2.rt-thread标准版配置串口(中断接收)(基于RT-Thread-Studio)
目录
rt-thread标准版配置串口(基于RT-Thread-Studio)
1 配置串口示例
board.h中的注释
/** After configuring corresponding UART or UART DMA, you can use it.
*
* STEP 1, define macro define related to the serial port opening based on the serial port number
* such as #define BSP_USING_UART1
*
* STEP 2, according to the corresponding pin of serial port, define the related serial port information macro
* such as #define BSP_UART1_TX_PIN "PA9"
* #define BSP_UART1_RX_PIN "PA10"
*
* STEP 3, if you want using SERIAL DMA, you must open it in the RT-Thread Settings.
* RT-Thread Setting -> Components -> Device Drivers -> Serial Device Drivers -> Enable Serial DMA Mode
*
* STEP 4, according to serial port number to define serial port tx/rx DMA function in the board.h file
* such as #define BSP_UART1_RX_USING_DMA
1. 第一步:首先在board.h中宏定义
-->board.h
#define BSP_USING_UART2
#define BSP_UART2_TX_PIN "PA2"
#define BSP_UART2_RX_PIN "PA3"
//配置DMA模式使用
//#define BSP_UART2_TX_USING_DMA
//#define BSP_UART2_RX_USING_DMA
2. 第二步:获取设备句柄
-->main.c
static rt_device_t test_serial;
test_serial = rt_device_find("uart2");
3. 第三步:打开设备
-->rtdef.h
//===============
#define RT_DEVICE_OFLAG_RDONLY 0x001 /**< read only access */
#define RT_DEVICE_OFLAG_WRONLY 0x002 /**< write only access */
#define RT_DEVICE_OFLAG_RDWR 0x003 /**< read and write */
#define RT_DEVICE_FLAG_INT_RX 0x100 /**< INT mode on Rx */
#define RT_DEVICE_FLAG_DMA_RX 0x200 /**< DMA mode on Rx */
#define RT_DEVICE_FLAG_INT_TX 0x400 /**< INT mode on Tx */
#define RT_DEVICE_FLAG_DMA_TX 0x800 /**< DMA mode on Tx */
//===============
-->main.c
//===============
//读写模式,中断接收,轮询发送
rt_device_open(test_serial,
RT_DEVICE_OFLAG_RDWR
| RT_DEVICE_FLAG_INT_RX);
4. 第四步:配置串口参数
-->serial.h
//=============
struct serial_configure//可定义结构体,按照下面格式定义就可以
//默认参数
/* Default config for serial_configure structure */
#define RT_SERIAL_CONFIG_DEFAULT \
{ \
BAUD_RATE_115200, /* 115200 bits/s */ \
DATA_BITS_8, /* 8 databits */ \
STOP_BITS_1, /* 1 stopbit */ \
PARITY_NONE, /* No parity */ \
BIT_ORDER_LSB, /* LSB first sent */ \
NRZ_NORMAL, /* Normal mode */ \
RT_SERIAL_RB_BUFSZ, /* Buffer size */ \
0 \
}
//===========
-->main.c
struct serial_configure uart2_set_parg={ \
BAUD_RATE_115200, /* 115200 bits/s */ \
DATA_BITS_8, /* 8 databits */ \
STOP_BITS_1, /* 1 stopbit */ \
PARITY_NONE, /* No parity */ \
BIT_ORDER_LSB, /* LSB first sent */ \
NRZ_NORMAL, /* Normal mode */ \
RT_SERIAL_RB_BUFSZ, /* Buffer size */ \
0 \
};
rt_device_control(test_serial, RT_DEVICE_CTRL_CONFIG, &uart2_set_parg);
5. 第五步:有需要设置接收/发送回调函数
-->mian.c
//如果设置的是中断/DMA可以设置回调函数
rt_err_t rt_device_set_tx_complete(rt_device_t dev, rt_err_t (*tx_done)(rt_device_t dev,void *buffer));
