Linux write系统调用流程
源码
.global _start
.text
_start:
mov $1,%rax # 1代表 x86_64架构下 write系统调用编号
mov $1,%rdi # 1代表 标准输出
mov $msg,%rsi # 输出的字符串
mov $len,%rdx # 字符串长度
syscall # 执行系统调用 write(1,msg,len)
mov $60,%rax # exit系统调用编号
xor %rdi,%rdi # 参数清空
syscall # 执行系统调用 exit(0)
.data:
msg:
.ascii "hello world\n"
len = . - msg
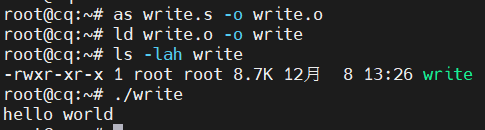
编译执行
as write.s -o write.o
ld write.o -o write
./write
流程分析
我使用的linux源码版本是6.1.115,在arch/x86/entry/entry_64.S中介绍了系统调用时寄存器的状态。syscall使得内核从用户态切换到内核态并执行对应的系统调用。
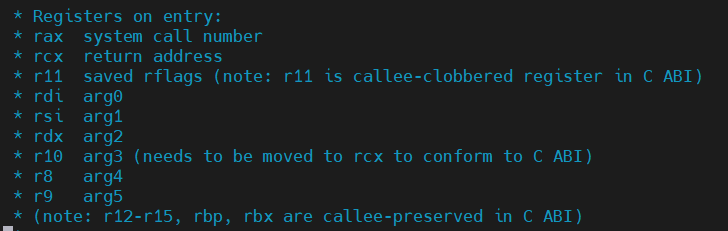
- rax 系统调用编号
- rdi 系统调用第一个参数
- rsi 系统调用第二个参数
- rdx 系统调用第三个参数
- r10 系统调用第四个参数
- r8 系统调用第五个参数
- r9 系统调用第六个参数
syscall_init
在内核系统初始化时cpu_init --> syscall_init(arch/x86/kernel/cpu/common.c)会指定系统调用入口地址。
void syscall_init(void)
{
wrmsr(MSR_STAR, 0, (__USER32_CS << 16) | __KERNEL_CS);
// 注册系统调用入口
// 因为MSR_LSTAR 是syscall入口地址寄存器
// 所以系统调用的入口都是 entry_SYSCALL_64
wrmsrl(MSR_LSTAR, (unsigned long)entry_SYSCALL_64);
......
}
entry_SYSCALL_64
**arch/x86/entry/entry_64.S**
SYM_CODE_START(entry_SYSCALL_64) #系统调用入口
......
SYM_INNER_LABEL(entry_SYSCALL_64_safe_stack, SYM_L_GLOBAL)
......
SYM_INNER_LABEL(entry_SYSCALL_64_after_hwframe, SYM_L_GLOBAL)
pushq %rax /* pt_regs->orig_ax */
PUSH_AND_CLEAR_REGS rax=$-ENOSYS
/* IRQs are off. */
movq %rsp, %rdi
/* Sign extend the lower 32bit as syscall numbers are treated as int */
movslq %eax, %rsi
/* clobbers %rax, make sure it is after saving the syscall nr */
call do_syscall_64 /* returns with IRQs disabled */
......
do_syscall_64
当进程调用write系统函数时,会通过syscall 进入entry_64.S中并继续调用do_syscall_64。
arch/x86/entry/common.c
__visible noinstr void do_syscall_64(struct pt_regs *regs, int nr)
{
add_random_kstack_offset();
nr = syscall_enter_from_user_mode(regs, nr);
instrumentation_begin();
if (!do_syscall_x64(regs, nr) && !do_syscall_x32(regs, nr) && nr != -1) {
/* Invalid system call, but still a system call. */
regs->ax = __x64_sys_ni_syscall(regs);
}
instrumentation_end();
syscall_exit_to_user_mode(regs);
}
do_syscall_x64
接着调用do_syscall_x64,arch/x86/entry/common.c
static __always_inline bool do_syscall_x64(struct pt_regs *regs, int nr)
{
unsigned int unr = nr;
if (likely(unr < NR_syscalls)) {
unr = array_index_nospec(unr, NR_syscalls);
regs->ax = x64_sys_call(regs, unr);
return true;
}
return false;
}
NR_syscalls
NR_syscalls 系统调用数量 由内核自动生成
arch/x86/include/generated/uapi/asm/unistd_64.h
define __NR_syscalls 451
arch/x86/include/unistd.h
define NR_syscalls (__NR_syscalls)
x64_sys_call
然后调用x64_sys_call, arch/x86/entry/syscall_64.c
#define __SYSCALL(nr, sym) extern long __x64_##sym(const struct pt_regs *);
#include <asm/syscalls_64.h>
#undef __SYSCALL
#define __SYSCALL(nr, sym) __x64_##sym,
const sys_call_ptr_t sys_call_table[] = {
#include <asm/syscalls_64.h>
};
#undef __SYSCALL
#define __SYSCALL(nr, sym) case nr: return __x64_##sym(regs);
long x64_sys_call(const struct pt_regs *regs, unsigned int nr)
{
switch (nr) {
#include <asm/syscalls_64.h>
default: return __x64_sys_ni_syscall(regs);
}
};
展开后,对于write()最终会执行 __x64_sys_write(regs)
