uboot&&grub 调试内核时的参数
目前信创设备有bootloader or grub引导内核,其中
grub:
linux /bzImage console=ttyS0,115200 ramdisk_size=60000 earlycon=ppl011,mmio32,0x28001000 bonding.miimon=100 bonding.mode=active-backup libata.dma=5 quiet root=/dev/ram0 rw pci=noaer pcie_aspm=off net.ifnames=0 initrd /initrd.gz
bootload:
bootargs root=/dev/mtdblock2 console=ttySAC0 init=/linuxrc
- root:指定根文件系统的位置,比如:root=/dev/mtdblock3 , mtdblock3 代表mtdparts的第4分区 (第一个分区为mtdblock0) 如果指定 root=/dev/nfs,还需要指定nfsroot=serverip:nfs_dir
- console:设置控制台参数,比如:console=ttySAC0,115200 , 使用串口0作为控制台,波特率为115200 。串口设备要根据实际的设备名称来设置。
- rootfstype:指定根文件系统的类型,这个选项需要跟root一起配合使用,一般如果根文件系统是ext2的话,有没有这个选项是无所谓的,但是如果是jffs2,squashfs等文件系统的话,就需要rootfstype指明文件系统的类型,不然会无法挂载根分区。
- ramdisk_size:指定创建的ramdisk的大小,ramdisk是将内存中的一块区域作为物理磁盘使用的一种技术
- init:指定内核启动后第一个执行的脚本,比如:init=/linuxrc
- initrd:指定ramdisk在内存中的位置和大小
有个疑问grub or uboot 解析完参数后传给内核! 内核怎样解析参数。
以quite net.ifname=0 log_level为例:
init/main.c中:
static int __init quiet_kernel(char *str) { console_loglevel = CONSOLE_LOGLEVEL_QUIET; return 0; } early_param("quiet", quiet_kernel);
static int __init loglevel(char *str) { int newlevel; /* * Only update loglevel value when a correct setting was passed,to prevent blind crashes (when loglevel being set to 0) thatare quite hard to debug */ if (get_option(&str, &newlevel)) { console_loglevel = newlevel; return 0; } return -EINVAL; } early_param("loglevel", loglevel);
当内核 cmdline 中设定了 quiet 参数后,quiet_kernel 函数会被调用,这个函数会将 console_loglevel 设定为CONSOLE_LOGLEVEL_QUIET=4
static int __init root_dev_setup(char *line) { strlcpy(saved_root_name, line, sizeof(saved_root_name)); return 1; } __setup("root=", root_dev_setup);
#define __setup(str, fn) \ __setup_param(str, fn, fn, 0) /* * NOTE: fn is as per module_param, not __setup! * Emits warning if fn returns non-zero. */ #define early_param(str, fn) \ __setup_param(str, fn, fn, 1)
我们知道内核是依次执行各个section代码段代码。来看early_param的宏定义展开。
/* * Only for really core code. See moduleparam.h for the normal way. * * Force the alignment so the compiler doesn't space elements of the * obs_kernel_param "array" too far apart in .init.setup. */ #define __setup_param(str, unique_id, fn, early) \ static const char __setup_str_##unique_id[] __initconst \ __aligned(1) = str; \ static struct obs_kernel_param __setup_##unique_id \ __used __section(.init.setup) \ __attribute__((aligned((sizeof(long))))) \ = { __setup_str_##unique_id, fn, early } #define __setup(str, fn) \ __setup_param(str, fn, fn, 0) /* * NOTE: fn is as per module_param, not __setup! * Emits warning if fn returns non-zero. */ #define early_param(str, fn) \ __setup_param(str, fn, fn, 1)