/*用程序调用 rt_device_write() 写入数据时,如果底层硬件能够支持自动发送,
那么上层应用可以设置一个回调函数。
这个回调函数会在底层硬件数据发送完成后 (例如 DMA 传送完成或 FIFO 已经写入完毕产生完成中断时) 调用。
调用个函数时,回调函数由调用者提供,当硬件设备发送完数据时,由设备驱动程序回调这个函数并把发送完成的数据块地址 buffer 作为参数传递给上层应用。上层应用(线程)在收到指示时会根据发送 buffer 的情况,释放 buffer 内存块或将其作为下一个写数据的缓存。*/
rt_err_t rt_device_set_rx_indicate(rt_device_t dev, rt_err_t (*rx_ind)(rt_device_t dev,rt_size_t size));
/*
该函数的回调函数由调用者提供。
若串口以中断接收模式打开,当串口接收到一个数据产生中断时,就会调用回调函数,并且会把此时缓冲区的数据大小放在 size 参数里,把串口设备句柄放在 dev 参数里供调用者获取。
若串口以 DMA 接收模式打开,当 DMA 完成一批数据的接收后会调用此回调函数。*/
uint16_t count;
uint8_t test_buff[10];
rt_err_t rx_irq(rt_device_t dev,rt_size_t size)
{
rt_kprintf("count:%d",count++);
if(count == 10)
{
count=0;
rt_device_write(test_serial, 0, "receive 10 bytes!", strlen("receive 10 bytes!"));
rt_device_read(test_serial, 0, test_buff, 10);//读一次清除内部环形缓冲区
}
return 0;
}
rt_device_set_rx_indicate(test_serial, rx_irq);
6. 第六步:使用 rt_device_write/rt_device_read 读取或者写入数据
7. 源代码示例
board.h
/*
* Copyright (c) 2006-2025, RT-Thread Development Team
*
* SPDX-License-Identifier: Apache-2.0
*
* Change Logs:
* Date Author Notes
* 2025-03-23 RealThread first version
*/
#ifndef __BOARD_H__
#define __BOARD_H__
#include <stm32f1xx.h>
#include <drv_common.h>
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C"
{
#endif
/*-------------------------- CHIP CONFIG BEGIN --------------------------*/
#define CHIP_FAMILY_STM32
#define CHIP_SERIES_STM32F1
#define CHIP_NAME_STM32F103ZE
/*-------------------------- CHIP CONFIG END --------------------------*/
/*-------------------------- ROM/RAM CONFIG BEGIN --------------------------*/
#define ROM_START ((uint32_t)0x08000000)
#define ROM_SIZE (512 * 1024)
#define ROM_END ((uint32_t)(ROM_START + ROM_SIZE))
#define RAM_START (0x20000000)
#define RAM_SIZE (64 * 1024)
#define RAM_END (RAM_START + RAM_SIZE)
/*-------------------------- ROM/RAM CONFIG END --------------------------*/
/*-------------------------- CLOCK CONFIG BEGIN --------------------------*/
#define BSP_CLOCK_SOURCE ("HSE")
#define BSP_CLOCK_SOURCE_FREQ_MHZ ((int32_t)8)
#define BSP_CLOCK_SYSTEM_FREQ_MHZ ((int32_t)72)
/*-------------------------- CLOCK CONFIG END --------------------------*/
/*-------------------------- UART CONFIG BEGIN --------------------------*/
/** After configuring corresponding UART or UART DMA, you can use it.
*
* STEP 1, define macro define related to the serial port opening based on the serial port number
* such as #define BSP_USING_UART1
*
* STEP 2, according to the corresponding pin of serial port, define the related serial port information macro
* such as #define BSP_UART1_TX_PIN "PA9"
* #define BSP_UART1_RX_PIN "PA10"
*
* STEP 3, if you want using SERIAL DMA, you must open it in the RT-Thread Settings.
