卡码java基础课 | 14.链表的基础操作II
学习内容:
链表基础,加深对上一节课的理解
重点归纳:
见例题。
例题:
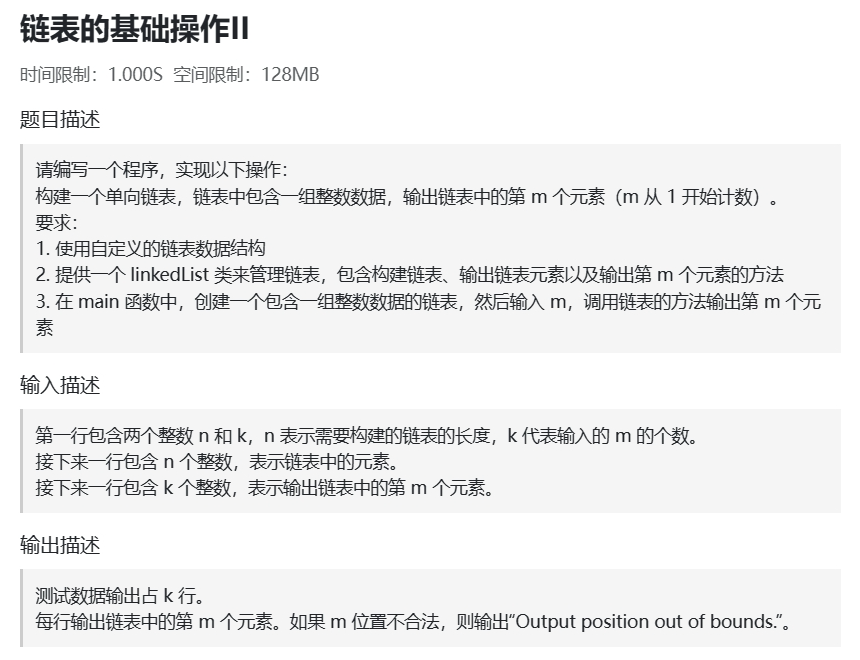
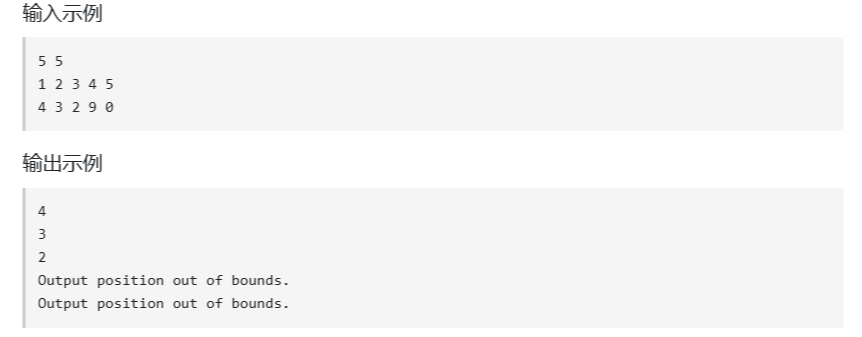
解:
点击查看代码
import java.util.Scanner;
//定义链表
class LinkedList{
//定义链表中的链表节点
public static class Node{
int data; //数据
Node next; //指针
public Node(int data){ //构造函数
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
private Node headNode; //头节点
private int length; //链表长度
public LinkedList(){ //链表的构造函数
this.length = 0;
this.headNode = null;
}
//插入数据函数
public Node Insert(int data){
Node newNode = new Node(data);
this.length++;
if(this.headNode == null){
this.headNode = newNode;
return this.headNode;
}
else{
Node currentNode = this.headNode;
while(currentNode.next != null){
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
currentNode.next = newNode;
return newNode;
}
}
//打印数据,输出第m个元素
public void printLinkedList(int m){
if(m > this.length || m <= 0){
System.out.println("Output position out of bounds.");
}
else{
Node currentNode = this.headNode;
int i = 0;
while(currentNode != null){
i++;
if(m == i){
System.out.println(currentNode.data);
break;
}
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
}
}
}
public class Main{
public static void main (String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while(sc.hasNext()){
int n = sc.nextInt();
int k = sc.nextInt();
LinkedList newLinkList = new LinkedList();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
newLinkList.Insert(sc.nextInt());
}
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++){
newLinkList.printLinkedList(sc.nextInt());
}
}
sc.close();
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号