack(); while(num>0){ stack.push(num%10); num=num/10; } while(!stack.isEmpty()){ int curr = stack.pop(); if(root.children[curr]==null) root.children[curr] = new Trie(); root=root.children[curr]; } root.isNumber=true; } }
1233. Remove Sub-Folders from the Filesystem
Given a list of folders folder, return the folders after removing all sub-folders in those folders. You may return the answer in any order.
If a folder[i] is located within another folder[j], it is called a sub-folder of it.
The format of a path is one or more concatenated strings of the form: '/' followed by one or more lowercase English letters.
- For example,
"/leetcode"and"/leetcode/problems"are valid paths while an empty string and"/"are not.
Example 1:
Input: folder = ["/a","/a/b","/c/d","/c/d/e","/c/f"] Output: ["/a","/c/d","/c/f"] Explanation: Folders "/a/b/" is a subfolder of "/a" and "/c/d/e" is inside of folder "/c/d" in our filesystem.
Example 2:
Input: folder = ["/a","/a/b/c","/a/b/d"] Output: ["/a"] Explanation: Folders "/a/b/c" and "/a/b/d/" will be removed because they are subfolders of "/a".
Example 3:
Input: folder = ["/a/b/c","/a/b/ca","/a/b/d"] Output: ["/a/b/c","/a/b/ca","/a/b/d"]
Constraints:
1 <= folder.length <= 4 * 1042 <= folder[i].length <= 100folder[i]contains only lowercase letters and'/'.folder[i]always starts with the character'/'.- Each folder name is unique.
class Solution { public List<String> removeSubfolders(String[] folder) { //1.build Trie root = new Trie(); for(String s:folder) build(root,s); //2.traverse List<String> result = new ArrayList(); traversal(root,result,""); return result; } private void traversal(Trie root,List<String> result,String path){ for(String key:root.children.keySet()){ Trie val = root.children.get(key); if(val.isPath) result.add(path+"/"+key); else traversal(val,result,path+"/"+key); } } private void build(Trie root,String s){ String[] arr = s.substring(1).split("/"); for(String str:arr){ Trie sub = root.children.get(str); if(sub==null) sub = new Trie(); root.children.put(str,sub); root = sub; } root.isPath=true; } class Trie{ Map<String,Trie> children = new HashMap(); boolean isPath; } }
Design a data structure that simulates an in-memory file system.
Implement the FileSystem class:
FileSystem()Initializes the object of the system.List<String> ls(String path)- If
pathis a file path, returns a list that only contains this file's name. - If
pathis a directory path, returns the list of file and directory names in this directory.
- If
void mkdir(String path)Makes a new directory according to the givenpath. The given directory path does not exist. If the middle directories in the path do not exist, you should create them as well.void addContentToFile(String filePath, String content)- If
filePathdoes not exist, creates that file containing givencontent. - If
filePathalready exists, appends the givencontentto original content.
- If
String readContentFromFile(String filePath)Returns the content in the file atfilePath.
