[教育题[持续更新2023.5.30]]自用理解
牛客:猫猫与数列
首先想的是直接暴力求解,则答案会导致溢出,然后等式两边同时加上log(以2为底)来防止溢出,并且能进行判断

if(a[n-1]*log(a[n-2])>M) { cout<<n-1<<endl; break; }
当然这种情况一是成立时用的,else呢?则应该用long long来暴力进行枚举进行判断是否会出界,假设用n当作下标,那么就是求a[n-2]a[n-1]
else { a[n]=1; for(int i=1;i<=a[n-1];i++)//求a[n-2]^a[n-1]; a[n]*=a[n-2]; if(a[n]>1e18) { cout<<n-1<<endl; break; } n++; }
牛客:猫猫与主人
本题要求猫的期望值与人的友善作比较,
1.要求人的友善>=猫的期望 也就是可以当作b,c为y轴,要求最高的y值,即答案
2.要求人的期望<=猫的友善 也就是a,d相作比较为x轴,要求枚举从左到右,也就是找到猫的点左上位置合法的人的友善值的最大值
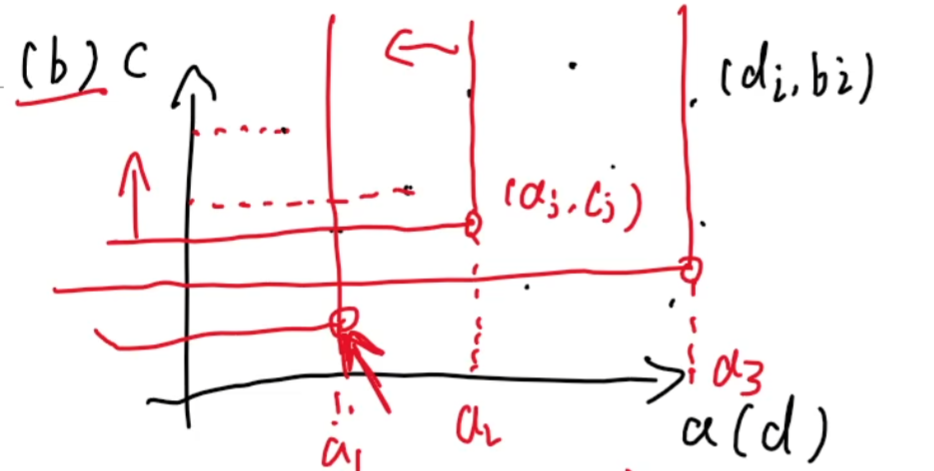
const int N=2e5+10; int n,m; int ans[N]; struct node { int x,y,id; }c[N],p[N]; bool cmp(node a,node b) { if(a.x!=b.x)return a.x<b.x; if(a.y!=b.y)return a.y<b.y; return a.id<b.id; } int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr); cin>>n>>m; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cin>>c[i].x; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cin>>c[i].y; for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)//主人的期望值必小于等于猫的友善 cin>>p[i].y; for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) cin>>p[i].x; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) c[i].id=i; sort(c+1,c+n+1,cmp); sort(p+1,p+m+1,cmp); int pos=1,maxx=-1; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)//maxx求出p的最大y轴的值 { //枚举的是猫,再枚举m个人 while(pos<=m&&p[pos].x<=c[i].x) { maxx=max(maxx,p[pos].y); pos++; } if(maxx>=c[i].y)ans[c[i].id]=maxx;//如果说人的友善大于猫的期望,那么成立 else ans[c[i].id]=-1;//否则不成立 } for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cout<<ans[i]<<' '; return 0; }
牛客:猫猫与数学
更相减损法
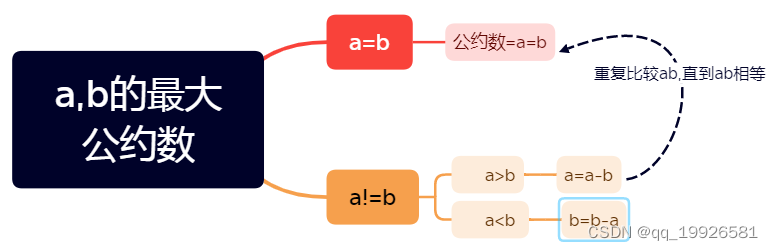
辗转相除法
return b?gcd(b,a%b):a;
本身gcd(a+c,b+c)!=1,可以有更相法=>gcd(a-b,a+c)!=1(由gcd(x,y)==gcd(x-y,x)(x>y)推导)
cf:Super-Permutation(打表教学)
bi是ai+1的前缀和,通过b数组%n后与a进行匹配观察是否相等进行打表找规律
打表代码(借鉴大佬)
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int main() { int n; cin >> n; vector<int> a(n); vector<int> idx(n); for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) a[i] = i + 1, idx[i] = i; do { vector<int> b = a; b[0] %= n; for(int i = 1; i < n; i++) b[i] = (b[i] + b[i - 1]) % n; sort(b.begin(), b.end()); if (b == idx) { for(auto x : a) cout << x << ' '; cout << endl; } }while(next_permutation(a.begin(), a.end())); }
正解
n为偶数可以构造,奇数不行,答案有多种情况
方法规律:(n)(n-1)(2)(n-3)(4)(n-5)(6)...(n-6)(5)(n-4)(3)(n-2)(1)
n放首位,1,3,5,7,倒着的2,4,6,8交错组成 || 倒着的1,3,5,7(多种情况均成立)
ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr); int T; cin >> T; while(T--) { int n; cin>>n; if (n==1) { cout << 1 << endl; continue; } if (n&1) { cout << -1 << endl; continue; } vector<int> a(n); a[0] = n; for(int i = 1, j = n - 1; i < n; i += 2, j -= 2) a[i] = j; for(int i = 2, j = 2; i < n; i += 2, j += 2) a[i] = j; for(auto x : a) cout << x << ' '; cout << endl; }
acwing: 字符串排序II
补充知识点:字母转换等...
