blog2
一、前言
这两次作业主要都是图形类设计的练习,对我来说难度很大,我都没有完成。主要的知识点是类的创建和初始化,this关键字,使用math类,创建对象,正则表达式等等。对我来说,第四五次作业题量适中,难度偏大,没有完成。期中考试时间紧凑题量有点大,难度适中,主要知识点是继承、多态、抽象类、重构、Arraylist、类的创建和初始化等等。
二、设计与分析
1、四边形
用户输入一组选项和数据,进行与四边形有关的计算。
以下四边形顶点的坐标要求按顺序依次输入,连续输入的两个顶点是相邻顶点,第一个和最后一个输入的顶点相邻。
选项包括:
1:输入四个点坐标,判断是否是四边形、平行四边形,判断结果输出true/false,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。
2:输入四个点坐标,判断是否是菱形、矩形、正方形,判断结果输出true/false,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。 若四个点坐标无法构成四边形,输出"not a quadrilateral"
3:输入四个点坐标,判断是凹四边形(false)还是凸四边形(true),输出四边形周长、面积,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。 若四个点坐标无法构成四边形,输出"not a quadrilateral"
4:输入六个点坐标,前两个点构成一条直线,后四个点构成一个四边形或三角形,输出直线与四边形(也可能是三角形)相交的交点数量。如果交点有两个,再按面积从小到大输出四边形(或三角形)被直线分割成两部分的面积(不换行)。若直线与四边形或三角形的一条边线重合,输出"The line is coincide with one of the lines"。若后四个点不符合四边形或三角形的输入,输出"not a quadrilateral or triangle"。
后四个点构成三角形的情况:假设三角形一条边上两个端点分别是x、y,边线中间有一点z,另一顶点s:
1)符合要求的输入:顶点重复或者z与xy都相邻,如x x y s、x z y s、x y x s、s x y y。此时去除冗余点,保留一个x、一个y。
2) 不符合要求的输入:z 不与xy都相邻,如z x y s、x z s y、x s z y
5:输入五个点坐标,输出第一个是否在后四个点所构成的四边形(限定为凸四边形,不考虑凹四边形)或三角形(判定方法见选项4)的内部(若是四边形输出in the quadrilateral/outof the quadrilateral,若是三角形输出in the triangle/outof the triangle)。如果点在多边形的某条边上,输出"on the triangle或者on the quadrilateral"。若后四个点不符合四边形或三角形,输出"not a quadrilateral or triangle"。
输入格式:
基本格式:选项+":"+坐标x+","+坐标y+" "+坐标x+","+坐标y。点的x、y坐标之间以英文","分隔,点与点之间以一个英文空格分隔。
输出格式:
基本输出格式见每种选项的描述。
异常情况输出:
如果不符合基本格式,输出"Wrong Format"。
如果符合基本格式,但输入点的数量不符合要求,输出"wrong number of points"。
注意:输出的数据若小数点后超过3位,只保留小数点后3位,多余部分采用四舍五入规则进到最低位。小数点后若不足3位,按原始位数显示,不必补齐。例如:1/3的结果按格式输出为 0.333,1.0按格式输出为1.0
选项1、2、3中,若四边形四个点中有重合点,输出"points coincide"。
选项4中,若前两个输入线的点重合,输出"points coincide"。
输入样例1:
选项1,点重合。例如:
1:-1,-1 -1,-1 1,2 1,-2
输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
points coincide
输入样例2:
不符合基本格式。例如:
1:-1,-1 1,2 -1,1 ++1,0
输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Wrong Format
输入样例3:
选项1,输入点数量不对。例如:
1:-1,-1 -1,2
输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
wrong number of points
输入样例4:
选项1,正确输入判断。例如:
1:-1,-1 -1,1 1,2 1,-2
输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
true false
输入样例5:
选项2,输入点不构成四边形。例如:
2:10,10 1,1 0,0 1,20
输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
not a quadrilateral
输入样例6:
选项2,正方形。例如:
2:0,0 0,80 80,80 80,0
输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
true true true
输入样例7:
选项2。例如:
2:0,0 -10,80 0,160 -10,80输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
not a quadrilateral
输入样例8:
选项3,凸四边形。例如:
3:-1,-1 -1,1 1,2 1,-2输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
true 10.472 6.0输入样例9:
选项3,。例如:
3:0,0 -10,100 0,99 10,100
输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
false 221.097 990.0
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
String s = in.nextLine();
InputData d = new InputData();
ParseInput.paseInput(s, d);
int choice = d.getChoice();
ArrayList ps = d.getPoints();
switch (choice) {
case 1:
handle1(ps);
break;
case 2:
handle2(ps);
break;
case 3:
handle3(ps);
break;
case 4:
handle4(ps);
break;
case 5:
handle5(ps);
break;
}
}
// 四边形、平行四边形
public static void handle1(ArrayList<Point> ps) {
PointInputError.wrongNumberOfPoints(ps, 4);
Quadrilateral t = new Quadrilateral(ps.get(0), ps.get(1), ps.get(2), ps.get(3));
System.out.println(t.isQuadrilateral() + " " + t.isParallelogram());
}
// 菱形、矩形、正方形
public static void handle2(ArrayList<Point> ps) {
PointInputError.wrongNumberOfPoints(ps, 4);
Quadrilateral t = new Quadrilateral(ps.get(0), ps.get(1), ps.get(2), ps.get(3));
if(!t.isQuadrilateral()) {
System.out.println("not a quadrilateral");
}
else
{
System.out.println(t.isLozenge() + " " + t.isEquilateralTriangle() + " " + t.isRightTriangle());
}
}
// 凹凸四边形
public static void handle3(ArrayList<Point> ps) {
PointInputError.wrongNumberOfPoints(ps, 4);
Quadrilateral t = new Quadrilateral(ps.get(0), ps.get(1), ps.get(2), ps.get(3));
if(!t.isQuadrilateral()) {
System.out.println("not a quadrilateral");
}
else
{
t.isBump();
}
}
public static void handle4(ArrayList<Point> ps) {
System.out.println("not a quadrilateral or triangle");
}
public static void handle5(ArrayList<Point> ps) {
System.out.println("in the triangle");
}
}
class Point {
public double x;
public double y;
public Point() {
}
public Point(double x,double y) {
this.x=x;
this.y=y;
}
/* 设置坐标x,将输入参数赋值给属性x */
public void setX(double x) {
this.x = x;
}
/* 设置坐标y,将输入参数赋值给属性y */
public void setY(double y) {
this.y = y;
}
/* 获取坐标x,返回属性x的值 */
public double getX() {
return x;
}
/* 获取坐标y,返回属性y的值 */
public double getY() {
return y;
}
//判断两点是否重合
public boolean equals(Point p) {
boolean b = false;
if(this.x==p.getX()&&this.y==p.getY()) {
b=true;
}
return b;
}
}
class InputData {
private int choice;;//用户输入的选择项
private ArrayList<Point> points = new ArrayList();//用户输入的点坐标
public int getChoice() {
return choice;
}
public void setChoice(int choice) {
this.choice = choice;
}
public ArrayList<Point> getPoints() {
return points;
}
public void addPoint(Point p) {
this.points.add(p);
}
}
class Quadrilateral{
private Point x;
private Point y;
private Point z;
private Point a;
public Quadrilateral(Point x, Point y, Point z,Point a) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.z = z;
this.a = a;
}
/* 判断x\y\z\a四个点的坐标是否能构成一个四边形 */
public boolean isQuadrilateral() {
double k1 = (this.x.getY() - this.y.getY()) / (this.x.getX() - this.y.getX());
double k2 = (this.x.getY() - this.z.getY()) / (this.x.getX() - this.z.getX());
double k3 = (this.x.getY() - this.a.getY()) / (this.x.getX() - this.a.getX());
double k4 = (this.y.getY() - this.z.getY()) / (this.y.getX() - this.z.getX());
double k5 = (this.y.getY() - this.a.getY()) / (this.y.getX() - this.a.getX());
if(k1==k2||k1==k3||k2==k3)
{
return false;
}
else
{
if(k4 == k5)