扩展后结果为:
static const char __setup_str_loglevel[] __initconst __aligned(1) = "loglevel";
struct obs_kernel_param _setup_loglevel
__used __section(.init.setup)
__attribute__((aligned((sizeof(long)))))
= { .str = "__setup_str_loglevel", .setup_func = loglevel, .early = 1, };
/* These are for everybody (although not all archs will actually discard it in modules) */ #define __init __section(.init.text) __cold notrace #define __initdata __section(.init.data) #define __initconst __constsection(.init.rodata) #define __exitdata __section(.exit.data) #define __exit_call __used __section(.exitcall.exit)
其含义为:
- const char __setup_str_loglevel[]其值为 “loglevel”,存放在 .init.rodata section 中并以 1 字节为单位对齐
-
struct obs_kernel_param _setup_loglevel 此结构体以 sizeof(long) 字节对齐并存放到 .init_setup section 中
内核启动的时候其会调用如下函数:
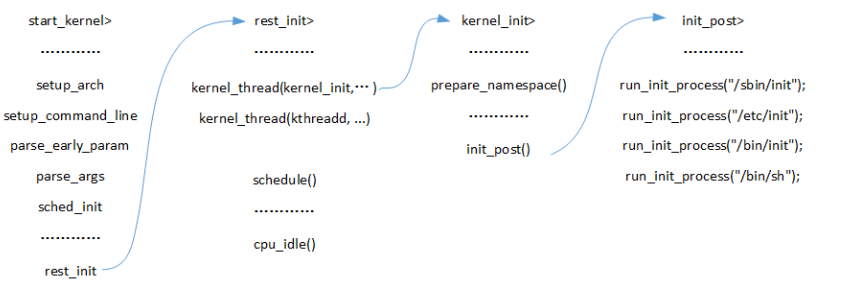
start_kernel
setup_arch
parse_early_param
parse_early_options
parse_args
parse_one
do_early_param
reserve_initrd ----->比如调用reserve_initrd 保存 initrd
/* Arch code calls this early on, or if not, just before other parsing. */ void __init parse_early_param(void) { static int done __initdata; static char tmp_cmdline[COMMAND_LINE_SIZE] __initdata; if (done) return; /* All fall through to do_early_param. */ strlcpy(tmp_cmdline, boot_command_line, COMMAND_LINE_SIZE); parse_early_options(tmp_cmdline); done = 1; }
/* Check for early params. */ static int __init do_early_param(char *param, char *val, const char *unused, void *arg) { const struct obs_kernel_param *p; for (p = __setup_start; p < __setup_end; p++) { if ((p->early && parameq(param, p->str)) || (strcmp(param, "console") == 0 && strcmp(p->str, "earlycon") == 0) ) { if (p->setup_func(val) != 0) pr_warn("Malformed early option '%s'\n", param); } } /* We accept everything at this stage. */ return 0; }
#define INIT_SETUP(initsetup_align) \ . = ALIGN(initsetup_align); \ VMLINUX_SYMBOL(__setup_start) = .; \ *(.init.setup) \ VMLINUX_SYMBOL(__setup_end) = .;
do_early_params 函数的第一个参数是上层传入的 cmd 的唯一标识,然后 do_early_params 函数遍历 __setup_start以及 __setup_end代码段区域内遍历每一个 cmd实例--->obs_kernel_param,匹配到了则调用相应的 setup_func hook函数!!