* RT-Thread Setting -> Components -> Device Drivers -> Serial Device Drivers -> Enable Serial DMA Mode
*
* STEP 4, according to serial port number to define serial port tx/rx DMA function in the board.h file
* such as #define BSP_UART1_RX_USING_DMA
*
*/
#define BSP_USING_UART1
#define BSP_UART1_TX_PIN "PA9"
#define BSP_UART1_RX_PIN "PA10"
#define BSP_USING_UART2
#define BSP_UART2_TX_PIN "PA2"
#define BSP_UART2_RX_PIN "PA3"
/*-------------------------- UART CONFIG END --------------------------*/
/*-------------------------- I2C CONFIG BEGIN --------------------------*/
/** if you want to use i2c bus(soft simulate) you can use the following instructions.
*
* STEP 1, open i2c driver framework(soft simulate) support in the RT-Thread Settings file
*
* STEP 2, define macro related to the i2c bus
* such as #define BSP_USING_I2C1
*
* STEP 3, according to the corresponding pin of i2c port, modify the related i2c port and pin information
* such as #define BSP_I2C1_SCL_PIN GET_PIN(port, pin) -> GET_PIN(C, 11)
* #define BSP_I2C1_SDA_PIN GET_PIN(port, pin) -> GET_PIN(C, 12)
*/
/*#define BSP_USING_I2C1*/
#ifdef BSP_USING_I2C1
#define BSP_I2C1_SCL_PIN GET_PIN(port, pin)
#define BSP_I2C1_SDA_PIN GET_PIN(port, pin)
#endif
/*#define BSP_USING_I2C2*/
#ifdef BSP_USING_I2C2
#define BSP_I2C2_SCL_PIN GET_PIN(port, pin)
#define BSP_I2C2_SDA_PIN GET_PIN(port, pin)
#endif
/*-------------------------- I2C CONFIG END --------------------------*/
/*-------------------------- SPI CONFIG BEGIN --------------------------*/
/** if you want to use spi bus you can use the following instructions.
*
* STEP 1, open spi driver framework support in the RT-Thread Settings file
*
* STEP 2, define macro related to the spi bus
* such as #define BSP_USING_SPI1
*
* STEP 3, copy your spi init function from stm32xxxx_hal_msp.c generated by stm32cubemx to the end of board.c file
* such as void HAL_SPI_MspInit(SPI_HandleTypeDef* hspi)
*
* STEP 4, modify your stm32xxxx_hal_config.h file to support spi peripherals. define macro related to the peripherals
* such as #define HAL_SPI_MODULE_ENABLED
*/
/*#define BSP_USING_SPI1*/
/*#define BSP_USING_SPI2*/
/*#define BSP_USING_SPI3*/
/*-------------------------- SPI CONFIG END --------------------------*/
/*-------------------------- QSPI CONFIG BEGIN --------------------------*/
/** if you want to use qspi you can use the following instructions.
*
* STEP 1, open qspi driver framework support in the RT-Thread Settings file
*
* STEP 2, define macro related to the qspi
* such as #define BSP_USING_QSPI
*
* STEP 3, copy your qspi init function from stm32xxxx_hal_msp.c generated by stm32cubemx to the end of board.c file
* such as void HAL_QSPI_MspInit(QSPI_HandleTypeDef* hqspi)
*
* STEP 4, modify your stm32xxxx_hal_config.h file to support qspi peripherals. define macro related to the peripherals
* such as #define HAL_QSPI_MODULE_ENABLED
*
*/
/*#define BSP_USING_QSPI*/
/*-------------------------- QSPI CONFIG END --------------------------*/
/*-------------------------- PWM CONFIG BEGIN --------------------------*/
/** if you want to use pwm you can use the following instructions.
