树链剖分
树链剖分
概念
-> 对于节点 u
- 重儿子:
size最大的儿子 - 轻儿子:除开重儿子的儿子
- 重边:连接
u和 重儿子 的边 - 轻边:连接
u和 轻儿子 的边 - 重子树:重儿子 所在的子树
- 轻子树:轻儿子 所在的子树
算法
-> 链 的选择
优先选择 重儿子
明确对于节点 u,若选择它儿子中的一个 v,则后续查询次数为 size[u]-size[v]
我们要使这一坨最小,就是让 size[v] 最大
记法与约定
记节点 u 的重儿子为 hson[u]
节点 u 的轻儿子是个集合,记为 lson[u]
.
复杂度
引理
Proof
\(\blacksquare\)
取极限情况,仅有两个子节点
其中之一肯定是轻儿子,记为 \(\text v\in \text{lson[u]}\)
有:
又有:
结合得:
将 size[v] 看成变量,解得:
得证
\(\square\)
复杂度
树链剖分的均摊复杂度为 $\Omicron(\log_2 n) $
Proof
\(\blacksquare\)
从一条重链跳至另一条,一定要经过一条轻边
取极限(u 为根节点)
size 最小为 \(1\) (叶节点)
从 \(n\) 到 \(1\) ,每次缩为上次的 \(\frac12\) ,至多 \(\Omicron(\log_2 n)\),就到了 \(1\)
\(\therefore\) 至多经过 \(\Omicron(\log_2 n)\) 条轻边
而此时经过的重链数就是:\(\Omicron(\log_2 n) + 1\),即 \(\Omicron(\log_2 n)\)
得证
\(\square\)
例题
P3384 【模板】重链剖分 / 树链剖分
题目描述
题目描述
如题,已知一棵包含 \(N\) 个结点的树(连通且无环),每个节点上包含一个数值,需要支持以下操作:
-
1 x y z,表示将树从 \(x\) 到 \(y\) 结点最短路径上所有节点的值都加上 \(z\)。 -
2 x y,表示求树从 \(x\) 到 \(y\) 结点最短路径上所有节点的值之和。 -
3 x z,表示将以 \(x\) 为根节点的子树内所有节点值都加上 \(z\)。 -
4 x,表示求以 \(x\) 为根节点的子树内所有节点值之和。
输入格式
第一行包含 \(4\) 个正整数 \(N,M,R,P\),分别表示树的结点个数、操作个数、根节点序号和取模数(即所有的输出结果均对此取模)。
接下来一行包含 \(N\) 个非负整数,分别依次表示各个节点上初始的数值。
接下来 \(N-1\) 行每行包含两个整数 \(x,y\),表示点 \(x\) 和点 \(y\) 之间连有一条边(保证无环且连通)。
接下来 \(M\) 行每行包含若干个正整数,每行表示一个操作。
输出格式
输出包含若干行,分别依次表示每个操作 \(2\) 或操作 \(4\) 所得的结果(对 \(P\) 取模)。
输入输出样例 #1
输入 #1
5 5 2 24
7 3 7 8 0
1 2
1 5
3 1
4 1
3 4 2
3 2 2
4 5
1 5 1 3
2 1 3
输出 #1
2
21
说明/提示
【数据规模】
对于 \(30\%\) 的数据: \(1 \leq N \leq 10\),\(1 \leq M \leq 10\);
对于 \(70\%\) 的数据: \(1 \leq N \leq {10}^3\),\(1 \leq M \leq {10}^3\);
对于 \(100\%\) 的数据: \(1\le N \leq {10}^5\),\(1\le M \leq {10}^5\),\(1\le R\le N\),\(1\le P \le 2^{30}\)。所有输入的数均在 int 范围内。
【样例说明】
树的结构如下:
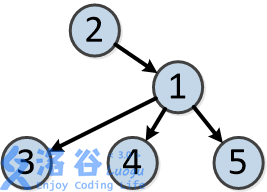
各个操作如下:
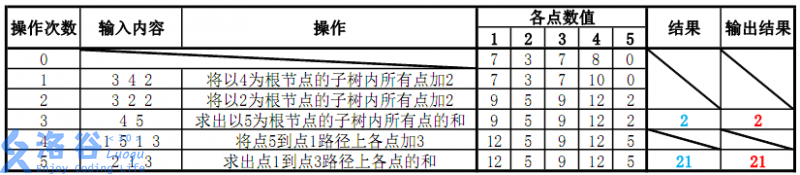
故输出应依次为 \(2\) 和 \(21\)。
板子
View Code
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define mod %
#define mode %=
using lf = double;
using ll = long long;
using ull = unsigned long long;
const int maxn = 1e5 + 5;
int wealth[maxn];
int n, m, root, p; // about the question
namespace TREE_CHAIN {
vector<int> adj[maxn];
int depth[maxn], father[maxn], size[maxn];
int dfn[maxn], out[maxn], dfs[maxn], cnt;
int heavy_son[maxn], top[maxn]; // tree chain
struct segment_tree{
ll tree[maxn << 2];
ll lazy_tag[maxn << 2];
ll ls(int id) {return id << 1;}
ll rs(int id) {return id << 1 | 1;}
void maintain(int id) {
return tree[id] = (tree[ls(id)] + tree[rs(id)]) mod p, void();
}
void build(int id, int left, int right) {
lazy_tag[id] = 0;
if (left == right) {
tree[id] = wealth[dfs[left]];
return ;
}
int mid = (left + right) >> 1;
build(ls(id), left, mid);
build(rs(id), mid + 1, right);
maintain(id);
}
void addtag(ll d, int id, int left, int right) {
lazy_tag[id] += d;
tree[id] = (tree[id] + d * (right - left + 1) mod p + p) mod p;
}
void pushdown(int id, int left, int right) {
if (lazy_tag[id]) {
ll mid = (left + right) >> 1;
addtag(lazy_tag[id], ls(id), left, mid);
addtag(lazy_tag[id], rs(id), mid + 1, right);
