Producer and Consumer模式
生产线程负责生产,消费线程负责消费。
保证生产的个数不超过仓库能储存的上限。
扔出我的代码
package com.cy.javase.producerandconsumer; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; public class Test01 { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建仓库 List list = new ArrayList(); //创建生产线程与取货线程 Thread t1 = new Thread(new Producer(list)); Thread t2 = new Thread(new Consumer(list)); t1.setName("生产线程"); t2.setName("取货线程"); t1.start(); t2.start(); } } class Producer implements Runnable{ //给生产的商品编号 private int index = 1; //线程共享的仓库 private List list; //生产商品方法 private String produceMethod(){ return String.valueOf(index++)+"号商品"; } public Producer(List list) { this.list = list; } @Override public void run() { while (true){ //给线程共用的仓库上锁 synchronized(list){ //定义假设仓库上限为10,生产至上限后调用wait()方法进入等待状态,释放list锁,以便取货线程取走货物 if(list.size()==10){ try { list.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } //程序能运行至此处说明仓库未满可以继续生产,向仓库list里添加货物 list.add(produceMethod()); //显示当前添加的货物编号 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"生产了--->"+list.get(list.size()-1)); //此处唤醒取货程序以防止生产产品放满仓库后取货程序仍然处于等待状态 list.notify(); } } } } class Consumer implements Runnable{ //线程共享的仓库 private List list; public Consumer(List list) { this.list = list; } @Override public void run() { while (true){ synchronized(list){ //当取光仓库里的货物时进入等待状态,释放list锁 if(list.size()==0){ try { list.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } //以后进先出的方式取出仓库里的货物 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"取出了--->"+list.remove(list.size()-1)); //此处唤醒生产线程以防止货物取光后生产线程仍处于等待状态 list.notify(); } } } }
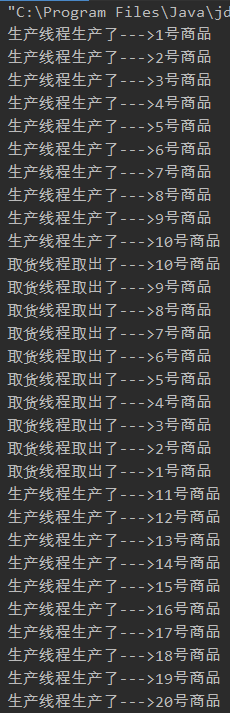
运行结果如下图所示




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号