*
* STEP 1, open pwm driver framework support in the RT-Thread Settings file
*
* STEP 2, define macro related to the pwm
* such as #define BSP_USING_PWM1
*
* STEP 3, copy your pwm timer init function from stm32xxxx_hal_msp.c generated by stm32cubemx to the end if board.c file
* such as void HAL_TIM_Base_MspInit(TIM_HandleTypeDef* htim_base) and
* void HAL_TIM_MspPostInit(TIM_HandleTypeDef* htim)
*
* STEP 4, modify your stm32xxxx_hal_config.h file to support pwm peripherals. define macro related to the peripherals
* such as #define HAL_TIM_MODULE_ENABLED
*
*/
/*#define BSP_USING_PWM1*/
/*#define BSP_USING_PWM2*/
/*#define BSP_USING_PWM3*/
/*-------------------------- PWM CONFIG END --------------------------*/
/*-------------------------- ADC CONFIG BEGIN --------------------------*/
/** if you want to use adc you can use the following instructions.
*
* STEP 1, open adc driver framework support in the RT-Thread Settings file
*
* STEP 2, define macro related to the adc
* such as #define BSP_USING_ADC1
*
* STEP 3, copy your adc init function from stm32xxxx_hal_msp.c generated by stm32cubemx to the end of board.c file
* such as void HAL_ADC_MspInit(ADC_HandleTypeDef* hadc)
*
* STEP 4, modify your stm32xxxx_hal_config.h file to support adc peripherals. define macro related to the peripherals
* such as #define HAL_ADC_MODULE_ENABLED
*
*/
/*#define BSP_USING_ADC1*/
/*#define BSP_USING_ADC2*/
/*#define BSP_USING_ADC3*/
/*-------------------------- ADC CONFIG END --------------------------*/
/*-------------------------- WDT CONFIG BEGIN --------------------------*/
/** if you want to use wdt you can use the following instructions.
*
* STEP 1, open wdt driver framework support in the RT-Thread Settings file
*
* STEP 2, modify your stm32xxxx_hal_config.h file to support wdt peripherals. define macro related to the peripherals
* such as #define HAL_IWDG_MODULE_ENABLED
*
*/
/*-------------------------- WDT CONFIG END --------------------------*/
/*-------------------------- HARDWARE TIMER CONFIG BEGIN --------------------------*/
/** if you want to use hardware timer you can use the following instructions.
*
* STEP 1, open hwtimer driver framework support in the RT-Thread Settings file
*
* STEP 2, define macro related to the hwtimer
* such as #define BSP_USING_TIM and
* #define BSP_USING_TIM1
*
* STEP 3, copy your hardwire timer init function from stm32xxxx_hal_msp.c generated by stm32cubemx to the end of board.c file
* such as void HAL_TIM_Base_MspInit(TIM_HandleTypeDef* htim_base)
*
* STEP 4, modify your stm32xxxx_hal_config.h file to support hardwere timer peripherals. define macro related to the peripherals
* such as #define HAL_TIM_MODULE_ENABLED
*
*/
/*#define BSP_USING_TIM*/
#ifdef BSP_USING_TIM
/*#define BSP_USING_TIM15*/
/*#define BSP_USING_TIM16*/
/*#define BSP_USING_TIM17*/
#endif
/*-------------------------- HAREWARE TIMER CONFIG END --------------------------*/
/*-------------------------- RTC CONFIG BEGIN --------------------------*/
/** if you want to use rtc(hardware) you can use the following instructions.
*
* STEP 1, open rtc driver framework(hardware) support in the RT-Thread Settings file
*
* STEP 2, define macro related to the rtc
* such as BSP_USING_ONCHIP_RTC
*
* STEP 3, modify your stm32xxxx_hal_config.h file to support rtc peripherals. define macro related to the peripherals
* such as #define HAL_RTC_MODULE_ENABLED
*
*/
/*#define BSP_USING_ONCHIP_RTC*/
/*-------------------------- RTC CONFIG END --------------------------*/
/*-------------------------- SDIO CONFIG BEGIN --------------------------*/
/** if you want to use sdio you can use the following instructions.