lazy_tag[id] = 0;
}
}
void update(int L, int R, ll d, int id = 1, int left = 1, int right = n) {
if (L <= left and right <= R) {
addtag(d, id, left, right);
return;
}
pushdown(id, left, right);
ll mid = (left + right) >> 1;
if (L <= mid) update(L, R, d, ls(id), left, mid);
if (R > mid) update(L, R, d, rs(id), mid + 1, right);
maintain(id);
}
ll query(int L, int R, int id = 1, int left = 1, int right = n) {
if (L <= left and right <= R)
return tree[id];
pushdown(id, left, right);
ll mid = (left + right) >> 1;
ll res = 0;
if (L <= mid) res = ((res + query(L, R, ls(id), left, mid) mod p) + p) mod p;
if (R > mid) res = ((res + query(L, R, rs(id), mid + 1, right) mod p) + p) mod p;
return res;
}
} st;
void all_init() {
st.build(1, 1, n);
}
void init(int u, int fath, int dep) {
size[u] = 1;
father[u] = fath;
depth[u] = dep;
for (int v : adj[u]) {
if (v == fath) continue;
init(v, u, dep + 1);
size[u] += size[v];
if (size[v] > size[heavy_son[u]]) heavy_son[u] = v;
}
}
void another_init(int u, int fath, int head) {
top[u] = head;
dfn[u] = ++cnt;
dfs[cnt] = u;
if (heavy_son[u]) another_init(heavy_son[u], u, head);
for (int v : adj[u]) {
if (v == fath or v == heavy_son[u]) continue;
another_init(v, u, v);
}
out[u] = cnt;
}
void chain_update(int x, int y, ll delta) {
while (top[x] != top[y]) {
if (depth[top[x]] < depth[top[y]]) swap(x, y);
st.update(dfn[top[x]], dfn[x], delta);// segment tree
x = father[top[x]];
}
if (depth[x] > depth[y]) swap(x, y);
st.update(dfn[x], dfn[y], delta);
}
ll chain_query(int x, int y) {
ll res = 0;
while (top[x] != top[y]) {
if (depth[top[x]] < depth[top[y]]) swap(x, y);
res = ((res + st.query(dfn[top[x]], dfn[x])) mod p + p) mod p;// segment tree
x = father[top[x]];
}
if (depth[x] > depth[y]) swap(x, y);
res = ((res + st.query(dfn[x], dfn[y])) mod p + p) mod p;
return res;
}
}
using namespace TREE_CHAIN;
void solve() {
cin >> n >> m >> root >> p;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> wealth[i];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int u, v;
cin >> u >> v;
adj[u].push_back(v);
adj[v].push_back(u);
}
init(root, 0, 1);
another_init(root, 0, root);
all_init();
while (m--) {
int opt, x, y;
ll delta;
cin >> opt >> x;
switch (opt) {
case 1:cin >> y >> delta; chain_update(x, y, delta); break;
case 2:cin >> y; cout << chain_query(x, y) mod p << "\n"; break;
case 3:cin >> delta; st.update(dfn[x], out[x], delta); break;
case 4:cout << st.query(dfn[x], out[x]) mod p << "\n"; break;
default:break;
}
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
// freopen("T1.in", "r", stdin);
// freopen("T1.out", "w", stdout);
int T = 1;
// cin >> T;
while (T--) solve();
return 0;
}
P3038 [USACO11DEC] Grass Planting G
题目描述
题目描述
给出一棵有 \(n\) 个节点的树,有 \(m\) 个如下所示的操作:
-
将两个节点之间的路径上的边的权值均加一。
-
查询两个节点之间的那一条边的权值,保证两个节点直接相连。
初始边权均为 \(0\)。
输入格式
第一行两个整数 \(n,m\),含义如上。
接下来 \(n-1\) 行,每行两个整数 \(u,v\),表示 \(u,v\) 之间有一条边。
接下来 \(m\) 行,每行格式为 op u v,\(op=\texttt{P}\) 代表第一个操作,\(op=\texttt{Q}\) 代表第二个操作。
