day04_数组_多维数组_冒泡排序_稀疏数组
1、java数组

package array; public class 数组 { //变量的类型 变量的名字 = 变量的值 //数组类型 public static void main(String[] args) { int[] nums; //1.声明一个数组 //int nums2[];不常用 //静态初始化:创建 + 赋值 花括号固定了只有8个元素 int[] a = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8}; nums = new int[10]; //2.创建一个数组 //声明和创建一个数组组合 int[] nums2 = new int[10]; //3.给数组元素中赋值 nums[0] = 1; nums[1] = 2; nums[2] = 3; nums[3] = 4; nums[4] = 5; nums[5] = 6; nums[6] = 7; nums[7] = 8; nums[8] = 9; nums[9] = 10; //计算所有数值 int sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { sum+=nums[i]; } System.out.println("数组的和是:"+sum); } }
数组两种初始方法

package array; public class 数组两种初始方法 { public static void main(String[] args) { //静态初始化:创建 + 赋值 花括号固定了只有8个元素 int[] a = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8}; //动态初始化:包含默认初始化 int[] b = new int[10]; b[0] = 10; b[1] = 10; System.out.println(b[0]); //结果是:10 System.out.println(b[1]); //结果是:10 System.out.println(b[2]); //结果是:未设置值,默认是0 System.out.println(b[3]); //结果是:未设置值,默认是0 } }
数组的四个基本特点
◆其长度是确定的。数组一旦被创建,它的大小就是不可以改变的
◆其元素必须是相同类型不允许出现混合类型
◆数组中的元素可以是任何数据类型,包括基本类型和引用类型
◆数组变量属引用类型,数组也可以看成是对象,数组中的每个元素相当于该对象的成员变量数组本身就是对象,Java中对象是在堆中的,因此数组无论保存原始类型还是其他对象类型,数组对象本身是在堆中的
数组边界
◆下标的合法区间:[0, length-1],如果越界就会报错;
package array; public class 边界 { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] b = new int[2]; System.out.println(b[2]); } } 结果是: ArraylndexOutofBounds Exception:数组下标越界异常!
package array; public class 数组练习 { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arrays = {1,2,3,4,5}; //遍历数组 for (int i = 0; i < arrays.length; i++) { System.out.println(arrays[i]); } System.out.println("================="); //计算数组的和 int sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < arrays.length; i++) { sum += arrays[i]; } System.out.println(sum); System.out.println("================="); //查找max元素 int max = arrays[0]; for (int i = 1; i < arrays.length; i++) { if (arrays[i]>max){ max = arrays[i]; } } System.out.println(max); } }
package array; public class 增强for循环 { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arrays = {1,2,3,4,5}; //JDK1.5后支持,没有下标 //遍历数组每个元素 for (int array : arrays) { System.out.println(array); } } }
数组作方法入参
package array; public class 数组作方法入参 { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arrays = {1,2,3,4,5}; printArray(arrays); } public static void printArray(int[] arrays){ for (int i = 0; i < arrays.length; i++) { System.out.print(arrays[i]+" "); } } }
package array; public class 数组作返回值 { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arrays = {1,2,3,4,5}; int[] reverse = reverse(arrays); printArray(reverse); } //定义数组方法作返回值 public static int[] reverse(int[] arrays){ int[] result = new int[arrays.length]; for (int i = 0, j=result.length -1; i < arrays.length; i++,j--) { result[j] = arrays[i]; } return result; } //数组作方法入参 public static void printArray(int[] arrays){ for (int i = 0; i < arrays.length; i++) { System.out.print(arrays[i]+" "); } } }
2、多维数组
package array; public class 多维数组 { public static void main(String[] args) { //有点类似坐标 int[][] array = {{1,2},{2,3},{3,4},{4,5}}; for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) { for (int i1 = 0; i1 < array[i].length; i1++) { System.out.print(array[i][i1]+" "); } System.out.println(); } } } /*输出结果是: 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 5 */
1、联系:打印数组
package array; import java.util.Arrays; public class 打印数组 { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 9898, 31231, 543, 21, 3, 23}; System.out.println(a); //输出结果是:[I@10f87f48 Arrays.sort(a); //数组进行排序:升序 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a)); //输出结果是:[1, 2, 3, 4, 9898, 31231, 543, 21, 3, 23] //应用给自定义方法,同样的结果:[1, 2, 3, 4, 9898, 31231, 543, 21, 3, 23] printArrays(a); } //自定义toString()方法,重复造轮子 public static void printArrays(int[] a){ for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { if (i==0){ System.out.print("["); } if (i==a.length-1){ System.out.print(a[i]+"]"); }else { System.out.print(a[i]+", "); } } System.out.println(); } }
package array; import java.util.Arrays; public class 数组fill方法 { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 9898, 31231, 543, 21, 3, 23}; Arrays.sort(a); //排序:升序 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a)); //输出结果是:[1, 2, 3, 3, 4, 21, 23, 543, 9898, 31231] Arrays.fill(a,2,4,0); //fill方法是:从2到4之间的index数换成给定的0值 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a)); //输出结果是:[1, 2, 0, 0, 4, 21, 23, 543, 9898, 31231] } }
3、冒泡排序
package array; import java.util.Arrays; public class 冒泡排序 { //比较数组中, 两个相邻的元素, 如果第一个数比第二个数大, 我们就交换他们位置 //每一次比较, 对会产生一个最大的值, 或者最小的数字 //下一轮则可以少一次排序 //依次循环, 直到结束 public static void main(String[] args) { int[] a = {1, 4, 5, 6, 72, 2, 2, 2, 25, 6, 7}; // Arrays.sort(a); // System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a)); sort(a); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a)); } public static int[] sort(int[] arrays){ //临时变量 int temp = 0; //外层循环,判断我们这个要走多少次 for (int i = 0; i < arrays.length - 1; i++) { boolean flag = false; //通过flag标识位减少没有意义的比较 ///内层循环,比价判断两个数,如果第一个数,比第二个数大,则交换位置 for (int i1 = 0; i1 < arrays.length - 1 - i; i1++) { if (arrays[i1+1]<arrays[i1]){ temp = arrays[i1]; arrays[i1] = arrays[i1+1]; arrays[i1+1] = temp; flag = true; } } if (flag == false){ break; } } return arrays; } }
4、稀疏数组
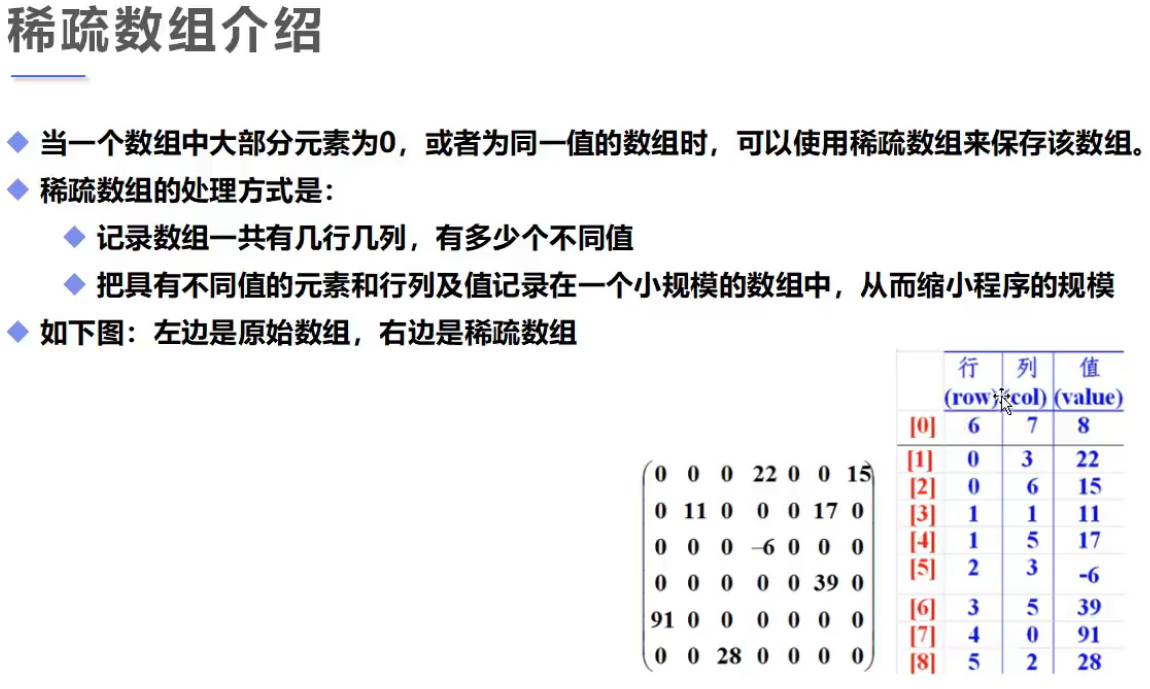
练习:稀疏数组

