实验4
task1
代码
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #define N 4 3 4 void test1(){ 5 int a[N]={1,9,8,4}; 6 int i; 7 8 printf("sizeof(a) = %d\n",sizeof(a)); 9 10 for(i=0;i<N;++i){ 11 printf("%p: %d\n",&a[i],a[i]); 12 } 13 14 printf("a = %p\n",a); 15 } 16 17 void test2(){ 18 char b[N] = {'1','9','8','4'}; 19 int i; 20 21 printf("sizeof(b) = %d\n",sizeof(b)); 22 23 for(i = 0;i < N; ++i){ 24 printf("%p: %c\n",&b[i],b[i]); 25 } 26 printf("b = %p\n",b); 27 } 28 29 int main(){ 30 printf("测试1:int类型一维数组\n"); 31 test1(); 32 33 printf("\n测试2:char类型一维数组\n"); 34 test2(); 35 36 return 0; 37 }
结果
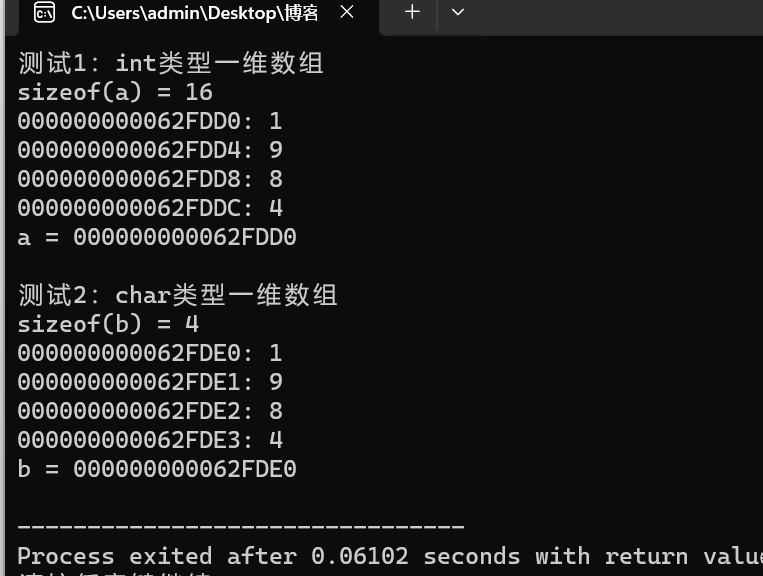
回答
一:int型数组a在内存中是连续存放的,每个元素占用4个内存字节单元。数组名a对应的值和&a[0]是一样的,都是第一个元素的地址。
二 :char型数组b在内存中是连续存放的,每个元素占用1个内存字节单元。数组名b对应的值和&b[0]是一样的,都是第一个元素的地址。
task1_2
代码
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #define N 2 3 #define M 4 4 5 void test1(){ 6 int a[N][M]={{1,9,8,4},{2,0,4,9}}; 7 int i,j; 8 9 printf("sizeof(a) = %d\n",sizeof(a)); 10 for(i=0;i<N;++i){ 11 for(j=0;j<M;++j){ 12 printf("%p: %d\n",&a[i][j],a[i][j]); 13 } 14 } 15 printf("\n"); 16 17 printf("a = %p\n",a); 18 printf("a[0] = %p\n",a[0]); 19 printf("a[1] = %p\n",a[1]); 20 printf("\n"); 21 } 22 23 void test2(){ 24 char b[N][M]={{'1','9','8','4'},{'2','0','4','9'}}; 25 int i,j; 26 27 printf("sizeof(b) = %d\n",sizeof(b)); 28 29 for(i=0;i<N;++i){ 30 for(j=0;j<M;++j){ 