路由fib 数据结构
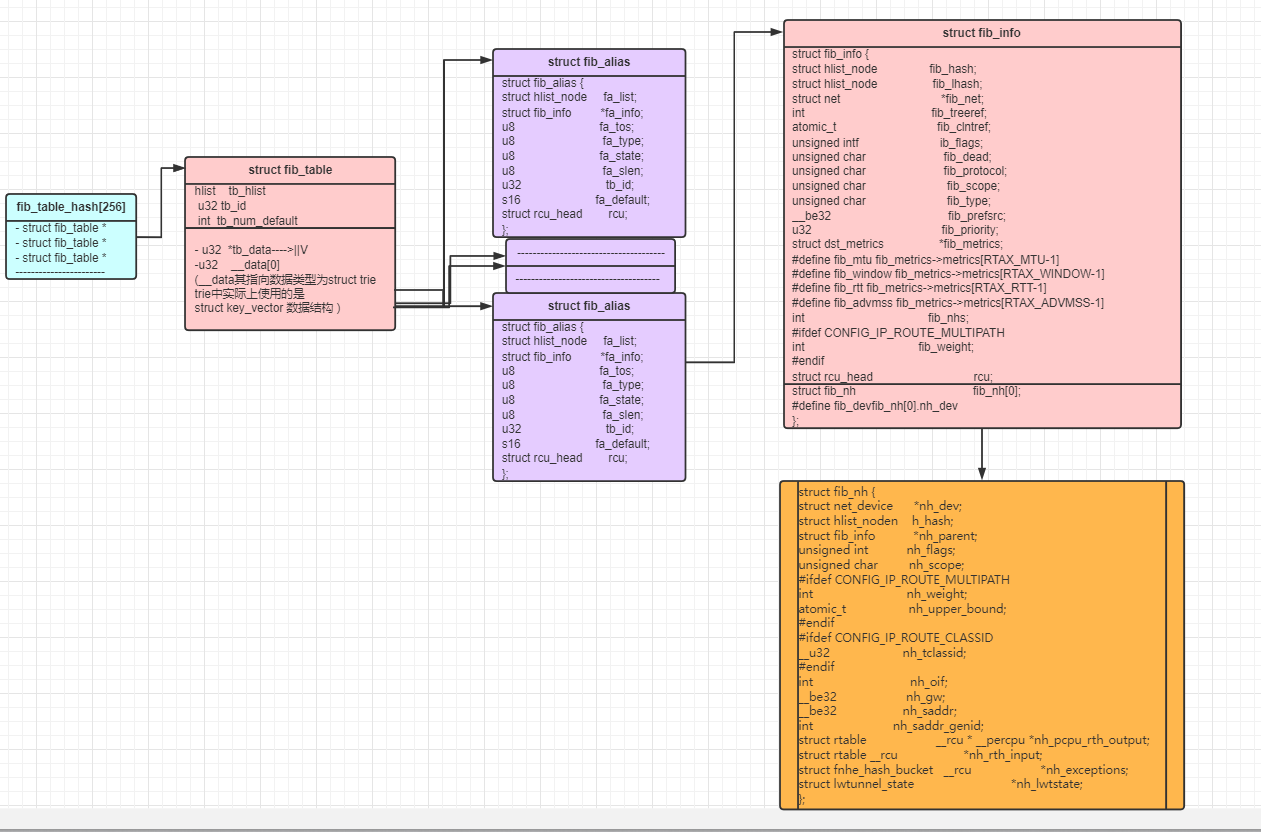
- 全局散列表net->ipv4.fib_table_hash中,存放所有的路由表fib_table;
结构体fib_alias
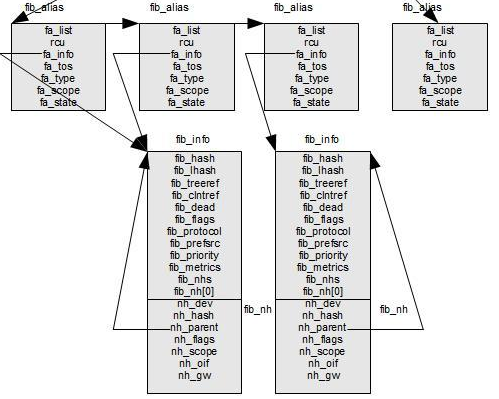
相同网段的每一条路由表项有各自的fib_alias结构;多个fib_alias可以共享一个fib_info结构;
struct fib_alias { struct hlist_node fa_list;// 将路由项组织到路由结点的fn_alias链表中 struct fib_info *fa_info; // fa_info保存了路由项所包含的所有信息 u8 fa_tos;// 路由项的tos 比特位字段 u8 fa_type;// 路由项的类型 间接定义了当路由查找匹配时,应采取的动作 u8 fa_state;// 路由项的状态一些标志位,目前只有FA_S_ACCESSED。表示该表项已经被访问过 u8 fa_slen;//后缀长度 inet_make_mask(KEYLENGTH - fa->fa_slen) 就是子网掩码 u32 tb_id;// 表id s16 fa_default; struct rcu_head rcu; };
FIB Alias (fib_alias)
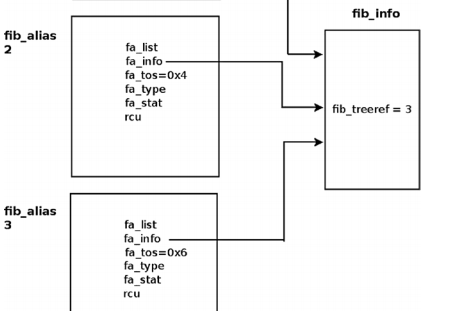
There are cases when several routing entries to the same destination address or to the same subnet are created. These
routing entries differ only in the value of their TOS. Instead of creating a fib_info for each such route, a fib_alias
object is created. A fib_alias is smaller, which reduces memory consumption. Here is a simple example of creating 3
fib_alias objects:
ip route add 192.168.1.10 via 192.168.2.1 tos 0x2
ip route add 192.168.1.10 via 192.168.2.1 tos 0x4
ip route add 192.168.1.10 via 192.168.2.1 tos 0x6
enum { RTN_UNSPEC, RTN_UNICAST, /* Gateway or direct route //单播,网关或者直接路由 */ RTN_LOCAL, /* Accept locally//host地址,目的地址是本机 */ RTN_BROADCAST, /* Accept locally as broadcast,广播地址 send as broadcast 广播收 广播发*/ RTN_ANYCAST, /* Accept locally as broadcast, but send as unicast //广播接收数据,单播发送数据,IPV6协议规定的地址类型*/ RTN_MULTICAST, /* Multicast route多播 */ RTN_BLACKHOLE, /* Drop丢弃 */ RTN_UNREACHABLE, /* Destination is unreachable 目的不可达 */ RTN_PROHIBIT, /* Administratively prohibited管理员禁止IP地址 */ RTN_THROW, /* Not in this table */ RTN_NAT, /* Translate this address 需要进行网络地址转换 */ RTN_XRESOLVE, /* Use external resolver外部解析 */ __RTN_MAX };
结构体fib_info
结构体Fib_info存储真正重要路由信息,即如何到达目的地。
// 用于组织fib_info对象的全局哈希表和计数器 static DEFINE_SPINLOCK(fib_info_lock); static struct hlist_head *fib_info_hash; static struct hlist_head *fib_info_laddrhash; static unsigned int fib_hash_size; static unsigned int fib_info_cnt; // 当前路由项信息个数 /* * This structure contains data shared by many of routes. */ struct fib_info { // 系统中所有的fib_info对象都会被组织到全局的fib_hash_info哈希表中 struct hlist_node fib_hash; // 如果配置了首选源地址,那么该对象就会被插入到全局的fib_info_laddrhash哈希表中 struct hlist_node fib_lhash; struct net *fib_net;//对应设备所在网络命名空间中的一些信息 // 持有该fib_info对象的路由结点的个数(为什么不是fib_alias呢?) int fib_treeref; // 路由查询成功后,外部的TCB都会持有一个fib_info的引用计数 