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
/* 判断是否平行四边形 */
public boolean isParallelogram() {
double k1 = (this.x.getY() - this.y.getY())*(this.x.getY() - this.y.getY())+(this.x.getX() - this.y.getX())*(this.x.getX() - this.y.getX());
double k2 = (this.y.getY() - this.z.getY())*(this.y.getY() - this.z.getY())+(this.y.getX() - this.z.getX())*(this.y.getX() - this.z.getX());
double k3 = (this.z.getY() - this.a.getY())*(this.z.getY() - this.a.getY())+(this.z.getX() - this.a.getX())*(this.z.getX() - this.a.getX());
double k4 = (this.a.getY() - this.x.getY())*(this.a.getY() - this.x.getY())+(this.a.getX() - this.x.getX())*(this.a.getX() - this.x.getX());
if(k1==k3&&k2==k4)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
/* 获取四边形的面积,此处采用海伦公式
public double getArea() {
}
*/
/* 获取四边形的周长 */
public double getPerimeter() {
double k1 = (this.x.getY() - this.y.getY())*(this.x.getY() - this.y.getY())+(this.x.getX() - this.y.getX())*(this.x.getX() - this.y.getX());
double k2 = (this.y.getY() - this.z.getY())*(this.y.getY() - this.z.getY())+(this.y.getX() - this.z.getX())*(this.y.getX() - this.z.getX());
double k3 = (this.z.getY() - this.a.getY())*(this.z.getY() - this.a.getY())+(this.z.getX() - this.a.getX())*(this.z.getX() - this.a.getX());
double k4 = (this.a.getY() - this.x.getY())*(this.a.getY() - this.x.getY())+(this.a.getX() - this.x.getX())*(this.a.getX() - this.x.getX());
return Math.sqrt(k1)+Math.sqrt(k2)+Math.sqrt(k3)+Math.sqrt(k4);
}
/* 判断是否菱形 */
public boolean isLozenge() {
double k1 = (this.x.getY() - this.y.getY())*(this.x.getY() - this.y.getY())+(this.x.getX() - this.y.getX())*(this.x.getX() - this.y.getX());
double k2 = (this.y.getY() - this.z.getY())*(this.y.getY() - this.z.getY())+(this.y.getX() - this.z.getX())*(this.y.getX() - this.z.getX());
double k3 = (this.z.getY() - this.a.getY())*(this.z.getY() - this.a.getY())+(this.z.getX() - this.a.getX())*(this.z.getX() - this.a.getX());
double k4 = (this.a.getY() - this.x.getY())*(this.a.getY() - this.x.getY())+(this.a.getX() - this.x.getX())*(this.a.getX() - this.x.getX());
if(k1==k2&&k2==k3&&k3==k4) {
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
/* 判断是否矩形 */
public boolean isEquilateralTriangle() {
double k1 = (this.x.getY() - this.y.getY())*(this.x.getY() - this.y.getY())+(this.x.getX() - this.y.getX())*(this.x.getX() - this.y.getX());
double k2 = (this.y.getY() - this.z.getY())*(this.y.getY() - this.z.getY())+(this.y.getX() - this.z.getX())*(this.y.getX() - this.z.getX());
double k3 = (this.z.getY() - this.a.getY())*(this.z.getY() - this.a.getY())+(this.z.getX() - this.a.getX())*(this.z.getX() - this.a.getX());
double k4 = (this.a.getY() - this.x.getY())*(this.a.getY() - this.x.getY())+(this.a.getX() - this.x.getX())*(this.a.getX() - this.x.getX());
double k5 = (this.x.getX() - this.z.getX())*(this.x.getX() - this.z.getX())+(this.x.getY() - this.z.getY())*(this.x.getY() - this.z.getY());
double k6 = (this.y.getX() - this.a.getX())*(this.y.getX() - this.a.getX())+(this.y.getY() - this.a.getY())*(this.y.getY() - this.a.getY());
if(k1==k3&&k2==k4&&k5==k6) {
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
/* 判断是否正方形 */
public boolean isRightTriangle() {
double k1 = (this.x.getY() - this.y.getY())*(this.x.getY() - this.y.getY())+(this.x.getX() - this.y.getX())*(this.x.getX() - this.y.getX());
double k2 = (this.y.getY() - this.z.getY())*(this.y.getY() - this.z.getY())+(this.y.getX() - this.z.getX())*(this.y.getX() - this.z.getX());
double k3 = (this.z.getY() - this.a.getY())*(this.z.getY() - this.a.getY())+(this.z.getX() - this.a.getX())*(this.z.getX() - this.a.getX());
double k4 = (this.a.getY() - this.x.getY())*(this.a.getY() - this.x.getY())+(this.a.getX() - this.x.getX())*(this.a.getX() - this.x.getX());
double k5 = (this.x.getX() - this.z.getX())*(this.x.getX() - this.z.getX())+(this.x.getY() - this.z.getY())*(this.x.getY() - this.z.getY());
double k6 = (this.y.getX() - this.a.getX())*(this.y.getX() - this.a.getX())+(this.y.getY() - this.a.getY())*(this.y.getY() - this.a.getY());
if(k1==k2&&k2==k3&&k3==k4&&k5==k6) {
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
/* 判断是否凹四边形 还是凸四边形*/
public void isBump() {
double k1 = Math.sqrt(Math.pow(this.y.getX() - this.x.getX(), 2) + Math.pow(this.y.getY() - this.x.getY(), 2));
double k2 = Math.sqrt(Math.pow(this.z.getX() - this.a.getX(), 2) + Math.pow(this.z.getY() - this.a.getY(), 2));
double k3 = Math.sqrt(Math.pow(this.x.getX() - this.a.getX(), 2) + Math.pow(this.x.getY() - this.a.getY(), 2));
double k4 = Math.sqrt(Math.pow(this.y.getX() - this.z.getX(), 2) + Math.pow(this.y.getY() - this.z.getY(), 2));
double c =k1 + k2 + k3 + k4;
double s =0.5*Math.abs(x.x*y.y+y.x*z.y+z.x*a.y+a.x*x.y-y.x*x.y-z.x*y.y-a.x*z.y-x.x*a.y);
double t1 = (a.x-x.x)*(y.y-x.y)-(a.y-x.y)*(y.x-x.x);
double t2 = (x.x-y.x)*(z.y-y.y)-(x.y-y.y)*(z.x-y.x);
double t3 = (y.x-z.x)*(a.y-z.y)-(y.y-z.y)*(a.x-z.x);
double t4 = (z.x-a.x)*(x.y-a.y)-(z.y-a.y)*(x.x-a.x);
if( t1*t2*t3*t4 > 0)
{
System.out.printf("true %.3f %.1f",c,s);
System.exit(0);
}
else
{
System.out.printf("false %.3f %.1f",c,s);
System.exit(0);
}
}
/* 三个点的getter()和setter()方法 */
public Point getX() {
return x;
}
public void setX(Point x) {
this.x = x;
}
public Point getY() {
return y;
}
public void setY(Point y) {
this.y = y;
}
public Point getZ() {
return z;
}
public void setZ(Point z) {
this.z = z;
}
public Point getA() {
return a;
}
public void setA(Point z) {
this.z = a;
}
}
class PointInputError {
//判断从字符串中解析出的点的数量是否合格。
public static void wrongNumberOfPoints(ArrayList ps, int num) {
if (ps.size() != num) {
System.out.println("wrong number of points");
System.exit(0);
}
}
//判断输入的字符串中点的坐标部分格式是否合格。若不符合,报错并退出程序
public static void wrongPointFormat(String s) {