31 printf("%p: %c\n",&b[i][j],b[i][j]); 32 } 33 } 34 printf("\n"); 35 36 printf("b = %p\n",b); 37 printf("b[0] = %p\n",b[0]); 38 printf("b[1] = %p\n",b[1]); 39 } 40 41 int main(){ 42 printf("测试1:int型两维数组"); 43 test1(); 44 45 printf("测试2:char型两维数组"); 46 test2(); 47 48 return 0; 49 }
结果
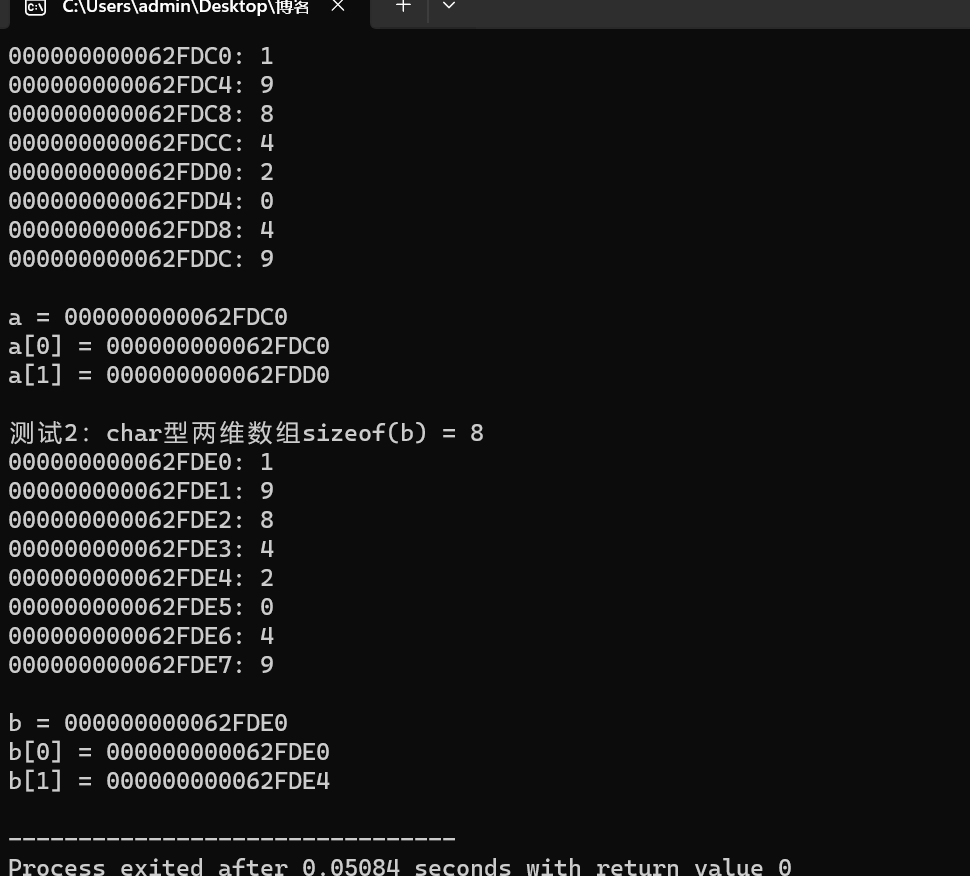
回答
一:int型二维数组a,在内存中是"按行连续存放"的,每个元素占用4个内存字节单元。a和a[0][0],&a[0][0]是一样的。
二:char型二维数组b,在内存中是"按行连续存放"的,每个元素占用1个内存字节单元。b和b[0][0],&b[0][0]是一样的。
三:16个,4个。二维数组中相邻行之间的元素相差的地址值是根据每行元素的大小来决定的。
task2
代码
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <string.h> 3 4 #define N 80 5 6 void swap_str(char s1[N],char s2[N]); 7 void test1(); 8 void test2(); 9 10 int main(){ 11 printf("测试1:用两个一维char数组,实现两个字符串交换\n"); 12 test1(); 13 14 printf("测试2:用二维char数组,实现两个字符串交换\n"); 15 test2(); 16 17 return 0; 18 } 19 20 void test1(){ 21 char views1[N] = "hey,C,I hate u."; 22 char views2[N] = "hey,C,I love u."; 23 24 printf("交换前:\n"); 25 puts(views1); 26 puts(views2); 27 28 swap_str(views1,views2); 29 30 printf("交换后:\n"); 31 puts(views1); 32 puts(views2); 33 } 34 35 void test2(){ 36 char views [2][N]= {"hey,C,I hate u.", 37 "hey,C,I love u."}; 38 39 printf("交换前:\n"); 40 puts(views[0]); 41 puts(views[1]); 42 43 swap_str(views[0],views[1]); 44 45 printf("交换后:\n"); 46 puts(views[0]); 47 puts(views[1]); 48 49 } 50 51 void swap_str(char s1[N],char s2[N]){ 52 char tmp[N]; 53 54 strcpy(tmp,s1); 55 strcpy(s1,s2); 56 strcpy(s2,tmp); 57 }