*
* STEP 1, open sdio driver framework support in the RT-Thread Settings file
*
* STEP 2, define macro related to the sdio
* such as BSP_USING_SDIO
*
* STEP 3, copy your sdio init function from stm32xxxx_hal_msp.c generated by stm32cubemx to the end of board.c file
* such as void HAL_SD_MspInit(SD_HandleTypeDef* hsd)
*
* STEP 4, modify your stm32xxxx_hal_config.h file to support sdio peripherals. define macro related to the peripherals
* such as #define HAL_SD_MODULE_ENABLED
*
* STEP 5, config your device file system or another applications
*
*/
/*#define BSP_USING_SDIO*/
/*-------------------------- SDIO CONFIG END --------------------------*/
/*-------------------------- ETH CONFIG BEGIN --------------------------*/
/** if you want to use eth you can use the following instructions.
*
* STEP 1, define macro related to the eth
* such as BSP_USING_ETH
*
* STEP 2, copy your eth init function from stm32xxxx_hal_msp.c generated by stm32cubemx to the end if board.c file
* such as void HAL_ETH_MspInit(ETH_HandleTypeDef* heth)
*
* STEP 3, modify your stm32xxxx_hal_config.h file to support eth peripherals. define macro related to the peripherals
* such as #define HAL_ETH_MODULE_ENABLED
*
* STEP 4, config your phy type
* such as #define PHY_USING_LAN8720A
* #define PHY_USING_DM9161CEP
* #define PHY_USING_DP83848C
* STEP 5, implement your phy reset function in the end of board.c file
* void phy_reset(void)
*
* STEP 6, config your lwip or other network stack
*
*/
/*#define BSP_USING_ETH*/
#ifdef BSP_USING_ETH
/*#define PHY_USING_LAN8720A*/
/*#define PHY_USING_DM9161CEP*/
/*#define PHY_USING_DP83848C*/
#endif
/*-------------------------- ETH CONFIG END --------------------------*/
/*-------------------------- USB HOST CONFIG BEGIN --------------------------*/
/** if you want to use usb host you can use the following instructions.
*
* STEP 1, open usb host driver framework support in the RT-Thread Settings file
*
* STEP 2, define macro related to the usb host
* such as BSP_USING_USBHOST
*
* STEP 3, copy your usb host init function from stm32xxxx_hal_msp.c generated by stm32cubemx to the end of board.c file
* such as void HAL_HCD_MspInit(HCD_HandleTypeDef* hhcd)
*
* STEP 4, config your usb peripheral clock in SystemClock_Config() generated by STM32CubeMX and replace this function in board.c
*
* STEP 5, modify your stm32xxxx_hal_config.h file to support usb host peripherals. define macro related to the peripherals
* such as #define HAL_HCD_MODULE_ENABLED
*
*/
/*#define BSP_USING_USBHOST*/
/*-------------------------- USB HOST CONFIG END --------------------------*/
/*-------------------------- USB DEVICE CONFIG BEGIN --------------------------*/
/** if you want to use usb device you can use the following instructions.
*
* STEP 1, open usb device driver framework support in the RT-Thread Settings file
*
* STEP 2 define macro related to the usb device
* such as BSP_USING_USBDEVICE
*
* STEP 3, copy your usb device init function from stm32xxxx_hal_msp.c generated by stm32cubemx to the end of board.c file
* such as void HAL_PCD_MspInit(PCD_HandleTypeDef* hpcd)
*
* STEP 4, config your usb peripheral clock in SystemClock_Config() generated by STM32CubeMX and replace this function in board.c
*
* STEP 5, modify your stm32xxxx_hal_config.h file to support usb device peripherals. define macro related to the peripherals
* such as #define HAL_PCD_MODULE_ENABLED
*
*/
/*#define BSP_USING_USBDEVICE*/
/*-------------------------- USB DEVICE CONFIG END --------------------------*/
/*-------------------------- ON_CHIP_FLASH CONFIG BEGIN --------------------------*/
/** if you want to use on chip flash you can use the following instructions.