输出格式
若干行。对于每个查询操作,输出一行整数,代表查询的答案。
输入输出样例 #1
输入 #1
4 6
1 4
2 4
3 4
P 2 3
P 1 3
Q 3 4
P 1 4
Q 2 4
Q 1 4
输出 #1
2
1
2
说明/提示
对于 \(100\%\) 的数据,\(2\le n\le 10^5\),\(1\le m\le 10^5\)。
稍微改一下:
void chain_update(int x, int y, ll delta) {
while (top[x] != top[y]) {
if (depth[top[x]] < depth[top[y]]) swap(x, y);
st.update(dfn[top[x]], dfn[x], delta);// segment tree
x = father[top[x]];
}
if (depth[x] > depth[y]) swap(x, y);
st.update(dfn[x], dfn[y], delta);
}
\(\ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \dArr \dArr \dArr\)
void chain_update(int x, int y, ll delta) {
while (top[x] != top[y]) {
if (depth[top[x]] < depth[top[y]]) swap(x, y);
st.update(dfn[top[x]], dfn[x], delta);// segment tree
x = father[top[x]];
}
if (dfn[x] > dfn[y]) swap(x, y);
if (dfn[x] < dfn[y]) st.update(dfn[x] + 1, dfn[y], delta);
}
chain_query 同理
View Code
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define mod %
#define mode %=
using lf = double;
using ll = long long;
using ull = unsigned long long;
const int maxn = 1e5 + 5;
int wealth[maxn];
int n, m, root = 1, p; // about the question
namespace TREE_CHAIN {
vector<int> adj[maxn];
int depth[maxn], father[maxn], size[maxn];
int dfn[maxn], out[maxn], dfs[maxn], cnt;
int heavy_son[maxn], top[maxn]; // tree chain
struct segment_tree{
ll tree[maxn << 2];
ll lazy_tag[maxn << 2];
ll ls(int id) {return id << 1;}
ll rs(int id) {return id << 1 | 1;}
void maintain(int id) {
return tree[id] = (tree[ls(id)] + tree[rs(id)]), void();
}
void build(int id, int left, int right) {
lazy_tag[id] = 0;
if (left == right) {
tree[id] = wealth[dfs[left]];
return ;
}
int mid = (left + right) >> 1;
build(ls(id), left, mid);
build(rs(id), mid + 1, right);
maintain(id);
}
void addtag(ll d, int id, int left, int right) {
lazy_tag[id] += d;
tree[id] = (tree[id] + d * (right - left + 1));
}
void pushdown(int id, int left, int right) {
if (lazy_tag[id]) {
ll mid = (left + right) >> 1;
addtag(lazy_tag[id], ls(id), left, mid);
addtag(lazy_tag[id], rs(id), mid + 1, right);
lazy_tag[id] = 0;
}
}
void update(int L, int R, ll d, int id = 1, int left = 1, int right = n) {
if (L <= left and right <= R) {
addtag(d, id, left, right);
return;
}
pushdown(id, left, right);
ll mid = (left + right) >> 1;
if (L <= mid) update(L, R, d, ls(id), left, mid);
if (R > mid) update(L, R, d, rs(id), mid + 1, right);
maintain(id);
}
ll query(int L, int R, int id = 1, int left = 1, int right = n) {
if (L <= left and right <= R)
return tree[id];
pushdown(id, left, right);
ll mid = (left + right) >> 1;
ll res = 0;
if (L <= mid) res = ((res + query(L, R, ls(id), left, mid)));
if (R > mid) res = ((res + query(L, R, rs(id), mid + 1, right)));
return res;
}
} st;
void all_init() {
st.build(1, 1, n);
}
void init(int u, int fath, int dep) {
size[u] = 1;
father[u] = fath;
depth[u] = dep;
for (int v : adj[u]) {
if (v == fath) continue;
init(v, u, dep + 1);
size[u] += size[v];