结果
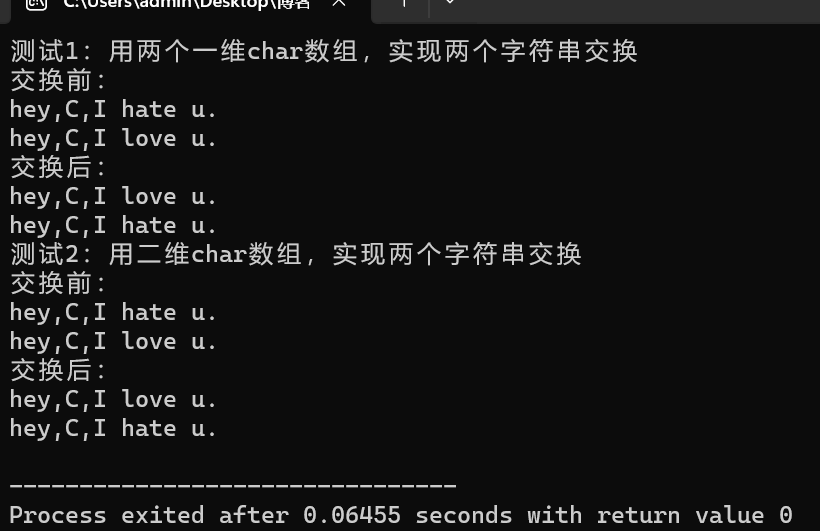
回答:
test1调用整个字符数组,会默认一起,所以不用[],test2只要选择一个,要更精确。
test3
代码
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 3 #define N 80 4 5 int count(char x[]); 6 7 int main(){ 8 char words[N+1]; 9 int n; 10 11 while(gets(words)!=NULL){ 12 n = count(words); 13 printf("单词数:%d\n\n",n); 14 } 15 return 0; 16 } 17 18 int count(char x[]){ 19 int i; 20 int word_flag = 0; 21 int number = 0; 22 23 for(i = 0;x[i] != '\0'; ++i){ 24 if(x[i] ==' '){ 25 word_flag = 0; 26 }else if(word_flag ==0){ 27 word_flag = 1; 28 number++; 29 } 30 } 31 32 return number; 33 }
结果
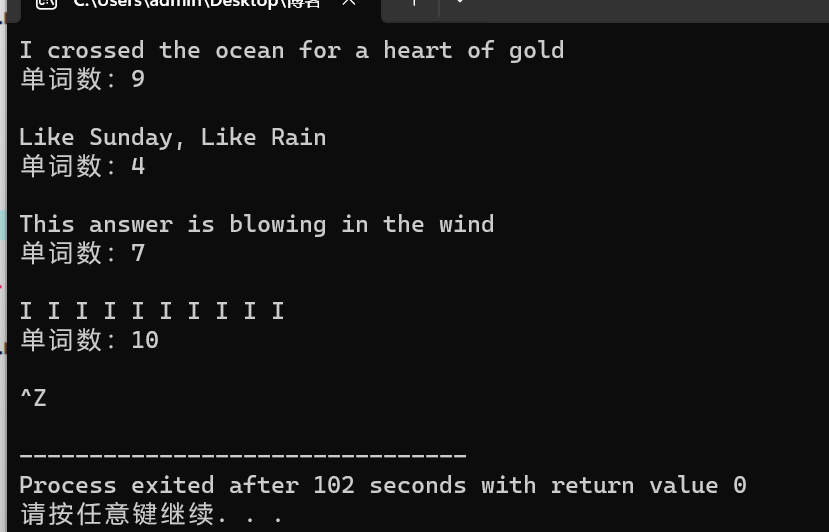
task3_2
代码
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #define N 1000 3 4 int main(){ 5 char line[N]; 6 int word_len; 7 int max_len; 8 int end; 9 int i; 10 11 while(gets(line)!=NULL){ 12 word_len=0; 13 max_len=0; 14 end=0; 15 16 i=0; 17 while(1){ 18 while(line[i]==' '){ 19 word_len=0; 20 i++; 21 } 22 23 while(line[i] != '\0' && line[i] != ' '){ 24 word_len++; 25 i++; 26 } 27 28 if(max_len<word_len){ 29 max_len = word_len; 30 end = i; 31 } 32 33 if(line[i] == '\0'){ 34 break; 35 } 36 } 37 38 printf("最长单词:"); 39 for(i = end - max_len; i<end;++i){ 40 printf("%c",line[i]); 41 } 42 printf("\n\n"); 43 } 44 45 return 0; 46 }
结果
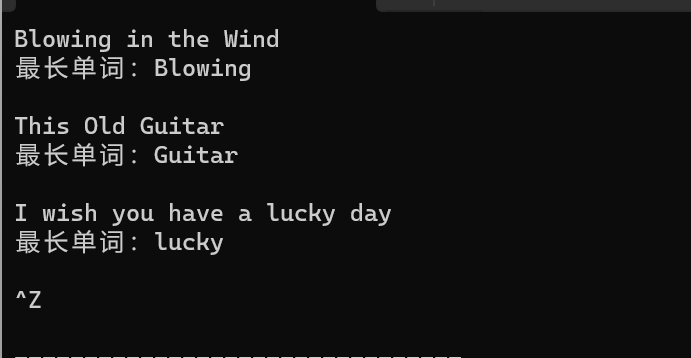