*
* STEP 1 define macro related to the on chip flash
* such as BSP_USING_ON_CHIP_FLASH
*
* STEP 2, modify your stm32xxxx_hal_config.h file to support on chip flash peripherals. define macro related to the peripherals
* such as #define HAL_FLASH_MODULE_ENABLED
*
*/
/*#define BSP_USING_ON_CHIP_FLASH*/
/*-------------------------- ON_CHIP_FLASH CONFIG END --------------------------*/
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
#endif /* __BOARD_H__ */
main.c
/*
* Copyright (c) 2006-2025, RT-Thread Development Team
*
* SPDX-License-Identifier: Apache-2.0
*
* Change Logs:
* Date Author Notes
* 2025-03-21 RT-Thread first version
*/
#include <rtthread.h>
#define DBG_TAG "main"
#define DBG_LVL DBG_LOG
#include <rtdbg.h>
#include <stm32f1xx.h>
#include "rtdevice.h"
#include "board.h"
#define LED1_PIN GET_PIN(B,5)//亮为低电平
#define LED2_PIN GET_PIN(E,5)//亮为低电平
#define WAKE_PIN GET_PIN(A,0)//唤醒按钮
#define KEY1_PIN GET_PIN(E,4) //触发为高电平
#define KEY2_PIN GET_PIN(E,3) //触发为高电平
static rt_device_t test_serial;
uint16_t count;
uint8_t test_buff[10];
rt_err_t rx_irq(rt_device_t dev,rt_size_t size)
{
rt_kprintf("count:%d",count++);
if(count == 10)
{
count=0;