Example 1:
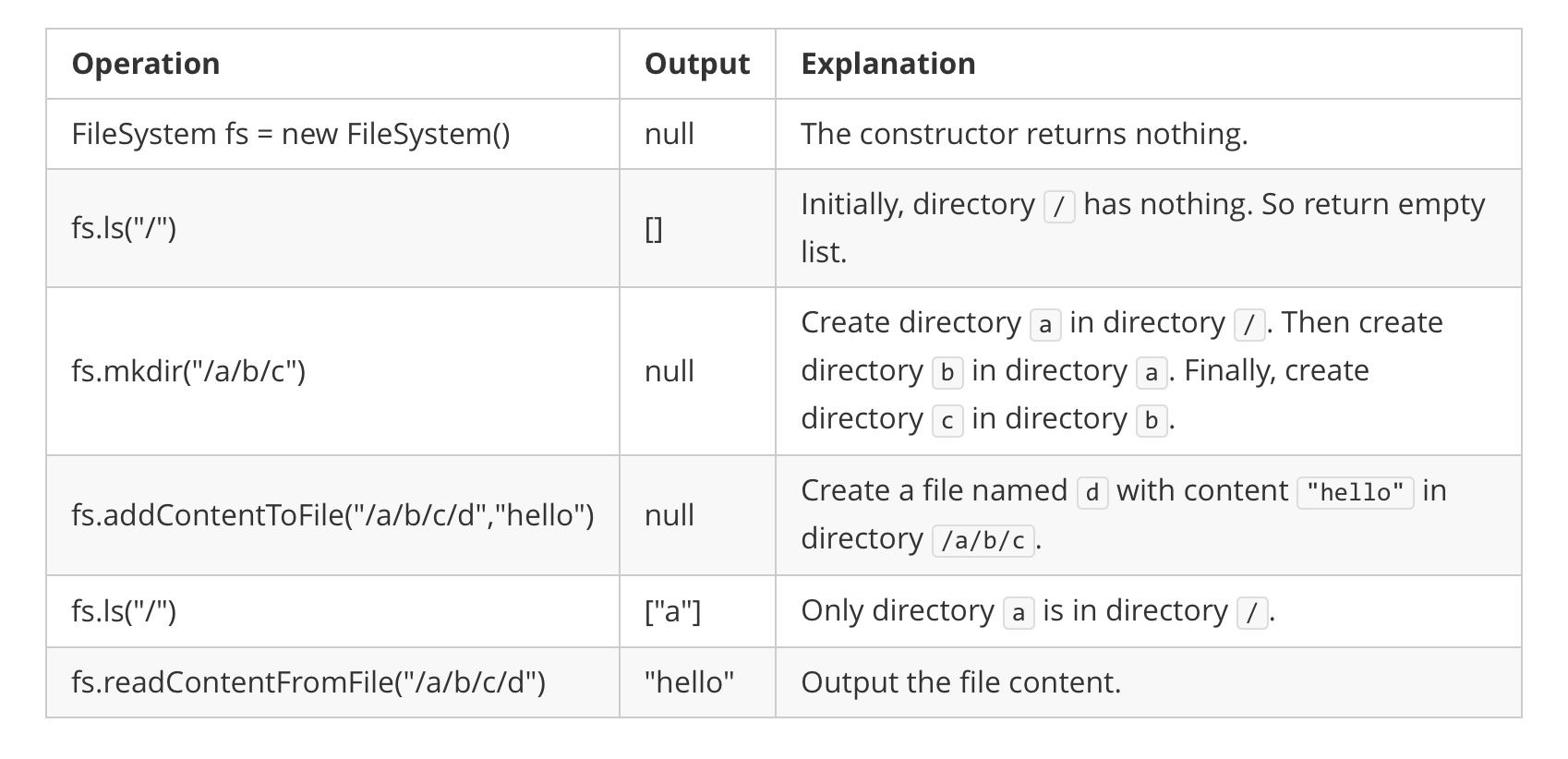
Input
["FileSystem", "ls", "mkdir", "addContentToFile", "ls", "readContentFromFile"]
[[], ["/"], ["/a/b/c"], ["/a/b/c/d", "hello"], ["/"], ["/a/b/c/d"]]
Output
[null, [], null, null, ["a"], "hello"]
Explanation
FileSystem fileSystem = new FileSystem();
fileSystem.ls("/"); // return []
fileSystem.mkdir("/a/b/c");
fileSystem.addContentToFile("/a/b/c/d", "hello");
fileSystem.ls("/"); // return ["a"]
fileSystem.readContentFromFile("/a/b/c/d"); // return "hello"
Constraints:
1 <= path.length, filePath.length <= 100pathandfilePathare absolute paths which begin with'/'and do not end with'/'except that the path is just"/".- You can assume that all directory names and file names only contain lowercase letters, and the same names will not exist in the same directory.
