day02 java_八大基本数据类型
1、八大基本数据类型
public class hello { public static void main(String[] args) { //八大基本数据类型 int num1 = 10; //最常用 byte num2 = 20; short num3 =30; long num4 = 30l; //Long类型要再数字后面加个L //小数:浮点数 float num5 = 50.1F;//Lfloat类型要在数字后面加个F double num6 = 3.143254125412453423143132453321; //字符,只能一个数字,不能两个数字 //String不是关键字,类 char name = '数'; String namea = "yuhua"; //布尔值.要么ture,或false boolean flag = true; // boolean flag = false; } }

public class 进制 { public static void main(String[] args) { int i = 10; int i2 = 010; //八进制 int i3 = 0x10; //十六进制ox 0-9 A-F System.out.println(i); System.out.println(i2); System.out.println(i3); System.out.println("=========================="); //========================================================== //浮点数拓展,银行业务怎么表示? 钱 //BigDecimal 数学工具类 //========================================================== //float 有限 离散 舍入误差 大约 接近但不等于 //double //最好完全不适用浮点数进行比较 //最好完全不适用浮点数进行比较 //最好完全不适用浮点数进行比较 float f = 0.1f; double d = 1.0/10; System.out.println(f==d);//false System.out.println(f); System.out.println(d); float d1 = 222232344444444444423423f; //true float d2 = d1 + 1; System.out.println(d1==d2); //========================================================== //字符拓展? //========================================================== System.out.println("=========================="); char c1 = 'a'; char c2 = '中'; System.out.println(c1); System.out.println((int)c1); //强行转换 System.out.println(c2); System.out.println((int)c2); //强行转换 //所有字符本质还是数字 //编码 Unicode 表 2字节 0 - 65536 char c3 = '\u0061'; System.out.println(c3); //a //转义字符 // \t 制表符 // \n 换行 // .... System.out.println("hello\tworld"); //new 新的内存空间地址,地址不一样,false System.out.println("=========================="); String sa = new String("hello world"); String sb = new String("hello world"); System.out.println(sa==sb); //字符串比较true String sc = "hello world"; String sd = "hello world"; System.out.println(sc==sd); //对象 从内存分析 //布尔值扩展 boolean flag = true; if (flag==true){}//新手 if (flag){} //老手 // less is more 代码要精简易读 } }

public class 类型转换 { public static void main(String[] args) { int i = 128; byte b = (byte)i; System.out.println(i); System.out.println(b); //输出结果-128,最大值127,内存溢出,超出范围 //低 ----------------------------------> 高 //byte,short,char->int->long->float->double //强制转换 (类型)变量名 高 -- 低 //自动转换 低 -- 高 /*1、不能对布尔值进行转换 * 2、不能把对象类转换为不相干的类型 * 3、在高容量转换到低容量的时候,强制转换 * 4、转换的时候可能存在内存溢出,或者精度问题 * */ System.out.println("=========================="); //操作比较大的数的时候,注意溢出问题 //jdk7新特性,数字之间可以用下划线分割 int money = 10_0000_0000; int years = 20; int total = money*years; long total2 = money*years; System.out.println(total); //输出-1474836480 System.out.println(total2); //输出还是-1474836480,因为转换之前已经存在问题 long total3 = money*((long)years); //运算时解决内存溢出问题, System.out.println(total3); //输出20000000000 } }

public class demo { //属性:变量 //实例变量:从属于对象, String name = "yuhua"; int age = 24; static double salary = 2500; //main 方法 public static void main(String[] args) { //局部变量;必须声明和初始化值 int i = 10; System.out.println(i); //变量类型 变量名字 = new demo(); demo demo = new demo(); //new demo().var+回车 System.out.println(demo.age); System.out.println(demo.name); System.out.println(salary); System.out.println("====================="); } //其他方法 public void add(){ } }

public class demo1 { //常量 //修饰符不存在先后顺序,可以static final 或者 final static final static double pi = 3.14; public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(pi); } }

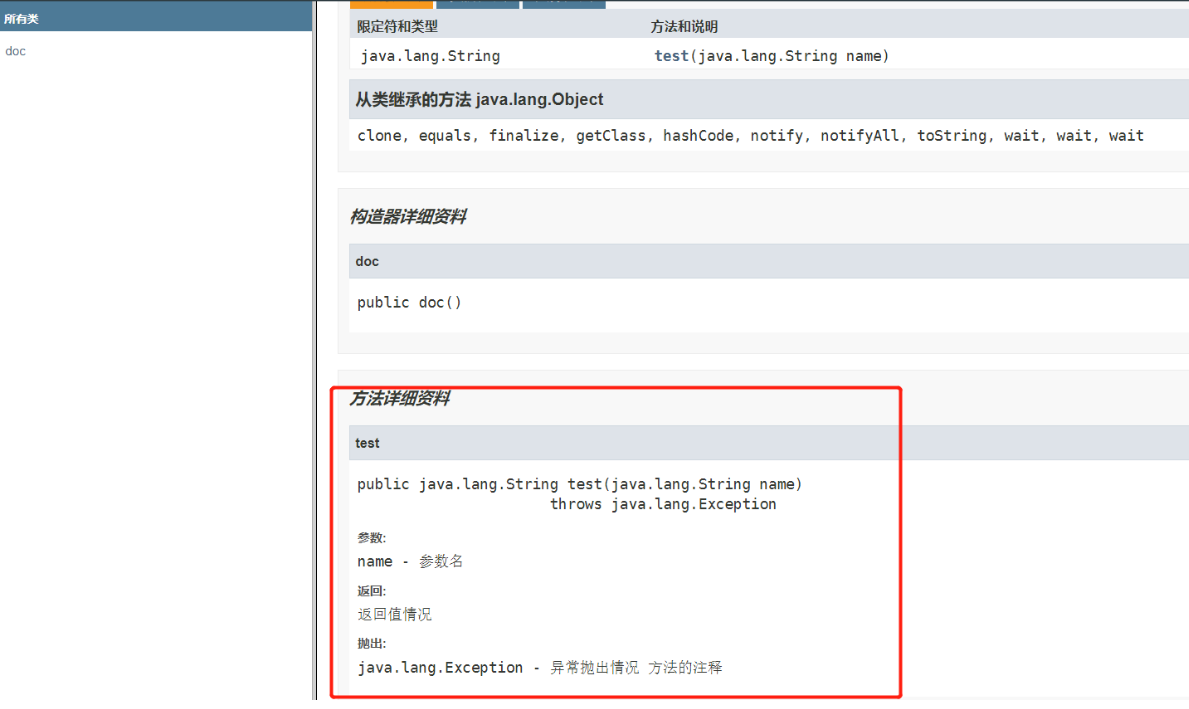
/** * @author 作者名 * @version 版本号 * 放到类上面就是类的注释 */ public class doc { String name; /** * @author 作者名 按/**回车就可以自动补全所有doc文档信息 * @version 版本号 * @param name 参数名 * @return 返回值情况 * @throws Exception 异常抛出情况 * 方法的注释 */ public String test(String name) throws Exception{ return name; } } javadoc -encoding UTF-8 -charset UTF-8 Doc.java
生成html文件,打开index 文件就可以看到doc文档帮助



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号