test4
代码
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #define N 100 3 void dec_to_n(int x, int n); 4 5 int main(){ 6 int x; 7 8 printf("输入一个十进制整数:"); 9 while(scanf("%d",&x) != EOF){ 10 dec_to_n(x, 2); 11 dec_to_n(x, 8); 12 dec_to_n(x, 16); 13 14 printf("\n输入一个十进制整数:"); 15 } 16 return 0; 17 } 18 19 void dec_to_n(int x,int n){ 20 char map[16] = {"0123456789ABCDEF"}; 21 char ans[N]; 22 int r,i; 23 int cnt = 0; 24 25 do{ 26 r = x%n; 27 ans[cnt++]=map[r]; 28 x/=n; 29 }while(x!=0); 30 31 for(i=cnt-1;i>=0;i--){ 32 printf("%c",ans[i]); 33 } 34 35 printf("\n"); 36 }
结果
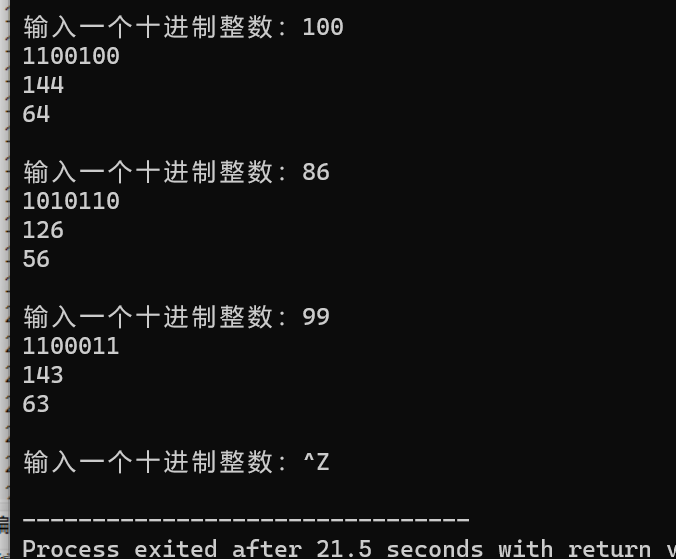
tast5
代码
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #define N 5 3 4 void input(int x[], int n); 5 void output(int x[], int n); 6 double average(int x[], int n); 7 void bubble_sort(int x[], int n); 8 9 int main(){ 10 int scores[N]; 11 double ave; 12 13 printf("录入%d个分数:\n",N); 14 input(scores,N); 15 16 printf("\n输出课程分数: \n"); 17 output(scores,N); 18 19 printf("\n课程分数处理:计算均分、排序...\n"); 20 ave=average(scores,N); 21 bubble_sort(scores,N); 22 23 printf("\n输出课程均分:%.2f\n",ave); 24 printf("\n输出课程分数(高->低):\n"); 25 output(scores,N); 26 27 return 0; 28 } 29 30 void input(int x[], int n){ 31 int i; 32 33 for(i=0;i<n;++i){ 34 scanf("%d",&x[i]); 35 } 36 } 37 38 void output(int x[], int n){ 39 int i; 40 41 for(i=0;i<n;++i){ 42 printf("%d ",x[i]); 