关于section,目前内核连接各个模块等都是通过section来存放链接。
static void __init reserve_initrd(void) { /* Assume only end is not page aligned */ u64 ramdisk_image = get_ramdisk_image(); u64 ramdisk_size = get_ramdisk_size(); u64 ramdisk_end = PAGE_ALIGN(ramdisk_image + ramdisk_size); u64 mapped_size; if (!boot_params.hdr.type_of_loader || !ramdisk_image || !ramdisk_size) return; /* No initrd provided by bootloader */ initrd_start = 0; mapped_size = memblock_mem_size(max_pfn_mapped); if (ramdisk_size >= (mapped_size>>1)) panic("initrd too large to handle, " "disabling initrd (%lld needed, %lld available)\n", ramdisk_size, mapped_size>>1); printk(KERN_INFO "RAMDISK: [mem %#010llx-%#010llx]\n", ramdisk_image, ramdisk_end - 1); if (pfn_range_is_mapped(PFN_DOWN(ramdisk_image), PFN_DOWN(ramdisk_end))) { /* All are mapped, easy case */ initrd_start = ramdisk_image + PAGE_OFFSET; initrd_end = initrd_start + ramdisk_size; return; } relocate_initrd(); memblock_free(ramdisk_image, ramdisk_end - ramdisk_image); } static void __init relocate_initrd(void) { /* Assume only end is not page aligned */ u64 ramdisk_image = get_ramdisk_image(); u64 ramdisk_size = get_ramdisk_size(); u64 area_size = PAGE_ALIGN(ramdisk_size); /* We need to move the initrd down into directly mapped mem */ relocated_ramdisk = memblock_find_in_range(0, PFN_PHYS(max_pfn_mapped), area_size, PAGE_SIZE); if (!relocated_ramdisk) panic("Cannot find place for new RAMDISK of size %lld\n", ramdisk_size); /* Note: this includes all the mem currently occupied by the initrd, we rely on that fact to keep the data intact. */ memblock_reserve(relocated_ramdisk, area_size); initrd_start = relocated_ramdisk + PAGE_OFFSET; initrd_end = initrd_start + ramdisk_size; printk(KERN_INFO "Allocated new RAMDISK: [mem %#010llx-%#010llx]\n", relocated_ramdisk, relocated_ramdisk + ramdisk_size - 1); copy_from_early_mem((void *)initrd_start, ramdisk_image, ramdisk_size); printk(KERN_INFO "Move RAMDISK from [mem %#010llx-%#010llx] to" " [mem %#010llx-%#010llx]\n", ramdisk_image, ramdisk_image + ramdisk_size - 1, relocated_ramdisk, relocated_ramdisk + ramdisk_size - 1); }
可以看到 initrd 通过boot相关参数赋值:
struct boot_params *make_boot_params(struct efi_config *c) { struct boot_params *boot_params; struct apm_bios_info *bi; struct setup_header *hdr; struct efi_info *efi; efi_loaded_image_t *image; void *options, *handle; efi_guid_t proto = LOADED_IMAGE_PROTOCOL_GUID; int options_size = 0; efi_status_t status; char *cmdline_ptr; u16 *s2; u8 *s1; int i; unsigned long ramdisk_addr; unsigned long ramdisk_size; -------------------------- status = handle_cmdline_files(sys_table, image, (char *)(unsigned long)hdr->cmd_line_ptr, "initrd=", hdr->initrd_addr_max, &ramdisk_addr, &ramdisk_size); if (status != EFI_SUCCESS) goto fail2; hdr->ramdisk_image = ramdisk_addr & 0xffffffff; hdr->ramdisk_size = ramdisk_size & 0xffffffff; boot_params->ext_ramdisk_image = (u64)ramdisk_addr >> 32; boot_params->ext_ramdisk_size = (u64)ramdisk_size >> 32; return boot_params; fail2: efi_free(sys_table, options_size, hdr->cmd_line_ptr); fail: efi_free(sys_table, 0x4000, (unsigned long)boot_params); return NULL; }