if (size[v] > size[heavy_son[u]]) heavy_son[u] = v;
}
}
void another_init(int u, int fath, int head) {
top[u] = head;
dfn[u] = ++cnt;
dfs[cnt] = u;
if (heavy_son[u]) another_init(heavy_son[u], u, head);
for (int v : adj[u]) {
if (v == fath or v == heavy_son[u]) continue;
another_init(v, u, v);
}
out[u] = cnt;
}
void chain_update(int x, int y, ll delta) {
while (top[x] != top[y]) {
if (depth[top[x]] < depth[top[y]]) swap(x, y);
st.update(dfn[top[x]], dfn[x], delta);// segment tree
x = father[top[x]];
}
if (dfn[x] > dfn[y]) swap(x, y);
if (dfn[x] < dfn[y]) st.update(dfn[x] + 1, dfn[y], delta);
}
ll chain_query(int x, int y) {
ll res = 0;
while (top[x] != top[y]) {
if (depth[top[x]] < depth[top[y]]) swap(x, y);
res = ((res + st.query(dfn[top[x]], dfn[x])));// segment tree
x = father[top[x]];
}
if (dfn[x] > dfn[y]) swap(x, y);
if (dfn[x] < dfn[y]) res = ((res + st.query(dfn[x] + 1, dfn[y])));
return res;
}
}
using namespace TREE_CHAIN;
void solve() {
cin >> n >> m;
// for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> wealth[i];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int u, v;
cin >> u >> v;
adj[u].push_back(v);
adj[v].push_back(u);
}
init(root, 0, 1);
another_init(root, 0, root);
all_init();
while (m--) {
char opt;
int x , y;
cin >> opt >> x >> y;
if (opt == 'P') chain_update(x, y, 1);
else cout << chain_query(x, y) << "\n";
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
// freopen("T1.in", "r", stdin);
// freopen("T1.out", "w", stdout);
int T = 1;
// cin >> T;
while (T--) solve();
return 0;
}
P3258 [JLOI2014] 松鼠的新家
why wei ni 打不出来
题目描述
题目描述
松鼠的新家是一棵树,前几天刚刚装修了新家,新家有 \(n\) 个房间,并且有 \(n-1\) 根树枝连接,每个房间都可以相互到达,且俩个房间之间的路线都是唯一的。天哪,他居然真的住在“树”上。
松鼠想邀请****前来参观,并且还指定一份参观指南,他希望维尼能够按照他的指南顺序,先去 \(a_1\),再去 \(a_2\),……,最后到 \(a_n\),去参观新家。可是这样会导致重复走很多房间,懒惰的维尼不停地推辞。可是松鼠告诉他,每走到一个房间,他就可以从房间拿一块糖果吃。
维尼是个馋家伙,立马就答应了。现在松鼠希望知道为了保证维尼有糖果吃,他需要在每一个房间各放至少多少个糖果。
因为松鼠参观指南上的最后一个房间 \(a_n\) 是餐厅,餐厅里他准备了丰盛的大餐,所以当维尼在参观的最后到达餐厅时就不需要再拿糖果吃了。
输入格式
第一行一个正整数 \(n\),表示房间个数。第二行 \(n\) 个正整数,依次描述 \(a_1, a_2,\cdots,a_n\)。
接下来 \(n-1\) 行,每行两个正整数 \(x,y\),表示标号 \(x\) 和 \(y\) 的两个房间之间有树枝相连。
输出格式
一共 \(n\) 行,第 \(i\) 行输出标号为 \(i\) 的房间至少需要放多少个糖果,才能让维尼有糖果吃。
输入输出样例 #1
输入 #1
5
1 4 5 3 2
1 2
2 4
2 3
4 5
输出 #1
1
2
1
2
1
说明/提示
对于全部的数据,\(2 \le n \le 3 \times 10^5\),\(1 \le a_i \le n\)。
肥肠滴煎蛋
细节看代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define mod %
#define mode %=
using lf = double;
using ll = long long;
using ull = unsigned long long;
const int maxn = 6e5 + 5;
int position[maxn];
int n, m, root = 1, p; // about the question
namespace TREE_CHAIN {
vector<int> adj[maxn];
int depth[maxn], father[maxn], size[maxn];
int dfn[maxn], out[maxn], dfs[maxn], cnt;
int heavy_son[maxn], top[maxn]; // tree chain
struct segment_tree{
ll tree[maxn << 2];
ll lazy_tag[maxn << 2];
ll ls(int id) {return id << 1;}
ll rs(int id) {return id << 1 | 1;}
void maintain(int id) {
return tree[id] = tree[ls(id)] + tree[rs(id)], void();
}