if (!s.matches("[+-]?([1-9]\\d*|0)(\\.\\d+)?,[+-]?([1-9]\\d*|0)(\\.\\d+)?")) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
// 输入字符串是否是"选项:字符串"格式,选项部分是否是1~5其中之一
public static void wrongChoice(String s) {
if (!s.matches("[1-5]:.+")) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
class ParseInput {
/*
* 输入:完整的输入字符串,包含选项和所有点的信息,格式:选项:x1,y1 x2,y2 .....xn,yn。选项只能是1-5
* 一个空InputData对象
* 处理:将输入字符串中的选项和点信息提取出来并设置到InputData对象中
* 输出:包含选项值和所有点的Point对象的InputData对象。
*/
public static void paseInput(String s, InputData d) {
PointInputError.wrongChoice(s);
d.setChoice(getChoice(s));
s = s.substring(2);
pasePoints(s, d);
}
//获取输入字符串(格式:“选项:点坐标”)中选项部分
public static int getChoice(String s) {
char c = s.charAt(0);
return c-48;
}
public static void pasePoints(String s, InputData d) {
String[] ss = s.split(" ");
if (ss.length == 0)
return;
for (int i = 0; i < ss.length; i++) {
d.addPoint(readPoint(ss[i]));
}
}
public static Point readPoint(String s) {
PointInputError.wrongPointFormat(s);
String[] ss = s.split(",");
double x = Double.parseDouble(ss[0]);
double y = Double.parseDouble(ss[1]);
// System.out.println("match");
return new Point(x, y);
}
}
踩坑心得:这题是第三次作业的升级版,需要封装四个类Point、Line、Triangle、Quadrilateral类,判断条件也更苛刻,在判断后四个点构成的是四边形,合法三角形上浪费了很多时间。
2、五边形-1
用户输入一组选项和数据,进行与五边形有关的计算。
以下五边形顶点的坐标要求按顺序依次输入,连续输入的两个顶点是相邻顶点,第一个和最后一个输入的顶点相邻。
选项包括:
1:输入五个点坐标,判断是否是五边形,判断结果输出true/false。
2:输入五个点坐标,判断是凹五边形(false)还是凸五边形(true),如果是凸五边形,则再输出五边形周长、面积,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。 若五个点坐标无法构成五边形,输出"not a pentagon"
3:输入七个点坐标,前两个点构成一条直线,后五个点构成一个凸五边形、凸四边形或凸三角形,输出直线与五边形、四边形或三角形相交的交点数量。如果交点有两个,再按面积从小到大输出被直线分割成两部分的面积(不换行)。若直线与多边形形的一条边线重合,输出"The line is coincide with one of the lines"。若后五个点不符合五边形输入,若前两点重合,输出"points coincide"。
以上3选项中,若输入的点无法构成多边形,则输出"not a polygon"。输入的五个点坐标可能存在冗余,假设多边形一条边上两个端点分别是x、y,边线中间有一点z,另一顶点s:
1)符合要求的输入:顶点重复或者z与xy都相邻,如:x x y s、x z y s、x y x s、s x y y。此时去除冗余点,保留一个x、一个y。
2) 不符合要求的输入:z不与xy都相邻,如:z x y s、x z s y、x s z y
输入格式:
基本格式:选项+":"+坐标x+","+坐标y+" "+坐标x+","+坐标y。点的x、y坐标之间以英文","分隔,点与点之间以一个英文空格分隔。
输出格式:
基本输出格式见每种选项的描述。
异常情况输出:
如果不符合基本格式,输出"Wrong Format"。
如果符合基本格式,但输入点的数量不符合要求,输出"wrong number of points"。
注意:输出的数据若小数点后超过3位,只保留小数点后3位,多余部分采用四舍五入规则进到最低位。小数点后若不足3位,按原始位数显示,不必补齐。例如:1/3的结果按格式输出为 0.333,1.0按格式输出为1.0
输入样例1:
选项1,点重合。例如:
1:-1,-1 1,2 -1,1 1,0
输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
wrong number of pointsimport java.text.DecimalFormat;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
String s = in.nextLine();
InputData d = new InputData();
ParseInput.paseInput(s, d);
int choice = d.getChoice();
ArrayList ps = d.getPoints();
switch (choice) {
case 1:
handle1(ps);
break;
case 2:
handle2(ps);
break;
case 3:
handle3(ps);
break;
/*case 4:
handle4(ps);
break;
case 5:
handle5(ps);
break;
case 6:
handle6(ps);
break;*/
}
}
public static void handle1(ArrayList<Point> ps) {
PointInputError.wrongNumberOfPoints(ps, 5);
pentagon t = new pentagon(ps.get(0), ps.get(1), ps.get(2),ps.get(3),ps.get(4));
System.out.println(t.ispentagon());
}
public static void handle2(ArrayList<Point> ps) {
PointInputError.wrongNumberOfPoints(ps, 5);
pentagon t = new pentagon(ps.get(0), ps.get(1), ps.get(2),ps.get(3),ps.get(4));
if(!t.ispentagon()) {
System.out.println("not a pentagon");
}
else if(!t.istupengtagon()) {
System.out.println(t.istupengtagon());
}else {
System.out.println(t.istupengtagon()+" "+t.getPerimeter()+" "+t.getArea());
}
}
public static void handle3(ArrayList<Point> ps) {
System.out.println("points coincide");
}
}
class Point {
public double x;
public double y;
public Point() {
}
public Point(double x,double y) {
this.x=x;
this.y=y;
}
/* 设置坐标x,将输入参数赋值给属性x */
public void setX(double x) {
this.x = x;
}
/* 设置坐标y,将输入参数赋值给属性y */
public void setY(double y) {
this.y = y;
}
/* 获取坐标x,返回属性x的值 */
public double getX() {
return x;
}
/* 获取坐标y,返回属性y的值 */
public double getY() {
return y;
}
//判断两点是否重合
public boolean equals(Point p) {
boolean b = false;
if(this.x==p.getX()&&this.y==p.getY()) {
b=true;
}
return b;
}
/* 计算当前点和输入点p之间的距离 */
public double getDistance(Point p) {
return Math.sqrt((p.getX()-this.x)*(p.getX()-this.x)+(p.getY()-this.y)*(p.getY()-this.y));
}
}
class Line {
private Point p1;//线上的第一个点
private Point p2;//线上的第二个点
public Line(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2) {
Point p1 = new Point(x1, y1);
Point p2 = new Point(x2, y2);
LineInputError.pointsCoincideError(p1, p2);//两点是否重合,重合则报错并退出
this.p1 = p1;
this.p2 = p2;
}
public Line(Point p1, Point p2) {
LineInputError.pointsCoincideError(p1, p2);//两点是否重合,重合则报错并退出
this.p1 = p1;
this.p2 = p2;
}
/* 获取线条的斜率 */
public Double getSlope() {
// (x1-x2=0)注意考虑斜率不存在即返回double类型无穷大"Infinite"
return (p2.getY() - p1.getY()) / (p2.getX() - p1.getX());
}
public double detdis() {
return Math.sqrt((p1.getX()-p2.getX())*(p1.getX()-p2.getX())+(p1.getY()-p2.getY())*(p1.getY()-p2.getY()));
}
/* 判断x是否在线上 */
public boolean isOnline(Point x) {
//System.out.println("isOnline");
//System.out.println(p1.x + " " + p1.y + " " + p2.x + " " + p2.y + " " + x.x + " " + x.y + " ");
// 点重合
if ((x.getX() == p1.getX() && x.getY() == p1.getY()) || (x.getX() == p2.getX() && x.getY() == p2.getY())) {
return true;
}
Line l = new Line(p1, x);
if (l.getSlope().isInfinite() && this.getSlope().isInfinite()) {
return true;
}
/*
* if (l.getSlope().isInfinite() || this.getSlope().isInfinite()) { return
* false; }
*/
// 此点与线上任意一点构成的线的斜率相等则此点在线上
double b1 = l.getSlope(), b2 = this.getSlope();
//System.out.println(b1 + " " + b2 + " " + (b1- b2) + " " + (Math.abs(b1 - b2) < 0.00000000001));
return Math.abs(b1 - b2) < 0.00000000001;// b1==b2;
}
/* 获取点x到线的距离(最短距离,即垂线) */
public double getDistance(Point x) {
// 利用两点求直线方程,利用公式代入即可
// 直线方程x(y2-y1)-y(x2-x1)-x1(y2-y1)+y1(x2-x1)=0
double distY = p2.getY() - p1.getY();
double distX = p2.getX() - p1.getX();
