11.19
软件设计 石家庄铁道大学信息学院
实验18:迭代器模式
本次实验属于模仿型实验,通过本次实验学生将掌握以下内容:
1、理解迭代器模式的动机,掌握该模式的结构;
2、能够利用迭代器模式解决实际问题。
[实验任务一]:JAVA和C++常见数据结构迭代器的使用
信1305班共44名同学,每名同学都有姓名,学号和年龄等属性,分别使用JAVA内置迭代器和C++中标准模板库(STL)实现对同学信息的遍历,要求按照学号从小到大和从大到小两种次序输出学生信息。
实验要求:
1. 搜集并掌握JAVA和C++中常见的数据结构和迭代器的使用方法,例如,vector, list, map和set等;
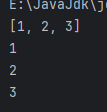
①、ArrayList1.java
package org.example.shiyanshiba;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class ArrayList1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
arrayList.add(1);
arrayList.add(2);
arrayList.add(3);
System.out.println(arrayList);
Iterator<Integer> iterator = arrayList.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
}
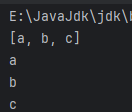
②、LinkedList.java
package org.example.shiyanshiba;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class LinkedList1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<String> linkedList = new LinkedList<>();
linkedList.add("a");
linkedList.add("b");
linkedList.add("c");
System.out.println(linkedList);
Iterator<String> iterator = linkedList.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
String element = iterator.next();
System.out.println(element);
}
}
}
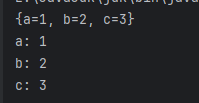
③、HashMap.java
package org.example.shiyanshiba;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class HashMap1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String,Integer> hashMap=new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put("a",1);
hashMap.put("b",2);
hashMap.put("c",3);
System.out.println(hashMap);
for(Map.Entry<String,Integer> entry:hashMap.entrySet()){
System.out.println(entry.getKey()+": "+entry.getValue());
}
}
}
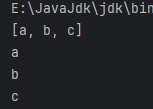
④、HashSet.java
package org.example.shiyanshiba;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class HashSet1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet<String> hashSet=new HashSet<>();
hashSet.add("a");
hashSet.add("b");
hashSet.add("c");
System.out.println(hashSet);
Iterator<String> iterator=hashSet.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
String element=iterator.next();
System.out.println(element);
}
}
}
2. 提交源代码;
①、Student.java
package org.example.shiyanshiba;
public class Student implements Comparable<Student> {
private int studentid;
private String name;
private int age;
public Student(int studentid, String name, int age) {
this.studentid = studentid;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Student o) {
if (this.studentid < o.studentid) {
return -1;
} else if (this.studentid > o.studentid) {
return 1;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "姓名:"+this.name+",学号:"+this.studentid+",年龄:"+this.age;
}
}
②、Student2.java
package org.example.shiyanshiba;
public class Student2 implements Comparable<Student2> {
private int studentid;
private String name;
private int age;
public Student2(int studentid, String name, int age) {
super();
this.studentid = studentid;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Student2 o) {
if (this.studentid < o.studentid) {
return -1;
} else if (this.studentid > o.studentid) {
return 1;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "姓名:"+this.name+",学号:"+this.studentid+",年龄:"+this.age;
}
}
③、Client.java
package org.example.shiyanshiba;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1=new Student(20223730,"陈志峰",21);
Student s2=new Student(20223731,"叶振钧",21);
Student s3=new Student(20223732,"王晓菲",21);
Student s4=new Student(20223733,"梁家显",21);
Student s5=new Student(20223734,"李文举",21);
Student s6=new Student(20223735,"陈庆振",20);
Student2 s7=new Student2(20223730,"陈志峰",21);
Student2 s8=new Student2(20223731,"叶振钧",21);
Student2 s9=new Student2(20223732,"王晓菲",21);
Student2 s10=new Student2(20223733,"梁家显",21);
Student2 s11=new Student2(20223734,"李文举",21);
Student2 s12=new Student2(20223735,"陈庆振",20);
List<Student> list=new ArrayList<>();
list.add(s1);
list.add(s2);
list.add(s3);
list.add(s4);
list.add(s5);
list.add(s6);
Collections.sort(list);
System.out.println("学号按从大到小输出:");
for(Student student:list){
System.out.println(student.toString());
}
System.out.println("``````````````````````");
List<Student2> list2=new ArrayList<>();
list2.add(s7);
list2.add(s8);
list2.add(s9);
list2.add(s10);
list2.add(s11);
list2.add(s12);
Collections.sort(list2);
System.out.println("年龄从大到小输出:");
for(Student2 student:list2){
System.out.println(student.toString());
}
System.out.println("``````````````````````");
}
}
3. 注意编程规范。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号