今天终于更换了编辑器,可以插入代码块了😂

1.
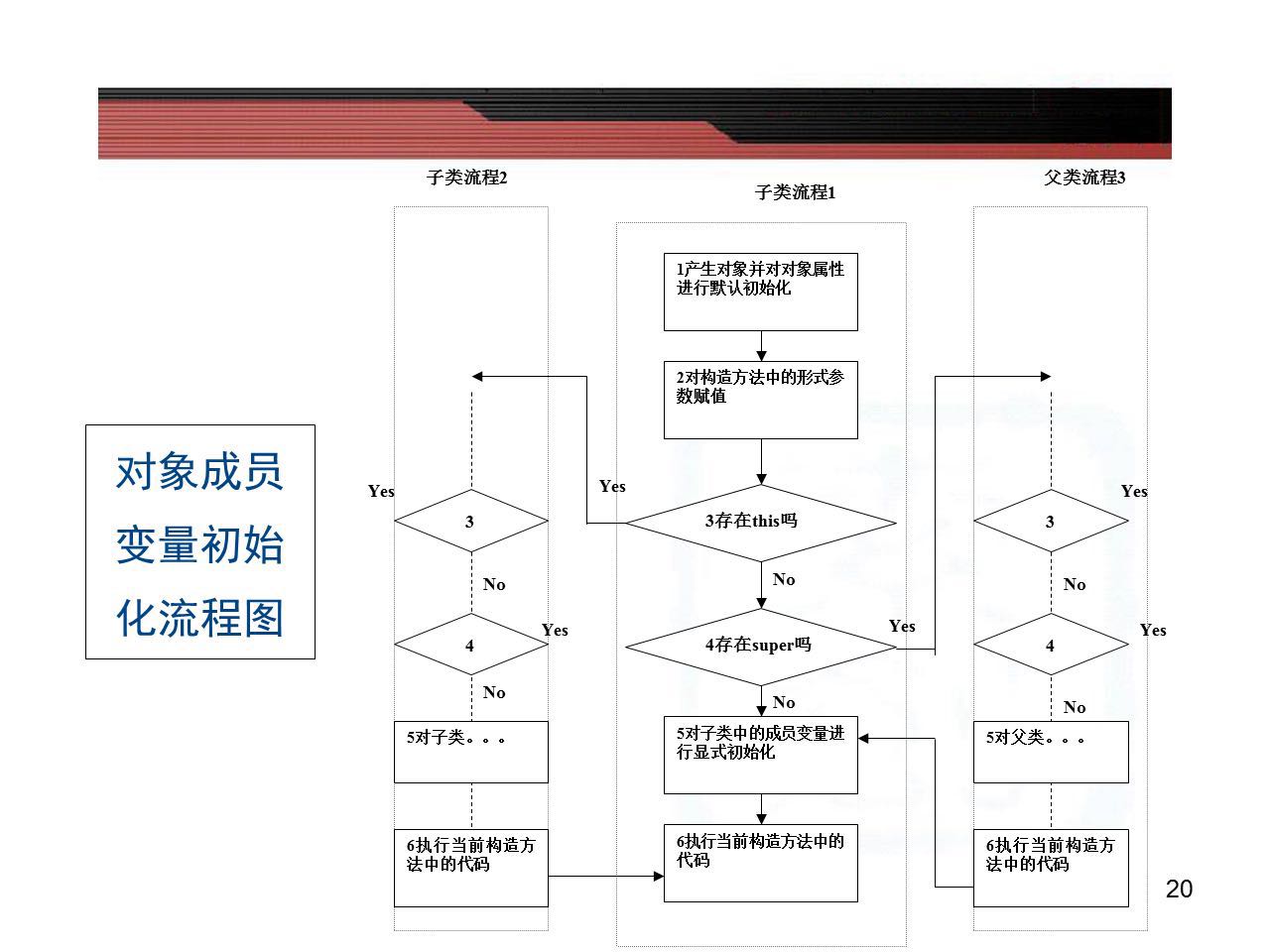
1)为对象分配内存空间,对成员变量进行默认的初始化。(局部变量必须进行显示初始化)
2)绑定构造方法,将new中的参数传递给构造方法的形式参数。
3)调用this或super语句(二者必居其一,不能同时存在),执行流程如图所示。
2.
两个对象之间互发消息
1 class FighterPlane{ 2 3 String name; 4 int missileNum; 5 public FighterPlane(String _name,int _missileNum){ 6 name = _name; 7 missileNum = _missileNum; 8 } 9 public void fire(){ 10 if (missileNum>0){ 11 System.out.println("now fire a missile !"); 12 missileNum -= 1; 13 } 14 else{ 15 System.out.println("No missile left !"); 16 } 17 } 18 } 19 20 class A 21 { 22 FighterPlane fp; 23 public A(FighterPlane fpp){ 24 this.fp = fpp; //A对象中拥有了FighterPlane对象的引用 25 } 26 public void invoke(){ 27 //A中对象发送消息给FighterPlane的对象 28 System.out.println(fp.name); 29 } 30 } 31 public class Run{ 32 public static void main(String[] args) 33 { 34 FighterPlane ftp = new FighterPlane("su35",10); 35 //产生A对象,并将ftp对象引用作为参数传入 36 A a = new A(ftp); 37 //发送消息,产生调用关系 38 a.invoke(); 39 } 40 }
3.