package array; public class 稀疏数组 { public static void main(String[] args){ //1.创建一个二维数组11*11 0:没有棋子,1:黑棋 2:白棋 int[][] array1 = new int[11][11]; array1[1][2]=1; array1[2][3]=2; // 翰出原始的数组 System.out.println("输出原始的数组"); for (int[] ints :array1){ for (int anInt : ints){ System.out.print(anInt+"\t"); } //转换为稀疏数组保存 System.out.println(); } //转换为稀疏数组保存 //获取有效值的个数 int sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 11; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < 11; j++) { if (array1[i][j]!=0){ sum++; } } } System.out.println("有效值的个数: "+sum); System.out.println("====================="); //2.创建一个稀疏数组的数组 int[][] array2 = new int[sum+1][3]; array2[0][0] = 11; //第一例 array2[0][1] = 11; //第二列 array2[0][2] = sum; //第三列 //遍历二维数组,将非零的值,存放稀疏数组中 int count = 0; for (int i = 0; i < array1.length; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < array1[i].length; j++) { if (array1[i][j]!=0){ count++; array2[count][0]=i; //第一列 array2[count][1]=j; //第二列 array2[count][2]=array1[i][j]; //第三列 } } } //输出稀疏数组 System.out.println("输出稀疏数组"); for (int i = 0; i < array2.length; i++) { System.out.println(array2[i][0]+"\t" +array2[i][1]+"\t" +array2[i][2]+"\t"); } System.out.println("====================="); //1.读取稀疏数组 int[][] array3 = new int[array2[0][0]][array2[0][1]]; //2.给其中的元素还原它的值 for (int i = 1; i < array2.length; i++) { array3[array2[i][0]][array2[i][1]] = array2[i][2]; } //3.打印 System.out.println("输出还原的数组"); for (int[] ints :array3){ for (int anInt : ints){ System.out.print(anInt+"\t"); } //转换为稀疏数组保存 System.out.println(); } } } /* 输出原始的数组 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 有效值的个数: 2 ===================== 输出稀疏数组 11 11 2 1 2 1 2 3 2 ===================== 输出还原的数组 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 进程已结束,退出代码 0 */



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号