以下为内核启动参数参考:
| Console Options | |||||||||||||||
| 参数 | 说明 | 选项 | 内核配置/文件 | ||||||||||||
| console=Options | 用于说明输出设备 | ttyn 终端 ttySn[,options], ttyUSB0[,options] 串口uart,io,addr[,options],uart,mmio,addr[,options]&<60; | |||||||||||||
| netconsole=[src-port]@[src-ip]/[dev],[target-port]@target-ip/[targetmac-address] | |||||||||||||||
| debug | Enable kernel debugging. | 启动时将所有的调试信息都输出到控制台 | |||||||||||||
| quiet | Disable all log messages. | 相当于loglevel=KERN_WARNING | |||||||||||||
| earlyprintk=[vga|serial][,ttySn[,baudrate]][,keep] | 打印传统的控制台初始化前的信息,主要是硬件相关的信息 | ||||||||||||||
| loglevel=level | 设置默认的控制台记录级别 | 所有的较高级别的信息将被打印(0-7) | /proc/sys/kernel/printk | ||||||||||||
| log_buf_len=n[KMG] | 设置内核记录缓冲区大小 | 为2的冥 | CONFIG_LOG_BUF_SHIFT | ||||||||||||
| initcall_debug | 调试系统初始化函数 | 跟踪系统启动时用到的所有的函数 | |||||||||||||
| kstack=n | Oops栈的多少个字被输出 | n为整数 | |||||||||||||
| time | 在记录信息前面显示时间 | ||||||||||||||
| Interrupt Options(Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller APIC) | |||||||||||||||
| apic=[quiet|verbose|debug] | 改变ACPI子系统启动时的记录级别 | 默认为quite | |||||||||||||
| noapic | 不用任何IOAPICs | ||||||||||||||
| lapic | 使本地ACPI有效 | 即使BOIS使得它无效,也要让它有效 | |||||||||||||
| nolapic | 不使用ACPI | ||||||||||||||
| noirqbalance | 使内核内建的Irq平衡逻辑无效 | ||||||||||||||
| irqfixup | 基本的中断问题修复 | 当一个中断没有被处理,搜索所有的中断处理看看能不能用 | |||||||||||||
| irqpoll | 扩展的中断问题修复 | 在每一个时钟中断,检查每一个中断处理 | |||||||||||||
| noirqdebug | 禁止未处理的中断自动探测 | 默认情况下,内核试着探测并且禁止未处理的中断源,以免引起未知的问题,这个选项禁止该功能。 | |||||||||||||
| Memory Options | |||||||||||||||
| highmem=n | 说明高内存区域的大小 | 强制高端内存有大小为n的精确的内存区域,不管系统有没有高端内存,也可以用于减少大内存系统中的高端内存大小 | |||||||||||||
| hugepages=n | 设置hugetlb页的数量 | ||||||||||||||
| ihash_entries=n | 设置Inode哈希表的大小 | 用于覆盖内核的默认值 | |||||||||||||
| max_addr=n | 设置内存的最大地址 | 内核将忽略在该地址以上的物理内存 | |||||||||||||
| mem=n[KMG] | 设置内存使用的内存数 | 当使用memmap选项时,能避免物理地址空间的冲突。如果不用memmap选项,可能引起PCI设备被放到未用的RAM空间。 | |||||||||||||
| mem=nopentium | 内核禁用大页(4M) | ||||||||||||||
| memmap=exactmap | 使用特定的内存映像 | ||||||||||||||
| memmap=n[KMG]@start[KMG] | 强制内核使用特定的内存区域 | n,是表内存区域的大小,start指内存区域的开始位位置 | |||||||||||||
| noexec=[on|off] | 禁/启用内核将一个内存区域映像为不可执行内存的的功能。默认为on. | ||||||||||||||
| reserve=n[KMG] | 强制内核忽略IO内存区域 | 预留IO内存区域 | |||||||||||||
| vmalloc=n[KMG] | 强制vmalloc有的个特定的大小 | 可用于增加vmalloc区域的最小值,也可以用于减少vmalloc的大小,增加更多的空间用于直接映射内核RAM | |||||||||||||
| norandmaps | 不用地址空间随机化 | 默认内核随机化程序启动的地址,该选项禁用该功能 | /proc/sys/kernel/randomize_va_space写0相当 | ||||||||||||