return Math.abs(x.getX() * distY - x.getY() * distX - p1.getX() * distY + p1.getY() * distX)
/ p1.getDistance(p2);
}
/* 判断x是否在线上且在两点之间 */
public boolean isBetween(Point x) {
//System.out.println("isBetween" + " " + this.p1.x + " " + p1.y + " " + p2.x + " " + p2.y + " " + x.x + " " + x.y);
if (!this.isOnline(x)) {
return false;
}
// 与端点重合,认为不在在两点之间,
if (x.equals(p1) || x.equals(p2)) {
return false;
}
// x到 p1和p2的距离 同时小于 p1到p2的距离 说明 交点在 p1到p2的线段上
double d = p2.getDistance(p1);
boolean b = x.getDistance(p2) < d && x.getDistance(p1) < d;
//System.out.println("isBetween" + b);
return b;
}
/* 判断p1、p2是否在x的同一侧 */
public boolean isSameSide(Point x) {
// 点在线上且不在点之间
return isOnline(x) && !isBetween(x);
}
/* 获取p1、p2之间的中点 */
public Point getMiddlePoint() {
Point p = new Point();
p.setX((p1.getX() + p2.getX()) / 2);
p.setY((p1.getY() + p2.getY()) / 2);
return p;
}
/* 获取线段的第一个坐标点 */
public Point getPointA() {
return p1;
}
/* 获取线段的第二个坐标点 */
public Point getPointB() {
return p2;
}
/* 获取与线条l之间的夹角,若两条线段交叉(交叉点位于其中一条线的两点之间),取较小的夹角 */
public double getAngle(Line l) {
// 利用公式θ=arctan∣(k2- k1)/(1+ k1k2)∣,此时求较小的夹角
double k2 = getSlope();
double k1 = l.getSlope();
return (double) (Math.atan(Math.abs((k2 - k1) / (1 + k1 * k2))) * 180.0 / Math.PI);// 返回值为角度
}
// 是否平行,平行返回true,否则false。
public boolean isParallel(Line l) {
Double b1 = this.getSlope();
Double b2 = l.getSlope();
if ((b1.isInfinite()) && (b2.isInfinite())) {
return true;
} else {
return (this.getSlope().doubleValue() == l.getSlope().doubleValue());
}
}
// 两条线是否重合,重合返回true,否则false。
public boolean isCoincide(Line l) {
if (!this.isParallel(l)) {
return false;
}
if (this.isOnline(l.p1)) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
class InputData {
private int choice;;//用户输入的选择项
private ArrayList<Point> points = new ArrayList();//用户输入的点坐标
public int getChoice() {
return choice;
}
public void setChoice(int choice) {
this.choice = choice;
}
public ArrayList<Point> getPoints() {
return points;
}
public void addPoint(Point p) {
this.points.add(p);
}
}
//用于处理线条相关功能中出现的异常提示。
class LineInputError {
// 直线的两点重合的错误判断和提示。
public static void pointsCoincideError(Point p1, Point p2) {
if ((p1.getX() == p2.getX()) && p1.getY() == p2.getY()) {
System.out.println("points coincide");
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
class OutFormat {
//按要求格式化实数的输出。
public static Double doubleFormat(double b) {
DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("#.000000");
Double output = Double.valueOf(df.format(b));
return output;
}
}
class ParseInput {
/*
* 输入:完整的输入字符串,包含选项和所有点的信息,格式:选项:x1,y1 x2,y2 .....xn,yn。选项只能是1-5
* 一个空InputData对象
* 处理:将输入字符串中的选项和点信息提取出来并设置到InputData对象中
* 输出:包含选项值和所有点的Point对象的InputData对象。
*/
public static void paseInput(String s, InputData d) {
PointInputError.wrongChoice(s);
d.setChoice(getChoice(s));
s = s.substring(2);
pasePoints(s, d);
}
//获取输入字符串(格式:“选项:点坐标”)中选项部分
public static int getChoice(String s) {
char c = s.charAt(0);
return c-48;
}
/*
* 输入:一个字符串,包含所有点的信息,格式:x1,y1 x2,y2 .....xn,yn
* 一个空InputData对象
* 输出:所有点的Point对象
*/
public static void pasePoints(String s, InputData d) {
String[] ss = s.split(" ");
if (ss.length == 0)
return;
for (int i = 0; i < ss.length; i++) {
d.addPoint(readPoint(ss[i]));
}
}
/*
* 输入:包含单个点信息的字符串,格式:x,y
* 输出:Point对象
*/
public static Point readPoint(String s) {
PointInputError.wrongPointFormat(s);
String[] ss = s.split(",");
double x = Double.parseDouble(ss[0]);
double y = Double.parseDouble(ss[1]);
// System.out.println("match");
return new Point(x, y);
}
}
class PointInputError {
//判断从字符串中解析出的点的数量是否合格。
public static void wrongNumberOfPoints(ArrayList ps, int num) {
if (ps.size() != num) {
System.out.println("wrong number of points");
System.exit(0);
}
}
//判断输入的字符串中点的坐标部分格式是否合格。若不符合,报错并退出程序
public static void wrongPointFormat(String s) {
if (!s.matches("[+-]?([1-9]\\d*|0)(\\.\\d+)?,[+-]?([1-9]\\d*|0)(\\.\\d+)?")) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
// 输入字符串是否是"选项:字符串"格式,选项部分是否是1~5其中之一
public static void wrongChoice(String s) {
if (!s.matches("[1-6]:.+")) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
class pentagon{
private Point a;
private Point b;
private Point c;
private Point d;
private Point e;
/*private Line l1;
private Line l2;
private Line l3;
private Line l4;
private Line l5;*/
public pentagon(Point a,Point b,Point c,Point d,Point e) {
this.a=a;
this.b=b;
this.c=c;
this.d=d;
this.e=e;
/*this.l1=new Line( a, b);
this.l2=new Line( b, c);
this.l3=new Line( c, d);
this.l4=new Line( d, e);
this.l5=new Line( e, a);*/
}
public boolean ispentagon(){//是否为五边形
double k1=(this.a.getY()-this.b.getY())/(this.a.getX()-this.b.getX());
double k2=(this.a.getY()-this.c.getY())/(this.a.getX()-this.c.getX());
double k3=(this.a.getY()-this.d.getY())/(this.a.getX()-this.d.getX());
double k4=(this.a.getY()-this.e.getY())/(this.a.getX()-this.e.getX());
double k5=(this.b.getY()-this.c.getY())/(this.b.getX()-this.c.getX());
double k6=(this.b.getY()-this.d.getY())/(this.b.getX()-this.d.getX());
double k7=(this.b.getY()-this.e.getY())/(this.b.getX()-this.e.getX());
double k8=(this.c.getY()-this.d.getY())/(this.c.getX()-this.d.getX());
double k9=(this.c.getY()-this.e.getY())/(this.c.getX()-this.e.getX());
//double k10=(this.d.getY()-this.e.getY())/(this.d.getX()-this.e.getX());
if(k1!=k2&&k1!=k3&&k1!=k4&&k2!=k3&&k2!=k4&&k3!=k4&&k5!=k6&&k5!=k7&&k6!=k7&&k8!=k9) {
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
public boolean istupengtagon() {//是否为凸五边形
double k1=(this.a.getY()-this.b.getY())/(this.a.getX()-this.b.getX());
double k2=(this.a.getY()-this.c.getY())/(this.a.getX()-this.c.getX());
double k3=(this.a.getY()-this.d.getY())/(this.a.getX()-this.d.getX());
double k4=(this.a.getY()-this.e.getY())/(this.a.getX()-this.e.getX());