atomic_t fib_clntref; // 如果该字段为1,表示路由项正在被删除,这时该路由项将不能被使用 int fib_dead; unsigned fib_flags; // 表示该路由项的来源,即是由哪个路由协议配置的,常见的有kernel、static int fib_protocol; // 首选源IP地址,即如果设置了该字段,那么当数据包匹配该路由项时,如果还没有源地址, // 那么会已该IP地址作为数据包的源IP __be32 fib_prefsrc; // 值越小,表示优先级越高,当添加路由时,如果没有指定,那么优先级为0,即最高优先级 u32 fib_priority; // 和路由netlink配置中的RTA_METRICS属性字段的内容对应,以属性类型为索引 u32 fib_metrics[RTAX_MAX]; #define fib_mtu fib_metrics[RTAX_MTU-1] #define fib_window fib_metrics[RTAX_WINDOW-1] #define fib_rtt fib_metrics[RTAX_RTT-1] #define fib_advmss fib_metrics[RTAX_ADVMSS-1] // 可用的下一跳数量,一般为1,只有支持多路径路由时,才可能大于1 int fib_nhs; #ifdef CONFIG_IP_ROUTE_MULTIPATH int fib_power; #endif // 下一跳信息,0长度数组,内存分配时紧挨着fib_info,如果支持多路径路由,那么该数组长度大于1 struct fib_nh fib_nh[0]; #define fib_dev fib_nh[0].nh_dev };
struct fib_info
|
struct hlist_node fib_hash; |
//所有fib_info组成的散列表,该表为全局散列表fib_info_hash |
|
struct hlist_node fib_lhash; |
//当存在首源地址时,才会将fib_info插入该散列表,该表为全局散列表fib_info_laddrhash |
|
struct net *fib_net; |
|
|
Int fib_treeref; |
//使用该fib_info结构的fib_node的数目 |
|
atomic_t fib_clntref; |
//引用计数。路由查找成功而被持有的引用计数 |
|
Int fib_dead; |
//标记路由表项正在被删除的标志,当该标志被设置为1时,警告该数据结构将被删除而不能再使用 |
|
Unsigned fib_flags; |
//当前使用的唯一标志是RTNH_F_DEAD,表示下一跳已无效 |
|
Int fib_protocol; |
//设置路由的协议 |
|
__be32 fib_prefsrc; |
//首选源IP地址 |
|
u32 fib_priority; |
//路由优先级,默认为0,值越小优先级越高 |
|
u32 fib_metrics[RTAX_MAX]; |
//与路由相关的度量值 |
|
Int fib_nhs; |
//可用的下一跳数量,通常为1.只有支持多路径路由时,才大于1 |
|
struct fib_nh fib_nh[0]; |
//表示路由的下一跳 |
结构体fib_nh
该结构体中存放着下一跳路由的地址nh_gw。
// 将所有fib_info对象的下一跳地址fib_nh对象组织到全局哈希表中 #define DEVINDEX_HASHBITS 8 #define DEVINDEX_HASHSIZE (1U << DEVINDEX_HASHBITS) static struct hlist_head fib_info_devhash[DEVINDEX_HASHSIZE]; struct fib_nh { // 输出网络设备对象 struct net_device *nh_dev; // 所有的fib_nh实例被维护在全局的哈希表fib_info_devhash中 struct hlist_node nh_hash; // 指向上一级的fib_info对象 struct fib_info *nh_parent; unsigned nh_flags; // 路由作用域 unsigned char nh_scope; #ifdef CONFIG_IP_ROUTE_MULTIPATH int nh_weight; int nh_power; #endif #ifdef CONFIG_NET_CLS_ROUTE __u32 nh_tclassid; #endif // 输出网络设备索引 int nh_oif; // 路由项的网关IP地址,即匹配该路由项时,下一跳应该将数据包交给谁 __be32 nh_gw; };
struct fib_nh
|
struct net_device *nh_dev; |
//该路由表项输出网络设备 |
|
struct hlist_node nh_hash; |
//fib_nh组成的散列表 |
|
struct fib_info *nh_parent; |
//指向所属fib_info结构体 |
|
struct fib_info *nh_parent; |
|
|
Unsigned nh_flags; |
|
|
unsigned char nh_scope; |
|
|
Int nh_oif; |
//输出网络设备索引 |
|
__be32 nh_gw; |
//网关地址 |