rt_device_write(test_serial, 0, "receive 10 bytes!", strlen("receive 10 bytes!"));
rt_device_read(test_serial, 0, test_buff, 10);//读一次清除内部环形缓冲区
}
return 0;
}
int main(void)
{
LOG_D("System Clock information");
LOG_D("SYSCLK_Frequency = %d", HAL_RCC_GetSysClockFreq());
LOG_D("HCLK_Frequency = %d", HAL_RCC_GetHCLKFreq());
LOG_D("PCLK1_Frequency = %d", HAL_RCC_GetPCLK1Freq());
LOG_D("PCLK2_Frequency = %d", HAL_RCC_GetPCLK2Freq());
/* 配置推挽输出 */
rt_pin_mode(LED1_PIN, PIN_MODE_OUTPUT);
test_serial = rt_device_find("uart2");
rt_device_open(test_serial,
RT_DEVICE_OFLAG_RDWR
| RT_DEVICE_FLAG_INT_RX);
struct serial_configure uart2_set_parg={ \
BAUD_RATE_115200, /* 115200 bits/s */ \
DATA_BITS_8, /* 8 databits */ \
STOP_BITS_1, /* 1 stopbit */ \
PARITY_NONE, /* No parity */ \
BIT_ORDER_LSB, /* LSB first sent */ \
NRZ_NORMAL, /* Normal mode */ \
RT_SERIAL_RB_BUFSZ, /* Buffer size */ \
0 \
};
rt_device_control(test_serial, RT_DEVICE_CTRL_CONFIG, &uart2_set_parg);
rt_device_set_rx_indicate(test_serial, rx_irq);
while (1)
{
/* LED闪烁 */
rt_pin_write(LED1_PIN, !rt_pin_read(LED1_PIN));
/* 线程轮询时间 */
rt_thread_mdelay(500);
}
return RT_EOK;
}
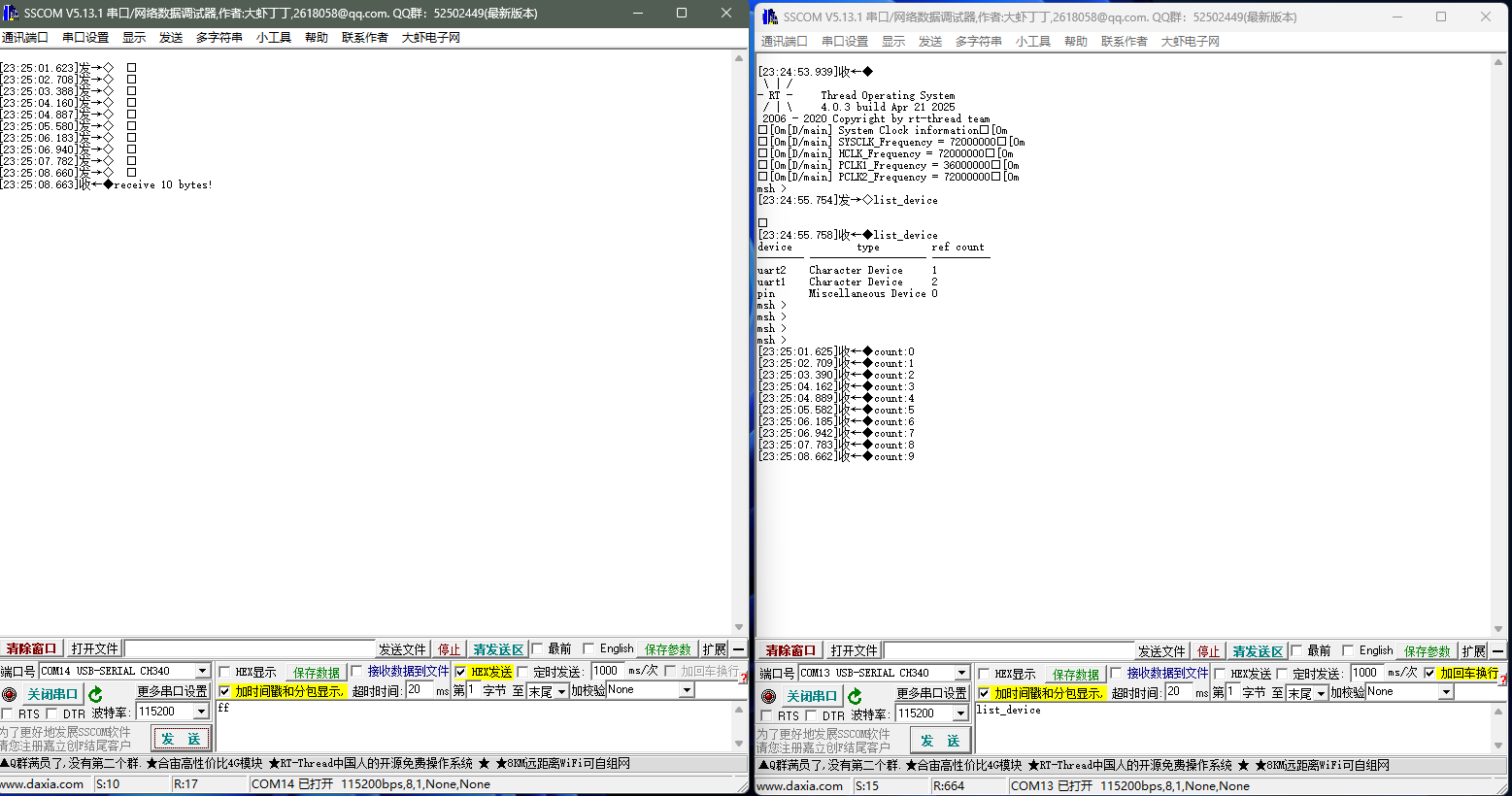
8. 实验结果




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号