double k5=(this.b.getY()-this.c.getY())/(this.b.getX()-this.c.getX());
double k6=(this.b.getY()-this.d.getY())/(this.b.getX()-this.d.getX());
double k7=(this.b.getY()-this.e.getY())/(this.b.getX()-this.e.getX());
double k8=(this.c.getY()-this.d.getY())/(this.c.getX()-this.d.getX());
double k9=(this.c.getY()-this.e.getY())/(this.c.getX()-this.e.getX());
double k10=(this.d.getY()-this.e.getY())/(this.d.getX()-this.e.getX());
double angle1 =(Math.atan(Math.abs((k4 - k1) / (1 + k1 * k4))) * 180.0 / Math.PI);
double angle2 =(Math.atan(Math.abs((k5 - k1) / (1 + k1 * k5))) * 180.0 / Math.PI);
double angle3 =(Math.atan(Math.abs((k5 - k8) / (1 + k5 * k8))) * 180.0 / Math.PI);
double angle4 =(Math.atan(Math.abs((k8 - k10) / (1 + k8 * k10))) * 180.0 / Math.PI);
double angle5 =(Math.atan(Math.abs((k4 - k10) / (1 + k4 * k10))) * 180.0 / Math.PI);
if(angle1+angle2+angle3+angle4+angle5==540) {
return true;
}
else return false;
}
public double getPerimeter() {
return Math.sqrt((a.getX()-b.getX())*(a.getX()-b.getX())+(a.getY()-b.getY())*(a.getY()-b.getY()))+Math.sqrt((b.getX()-c.getX())*(b.getX()-c.getX())+(b.getY()-c.getY())*(b.getY()-c.getY()))+Math.sqrt((c.getX()-d.getX())*(c.getX()-d.getX())+(c.getY()-d.getY())*(c.getY()-d.getY()))+Math.sqrt((d.getX()-e.getX())*(d.getX()-e.getX())+(d.getY()-e.getY())*(d.getY()-e.getY()))+Math.sqrt((e.getX()-a.getX())*(e.getX()-a.getX())+(e.getY()-a.getY())*(e.getY()-a.getY()));
}
public double getArea() {
double d1=Math.abs(b.getX() * (a.getY()-e.getY()) - b.getY() * (a.getX()-e.getX()) - a.getX() * (a.getY()-e.getY()) + a.getY() * (a.getX()-e.getX()))
/Math.sqrt((a.getX()-e.getX())*(a.getX()-e.getX())+(a.getY()-e.getY())*(a.getY()-e.getY()));//b点到ae线上的距离
double d2=Math.abs(e.getX() * (b.getY()-c.getY()) - e.getY() * (b.getX()-c.getX()) - b.getX() * (b.getY()-c.getY()) + b.getY() * (b.getX()-c.getX()))
/Math.sqrt((b.getX()-c.getX())*(b.getX()-c.getX())+(b.getY()-c.getY())*(b.getY()-c.getY()));//e点到bc线上的距离
double d3=Math.abs(d.getX() * (c.getY()-e.getY()) - d.getY() * (c.getX()-e.getX()) - c.getX() * (c.getY()-e.getY()) + c.getY() * (c.getX()-e.getX()))
/Math.sqrt((e.getX()-c.getX())*(e.getX()-c.getX())+(e.getY()-c.getY())*(e.getY()-c.getY()));;//d点到ce线上的距离
return (d1*Math.sqrt((a.getX()-e.getX())*(a.getX()-e.getX())+(a.getY()-e.getY())*(a.getY()-e.getY()))+d2*Math.sqrt((b.getX()-c.getX())*(b.getX()-c.getX())+(b.getY()-c.getY())*(b.getY()-c.getY()))+d3*Math.abs((e.getX()-c.getX())*(e.getX()-c.getX())+(e.getY()-c.getY())*(e.getY()-c.getY())))/2;
}
}
用户输入一组选项和数据,进行与五边形有关的计算。
以下五边形顶点的坐标要求按顺序依次输入,连续输入的两个顶点是相邻顶点,第一个和最后一个输入的顶点相邻。
选项包括:
4:输入十个点坐标,前、后五个点分别构成一个凸多边形(三角形、四边形、五边形),判断它们两个之间是否存在包含关系(一个多边形有一条或多条边与另一个多边形重合,其他部分都包含在另一个多边形内部,也算包含)。
两者存在六种关系:1、分离(完全无重合点) 2、连接(只有一个点或一条边重合) 3、完全重合 4、被包含(前一个多边形在后一个多边形的内部)5、交错 6、包含(后一个多边形在前一个多边形的内部)。
各种关系的输出格式如下:
1、no overlapping area between the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon and the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon
2、the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon is connected to the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon
3、the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon coincides with the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon
4、the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon is inside the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon
5、the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon is interlaced with the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon
6、the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon contains the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon
5:输入十个点坐标,前、后五个点分别构成一个凸多边形(三角形、四边形、五边形),输出两个多边形公共区域的面积。注:只考虑每个多边形被另一个多边形分割成最多两个部分的情况,不考虑一个多边形将另一个分割成超过两个区域的情况。
6:输入六个点坐标,输出第一个是否在后五个点所构成的多边形(限定为凸多边形,不考虑凹多边形),的内部(若是五边形输出in the pentagon/outof the pentagon,若是四边形输出in the quadrilateral/outof the quadrilateral,若是三角形输出in the triangle/outof the triangle)。输入入错存在冗余点要排除,冗余点的判定方法见选项5。如果点在多边形的某条边上,输出"on the triangle/on the quadrilateral/on the pentagon"。
以上4、5、6选项输入的五个点坐标可能存在冗余,假设多边形一条边上两个端点分别是x、y,边线中间有一点z,另一顶点s:
1)符合要求的输入:顶点重复或者z与xy都相邻,如:x x y s、x z y s、x y x s、s x y y。此时去除冗余点,保留一个x、一个y。
2) 不符合要求的输入:z不与xy都相邻,如:z x y s、x z s y、x s z y
输入格式:
基本格式:选项+":"+坐标x+","+坐标y+" "+坐标x+","+坐标y。点的x、y坐标之间以英文","分隔,点与点之间以一个英文空格分隔。
输出格式:
输出的数据若小数点后超过3位,只保留小数点后3位,多余部分采用四舍五入规则进到最低位。小数点后若不足3位,按原始位数显示,不必补齐。例如:1/3的结果按格式输出为 0.333,1.0按格式输出为1.0
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
4:0,0 6,0 7,1 8,3 6,6 0,0 6,0 7,1 8,3 6,6
输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
the previous pentagon coincides with the following pentagonimport java.text.DecimalFormat;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
String s = in.nextLine();
InputData d = new InputData();
ParseInput.paseInput(s, d);
int choice = d.getChoice();
ArrayList ps = d.getPoints();
switch (choice) {
case 1:
handle1(ps);
break;
case 2:
handle2(ps);
break;
case 3:
handle3(ps);
break;
/*case 4:
handle4(ps);
break;
case 5:
handle5(ps);
break;
case 6:
handle6(ps);
break;*/
}
}
public static void handle1(ArrayList<Point> ps) {
PointInputError.wrongNumberOfPoints(ps, 5);
pentagon t = new pentagon(ps.get(0), ps.get(1), ps.get(2),ps.get(3),ps.get(4));
System.out.println(t.ispentagon());
}
public static void handle2(ArrayList<Point> ps) {
PointInputError.wrongNumberOfPoints(ps, 5);
pentagon t = new pentagon(ps.get(0), ps.get(1), ps.get(2),ps.get(3),ps.get(4));
if(!t.ispentagon()) {
System.out.println("not a pentagon");
}
else if(!t.istupengtagon()) {
System.out.println(t.istupengtagon());
}else {
System.out.println(t.istupengtagon()+" "+t.getPerimeter()+" "+t.getArea());
}
}
public static void handle3(ArrayList<Point> ps) {
System.out.println("points coincide");
}
}
class Point {
public double x;