/* rt_flags是一组标志位,按目的入口查询的执行顺序:如果路由使用本地环回接口,则rt_flags上加标志RTCF_LOCAL, 如果路由结果类 型是广播,则加标志RTCF_BROADCAST和RTCF_LOCAL,如果结果是组播,则加标志RTCF_MULTICAST和 RTCF_LOCAL, 该标志最终决定了目的入口使用哪一个IP数据报输入函数和输出函数,如果是RTCF_LOCAL,则使用输入函数 ip_local_deliver, 如果是RTCF_BROADCAST或RTCF_MULTICAST,并且带有RTCF_LOCAL标志,并且输出设 备不是环回接口设备,则使用输出函数ip_mc_output, 否则使用输出函数ip_output。 rt_type是路由类型,如果路由是LOOPBACK,则置类型为RTN_LOCAL,单播路由类型为RTN_UNICAST, 如果目的地址为 0xFFFFFFFF,则路由类型为RTN_BROADCAST, 如果目的地址是组播地址,则路由类型为RTN_MULTICAST。 rt_type跟 rt_flags关系比较密切。 */ struct rtable { struct dst_entry dst;//独立于协议的信息 int rt_genid; unsigned int rt_flags;//标识路由表项的特征 __u16 rt_type;//路由的类型 __u8 rt_is_input; __u8 rt_uses_gateway; int rt_iif;//输入设备的标识 /* Info on neighbour */ __be32 rt_gateway;//目的地址或下一跳网关 /* Miscellaneous cached information */ u32 rt_pmtu; u32 rt_table_id; struct list_head rt_uncached; struct uncached_list *rt_uncached_list; };
/* 下一跳缓存的作用就是尽量减少最初和最后的申请释放dst_entry,它将dst_entry缓存在下一跳结构(fib_nh)上。 这和之前的路由缓存有什么区别吗? 很大的区别!之前的路由缓存是以源IP和目的IP为KEY,有千万种可能性, 而现在是和下一跳绑定在一起,一台设备没有那么多下一跳的可能。这就是下一跳缓存的意义! __refcnt是目的入口的引用计数,创建成功后即设为1。__use是一个统计数值,该目的入口被使用一次(发送一个IP数据报),__use就加1。 dev是该路由的输出网络设备接口, flags是标志位,其取值可以是DST_HOST,DST_NOXFRM,DST_NOPOLICY,DST_NOHASH,DST_BALANCED(用在路由有多路径的情况下) input和output分别是该目的入口的输入和输出函数。 */ struct dst_entry { struct rcu_head rcu_head; struct dst_entry *child; struct net_device *dev;//输出网络设备 struct dst_ops *ops; unsigned long _metrics; unsigned long expires;//过期的时间戳 struct dst_entry *path; struct dst_entry *from; #ifdef CONFIG_XFRM struct xfrm_state *xfrm; #else void *__pad1; #endif int (*input)(struct sk_buff *);//ip_output int (*output)(struct net *net, struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb);//ip_local_deliver unsigned short flags; #define DST_HOST 0x0001 #define DST_NOXFRM 0x0002 #define DST_NOPOLICY 0x0004 #define DST_NOHASH 0x0008 #define DST_NOCACHE 0x0010 #define DST_NOCOUNT 0x0020 #define DST_FAKE_RTABLE 0x0040 #define DST_XFRM_TUNNEL 0x0080 #define DST_XFRM_QUEUE 0x0100 #define DST_METADATA 0x0200 short error;//fib_lookup查找失败时的错误码 /* A non-zero value of dst->obsolete forces by-hand validation * of the route entry. Positive values are set by the generic * dst layer to indicate that the entry has been forcefully * destroyed. * * Negative values are used by the implementation layer code to * force invocation of the dst_ops->check() method. */ short obsolete; #define DST_OBSOLETE_NONE 0//该结构有效且可以被使用 #define DST_OBSOLETE_DEAD 2// 该结构被删除而不能使用 #define DST_OBSOLETE_FORCE_CHK -1// 被IPSEC