Nacos-客户端续约
1.介绍
前面的章节说了,客户端每5秒会发送心跳请求注册中心,请求接口示例:
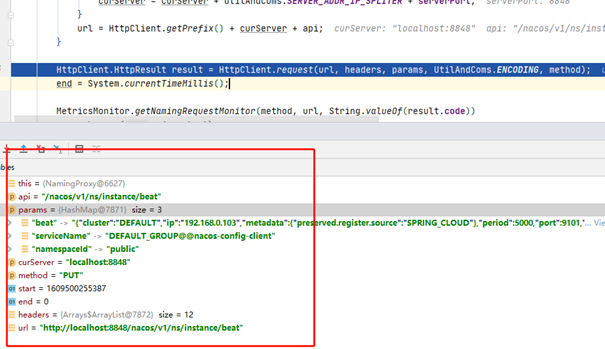
心跳处理基本流程
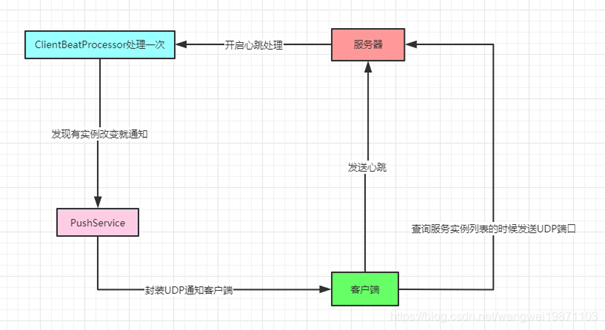
图片来源: https://blog.csdn.net/wangwei19871103/article/details/105838354
2. InstanceController.beat()接口
直接看 service.processClientBeat(clientBeat);这行代码;
2.1 processClientBeat
public void processClientBeat(final RsInfo rsInfo) {
ClientBeatProcessor clientBeatProcessor = new ClientBeatProcessor();
clientBeatProcessor.setService(this);
clientBeatProcessor.setRsInfo(rsInfo);
//创建一个0延迟的执行任务
HealthCheckReactor.scheduleNow(clientBeatProcessor);
}
public static ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleNow(Runnable task) {
return GlobalExecutor.scheduleNamingHealth(task, 0, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
初始化一个 ClientBeatProcessor 对象,该类实现了 Runnable 接口,最终将该任务丢到了线程池中立即执行;
2.2 ClientBeatProcessor
public class ClientBeatProcessor implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
//获取服务的service,例如: DEFAULT_GROUP@@nacos-config-client
Service service = this.service;
String ip = rsInfo.getIp();
String clusterName = rsInfo.getCluster();
int port = rsInfo.getPort();
Cluster cluster = service.getClusterMap().get(clusterName);
//获取该client服务的所有实例,比如 后台的nacos-config-client服务开了2个端口号
List<Instance> instances = cluster.allIPs(true);
//遍历客户端实例列表
for (Instance instance : instances) {
//从实例列表中找出与发起当前心跳请求,ip和端口一致的客户端实例
if (instance.getIp().equals(ip) && instance.getPort() == port) {
//更新最后一次心跳时间为当前时间
instance.setLastBeat(System.currentTimeMillis());
if (!instance.isMarked()) {
if (!instance.isHealthy()) {
instance.setHealthy(true);
//发布服务变更事件
getPushService().serviceChanged(service);
}
}
}
}
}
}
2.3 PushService.serviceChanged 发布事件
public void serviceChanged(Service service) {
// merge some change events to reduce the push frequency:
if (futureMap
.containsKey(UtilsAndCommons.assembleFullServiceName(service.getNamespaceId(), service.getName()))) {
return;
}
this.applicationContext.publishEvent(new ServiceChangeEvent(this, service));
}
2.4 Service定时任务心跳健康检查
服务端接收到心跳请求会更新该客户端实例最后一次的心跳时间。那这个心跳时间有什么用呢?
上一章中服务端处理客户端实例注册时,InstanceController#register--> ServiceManager#createServiceIfAbsent---->>> ServiceManager#putServiceAndInit ---->>> Service#init 到这里会初始化一个定时器,进行客户端心跳续约的健康检查,具体代码:
public void init() {
//初始化一个延迟任务,延迟5s执行,间隔5s循环一次
HealthCheckReactor.scheduleCheck(clientBeatCheckTask);
for (Map.Entry<String, Cluster> entry : clusterMap.entrySet()) {
entry.getValue().setService(this);
entry.getValue().init();
}
}
/**
* Schedule client beat check task with a delay.
* * @param task client beat check task
*/
public static void scheduleCheck(ClientBeatCheckTask task) {
futureMap.putIfAbsent(task.taskKey(), GlobalExecutor.scheduleNamingHealth(task, 5000, 5000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS));
}
2.4.1 ClientBeatCheckTask
定时5s循环的心跳检查任务已经初始化好了,接下来看看 ClientBeatCheckTask :
@Override
public void run() {
try { ...
List<Instance> instances = service.allIPs(true);
// first set health status of instances:
for (Instance instance : instances) {
//当前时间 - 最后一次续约时间 > 15s, 即客户端已经超过15s没有发送HTTP心跳请求了
if (System.currentTimeMillis() - instance.getLastBeat() > instance.getInstanceHeartBeatTimeOut()) {
if (!instance.isMarked()) {
//客户端的健康标志位,因为服务端在处理HTTP心跳请求时会set它为true
if (instance.isHealthy()) {
instance.setHealthy(false); //回置健康标志位
getPushService().serviceChanged(service); //发布ServiceChangeEvent事件
//发布InstanceHeartbeatTimeoutEvent事件
ApplicationUtils.publishEvent(new InstanceHeartbeatTimeoutEvent(this, instance));
}
}
}
}
if (!getGlobalConfig().isExpireInstance()) {
return;
}
// then remove obsolete instances:
for (Instance instance : instances) {
if (instance.isMarked()) {
continue;
}
//当前时间 - 最后一次心跳时间 > 30s
if (System.currentTimeMillis() - instance.getLastBeat() > instance.getIpDeleteTimeout()) {
deleteIp(instance);
}
}
}
}
服务端心跳检测有两部分
1.客户端超过15s没有发送HTTP心跳请求,服务端会发布 InstanceHeartbeatTimeoutEvent 事件
2.客户端超过30s没有发送HTTP心跳请求,服务端会移除客户端实例
2.4.2 本地演示
步骤:
- 启动userservice服务并注册
-
userservice断点不要取消,并观察服务端断点情况
![]()
-
服务端发现超时了,异步删除
![]()
后面会继续分析PushService这个类。
参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/m0_37268363/article/details/109548821,
https://blog.csdn.net/wanghao112956/article/details/102542952 ,



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号