void build(int id, int left, int right) {
lazy_tag[id] = 0;
if (left == right) {
tree[id] = 0;
return ;
}
int mid = (left + right) >> 1;
build(ls(id), left, mid);
build(rs(id), mid + 1, right);
maintain(id);
}
void addtag(ll d, int id, int left, int right) {
lazy_tag[id] += d;
tree[id] = tree[id] + d * (right - left + 1);
}
void pushdown(int id, int left, int right) {
if (lazy_tag[id]) {
ll mid = (left + right) >> 1;
addtag(lazy_tag[id], ls(id), left, mid);
addtag(lazy_tag[id], rs(id), mid + 1, right);
lazy_tag[id] = 0;
}
}
void update(int L, int R, ll d, int id = 1, int left = 1, int right = n) {
if (L <= left and right <= R) {
addtag(d, id, left, right);
return;
}
pushdown(id, left, right);
ll mid = (left + right) >> 1;
if (L <= mid) update(L, R, d, ls(id), left, mid);
if (R > mid) update(L, R, d, rs(id), mid + 1, right);
maintain(id);
}
ll query(int L, int R, int id = 1, int left = 1, int right = n) {
if (L <= left and right <= R)
return tree[id];
pushdown(id, left, right);
ll mid = (left + right) >> 1;
ll res = 0;
if (L <= mid) res = res + query(L, R, ls(id), left, mid);
if (R > mid) res = res + query(L, R, rs(id), mid + 1, right);
return res;
}
} st;
void all_init() {
st.build(1, 1, n);
}
void init(int u, int fath, int dep) {
size[u] = 1;
father[u] = fath;
depth[u] = dep;
for (int v : adj[u]) {
if (v == fath) continue;
init(v, u, dep + 1);
size[u] += size[v];
if (size[v] > size[heavy_son[u]]) heavy_son[u] = v;
}
}
void another_init(int u, int fath, int head) {
top[u] = head;
dfn[u] = ++cnt;
dfs[cnt] = u;
if (heavy_son[u]) another_init(heavy_son[u], u, head);
for (int v : adj[u]) {
if (v == fath or v == heavy_son[u]) continue;
another_init(v, u, v);
}
out[u] = cnt;
}
void chain_update(int x, int y, ll delta) {
while (top[x] != top[y]) {
if (depth[top[x]] < depth[top[y]]) swap(x, y);
st.update(dfn[top[x]], dfn[x], delta);// segment tree
x = father[top[x]];
}
if (depth[x] > depth[y]) swap(x, y);
st.update(dfn[x], dfn[y], delta);
}
ll chain_query(int x, int y) {
ll res = 0;
while (top[x] != top[y]) {
if (depth[top[x]] < depth[top[y]]) swap(x, y);
res = res + st.query(dfn[top[x]], dfn[x]);// segment tree
x = father[top[x]];
}
if (depth[x] > depth[y]) swap(x, y);
res = res + st.query(dfn[x], dfn[y]);
return res;
}
}
using namespace TREE_CHAIN;
void solve() {
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> position[i];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int u, v;
cin >> u >> v;
adj[u].push_back(v);
adj[v].push_back(u);
}
init(root, 0, 1);
another_init(root, 0, root);
all_init();
chain_update(position[1], position[2], 1);
for (int i = 2; i <= n - 1; i++) {
chain_update(position[i], position[i + 1], 1);
st.update(dfn[position[i]], dfn[position[i]], -1);
}
st.update(dfn[position[n]], dfn[position[n]], -1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cout << st.query(dfn[i], dfn[i]) << "\n";
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
// freopen("T1.in", "r", stdin);