ipv6使用 不能被ipv4 使用 #define DST_OBSOLETE_KILL -2 unsigned short header_len; /* more space at head required */ unsigned short trailer_len; /* space to reserve at tail */ unsigned short __pad3; #ifdef CONFIG_IP_ROUTE_CLASSID __u32 tclassid; #else __u32 __pad2; #endif #ifdef CONFIG_64BIT struct lwtunnel_state *lwtstate; /* * Align __refcnt to a 64 bytes alignment * (L1_CACHE_SIZE would be too much) */ long __pad_to_align_refcnt[1]; #endif /* * __refcnt wants to be on a different cache line from * input/output/ops or performance tanks badly */ atomic_t __refcnt; /* client references引用计数*/ int __use; unsigned long lastuse;//最近一次使用该路由缓存的时间戳 #ifndef CONFIG_64BIT struct lwtunnel_state *lwtstate; #endif union { struct dst_entry *next; struct rtable __rcu *rt_next; struct rt6_info *rt6_next; struct dn_route __rcu *dn_next; }; };
策略规则结构体fib_rule
struct fib_rule { struct list_head list; int iifindex;//接 口 index int oifindex;// out 接口index u32 mark;//mark 值 u32 mark_mask;//mark 掩 码 值 u32 flags; u32 table;//路由表id u8 action;//规则 /* 3 bytes hole, try to use */ u32 target; __be64 tun_id; struct fib_rule __rcu *ctarget; struct net *fr_net; atomic_t refcnt;//引 用 计 数 u32 pref;//优先级, 值越小优先级越大 int suppress_ifgroup; int suppress_prefixlen; char iifname[IFNAMSIZ];//入接 口 名 称 char oifname[IFNAMSIZ];//出接 口 名 称 struct rcu_head rcu; };
策略操作函数fib_rules_ops
struct fib_rules_ops { int family;//对应协议簇 struct list_head list;//将注册到系统的fib_rules_ops链接到链表rules_ops int rule_size;//一个策略规则所占用的内存大小 int addr_size;//协议相关的地址长度 int unresolved_rules; int nr_goto_rules; //action函数,策略规则匹配后,所调用的action函数,执行后续的操作。 //一般是获取到相应的路由表,查找符合要求的路由项 int (*action)(struct fib_rule *, struct flowi *, int, struct fib_lookup_arg *); bool (*suppress)(struct fib_rule *, struct fib_lookup_arg *); //规则匹配函数,对于策略规则的匹配,首先是通用匹配,待通用匹配完成后, //则会调用该函数,进行协议相关参数(源、目的地址等)的匹配 int (*match)(struct fib_rule *, struct flowi *, int); //协议相关的配置参数 int (*configure)(struct fib_rule *, struct sk_buff *, struct fib_rule_hdr *, struct nlattr **); int (*delete)(struct fib_rule *); int (*compare)(struct fib_rule *, struct fib_rule_hdr *, struct nlattr **); int (*fill)(struct fib_rule *, struct sk_buff *, struct fib_rule_hdr *); size_t (*nlmsg_payload)(struct fib_rule *); /* Called after modifications to the rules set, must flush * the route cache if one exists. */ void (*flush_cache)(struct fib_rules_ops *ops); int nlgroup; const struct nla_policy *policy; struct list_head rules_list;//将该协议簇已添加的所有fib_rule规则链接在一起 struct module *owner; struct net *fro_net; struct rcu_head rcu; };