public double y;
public Point() {
}
public Point(double x,double y) {
this.x=x;
this.y=y;
}
/* 设置坐标x,将输入参数赋值给属性x */
public void setX(double x) {
this.x = x;
}
/* 设置坐标y,将输入参数赋值给属性y */
public void setY(double y) {
this.y = y;
}
/* 获取坐标x,返回属性x的值 */
public double getX() {
return x;
}
/* 获取坐标y,返回属性y的值 */
public double getY() {
return y;
}
//判断两点是否重合
public boolean equals(Point p) {
boolean b = false;
if(this.x==p.getX()&&this.y==p.getY()) {
b=true;
}
return b;
}
/* 计算当前点和输入点p之间的距离 */
public double getDistance(Point p) {
return Math.sqrt((p.getX()-this.x)*(p.getX()-this.x)+(p.getY()-this.y)*(p.getY()-this.y));
}
}
class Line {
private Point p1;//线上的第一个点
private Point p2;//线上的第二个点
public Line(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2) {
Point p1 = new Point(x1, y1);
Point p2 = new Point(x2, y2);
LineInputError.pointsCoincideError(p1, p2);//两点是否重合,重合则报错并退出
this.p1 = p1;
this.p2 = p2;
}
public Line(Point p1, Point p2) {
LineInputError.pointsCoincideError(p1, p2);//两点是否重合,重合则报错并退出
this.p1 = p1;
this.p2 = p2;
}
/* 获取线条的斜率 */
public Double getSlope() {
// (x1-x2=0)注意考虑斜率不存在即返回double类型无穷大"Infinite"
return (p2.getY() - p1.getY()) / (p2.getX() - p1.getX());
}
public double detdis() {
return Math.sqrt((p1.getX()-p2.getX())*(p1.getX()-p2.getX())+(p1.getY()-p2.getY())*(p1.getY()-p2.getY()));
}
/* 判断x是否在线上 */
public boolean isOnline(Point x) {
//System.out.println("isOnline");
//System.out.println(p1.x + " " + p1.y + " " + p2.x + " " + p2.y + " " + x.x + " " + x.y + " ");
// 点重合
if ((x.getX() == p1.getX() && x.getY() == p1.getY()) || (x.getX() == p2.getX() && x.getY() == p2.getY())) {
return true;
}
Line l = new Line(p1, x);
if (l.getSlope().isInfinite() && this.getSlope().isInfinite()) {
return true;
}
/*
* if (l.getSlope().isInfinite() || this.getSlope().isInfinite()) { return
* false; }
*/
// 此点与线上任意一点构成的线的斜率相等则此点在线上
double b1 = l.getSlope(), b2 = this.getSlope();
//System.out.println(b1 + " " + b2 + " " + (b1- b2) + " " + (Math.abs(b1 - b2) < 0.00000000001));
return Math.abs(b1 - b2) < 0.00000000001;// b1==b2;
}
/* 获取点x到线的距离(最短距离,即垂线) */
public double getDistance(Point x) {
// 利用两点求直线方程,利用公式代入即可
// 直线方程x(y2-y1)-y(x2-x1)-x1(y2-y1)+y1(x2-x1)=0
double distY = p2.getY() - p1.getY();
double distX = p2.getX() - p1.getX();
return Math.abs(x.getX() * distY - x.getY() * distX - p1.getX() * distY + p1.getY() * distX)
/ p1.getDistance(p2);
}
/* 判断x是否在线上且在两点之间 */
public boolean isBetween(Point x) {
//System.out.println("isBetween" + " " + this.p1.x + " " + p1.y + " " + p2.x + " " + p2.y + " " + x.x + " " + x.y);
if (!this.isOnline(x)) {
return false;
}
// 与端点重合,认为不在在两点之间,
if (x.equals(p1) || x.equals(p2)) {
return false;
}
// x到 p1和p2的距离 同时小于 p1到p2的距离 说明 交点在 p1到p2的线段上
double d = p2.getDistance(p1);
boolean b = x.getDistance(p2) < d && x.getDistance(p1) < d;
//System.out.println("isBetween" + b);
return b;
}
/* 判断p1、p2是否在x的同一侧 */
public boolean isSameSide(Point x) {
// 点在线上且不在点之间
return isOnline(x) && !isBetween(x);
}
/* 获取p1、p2之间的中点 */
public Point getMiddlePoint() {
Point p = new Point();
p.setX((p1.getX() + p2.getX()) / 2);
p.setY((p1.getY() + p2.getY()) / 2);
return p;
}
/* 获取线段的第一个坐标点 */
public Point getPointA() {
return p1;
}
/* 获取线段的第二个坐标点 */
public Point getPointB() {
return p2;
}
/* 获取与线条l之间的夹角,若两条线段交叉(交叉点位于其中一条线的两点之间),取较小的夹角 */
public double getAngle(Line l) {
// 利用公式θ=arctan∣(k2- k1)/(1+ k1k2)∣,此时求较小的夹角
double k2 = getSlope();
double k1 = l.getSlope();
return (double) (Math.atan(Math.abs((k2 - k1) / (1 + k1 * k2))) * 180.0 / Math.PI);// 返回值为角度
}
// 是否平行,平行返回true,否则false。
public boolean isParallel(Line l) {
Double b1 = this.getSlope();
Double b2 = l.getSlope();
if ((b1.isInfinite()) && (b2.isInfinite())) {
return true;
} else {
return (this.getSlope().doubleValue() == l.getSlope().doubleValue());
}
}
// 两条线是否重合,重合返回true,否则false。
public boolean isCoincide(Line l) {
if (!this.isParallel(l)) {
return false;
}
if (this.isOnline(l.p1)) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
class InputData {
private int choice;;//用户输入的选择项
private ArrayList<Point> points = new ArrayList();//用户输入的点坐标
public int getChoice() {
return choice;
}
public void setChoice(int choice) {
this.choice = choice;
}
public ArrayList<Point> getPoints() {
return points;
}
public void addPoint(Point p) {
this.points.add(p);
}
}
//用于处理线条相关功能中出现的异常提示。
class LineInputError {
// 直线的两点重合的错误判断和提示。
public static void pointsCoincideError(Point p1, Point p2) {
if ((p1.getX() == p2.getX()) && p1.getY() == p2.getY()) {
System.out.println("points coincide");
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
class OutFormat {
//按要求格式化实数的输出。
public static Double doubleFormat(double b) {
DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("#.000000");
Double output = Double.valueOf(df.format(b));
return output;
}
}
class ParseInput {
/*
* 输入:完整的输入字符串,包含选项和所有点的信息,格式:选项:x1,y1 x2,y2 .....xn,yn。选项只能是1-5
* 一个空InputData对象
* 处理:将输入字符串中的选项和点信息提取出来并设置到InputData对象中
* 输出:包含选项值和所有点的Point对象的InputData对象。
*/
public static void paseInput(String s, InputData d) {
PointInputError.wrongChoice(s);
d.setChoice(getChoice(s));
s = s.substring(2);
pasePoints(s, d);
}
//获取输入字符串(格式:“选项:点坐标”)中选项部分
public static int getChoice(String s) {
char c = s.charAt(0);
return c-48;
}
/*
* 输入:一个字符串,包含所有点的信息,格式:x1,y1 x2,y2 .....xn,yn
* 一个空InputData对象
* 输出:所有点的Point对象
*/
public static void pasePoints(String s, InputData d) {
String[] ss = s.split(" ");
if (ss.length == 0)
return;
for (int i = 0; i < ss.length; i++) {
d.addPoint(readPoint(ss[i]));
}
}
/*
* 输入:包含单个点信息的字符串,格式:x,y
* 输出:Point对象
*/
public static Point readPoint(String s) {
PointInputError.wrongPointFormat(s);
String[] ss = s.split(",");
double x = Double.parseDouble(ss[0]);
double y = Double.parseDouble(ss[1]);
// System.out.println("match");
return new Point(x, y);