43 } 44 printf("\n"); 45 } 46 47 double average(int x[], int n){ 48 int i,sum=0; 49 double j; 50 for(i=0;i<n;i++){ 51 sum+=x[i]; 52 } 53 j=1.0*sum/n; 54 return j; 55 } 56 57 void bubble_sort(int x[], int n){ 58 int i,j,temp; 59 for(i = 0; i < n; i++) { 60 for(j=0;j<n-i-1;j++) { 61 if(x[j]<x[j+1]) { 62 temp = x[j]; 63 x[j] = x[j+1]; 64 x[j+1] = temp; 65 } 66 } 67 } 68 }
结果
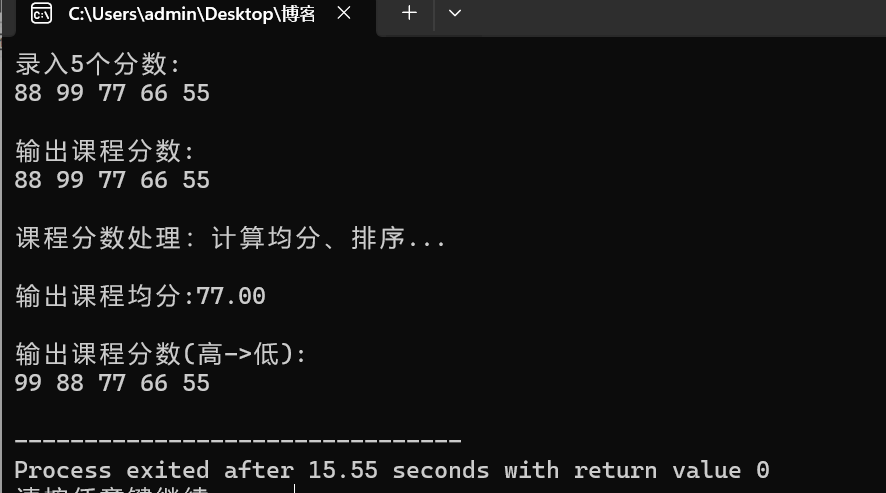
task6
代码
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <string.h> 3 4 #define N 5 5 #define M 20 6 7 void output(char str[][M],int n); 8 void bubble_sort(char str[][M],int n); 9 10 int main(){ 11 char name[][M]={"Bob","Bill","Joseph","Taylor","George"}; 12 int i; 13 14 printf("输出初始名单:\n"); 15 output(name,N); 16 17 printf("\n排列中...\n"); 18 bubble_sort(name,N); 19 20 printf("\n按字典序输出名单:\n"); 21 output(name,N); 22 23 return 0; 24 } 25 26 void output(char str[][M],int n){ 27 int i; 28 29 for(i=0;i<n;++i){ 30 printf("%s\n",str[i]); 31 } 32 } 33 34 void bubble_sort(char str[][M],int n){ 35 int i,j; 36 for(i=0;i<n;i++){ 37 for(j=0;j<n-i-1;j++){ 38 if(strcmp(str[j],str[j+1]) > 0){ 39 char temp[50]; 40 strcpy(temp,str[j]); 41 strcpy(str[j],str[j+1]); 42 strcpy(str[j+1],temp); 43 44 } 45 } 46 } 47 }
结果
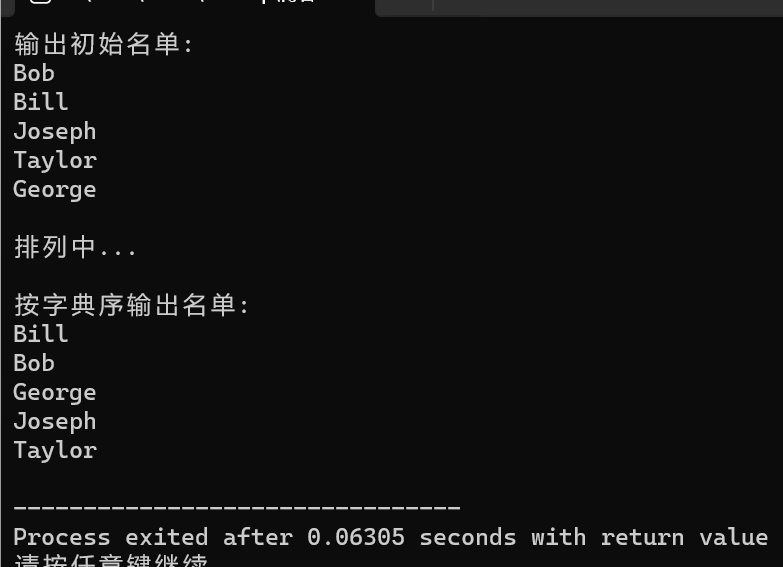
task7
代码
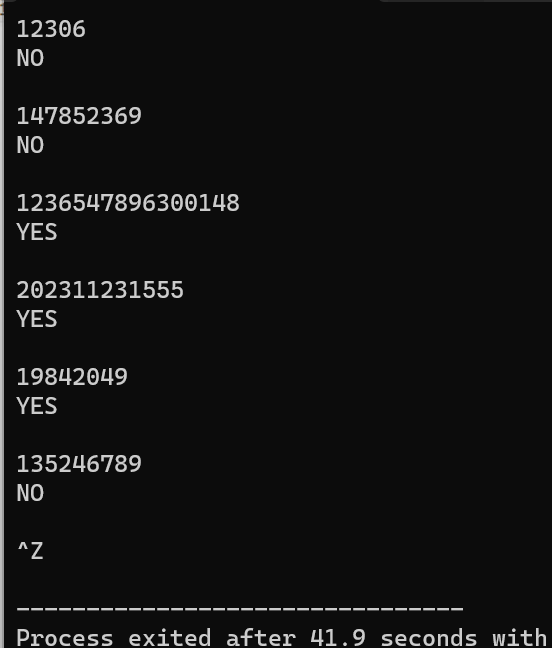
