IPv4路由查找2 fib_trie
之前有涉及到 table 查找https://www.cnblogs.com/codestack/p/15975344.html
fib的创建https://www.cnblogs.com/codestack/p/15964568.html
https://vincent.bernat.ch/en/blog/2017-ipv4-route-lookup-linux
目前看下fib_trie 查找
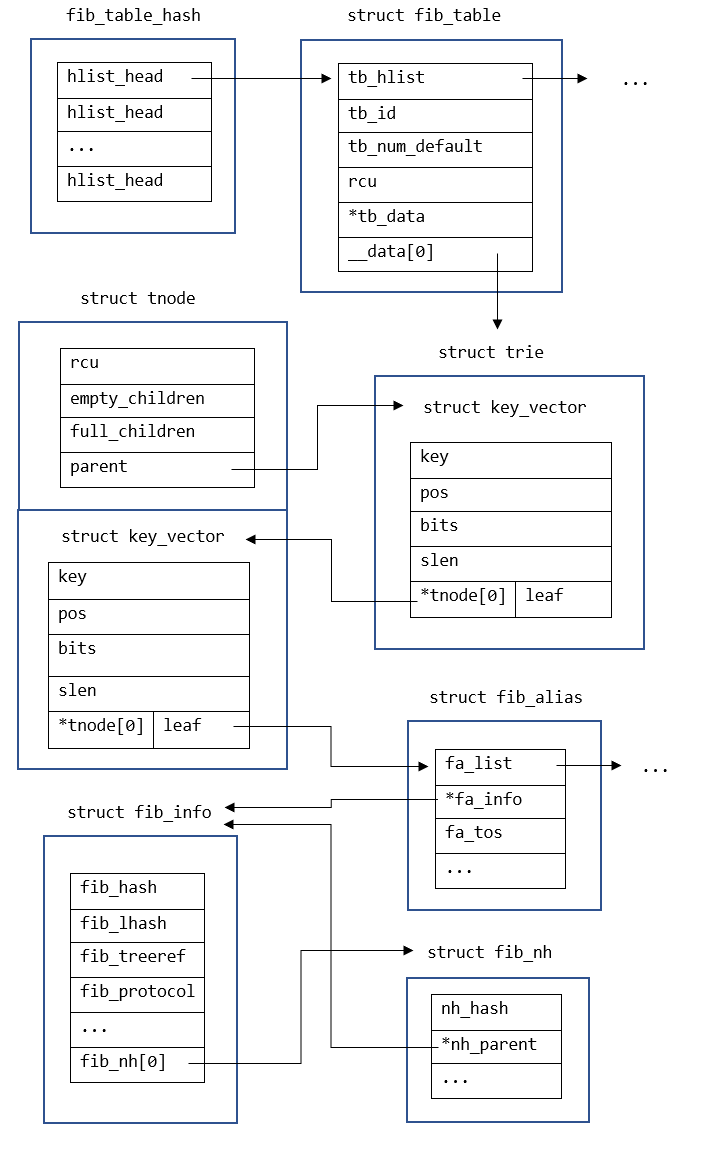
上图中,fib_table_hash表示路由表哈希数组,哈希值就是路由表 ID,每个路由表都由一个fib_table结构体表示,这个结构体尾部存放一个占位指针,用来指向路由 trie 树。
struct fib_table { struct hlist_node tb_hlist;//对于ipv4是&net->ipv4.fib_table_hash[TABLE_MAIN_INDEX]指向的哈希表,用于索引该路由项 u32 tb_id; int tb_num_default; struct rcu_head rcu; unsigned long *tb_data;//指向struct trie结构体 unsigned long __data[]; };
Trie 树中的节点都包含一个key_vector结构体,该结构体包含以下信息:
- key 为节点的关键字,前缀相同的节点存储在该节点下
- pos、bits 用于子节点的索引,key[pos, pos + bits]为子节点的索引。共有 bits 位二进制用于索引子节点,也就是该节点下能存储个子节点。leaf/tnode 用于指向叶子节点的路由信息或者子节点的信息,通过IS_LEAF宏来判断该节点是否是叶子节点,也就是 bits 为 0 的时候,该节点是叶子节点,否则是中间节点,该节点下存储其他子节点。
#define IS_TNODE(n) ((n)->bits) #define IS_LEAF(n) (!(n)->bits)
- slen 为后缀长度
struct key_vector { t_key key; unsigned char pos; /* 2log(KEYLENGTH) bits needed */ unsigned char bits; /* 2log(KEYLENGTH) bits needed */ unsigned char slen; union { /* This list pointer if valid if (pos | bits) == 0 (LEAF) */ struct hlist_head leaf; /* This array is valid if (pos | bits) > 0 (TNODE) */ struct key_vector __rcu *tnode[0]; }; };
struct tnode { struct rcu_head rcu; t_key empty_children; /* KEYLENGTH bits needed */ t_key full_children; /* KEYLENGTH bits needed */ struct key_vector __rcu *parent; struct key_vector kv[1]; #define tn_bits kv[0].bits };
|----------------------------| \|/ | | | |------------| | | tp | tn | | | |------------| | | tnode[i]-|--->| parent-|----| |------------| | | |------------| | tnode[j]-|------->| n | | tnode[k]-|----| | | |------------| | | tnode[i]-|--> | |------------| | | |------------| | | new leaf | |-->| | | | |------------|
对于LC-trie算法,了解大概;
LC-Trie有两种节点:一种是 leaf,保存了路由具体的信息的叶子结点,一种是 trie node(tnode)保存了中间节点;
创建leaf前需要找到公共前缀最多的leaf也就是fib_find_node;代码逻辑:不断匹配公共前缀直到直到找到叶子节点( pos|bits == 0)