系统调用映射
在arch/x86/entry/syscalls/syscall_64.tbl中系统调用之间的映射关系
# 64-bit system call numbers and entry vectors
# The format is:
# <number> <abi> <name> <entry point>
# The __x64_sys_*() stubs are created on-the-fly for sys_*() system calls
# The abi is "common", "64" or "x32" for this file.
0 common read sys_read
1 common write sys_write
2 common open sys_open
3 common close sys_close
4 common stat sys_newstat
5 common fstat sys_newfstat
6 common lstat sys_newlstat
......
所以__x64_sys_write 就是 sys_write。
sys_write
在 fs/read_write.c中定义了write
SYSCALL_DEFINE3(write, unsigned int, fd, const char __user *, buf,
size_t, count)
{
return ksys_write(fd, buf, count);
}
展开宏定义
/* 1. 诊断忽略区域开始(实际编译器指令) */
__diag_push();
__diag_ignore(GCC, 8, "-Wattribute-alias", "Type aliasing is used to sanitize syscall arguments");
/* 2. 声明 sys_write 为 __se_sys_write 的别名 */
asmlinkage long sys_write(unsigned int fd, const char __user * buf, size_t count)
__attribute__((alias("__se_sys_write")));
/* 3. 允许错误注入 */
ALLOW_ERROR_INJECTION(sys_write, ERRNO);
/* 4. 声明内联函数 __do_sys_write */
static inline long __do_sys_write(unsigned int fd, const char __user * buf, size_t count);
/* 5. 定义 __se_sys_write(参数类型转换为 long 形式) */
asmlinkage long __se_sys_write(unsigned long fd, long buf, long count)
{
long ret = __do_sys_write((unsigned int)fd, (const char __user *)buf, (size_t)count);
/* 参数检查(此处无操作,宏 __SC_TEST 展开为空) */
;
/* 系统调用保护(宏 __PROTECT 展开为空) */
return ret;
}
/* 6. 诊断忽略区域结束 */
__diag_pop();
/* 7. 定义内联函数 __do_sys_write */
static inline long __do_sys_write(unsigned int fd, const char __user * buf, size_t count)
{
return ksys_write(fd, buf, count);
}
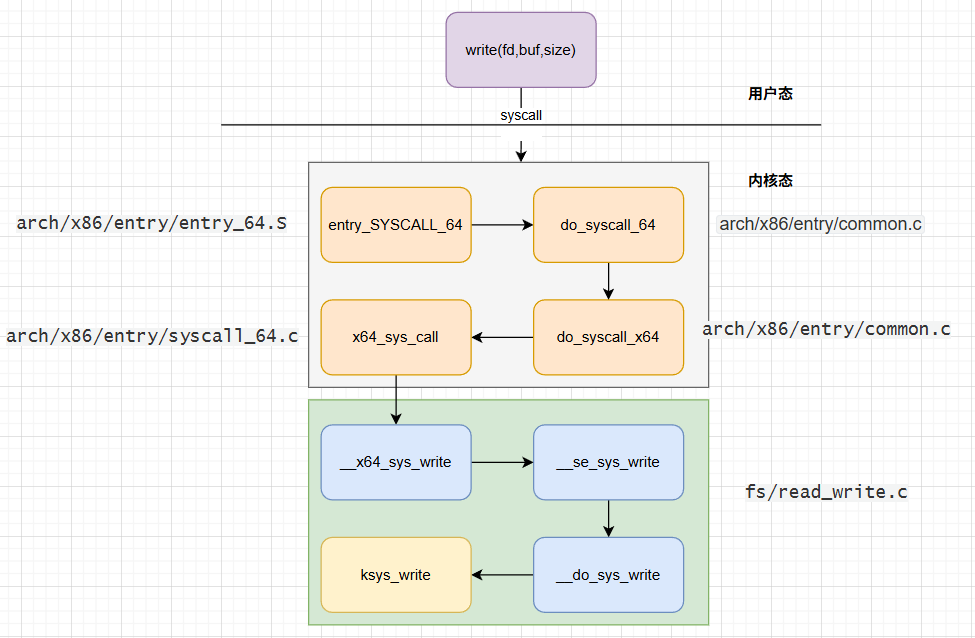
流程图
本文来自博客园,作者:只A有缘人,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/cq429958/p/19322228



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号