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <string.h> 3 void chong(char arr[]); 4 5 int main(){ 6 char arr[100]; 7 while(gets(arr)!=NULL){ 8 chong(arr); 9 } 10 11 return 0; 12 } 13 14 void chong(char arr[]){ 15 int i,j,count=0; 16 if(strlen(arr)>9){ 17 printf("YES\n"); 18 }else{ 19 for(i=0;i<strlen(arr);i++){ 20 for(j=i+1;j<strlen(arr);j++){ 21 if(arr[i]==arr[j]){ 22 count++; 23 } 24 } 25 } 26 if(count!=0){ 27 printf("YES\n"); 28 }else{ 29 printf("NO\n"); 30 } 31 } 32 printf("\n"); 33 }
结果
task8
代码
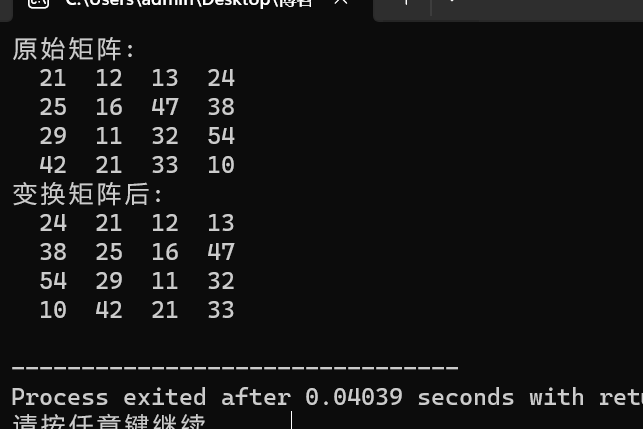
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #define N 100 3 #define M 4 4 5 void output(int x[][N], int n); 6 void rotate_to_right(int x[][N], int n); 7 8 9 int main(){ 10 int t[][N] = {{21, 12, 13, 24}, 11 {25, 16, 47, 38}, 12 {29, 11, 32, 54}, 13 {42, 21, 33, 10}}; 14 15 printf("原始矩阵:\n"); 16 output(t,M); 17 18 rotate_to_right(t,M); 19 20 printf("变换矩阵后:\n"); 21 output(t,M); 22 23 return 0; 24 } 25 26 void output(int x[][N],int n){ 27 int i,j; 28 29 for(i=0;i<n;++i){ 30 for(j=0;j<n;++j){ 31 printf("%4d",x[i][j]); 32 } 33 printf("\n"); 34 } 35 } 36 37 void rotate_to_right(int x[][N], int n){ 38 int temp[M]; 39 int i,j; 40 for(i=0;i<M;i++){ 41 temp[i]=x[i][M-1]; 42 } 43 for(i=M-2;i>=0;i--){ 44 for(j=0;j<M;j++){ 45 x[j][i+1]=x[j][i]; 46 } 47 } 48 for(i=0;i<M;i++){ 49 x[i][0]=temp[i]; 50 } 51 }
结果
task9


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号