ipv4类型的策略规则
IPV4协议相关的fib4_rule结构,该结构包含了基础的fib_rule,增加源IP、目的IP、tos等相关IPV4成员
struct fib4_rule//ipv4相关的结构 { struct fib_rule common; u8 dst_len; u8 src_len; u8 tos; __be32 src;//源ip __be32 srcmask; __be32 dst;//目的ip __be32 dstmask; #ifdef CONFIG_NET_CLS_ROUTE u32 tclassid; #endif }; rule4->src_len = frh->src_len; rule4->srcmask = inet_make_mask(rule4->src_len); rule4->dst_len = frh->dst_len; rule4->dstmask = inet_make_mask(rule4->dst_len); rule4->tos = frh->tos;
路由策略初始化
IPV4协议相关初始化fib4_rules_init
功能:(1)注册fib4_rules_ops
(2)创建local、main、default规则表,添到rules_list
(3)将fib4_rules_ops添到rules_ops中。
static const struct fib_rules_ops __net_initconst fib4_rules_ops_template = { .family = AF_INET, .rule_size = sizeof(struct fib4_rule), .addr_size = sizeof(u32), .action = fib4_rule_action, .suppress = fib4_rule_suppress, .match = fib4_rule_match, .configure = fib4_rule_configure, .delete = fib4_rule_delete, .compare = fib4_rule_compare, .fill = fib4_rule_fill, .nlmsg_payload = fib4_rule_nlmsg_payload, .flush_cache = fib4_rule_flush_cache, .nlgroup = RTNLGRP_IPV4_RULE, .policy = fib4_rule_policy, .owner = THIS_MODULE, }; int __net_init fib4_rules_init(struct net *net) { int err; struct fib_rules_ops *ops; ops = fib_rules_register(&fib4_rules_ops_template, net); //执行kdump-memcpy 拷贝一份fib4_rules_ops_template 同时list 到net->rules_ops上去 err = fib_default_rules_init(ops);/*创建 local main default 对应的 fib_rule,最后list 到 fib_rules_ops->rules-list 链表上去, 也就是ipv4 只有一个rules-ops 但是有很多table fiber_rule*/ net->ipv4.rules_ops = ops; net->ipv4.fib_has_custom_rules = false; return 0; } static int fib_default_rules_init(struct fib_rules_ops *ops) { int err; err = fib_default_rule_add(ops, 0, RT_TABLE_LOCAL, 0); err = fib_default_rule_add(ops, 0x7FFE, RT_TABLE_MAIN, 0); err = fib_default_rule_add(ops, 0x7FFF, RT_TABLE_DEFAULT, 0); } int fib_default_rule_add(struct fib_rules_ops *ops, u32 pref, u32 table, u32 flags) { struct fib_rule *r; r = kzalloc(ops->rule_size, GFP_KERNEL); atomic_set(&r->refcnt, 1); r->action = FR_ACT_TO_TBL; r->pref = pref; r->table = table; r->flags = flags; r->fr_net = ops->fro_net; r->suppress_prefixlen = -1; r->suppress_ifgroup = -1; /* The lock is not required here, the list in unreacheable * at the moment this function is called */ list_add_tail(&r->list, &ops->rules_list); return 0; }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号