- You can assume that all operations will be passed valid parameters, and users will not attempt to retrieve file content or list a directory or file that does not exist.
1 <= content.length <= 50- At most
300calls will be made tols,mkdir,addContentToFile, andreadContentFromFile.
class FileSystem { private TrieNode root = null; public FileSystem() { root = new TrieNode(""); } public List<String> ls(String path) { String[] arr = path.split("/"); TrieNode curr = root; for(int i=1;i<arr.length;i++){ if(curr.children.get(arr[i])==null) return null; curr = curr.children.get(arr[i]); } if(!curr.isFile) { List<String> result =new ArrayList(curr.children.keySet()); Collections.sort(result); return result; } return Arrays.asList(curr.name); } public void mkdir(String path) { String[] arr = path.split("/"); TrieNode curr = root; for(int i=1;i<arr.length;i++){ if(curr.children.get(arr[i])==null) curr.children.put(arr[i],new TrieNode(arr[i])); curr = curr.children.get(arr[i]); } } public void addContentToFile(String filePath, String content) { String[] arr = filePath.split("/"); TrieNode curr = root; for(int i=1;i<arr.length;i++){ if(curr.children.get(arr[i])==null) { curr.children.put(arr[i],new TrieNode(arr[i])); } curr = curr.children.get(arr[i]); } curr.content += content; curr.isFile=true; } public String readContentFromFile(String filePath) { String[] arr = filePath.split("/"); TrieNode curr = root; for(int i=1;i<arr.length;i++){ if(curr.children.get(arr[i])==null) return null; curr = curr.children.get(arr[i]); } return curr.content; } class TrieNode{ Map<String,TrieNode> children = new HashMap(); String name; String content = ""; boolean isFile; TrieNode(String name){ this.name = name; } } }
Design a special dictionary with some words that searchs the words in it by a prefix and a suffix.
Implement the WordFilter class:
WordFilter(string[] words)Initializes the object with thewordsin the dictionary.f(string prefix, string suffix)Returns the index of the word in the dictionary, which has the prefixprefixand the suffixsuffix. If there is more than one valid index, return the largest of them. If there is no such word in the dictionary, return-1.
Example 1:
Input
["WordFilter", "f"]
[[["apple"]], ["a", "e"]]
Output
[null, 0]
Explanation
WordFilter wordFilter = new WordFilter(["apple"]);
wordFilter.f("a", "e"); // return 0, because the word at index 0 has prefix = "a" and suffix = 'e".
Constraints:
1 <= words.length <= 150001 <= words[i].length <= 101 <= prefix.length, suffix.length <= 10words[i],prefixandsuffixconsist of lower-case English letters only.- At most
15000calls will be made to the functionf.
解法:
suffix_prefix 建trie
apple
e_apple
el_apple
elp_apple
elpp_apple
elppa_apple
class WordFilter { private Trie trie; public WordFilter(String[] words) { trie = new Trie(); for(int j = 0; j < words.length; j++ ){ String word=words[j]; String reverse = reverse(word); for(int i=1;i<=reverse.length();i++){ trie.insert(reverse.substring(0,i)+trie.DELEMITER+word,j); } } } public int f(String prefix, String suffix) { return trie.search(reverse(suffix)+trie.DELEMITER+prefix); } private String reverse(String origin){ StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(origin); return sb.reverse().toString(); } } class Trie{ public static final char DELEMITER='a'+26; static class Node{ Node[] children; int pos = 0; Node(){ children = new Node[27]; } } Node root=new Node(); public void insert(String s,int pos){ Node curr = root; for(char c:s.toCharArray()){ if(curr.children[c-'a']==null) curr.children[c-'a']=new Node(); curr = curr.children[c-'a']; curr.pos = pos; } curr.pos = pos; } public int search(String s){ Node node = root; for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++){ char c = s.charAt(i); if(node.children[c-'a']==null) return -1; node = node.children[c-'a']; } return node.pos; } }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号