继承是子类和父类之间的“ IS-A”关系,而组合是两个类之间的“ HAS-A”关系。组合会使对象之间的耦合性较为松散。
例如:
当创建一个蔬菜类(Vegetable)以其为父类,有如下子类胡萝卜类(Carrot),土豆类(Potato)等。这时描述的就是is-A的关系。即为子类与父类的继承。
当创建一个银河系类(Galaxy),以及地球类(Earth),火星类(Mars)等。显然银河系类与其他组成HAS-A的关系。即为类与类之间的组合。
4.
运行时的多态指的是程序中出现同名但不同方法共存的情况。参数类型个数不同,最终目的也许相同但是由于在完成同一功能时可能遇到不同的具体情况,所以提供了重载,使程序更加灵活。
网上找到的例子:(出处:https://my.oschina.net/u/1266221/blog/744524)
假设有一个类 叫 鸟类,它拥有属性翅膀,拥有方法鸣叫,如下 public class Bird{ private Wing wing; public void moo(){ System.out.println("鸟叫声"); } } 鸟类封装了 翅膀类和moo方法;另外有两个类都继承鸟类并重写了moo方法,分别是鹦鹉和麻雀如下: 鹦鹉类: public class Parrot extends Bird{ public void moo(){ System.out.println("鹦鹉的叫声"); } } 麻雀类: public class Sparrow extends Bird{ public void moo(){ System.out.println("麻雀的叫声"); } } 方法重写应该懂吧,不懂自己找书看吧;然后你有个妻子她想听鸟叫,就有个妻子类 public class Wife{ public void listen(Bird bird){ bird.moo(); } /*这时多态就很好的体现了,你妻子想听鸟叫,无论什么鸟都可以给她,但是你想让她和鹦鹉 *说话,你就买了一只鹦鹉传给listen方法,结果你妻子听到了鹦鹉的叫声,程序输出:鹦 *鹉的叫声 */ public static void main(String[] args) { new Wife().listen(new Parrot()); } }
6.
instanceof 用来判断指定 对象(实际引用的对象实例) 是否是 指定类或者指定类的子类

这个实例也是在csdn找到的,讲解的比较详细。(出处:https://blog.csdn.net/a704397849/article/details/89556450)
public class Test { static class A{ } static class B extends A{ } public static void main(String[] args) { A a = new A(); B b = new B(); System.out.println( "a instanceof A 的结果:" + ( a instanceof A ) ); System.out.println( "b instanceof A 的结果:" + ( b instanceof A ) ); System.out.println(); System.out.println( "a instanceof B 的结果:" + ( a instanceof B ) ); System.out.println( "b instanceof B 的结果:" + ( b instanceof B ) ); System.out.println(); /* 注意: 下面用Object类对象引用某个类实例 是实际应用中非常常见的 object instanceof class ,如果object 实际引用的对象实例 是 class 的实例对象 或者 class 的子类实例对象,则返回true 注意 “实际引用的对象实例” 这个词强调的'实际引用'. */ Object o = new A(); System.out.println( "o instanceof A 的结果:" + ( o instanceof A ) ); System.out.println( "o instanceof B 的结果:" + ( o instanceof B ) ); System.out.println(); o = new B(); System.out.println( "o instanceof A 的结果:" + ( o instanceof A ) ); System.out.println( "o instanceof B 的结果:" + ( o instanceof B ) ); System.out.println(); } }
结果:
a instanceof A 的结果:true b instanceof A 的结果:true a instanceof B 的结果:false b instanceof B 的结果:true o instanceof A 的结果:true o instanceof B 的结果:false o instanceof A 的结果:true o instanceof B 的结果:true
5.
改写接口
package runshape; public interface Shapes { public double getArea(); public double getPerimeter(); public void show(); } public class Circle implements Shapes{ private int r; public Circle(int r){ this.r=r; } public double getArea() { return Math.PI*Math.pow(r, 2); } public double getPerimeter(){ return 2*Math.PI*r; } public void show(){ System.out.println("圆形:"); System.out.println("圆的面积是"+this.getArea()); System.out.println("圆的周长是"+this.getPerimeter()); } } public class Rect implements Shapes{ private int height; private int width; public Rect(int height, int width){ this.height=height; this.width=width; } public double getArea(){ return height*width; } public double getPerimeter(){ return 2 * height + 2 * width; } public void show(){ System.out.println("矩形:"); System.out.println("矩形的面积是"+this.getArea()); System.out.println("矩形的周长是"+this.getPerimeter()); } } public class Triangle implements Shapes { private int x; private int y; private int z; public Triangle(int x, int y, int z){ this.x=x; this.y=y; this.z=z; } @Override public double getArea() { double m=(x+y+z)/2.0; return Math.sqrt(m*(m-x)*(m-y)*(m-z)); } @Override public double getPerimeter() { return x+y+z; } public void show(){ System.out.println("三角形:"); System.out.println("三角形的面积是"+this.getArea()); System.out.println("三角形的周长是"+this.getPerimeter()); }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号