// freopen("T1.out", "w", stdout);
int T = 1;
// cin >> T;
while (T--) solve();
return 0;
}
P2486 [SDOI2011] 染色
题目描述
题目描述
给定一棵 \(n\) 个节点的无根树,共有 \(m\) 个操作,操作分为两种:
- 将节点 \(a\) 到节点 \(b\) 的路径上的所有点(包括 \(a\) 和 \(b\))都染成颜色 \(c\)。
- 询问节点 \(a\) 到节点 \(b\) 的路径上的颜色段数量。
颜色段的定义是极长的连续相同颜色被认为是一段。例如 112221 由三段组成:11、222、1。
输入格式
输入的第一行是用空格隔开的两个整数,分别代表树的节点个数 \(n\) 和操作个数 \(m\)。
第二行有 \(n\) 个用空格隔开的整数,第 \(i\) 个整数 \(w_i\) 代表结点 \(i\) 的初始颜色。
第 \(3\) 到第 \((n + 1)\) 行,每行两个用空格隔开的整数 \(u, v\),代表树上存在一条连结节点 \(u\) 和节点 \(v\) 的边。
第 \((n + 2)\) 到第 \((n + m + 1)\) 行,每行描述一个操作,其格式为:
每行首先有一个字符 \(op\),代表本次操作的类型。
- 若 \(op\) 为
C,则代表本次操作是一次染色操作,在一个空格后有三个用空格隔开的整数 \(a, b, c\),代表将 \(a\) 到 \(b\) 的路径上所有点都染成颜色 \(c\)。 - 若 \(op\) 为
Q,则代表本次操作是一次查询操作,在一个空格后有两个用空格隔开的整数 \(a, b\),表示查询 \(a\) 到 \(b\) 路径上的颜色段数量。
输出格式
对于每次查询操作,输出一行一个整数代表答案。
输入输出样例 #1
输入 #1
6 5
2 2 1 2 1 1
1 2
1 3
2 4
2 5
2 6
Q 3 5
C 2 1 1
Q 3 5
C 5 1 2
Q 3 5
输出 #1
3
1
2
说明/提示
数据规模与约定
对于 \(100\%\) 的数据,\(1 \leq n, m \leq 10^5\),\(1 \leq w_i, c \leq 10^9\),\(1 \leq a, b, u, v \leq n\),\(op\) 一定为 C 或 Q,保证给出的图是一棵树。
除原数据外,还存在一组不计分的 hack 数据。
注意翻转
因为方向不同,所以说就需要进行翻转
考虑两种情况 (对 x,y)
depth[x] < depth[y]:此时仅需要翻转x的那条链
其余同理
调的有点崩溃,所以有些变量名很猎奇
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define mod %
#define mode %=
using lf = double;
using ll = long long;
using ull = unsigned long long;
const int maxn = 1e5 + 5;
int wealth[maxn];
int n, m, root, p; // about the question
namespace TREE_CHAIN {
vector<int> adj[maxn];
int depth[maxn], father[maxn], size[maxn];
int dfn[maxn], out[maxn], dfs[maxn], cnt;
int heavy_son[maxn], top[maxn]; // tree chain
struct node {
int lc, rc;
int ans;
node() = default;
node(int qwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnm, int asdfghjklqwertyuiopzxcvbnm, int zxcvbnmqwertyuiopasdfghjkl):
lc(qwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnm),
rc(asdfghjklqwertyuiopzxcvbnm),
ans(zxcvbnmqwertyuiopasdfghjkl) {}
node operator+(const node &ano) {
if (this->ans == 0) return ano; // notice
if (ano.ans == 0) return *this;
node res(0, 0, 0);
res.ans = this->ans + ano.ans - (this->rc == ano.lc);
res.lc = this->lc;
res.rc = ano.rc;
return res;
}
};
class segment_tree {
private:
public:
node tree[maxn << 2];
ll lazy_tag[maxn << 2];
int ls(int id) {
return id << 1;
}
int rs(int id) {
return id << 1 | 1;
}
void maintain(int id) {
return tree[id] = tree[ls(id)] + tree[rs(id)], void();
}
void build(int id, int left, int right) {
lazy_tag[id] = 0;
if (left == right) {
tree[id] = {wealth[dfs[left]], wealth[dfs[left]], 1};
return ;
}
int mid = (left + right) >> 1;
build(ls(id), left, mid);
build(rs(id), mid + 1, right);
maintain(id);
}
void addtag(ll d, int id, int left, int right) {
lazy_tag[id] = d;
tree[id] = {d, d, 1};
}
void pushdown(int id, int left, int right) {
if (lazy_tag[id]) {
int mid = (left + right) >> 1;
addtag(lazy_tag[id], ls(id), left, mid);
addtag(lazy_tag[id], rs(id), mid + 1, right);
lazy_tag[id] = 0;
}
}