}
}
class PointInputError {
//判断从字符串中解析出的点的数量是否合格。
public static void wrongNumberOfPoints(ArrayList ps, int num) {
if (ps.size() != num) {
System.out.println("wrong number of points");
System.exit(0);
}
}
//判断输入的字符串中点的坐标部分格式是否合格。若不符合,报错并退出程序
public static void wrongPointFormat(String s) {
if (!s.matches("[+-]?([1-9]\\d*|0)(\\.\\d+)?,[+-]?([1-9]\\d*|0)(\\.\\d+)?")) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
// 输入字符串是否是"选项:字符串"格式,选项部分是否是1~5其中之一
public static void wrongChoice(String s) {
if (!s.matches("[1-6]:.+")) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
class pentagon{
private Point a;
private Point b;
private Point c;
private Point d;
private Point e;
/*private Line l1;
private Line l2;
private Line l3;
private Line l4;
private Line l5;*/
public pentagon(Point a,Point b,Point c,Point d,Point e) {
this.a=a;
this.b=b;
this.c=c;
this.d=d;
this.e=e;
/*this.l1=new Line( a, b);
this.l2=new Line( b, c);
this.l3=new Line( c, d);
this.l4=new Line( d, e);
this.l5=new Line( e, a);*/
}
public boolean ispentagon(){//是否为五边形
double k1=(this.a.getY()-this.b.getY())/(this.a.getX()-this.b.getX());
double k2=(this.a.getY()-this.c.getY())/(this.a.getX()-this.c.getX());
double k3=(this.a.getY()-this.d.getY())/(this.a.getX()-this.d.getX());
double k4=(this.a.getY()-this.e.getY())/(this.a.getX()-this.e.getX());
double k5=(this.b.getY()-this.c.getY())/(this.b.getX()-this.c.getX());
double k6=(this.b.getY()-this.d.getY())/(this.b.getX()-this.d.getX());
double k7=(this.b.getY()-this.e.getY())/(this.b.getX()-this.e.getX());
double k8=(this.c.getY()-this.d.getY())/(this.c.getX()-this.d.getX());
double k9=(this.c.getY()-this.e.getY())/(this.c.getX()-this.e.getX());
//double k10=(this.d.getY()-this.e.getY())/(this.d.getX()-this.e.getX());
if(k1!=k2&&k1!=k3&&k1!=k4&&k2!=k3&&k2!=k4&&k3!=k4&&k5!=k6&&k5!=k7&&k6!=k7&&k8!=k9) {
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
public boolean istupengtagon() {//是否为凸五边形
double k1=(this.a.getY()-this.b.getY())/(this.a.getX()-this.b.getX());
double k2=(this.a.getY()-this.c.getY())/(this.a.getX()-this.c.getX());
double k3=(this.a.getY()-this.d.getY())/(this.a.getX()-this.d.getX());
double k4=(this.a.getY()-this.e.getY())/(this.a.getX()-this.e.getX());
double k5=(this.b.getY()-this.c.getY())/(this.b.getX()-this.c.getX());
double k6=(this.b.getY()-this.d.getY())/(this.b.getX()-this.d.getX());
double k7=(this.b.getY()-this.e.getY())/(this.b.getX()-this.e.getX());
double k8=(this.c.getY()-this.d.getY())/(this.c.getX()-this.d.getX());
double k9=(this.c.getY()-this.e.getY())/(this.c.getX()-this.e.getX());
double k10=(this.d.getY()-this.e.getY())/(this.d.getX()-this.e.getX());
double angle1 =(Math.atan(Math.abs((k4 - k1) / (1 + k1 * k4))) * 180.0 / Math.PI);
double angle2 =(Math.atan(Math.abs((k5 - k1) / (1 + k1 * k5))) * 180.0 / Math.PI);
double angle3 =(Math.atan(Math.abs((k5 - k8) / (1 + k5 * k8))) * 180.0 / Math.PI);
double angle4 =(Math.atan(Math.abs((k8 - k10) / (1 + k8 * k10))) * 180.0 / Math.PI);
double angle5 =(Math.atan(Math.abs((k4 - k10) / (1 + k4 * k10))) * 180.0 / Math.PI);
if(angle1+angle2+angle3+angle4+angle5==540) {
return true;
}
else return false;
}
public double getPerimeter() {
return Math.sqrt((a.getX()-b.getX())*(a.getX()-b.getX())+(a.getY()-b.getY())*(a.getY()-b.getY()))+Math.sqrt((b.getX()-c.getX())*(b.getX()-c.getX())+(b.getY()-c.getY())*(b.getY()-c.getY()))+Math.sqrt((c.getX()-d.getX())*(c.getX()-d.getX())+(c.getY()-d.getY())*(c.getY()-d.getY()))+Math.sqrt((d.getX()-e.getX())*(d.getX()-e.getX())+(d.getY()-e.getY())*(d.getY()-e.getY()))+Math.sqrt((e.getX()-a.getX())*(e.getX()-a.getX())+(e.getY()-a.getY())*(e.getY()-a.getY()));
}
public double getArea() {
double d1=Math.abs(b.getX() * (a.getY()-e.getY()) - b.getY() * (a.getX()-e.getX()) - a.getX() * (a.getY()-e.getY()) + a.getY() * (a.getX()-e.getX()))
/Math.sqrt((a.getX()-e.getX())*(a.getX()-e.getX())+(a.getY()-e.getY())*(a.getY()-e.getY()));//b点到ae线上的距离
double d2=Math.abs(e.getX() * (b.getY()-c.getY()) - e.getY() * (b.getX()-c.getX()) - b.getX() * (b.getY()-c.getY()) + b.getY() * (b.getX()-c.getX()))
/Math.sqrt((b.getX()-c.getX())*(b.getX()-c.getX())+(b.getY()-c.getY())*(b.getY()-c.getY()));//e点到bc线上的距离
double d3=Math.abs(d.getX() * (c.getY()-e.getY()) - d.getY() * (c.getX()-e.getX()) - c.getX() * (c.getY()-e.getY()) + c.getY() * (c.getX()-e.getX()))
/Math.sqrt((e.getX()-c.getX())*(e.getX()-c.getX())+(e.getY()-c.getY())*(e.getY()-c.getY()));;//d点到ce线上的距离
return (d1*Math.sqrt((a.getX()-e.getX())*(a.getX()-e.getX())+(a.getY()-e.getY())*(a.getY()-e.getY()))+d2*Math.sqrt((b.getX()-c.getX())*(b.getX()-c.getX())+(b.getY()-c.getY())*(b.getY()-c.getY()))+d3*Math.abs((e.getX()-c.getX())*(e.getX()-c.getX())+(e.getY()-c.getY())*(e.getY()-c.getY())))/2;
}
}
-
设计一个类表示平面直角坐标系上的点Point,私有属性分别为横坐标x与纵坐标y,数据类型均为实型数,除构造方法以及属性的getter与setter方法外,定义一个用于显示信息的方法display(),用来输出该坐标点的坐标信息,格式如下:
(x,y),数值保留两位小数。为简化题目,其中,坐标点的取值范围设定为(0,200]。若输入有误,系统则直接输出Wrong Format -
设计一个类表示平面直角坐标系上的线Line,私有属性除了标识线段两端的点point1、point2外,还有一个字符串类型的color,用于表示该线段的颜色,同样,除构造方法以及属性的getter与setter方法外,定义一个用于计算该线段长度的方法getDistance(),还有一个用于显示信息的方法display(),用来输出线段的相关信息,输出格式如下:
``` The line's color is:颜色值 The line's begin point's Coordinate is: (x1,y1) The line's end point's Coordinate is: (x2,y2) The line's length is:长度值 ```其中,所有数值均保留两位小数,建议可用
String.format("%.2f", data)方法。设计类图如下图所示。
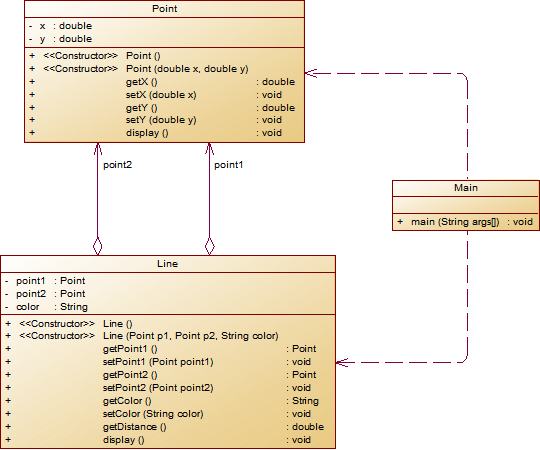
** 题目要求:在主方法中定义一条线段对象,从键盘输入该线段的起点坐标与终点坐标以及颜色,然后调用该线段的display()方法进行输出。**
- 以下情况为无效作业
- 无法运行
- 设计不符合所给类图要求
- 未通过任何测试点测试
- 判定为抄袭
输入格式:
分别输入线段的起点横坐标、纵坐标、终点的横坐标、纵坐标以及颜色,中间可用一个或多个空格、tab或者回车分隔。
输出格式:
The line's color is:颜色值
The line's begin point's Coordinate is:
(x1,y1)
The line's end point's Coordinate is:
(x2,y2)
The line's length is:长度值输入样例1:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