static struct key_vector *fib_find_node(struct trie *t, struct key_vector **tp, u32 key) { struct key_vector *pn, *n = t->kv; unsigned long index = 0; do { pn = n; n = get_child_rcu(n, index); if (!n) break; index = get_cindex(key, n); /* This bit of code is a bit tricky but it combines multiple * checks into a single check. The prefix consists of the * prefix plus zeros for the bits in the cindex. The index * is the difference between the key and this value. From * this we can actually derive several pieces of data. * if (index >= (1ul << bits)) * we have a mismatch in skip bits and failed * else * we know the value is cindex * * This check is safe even if bits == KEYLENGTH due to the * fact that we can only allocate a node with 32 bits if a * long is greater than 32 bits. */ if (index >= (1ul << n->bits)) { n = NULL; break; } /* keep searching until we find a perfect match leaf or NULL */ } while (IS_TNODE(n)); *tp = pn; return n; }
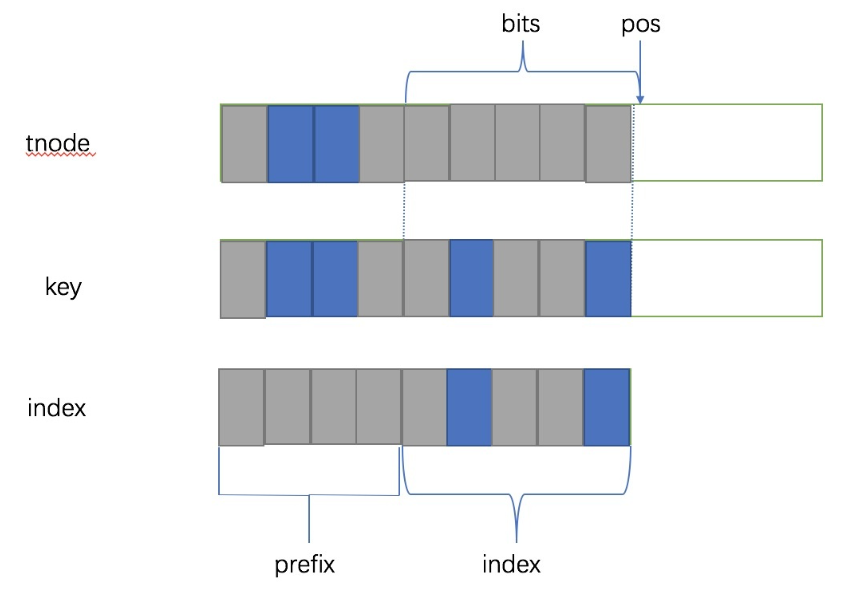
get_cindex 匹配的方式,#define get_cindex(key, kv) (((key) ^ (kv)->key) >> (kv)->pos),对 tnode 和 被比较的 key 做异或
灰色代表 0,蓝色代表 1,两个值进行异或的话,首先 pos 会被右移掉,然后 bits 的部分会原样保留,因为 tnode 的这部分都是 0。
然后bits的部分如果完全匹配的话结果就都是 0 ,但是如果不完全匹配的话,结果就会比 index 还要大,因为高位还有 1,所以这就是为什么 index >= (1ul << n->bits 能判断是否匹配的前缀的原因。
再看一下插入的流程。首先算出匹配到当前节点的子节点(有可能有,有可能没有)
static int fib_insert_node(struct trie *t, struct key_vector *tp, struct fib_alias *new, t_key key) { struct key_vector *n, *l; l = leaf_new(key, new); if (!l) goto noleaf; /* retrieve child from parent node */ n = get_child(tp, get_index(key, tp));
如果有子节点,就要创建一个新的 tnode,再把这个 key 给插入。
/* Case 2: n is a LEAF or a TNODE and the key doesn't match. * * Add a new tnode here * first tnode need some special handling * leaves us in position for handling as case 3 */ if (n) { struct key_vector *tn;
__fls find last set bit,就是找到 pos,然后扩展出有两个选择(2 的 1 次方)的 tnode。
tn = tnode_new(key, __fls(key ^ n->key), 1); if (!tn) goto notnode;
设置 tn 的 父节点为 tp,然后把 key 插入到 tn 当中。
/* initialize routes out of node */ NODE_INIT_PARENT(tn, tp); put_child(tn, get_index(key, tn) ^ 1, n); /* start adding routes into the node */ put_child_root(tp, key, tn); node_set_parent(n, tn); /* parent now has a NULL spot where the leaf can go */ tp = tn; } /* Case 3: n is NULL, and will just insert a new leaf */ node_push_suffix(tp, new->fa_slen); NODE_INIT_PARENT(l, tp); put_child_root(tp, key, l);
开始进行平衡调整树形。 这个位置没有看懂, 有机会再看,目前也就是只是使用而已
trie_rebalance(t, tp); return 0; notnode: node_free(l); noleaf: return -ENOMEM; }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号