
1.Java中流的分类
从流动方向:输入流&输出流,InputStream&Outputstream
从读取类型:字节流:如System.in是一个InputStream类型字节流
字符流:如new InputStreamReader(System.in)是一个字符流对象
从流发生的源头:节点流:直接操作目标设备对应的流 如文件流,标准输入输出流
过滤流:继承带有关键字Filter的流 用于包装操作节点流,方便读写各种类型的数据
———————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
2.


————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
3.流的装配
字节流——>解码——>字符流
用到InputstreamReader
InputStreamReader ins = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("c:\\text.txt"));
字符流——>译码——>字节流
用到OutputStreamWriter或者PrintWriter
没有改变流的内容,而是改变了看流的角度。
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("c:\\text.txt")));
Reader所有的子类都可以作为BufferedReader的参数,在ins中是一个字符一个字符读,br则是一行一行读。
———————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
4.流的装配
DataInputStream di = new DataInputStream(new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(f))); //可以利用DataInputStream对象方法进行读操作,写内容则同理
———————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
5.对象的串行化(序列化)与持久化
对象串行化:将内存中的动态对象表达为可以传输的串形式,为了便于网上传输和介质储存
对象持久化:将内存中的对象保存到硬盘介质上
实质上是要解决对象在内存和物理储存之间如何进行映射
对象——>串行化——>流
import java.io.*; public class Student implements Serializable //序列化 { int number=1; String name; Student(int number,String n1) { this.number = number; this.name = n1; } Student() { this(0,""); } void save(String fname) { try { FileOutputStream fout = new FileOutputStream(fname); ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(fout); out.writeObject(this); //写入对象 out.close(); } catch (FileNotFoundException fe){} catch (IOException ioe){} } void display(String fname) { try { FileInputStream fin = new FileInputStream(fname); ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(fin); Student u1 = (Student)in.readObject(); //读取对象 System.out.println(u1.getClass().getName()+" "+ u1.getClass().getInterfaces()[0]); System.out.println(" "+u1.number+" "+u1.name); in.close(); } catch (FileNotFoundException fe){} catch (IOException ioe){} catch (ClassNotFoundException ioe) {} } public static void main(String arg[]) { String fname = "Student.obj"; //文件名 Student s1 = new Student(1,"Wang"); s1.save(fname); s1.display(fname); } }
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
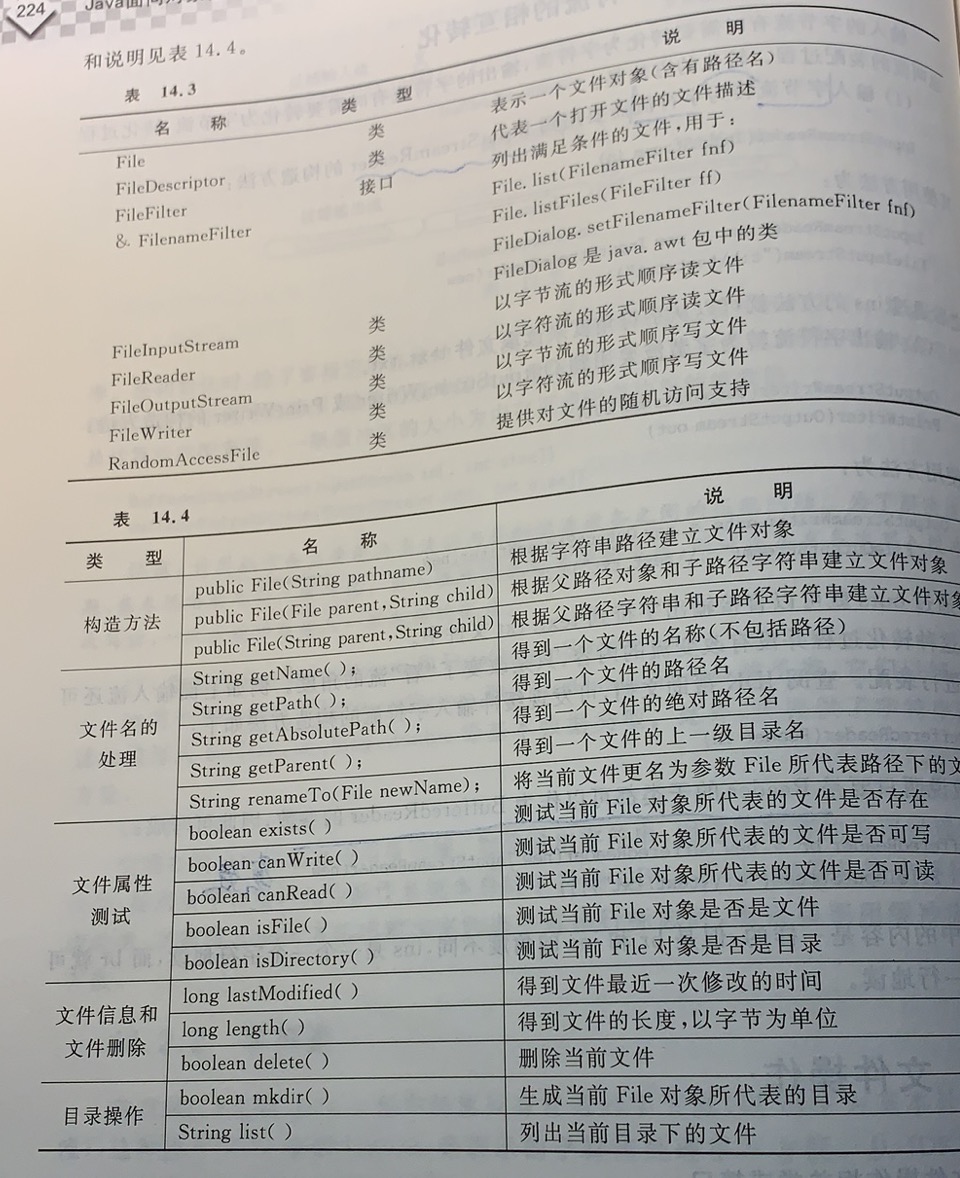
文件操作



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号