通过递归创建链表
递归就是数学上数学归纳法的一种代码化。
特殊化:当n==1时成立(在代码中特殊情况不一定是n==1,可能n==0,或者n==null),一般化的过程有时也会影响特殊情况。所以在写代码的时候应该尽量先写完一般化的逻辑过程再去考虑特殊化。
一般化:对于n-1成立某种关系,对于n也成立(在写程序中)数学中是n-1满足某种关系求证n也满足。
举个栗子:
下面的两个递归求和函数都是对的,但是却有所不同
//一般化的不同会导致特殊化的不同 int sum(int n){//求自然数1~n的和 if(n==1) return 1;//特殊化 return sum(n-1)+n;///一般化 }
int sum1(int n){//求自然数1~n的和 if(n==1) return 1;//特殊化 if(n==2) return 3; return sum(n-2)+n+n-1;//一般化 }


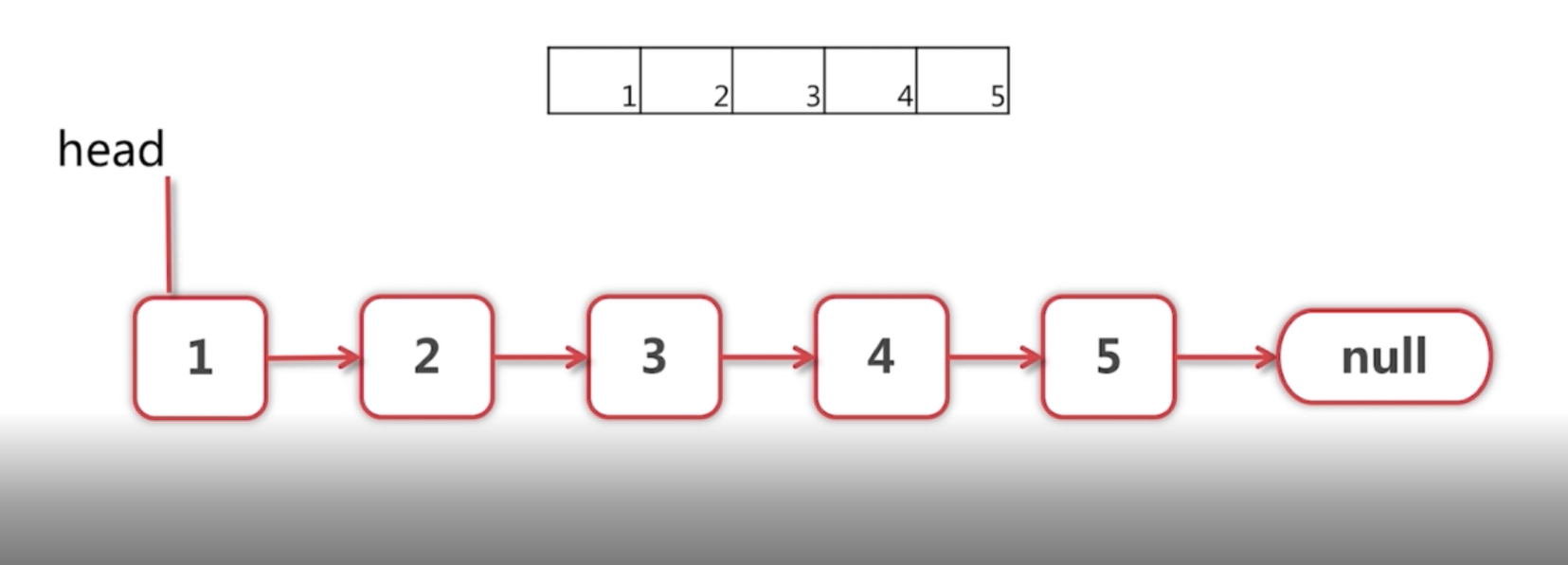

java代码如下:
节点类定义:
package interview; public class Node { private final int value; private Node next; public Node(int value) { super(); this.value = value; this.next = null; } public Node getNext() { return next; } public void setNext(Node next) { this.next = next; } public int getValue() { return value; } public static void printList(Node head){ while(head!=null){ System.out.print(head.getValue()); System.out.print(" "); head=head.getNext(); }System.out.println(); } }
主函数:
package interview; import java.util.List; import java.util.Arrays; public class list { /** * Creats a Linked List * * @param data the data to creat the list * @return head of the linked list.The return linked list * ends with last node with getNext() == null. */ public Node creatList(List<Integer> data){ if(data.isEmpty()){ return null; } Node firstNode = new Node(data.get(0)); Node headofSublist = creatList(data.subList(1,data.size())); firstNode.setNext(headofSublist); return firstNode; } public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub list creator = new list(); //Node.printList(new ArrayList<>()); Node.printList(creator.creatList(Arrays.asList(1))); Node.printList(creator.creatList(Arrays.asList(1,2,3,4,5))); } }
不一样的烟火


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号