| vdso=[0|1] | 禁/启用vdso映像 | (Virtual Dynamic Shared Object),默认为启用 | |||||||||||||
| Suspend Options | |||||||||||||||
| resume=suspend_device | 说明休眠文件的分区设备 | ||||||||||||||
| noresume | 禁用休眠功能 | ||||||||||||||
| Ramdisk Options | |||||||||||||||
| initrd=filename | initrd Ramdisk的位置 | 说明内核启动时要用到的Ramdisk的位置 | |||||||||||||
| load_ramdisk=n | 从软盘加载Ramdisk | n=1,则从软盘加载ramdisk | |||||||||||||
| noinitrd | 不用任何Initrd,即使参数时面指定了 | ||||||||||||||
| prompt_ramdisk=1 | 在从软驱中读取ramdisk之前提示用户 | ||||||||||||||
| ramdisk_blocksize=n | ramdisk的块尺寸 | ||||||||||||||
| ramdisk_size=n | 说明ramdisk的大小 | ||||||||||||||
| Root Disk Options | |||||||||||||||
| ro | 启动时以只读方式挂载根文件系统 | 如果在它之前有rw的选项,ro将会取代它 | |||||||||||||
| root=device | 说明系统启动的根文件系统 | nnnn 十六的制备号(以内核可识别的方式表示major和minor)/dev/nfs/dev/<diskname>/dev/<diskname><decimal>/dev/<diskname>p<decimal>(要求diskname以数字结尾) | |||||||||||||
| rootdelay=n | 挂载文件系统前的延迟 | 主要是当根文件系统在USB or FireWire设备上 | |||||||||||||
| rootflags=options | 根文件系统挂载选项 | ||||||||||||||
| rootfstype=type | 根文件系统的类型 | 例如:rootfstype=ext3 | |||||||||||||
| rw | 启动时以读写方式挂载根文件系统 | ||||||||||||||
| Init Options | |||||||||||||||
| init=filename | 在Init时,应该执行的程序 | 默认为/sbin/Init | |||||||||||||
| rdinit=full_path_name | 从ramdisk中运行Init进行 | 指定的文件必须是在ramdisk而不是在root文件系统中 | |||||||||||||
| S | 运行Init在单用户模式中 | ||||||||||||||
| Network Options | |||||||||||||||
| netdev=[irq],[io],[mem_start],[mem_end],[name] | 设备各咱网络参数 | ||||||||||||||
| thash_entries | 设置TCP连接哈希表的最大数目 | ||||||||||||||
| Network File System Options | |||||||||||||||
| lockd.nlm_grace_period=n | 设备恰当的锁管理周期 | 以秒为单位 | |||||||||||||
| lockd.nlm_tcpport=port | 为NFS锁管理者设置端口(TCP) | ||||||||||||||
| lockd.nlm_timeout=n | NFS锁管理者超时 | 默认为十秒 | |||||||||||||
| lockd.nlm_udpport=port | 为NFS锁管理者设置端口(UDP) | ||||||||||||||
| nfsroot=[server-ip:]root-dir[,nfs-options] | 为无盘系统,说明NFS根文件系统,如果参数没有设置默认为/tftpboot/client_ip_address | ||||||||||||||
| nfs.callback_tcpport=port | 为回调通道设置NFSv4&<60;TCP端口 | ||||||||||||||
| Hardware-Specific Options | |||||||||||||||
| nousb | 没有USB设备 | ||||||||||||||
| lp=[0|port[,port…]|reset|auto] | 设置并行端口和其模式 | lp=auto内核将检查所有端口,看有没有IEEE&<60;1284兼容的打印机 | |||||||||||||
| parport=[setting[,setting…] | 说明并行端口参数 | ||||||||||||||
| parport_init_mode=[spp|ps2|epp|ecp|ecpepp] | 并行端口初始化模式 | ||||||||||||||
| nr_uarts=n | 最大的UART被注册的数目 | ||||||||||||||
| panic=n | 系统panic后重启最大等时间 | 默认为0,系统将不重新启动,仅仅挂起 | |||||||||||||
| pause_on_oops=n | 告诉内核,当第一个Oops出现后,挂起所有的CPU,n秒,以便记录下现场 | ||||||||||||||
| combined_mode=[combined|ide|libata] | 说明IDE驱动 | ||||||||||||||
http代理服务器(3-4-7层代理)-网络事件库公共组件、内核kernel驱动 摄像头驱动 tcpip网络协议栈、netfilter、bridge 好像看过!!!!
但行好事 莫问前程
--身高体重180的胖子


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号