1.isalpha()函数用来判断一个字符是否为字母,如果是字母则返回非零,否则返回零。
2.isalnum()函数用来判断一个字符是否为数字或字母,是则输出非零,否则输出零。
3.islower()函数用来判断一个字符是否为小写字母。
4.ispuuer()函数用来判断一个字符是否为大写字母。
5.C/C++库函数(tolower/toupper)实现字母的大小写转换
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef pair<char, int> PCI; vector<PCI>ans; int main() { string s; while(getline(cin,s)) { for(int i=0;i<s.size();i++) { char c=s[i]; if(isalpha(c)) ans.push_back({tolower(c),i}); } sort(ans.begin(),ans.end()); for(int i=0,k=0;i<s.size();i++) { char c=s[i]; if(isalpha(c)) cout<<s[ans[k++].second]; else cout<<s[i]; } cout<<endl; ans.clear(); } return 0; } //AFamousSayingMuchAdoAboutNothing //tolower(afamoussayingmuchadoaboutnothing) //AaaAAbcdFgghhiimMnNnoooosSttuuuy
L1-094 剪切粘贴 (字符串模拟)
使用计算机进行文本编辑时常见的功能是剪切功能(快捷键:Ctrl + X)。请实现一个简单的具有剪切和粘贴功能的文本编辑工具。
工具需要完成一系列剪切后粘贴的操作,每次操作分为两步:
- 剪切:给定需操作的起始位置和结束位置,将当前字符串中起始位置到结束位置部分的字符串放入剪贴板中,并删除当前字符串对应位置的内容。例如,当前字符串为
abcdefg,起始位置为 3,结束位置为 5,则剪贴操作后, 剪贴板内容为cde,操作后字符串变为abfg。字符串位置从 1 开始编号。 - 粘贴:给定插入位置的前后字符串,寻找到插入位置,将剪贴板内容插入到位置中,并清除剪贴板内容。例如,对于上面操作后的结果,给定插入位置前为
bf,插入位置后为g,则插入后变为abfcdeg。如找不到应该插入的位置,则直接将插入位置设置为字符串最后,仍然完成插入操作。查找字符串时区分大小写。
每次操作后的字符串即为新的当前字符串。在若干次操作后,请给出最后的编辑结果。
输入格式:
输入第一行是一个长度小于等于 200 的字符串 S,表示原始字符串。字符串只包含所有可见 ASCII 字符,不包含回车与空格。
第二行是一个正整数 N (1≤N≤100),表示要进行的操作次数。
接下来的 N 行,每行是两个数字和两个长度不大于 5 的不包含空格的非空字符串,前两个数字表示需要剪切的位置,后两个字符串表示插入位置前和后的字符串,用一个空格隔开。如果有多个可插入的位置,选择最靠近当前操作字符串开头的一个。
剪切的位置保证总是合法的。
输出格式:
输出一行,表示操作后的字符串。
输入样例:
AcrosstheGreatWall,wecanreacheverycornerintheworld
5
10 18 ery cor
32 40 , we
1 6 tW all
14 18 rnerr eache
1 1 e r输出样例:
he,allcornetrrwecaneacheveryGreatWintheworldAcross
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int n,l,r; int main() { string s,a,b; cin>>s; cin>>n; while(n--) { cin>>l>>r; string jian=s.substr(l-1,r-l+1); cin>>a>>b; s.erase(l-1,r-l+1); int pos=s.find(a+b); if(pos!=-1) { s.insert(pos+a.size(),jian); } else { s+=jian; } } cout<<s<<endl; return 0; }
Educational Codeforces Round 137 (Rated for Div. 2)C. Save the Magazines

DP做法:(状态模拟机)
void solve() { cin >> n; string s; cin >> s; s = " " + s; vector<int>a(n + 1); for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i]; vector<vector<int>>f(n + 1, vector<int>(3, 0)); for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { if (s[i] == '1') { f[i][1] = max(f[i - 1][0], f[i - 1][1]) + a[i]; //留给当前i的情况 f[i][0] = f[i - 1][0] + a[i - 1]; //留给i-1的情况 } else f[i][0] = max(f[i - 1][1], f[i - 1][0]);//只是转移max,与盖子无关 } cout << max(f[n][0], f[n][1]) << endl; }
void solve() { cin >> n; string s; std::vector<int>a(n + 1); cin >> s; s = " " + s; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i]; int ans = 0, last = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { if (s[i] == '0') { last = i; continue; } if (!last)continue; if (a[last] > a[i]) { swap(s[last], s[i]); last = i; } } for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) if (s[i] == '1') ans += a[i]; cout << ans << endl; }
Codeforces Round 827 (Div. 4)D. Coprime
要求元素gcd(s[i],s[j])==1,但是数组的长度2e5,暴力枚举铁定超时,观察ai的最大范围是1000,进行桶排序
我们只要枚举1000*1000来求出互质并且max(i+j)即可
void solve() { cin >> n; std::vector<int>a(n + 1), s(N); for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i]; for (int i = 1; i <= 1000; i++) s[i] = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) s[a[i]] = i; int res = -1; for (int i = 1; i <= 1000; i++) { if (!s[i])continue; for (int j = 1; j <= 1000; j++) { if (!s[j])continue; if (__gcd(i, j) == 1) { res = max(res, s[i] + s[j]); } } } cout << res << endl; }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号