VGG实现
- VGG提出了可以通过重复使用简单的基础块来构建深度模型的思路。
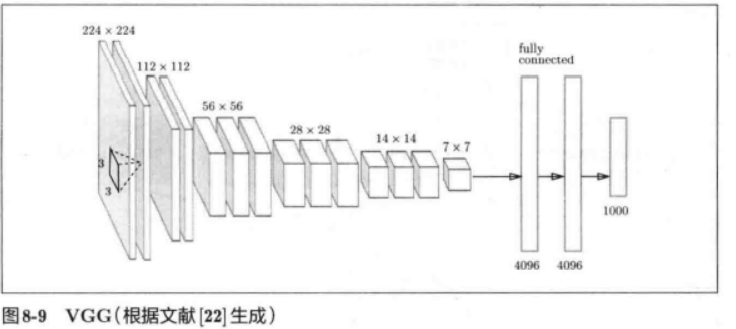
VGG块
对于给定的感受野(与输出有关的输入图片的局部大小),采用堆积的小卷积核优于采用大的卷积核,因为可以增加网络深度来保证学习更复杂的模式,而且代价还比较小(参数更少)。例如,在VGG中,使用了3个3x3卷积核来代替7x7卷积核,使用了2个3x3卷积核来代替5*5卷积核,这样做的主要目的是在保证具有相同感知野的条件下,提升了网络的深度,在一定程度上提升了神经网络的效果。
import time import torch from torch import nn,optim import sys sys.path.append('./Dive-into-DL-PyTorch-master/Dive-into-DL-PyTorch-master/code/') import d2lzh_pytorch as d2l device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu') def vgg_block(num_convs,in_channels,out_channels): blk = [] for i in range(num_convs): if i == 0: blk.append(nn.Conv2d(in_channels,out_channels,kernel_size=3, padding=1)) else: blk.append(nn.Conv2d(out_channels,out_channels,kernel_size=3, padding=1)) blk.append(nn.ReLU()) # 这里会使得高宽减半 blk.append(nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2,stride=2)) return nn.Sequential(*blk) # 列表blk加入Sequnrtial需要解引用
VGG网络
conv_arch = ((1, 1, 64), (1, 64, 128), (2, 128, 256), (2, 256, 512), (2, 512, 512)) # 经过5个vgg_block, 宽高会减半5次, 变成 224/32 = 7 fc_features = 512 * 7 * 7 # c * w * h fc_hidden_units = 4096 # 任意
def vgg(conv_arch,fc_features,fc_hidden_units=4096): net = nn.Sequential() # 卷积部分 for i,(num_convs,in_channels,out_channels) in enumerate(conv_arch): # 每经过一个vgg_block都会使高宽减半 net.add_module('vgg_block_'+str(i+1),vgg_block(num_convs, in_channels,out_channels)) # 全连接部分 net.add_module('fc',nn.Sequential(d2l.FlattenLayer(), nn.Linear(fc_features,fc_hidden_units), nn.ReLU(), nn.Dropout(0.5), nn.Linear(fc_hidden_units,fc_hidden_units), nn.ReLU(), nn.Dropout(0.5), nn.Linear(fc_hidden_units,10))) return net

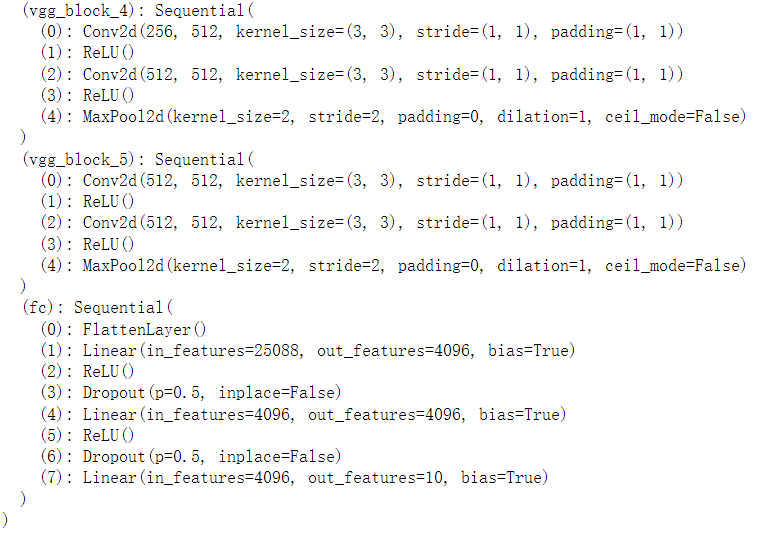
x = torch.rand(1,1,224,224) # named_children获取一级子模块及其名字(named_modules会返回所有子模块, # 包括子模块的子模块) for name,blk in net.named_children(): x = blk(x) print(name,'output shape:',x.shape)




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号