ipvs--eBPF转载
https://lwn.net/Articles/740157/
http://arthurchiao.art/blog/ebpf-and-k8s-zh/
https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.15/source/tools/bpf/bpftool/Documentation/bpftool.rst
https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.15/source/tools/bpf/bpftool
参考书籍:https://files.cnblogs.com/files/codestack/OReilly-Linux-Observability-with-BPF-2019.rar
腾讯云在其使用内核版本中实现了ipvs+ebpf 提升性能 , 解决了iptable-snat对其性能的影响
patch如下:
https://github.com/Tencent/TencentOS-kernel/blob/master/net/netfilter/ipvs/ip_vs_bpf_proc.c#L56
https://github.com/Tencent/TencentOS-kernel/blob/master/net/netfilter/ipvs/ip_vs_bpf_proc.c#L402
https://github.com/Tencent/TencentOS-kernel/commit/d1a590ff8758af2fc1055899c9bf49f3028243d5#diff-1a592df245508d5f30565cf2860fa670bf1ae15b0d69d07e5328a0b880fc1024
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/inventory/600/article/1685332
iptables模式
存在的问题:
1.可扩展性差。随着service数据达到数千个,其控制面和数据面的性能都会急剧下降。原因在于iptables控制面的接口设计中,每添加一条规则,需要遍历和修改所有的规则,使得其控制面性能是O(n²)。在数据面,规则是用链表组织的,使得其数据面的性能是O(n)
2.LB调度算法仅支持随机转发。
IPVS模式
IPVS 是专门为LB设计的。它用hash table管理service,对service的增删查找都是O(1)的时间复杂度。不过IPVS内核模块没有SNAT功能,因此借用了iptables的SNAT功能。IPVS 针对报文做DNAT后,将连接信息保存在nf_conntrack中,iptables据此接力做SNAT。该模式是目前Kubernetes网络性能最好的选择。但是由于nf_conntrack的复杂性,带来了很大的性能损耗
基于eBPF的IPVS-BPF优化方案
针对nf_conntrack带来的性能问题,腾讯TKE团队设计实现了IPVS-BPF。核心思想是绕过nf_conntrack,减少处理每个报文的指令数目,从而节约CPU,提高性能。其主要逻辑如下:
- 在IPVS内核模块中引入开关,支持原生IPVS逻辑和IPVS-BPF逻辑的切换
- 在IPVS-BPF模式下,将IPVS hook点从LOCALIN前移到PREROUTING,使访问service的请求绕过nf_conntrack
- 在IPVS新建连接和删除连接的代码中,相应的增删eBPF map中的session信息
- 在qdisc挂载eBPF的SNAT代码,根据eBPF map中的session信息执行SNAT
优化前后报文处理流程的对比
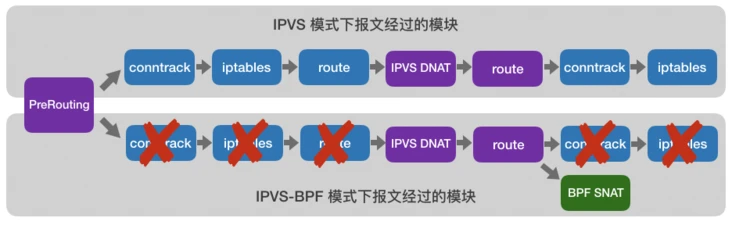
来自:https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000023012440
在腾讯云的技术实现细节中,就有通过IPVS模块向BPF Map插入数据的逻辑,其关键代码如下所示:
// https://github.com/Tencent/TencentOS-kernel/blob/master/net/netfilter/ipvs/ip_vs_bpf_proc.c#L56 struct bpf_map *conntrack_map; // https://github.com/Tencent/TencentOS-kernel/blob/master/net/netfilter/ipvs/ip_vs_bpf_proc.c#L402 static ssize_t ip_vs_bpf_write(struct file *file, const char __user *ubuf, size_t count, loff_t *ppos) { int err = 0; struct bpf_map *map = NULL; struct bpf_prog *prog1 = NULL; struct bpf_prog *prog2 = NULL; const char delim[2] = ":"; char ids[5][20]; char *token; int tag, pid; unsigned int mapid, progid1, progid2; char buf[100]; int i = 0; char *s = buf; ... /* singleton:conntrack_map is assigned once, * and be nulled in module exit */ if (conntrack_map) { pr_err("%s %d conntrack_map exists\n", __func__, __LINE__); return -EEXIST; } ... err = bpf_conntrack_map_get(pid, mapid, (long long)(resolve_addrs.bpf_map_fops), &map); if (err != 0 || !map) { pr_err("%s acquire bpf_map failed\n", __func__); return -EINVAL; } ... bpf_map_fd = mapid; ... // got the target bpf map via fd conntrack_map = map; ... } // https://github.com/Tencent/TencentOS-kernel/blob/master/net/netfilter/ipvs/ip_vs_bpf_proc.c#L306 static int bpf_conntrack_map_get(int pid, unsigned int fd, unsigned long long addr, struct bpf_map **map) { struct files_struct *files; struct task_struct *task; struct file *file; int err = 0; ... file = fcheck_files(files, fd); ... *map = file->private_data; if (*map) bpf_map_inc2(*map); ... }
简单说明下ip_vs_bpf_proc.c文件:
- 在
ip_vs_bpf_proc.c这个文件开头声明了一个bpf_map结构(来自内核bpf体系)的变量conntrack_map,这个就是将来被IPVS操作的BPF Map对象。 - 同样是在
ip_vs_bpf_proc.c这个文件里,函数ip_vs_bpf_write()内调用了bpf_conntrack_map_get()方法,而它的入参之一mapid在这里就是BPF Map的fd,这个方法内容就是通过fd找到了背后相关数据,并序列化为bpf_map结构的对象,最终赋值给conntrack_map,完成目标BPF Map的获取。
然后在IPVS模块创建新connection时,对上面conntrack_map插入了必要的元素,关键代码如下所示:
// https://github.com/Tencent/TencentOS-kernel/blob/master/net/netfilter/ipvs/ip_vs_conn.c#L1098 static bool ip_vs_conn_new_bpf(struct ip_vs_dest *dest, unsigned int flags, const struct ip_vs_conn_param *p, int *skip) { int i; struct ip_vs_service *svc; struct bpf_lb_conn_key key = {}; struct bpf_lb_conn_key reply_key = {}; struct bpf_lb_conn_value value = {}; struct bpf_lb_conn_value reply_value = {}; struct bpf_lb_conn_value *v; int inserted = 0; struct bpf_map *map; ... if (!bpf_mode_on) return true; ... // conntrack_map is the same one map = conntrack_map; ... lip = alloc_localip(); reply_key.sip = key.dip; reply_key.sport = key.dport; reply_key.dip = lip; reply_key.dport = key.sport; reply_key.proto = p->protocol; reply_key.vip = 0; reply_key.vport = 0; reply_key.pad = 0; atomic_set(&reply_value.ref, 0); reply_value.sip = key.dip; reply_value.sport = key.dport; reply_value.dip = key.sip; reply_value.dport = key.sport; reply_value.proto = p->protocol; ... if (likely(!map->ops->map_lookup_elem(map, &reply_key))) { if (likely(map->ops->map_update_elem(map, &reply_key, &reply_value, BPF_ANY) == 0)) { /* the common case! break the loop */ inserted = 1; nf_conntrack_single_unlock(&reply_key, map->key_size); break; } /* if lookup ok, shall insert ok since lock is held!*/ pr_err("map insert key failed\n"); BPF_STAT_INC(p->ipvs, BPF_NEW_INSERT); nf_conntrack_single_unlock(&reply_key, map->key_size); return false; } ... }
上面的代码里使用了map_lookup_elem()和map_update_elem()两个操作BPF Map的方法——先查询后更新(插入新的元素),完成对BPF Map的操作


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号