5
9.4
12.3
84
Red输出样例1:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
The line's color is:Red
The line's begin point's Coordinate is:
(5.00,9.40)
The line's end point's Coordinate is:
(12.30,84.00)
The line's length is:74.96
输入样例2:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
80.2356
352.12
24.5
100
Black
输出样例2:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Wrong Format在“点与线(类设计)”题目基础上,对题目的类设计进行重构,以实现继承与多态的技术性需求。
- 对题目中的点Point类和线Line类进行进一步抽象,定义一个两个类的共同父类Element(抽象类),将display()方法在该方法中进行声明(抽象方法),将Point类和Line类作为该类的子类。
- 再定义一个Element类的子类面Plane,该类只有一个私有属性颜色color,除了构造方法和属性的getter、setter方法外,display()方法用于输出面的颜色,输出格式如下:
The Plane's color is:颜色 - 在主方法内,定义两个Point(线段的起点和终点)对象、一个Line对象和一个Plane对象,依次从键盘输入两个Point对象的起点、终点坐标和颜色值(Line对象和Plane对象颜色相同),然后定义一个Element类的引用,分别使用该引用调用以上四个对象的display()方法,从而实现多态特性。示例代码如下:
element = p1;//起点Point element.display(); element = p2;//终点Point element.display(); element = line;//线段 element.display(); element = plane;//面 element.display();类结构如下图所示。
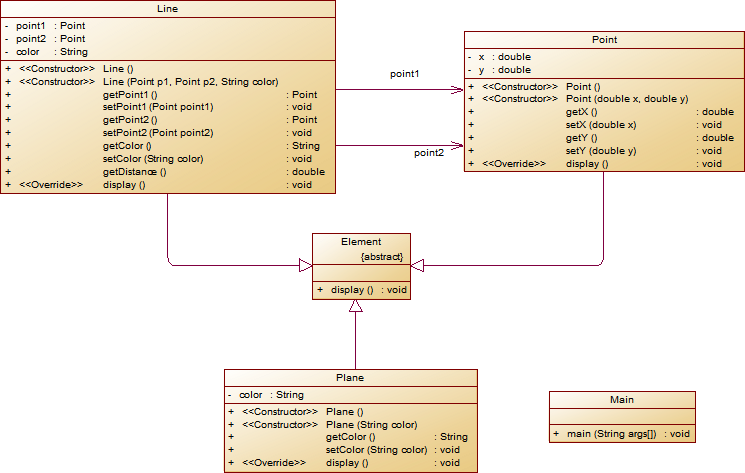
其中,所有数值均保留两位小数,建议可用String.format("%.2f", data)方法。
- 以下情况为无效作业
- 无法运行
- 设计不符合所给类图要求
- 未通过任何测试点测试
- 判定为抄袭
输入格式:
分别输入线段的起点横坐标、纵坐标、终点的横坐标、纵坐标以及颜色,中间可用一个或多个空格、tab或者回车分隔。
输出格式:
(x1,y1)
(x2,y2)
The line's color is:颜色值
The line's begin point's Coordinate is:
(x1,y1)
The line's end point's Coordinate is:
(x2,y2)
The line's length is:长度值
The Plane's color is:颜色值
输入样例1:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
5
9.4
12.3
84
Red
输出样例1:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
(5.00,9.40)
(12.30,84.00)
The line's color is:Red
The line's begin point's Coordinate is:
(5.00,9.40)
The line's end point's Coordinate is:
(12.30,84.00)
The line's length is:74.96
The Plane's color is:Red
输入样例2:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
5
9.4
12.3
845
Black
输出样例2:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Wrong Format
在“点与线(继承与多态)”题目基础上,对题目的类设计进行重构,增加容器类保存点、线、面对象,并对该容器进行相应增、删、遍历操作。
- 在原有类设计的基础上,增加一个GeometryObject容器类,其属性为
ArrayList<Element>类型的对象(若不了解泛型,可以不使用<Element>) - 增加该类的
add()方法及remove(int index)方法,其功能分别为向容器中增加对象及删除第index - 1(ArrayList中index>=0)个对象 - 在主方法中,用户循环输入要进行的操作(choice∈[0,4]),其含义如下:
- 1:向容器中增加Point对象
- 2:向容器中增加Line对象
- 3:向容器中增加Plane对象
- 4:删除容器中第index - 1个数据,若index数据非法,则无视此操作
- 0:输入结束
choice = input.nextInt(); while(choice != 0) { switch(choice) { case 1://insert Point object into list ... break; case 2://insert Line object into list ... break; case 3://insert Plane object into list ... break; case 4://delete index - 1 object from list int index = input.nextInt(); ... } choice = input.nextInt(); }输入结束后,按容器中的对象顺序分别调用每个对象的display()方法进行输出。
类图如下所示:
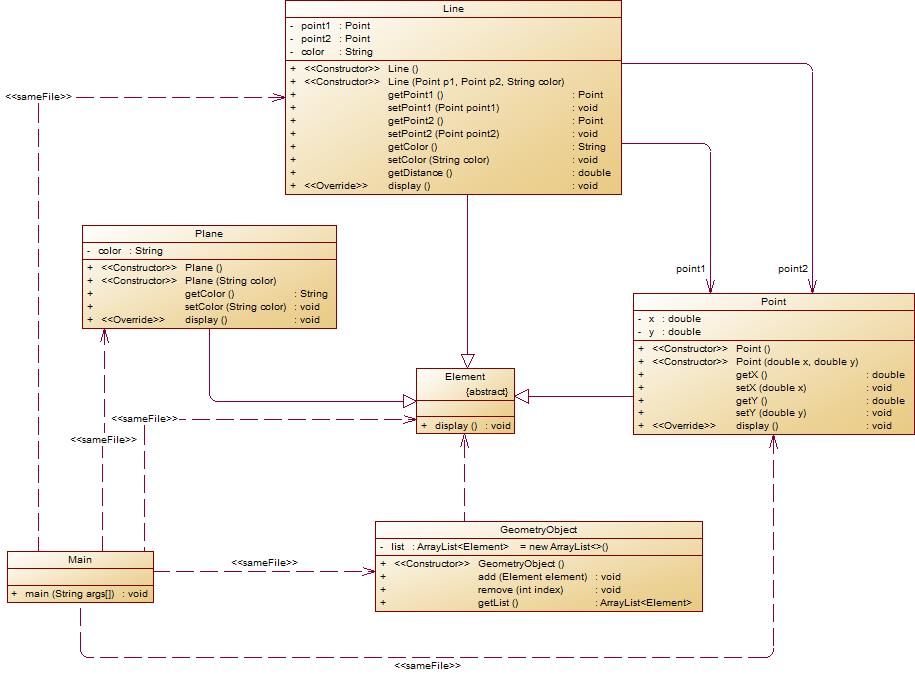
- 以下情况为无效作业
- 无法运行
- 设计不符合所给类图要求
- 未通过任何测试点测试
- 判定为抄袭
输入格式:
switch(choice) {
case 1://insert Point object into list
输入“点”对象的x,y值
break;
case 2://insert Line object into list
输入“线”对象两个端点的x,y值
break;
case 3://insert Plane object into list
输入“面”对象的颜色值
break;
case 4://delete index - 1 object from list
输入要删除的对象位置(从1开始)
...
}
输出格式:
- Point、Line、Plane的输出参考题目2
- 删除对象时,若输入的index超出合法范围,程序自动忽略该操作
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
1
3.4
5.6
2
4.4
8.0
0.98
23.888
Red
3
Black
1
9.8
7.5
3
Green
4
3
0
输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
(3.40,5.60)
The line's color is:Red
The line's begin point's Coordinate is:
(4.40,8.00)
The line's end point's Coordinate is:
(0.98,23.89)
The line's length is:16.25
(9.80,7.50)
The Plane's color is:Green
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String args[]){
Scanner s=new Scanner(System.in);
double x1,y1,x2,y2;
String color;
x1=s.nextDouble();
y1=s.nextDouble();
x2=s.nextDouble();
y2=s.nextDouble();
color=s.nextLine();
if(x1<0||x1>200||x2<0||x2>200||y1<0||y1>200||y2<0||y2>200){
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
color=s.nextLine();
Point p1=new Point(x1,y1);
Point p2=new Point(x2,y2);
Line l1=new Line(p1,p2,color);
l1.display();
}
}
/*class point{
private double x;
private double y;
point(){
this.x=0;
this.y=0;
}
point(double x,double y){
this.x=x;
this.y=y;
}
}
public double getX(double x){
return x;
}
public double setX(double x){
this.x=x;
}
public double getY(double y){
return y;}
public double setY(double y){
this.y=y;
}
*/
class Point{
private double x;
private double y;
Point(){
}
Point(double x,double y){
setX(x);
setY(y);
}
public double getX(){
return x;
}
public void setX(double x){
this.x=x;
}
public double getY(){
return y;
}
public void setY(double y){
this.y=y;
}
public void display(){
System.out.println("("+String.format("%.2f",getX( ))+","+String.format("%.2f",getY())+")");
}
}
class Line{
Point point1;
Point point2;
String color;
Line(){
}
Line(Point p1,Point p2,String color){
setPoint1(p1);
setPoint2(p2);
setColor(color);
}
public Point getPoint1(){
return point1;
}
public void setPoint1(Point point1){
this.point1=point1;
}
public Point getPoint2(){
return point2;
}
public void setPoint2(Point point2){
this.point2=point2;
}
public String getColor(){
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color){
this.color=color;
}
public double getDistance() {
return Math.sqrt(Math.pow((getPoint2().getY() - getPoint1().getY()),2) + Math.pow((getPoint2().getX() - getPoint1().getX()), 2));
}
public void display(){
System.out.println("The line's color is:"+getColor());
System.out.println("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:");
point1.display();
System.out.println("The line's end point's Coordinate is:");
point2.display();
System.out.println("The line's length is:"+String.format("%.2f", getDistance()));
}
}
三、总结
通过这两次的PTA作业和期中考试,我深刻的认识到自己太多知识点应用太不熟练了,如:Arraylist的使用、包装类、多态、容器类的使用等等。在之后的学习中,我会多看他人优秀的代码,改进我的代码,化繁为简介。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号