
1.volatile关键字:当线程没有执行结束就发生了互换这就有可能造成一个线程在主存中修改了一个变量的值,而另一个线程还继续使用它在寄存器中变量值的副本,造成数据的不一致,所以要把该变量声明为volatile,这样每次使用它都到主存中进行读取,因此多线程环境一般共享的变量都应该加volatile修饰。
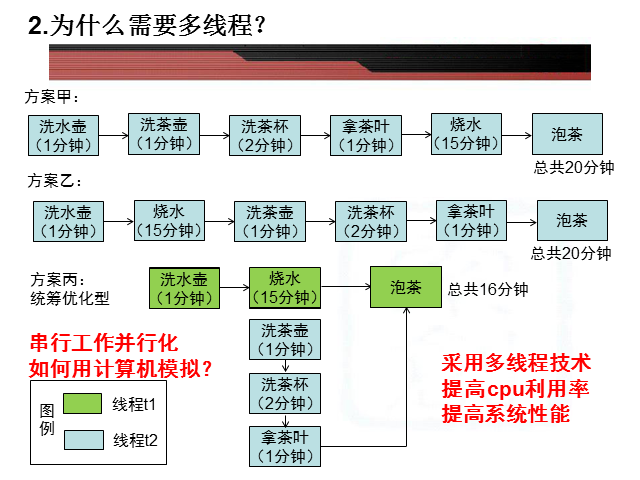
2.泡茶流程
class Thread1 implements Runnable{ public void run(){ System.out.println("第0分钟:洗水壶"); System.out.println("第1分钟:洗水壶完毕"); try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) {} } } class Thread2 implements Runnable{ public void run(){ for(int i=2;i<=5;i++){ if(i==2){ System.out.println("第"+i+"分钟:洗茶壶"); System.out.println("第"+(i+1)+"分钟:洗茶壶完毕"); } if(i==3){ System.out.println("第"+i+"分钟:洗茶杯"); System.out.println("第"+(i+1)+"分钟:洗茶杯完毕"); } if(i==4){ System.out.println("第"+i+"分钟:拿茶叶"); System.out.println("第"+(i+1)+"分钟:拿茶叶完毕"); } } try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) {} } } class Thread3 implements Runnable{ public void run(){ for(int i=2;i<=16;i++) { if(i==2){ System.out.println("第"+i+"分钟:烧水"); } try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) {} if(i==16){ System.out.println("第"+i+"分钟:烧水完毕"); } } } } class Thread4 implements Runnable{ public void run(){ System.out.println("泡茶"); try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) {} } } public class maketea { public static void main(String[] args) { Thread1 a=new Thread1(); Thread2 b=new Thread2(); Thread3 c=new Thread3(); Thread4 d=new Thread4(); Thread t1=new Thread (a); Thread t2=new Thread (b); Thread t3=new Thread (c); Thread t4=new Thread (d); t1.start(); try { t1.join(); } catch (InterruptedException e) {} t3.start(); t2.start(); try { t2.join(); } catch (InterruptedException e) {} try { t3.join(); } catch (InterruptedException e) {} t4.start(); } } /* 输出结果如下 第0分钟:洗水壶 第1分钟:洗水壶完毕 第2分钟:烧水 第2分钟:洗茶壶 第3分钟:洗茶壶完毕 第3分钟:洗茶杯 第4分钟:洗茶杯完毕 第4分钟:拿茶叶 第5分钟:拿茶叶完毕 第16分钟:烧水完毕 泡茶 Process finished with exit code 0*/



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号