void update(int L, int R, ll d, int id = 1, int left = 1, int right = n) {
if (L <= left and right <= R) {
addtag(d, id, left, right);
return;
}
pushdown(id, left, right);
ll mid = (left + right) >> 1;
if (L <= mid) update(L, R, d, ls(id), left, mid);
if (R > mid) update(L, R, d, rs(id), mid + 1, right);
maintain(id);
}
node query(int L, int R, int id = 1, int left = 1, int right = n) {
if (L <= left and right <= R)
return tree[id];
pushdown(id, left, right);
ll mid = (left + right) >> 1;
node res(0, 0, 0);
if (L <= mid) res = res + query(L, R, ls(id), left, mid);
if (R > mid) res = res + query(L, R, rs(id), mid + 1, right);
return res;
}
} st;
void all_init() {
st.build(1, 1, n);
}
void init(int u, int fath, int dep) {
size[u] = 1;
father[u] = fath;
depth[u] = dep;
for (int v : adj[u]) {
if (v == fath) continue;
init(v, u, dep + 1);
size[u] += size[v];
if (size[v] > size[heavy_son[u]]) heavy_son[u] = v;
}
}
void another_init(int u, int fath, int head) {
top[u] = head;
dfn[u] = ++cnt;
dfs[cnt] = u;
if (heavy_son[u]) another_init(heavy_son[u], u, head);
for (int v : adj[u]) {
if (v == fath or v == heavy_son[u]) continue;
another_init(v, u, v);
}
out[u] = cnt;
}
void chain_update(int x, int y, ll delta) {
while (top[x] != top[y]) {
if (depth[top[x]] < depth[top[y]]) swap(x, y);
st.update(dfn[top[x]], dfn[x], delta);// segment tree
x = father[top[x]];
}
if (depth[x] > depth[y]) swap(x, y);
st.update(dfn[x], dfn[y], delta);
}
ll chain_query(int x, int y) {
node resx(0, 0, 0), resy(0, 0, 0);
while (top[x] != top[y]) {
if (depth[top[x]] < depth[top[y]]) {
node res = st.query(dfn[top[y]], dfn[y]);
resy = res + resy;
y = father[top[y]];
} else {
node res = st.query(dfn[top[x]], dfn[x]);
resx = res + resx;
x = father[top[x]];
}
}
if (depth[x] < depth[y]) {
swap(resx.lc, resx.rc);
node res = st.query(dfn[x], dfn[y]);
return (resx + res + resy).ans;
} else {
swap(resy.lc, resy.rc);
node res = st.query(dfn[y], dfn[x]);
return (resy + res + resx).ans;
}
int qwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnm1234567890_0987654321 = 0;
return qwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnm1234567890_0987654321; // 've gone mmaadd
}
}
using namespace TREE_CHAIN;
void solve() {
cin >> n >> m;
root = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> wealth[i];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int u, v;
cin >> u >> v;
adj[u].push_back(v);
adj[v].push_back(u);
}
init(root, 0, 1);
another_init(root, 0, root);
all_init();
while (m--) {
char opt;
cin >> opt;
if (opt == 'C') {
int a, b, c;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
chain_update(a, b, c);
} else {
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
cout << chain_query(a, b) << "\n";
}
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
// freopen("T1.in", "r", stdin);
// freopen("T1.out", "w", stdout);
int T = 1;
// cin >> T;
while (T--) solve();
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号