IP/TCP/UDP checsum
今天调试bug时, 忘了将原始的check_sum值reset,导致发包-抓包后发现。check-sum 错误。
来看一看check-sum:简单讲就是对要计算的数据,以16bit为单元进行累加,然后取反
在内核中构造数据包的时候,我们需要关注三个校验和:分别是sk_buf中的csum,ip_summed,ip头部中的check和udp或者tcp头部中的check
用于计算校验和的API:L3校验和的计算比L4的校验和要快得多,因为它只包含IP报头。校验和的API都在checksum.h中。
checksum在收包和发包时意义不一样
/* * @csum: Checksum (must include start/offset pair) * @csum_start: Offset from skb->head where checksumming should start * @csum_offset: Offset from csum_start where checksum should be stored * @ip_summed: Driver fed us an IP checksum */ struct sk_buff { union { __wsum csum; struct { __u16 csum_start; __u16 csum_offset; }; }; __u8 ip_summed:2,

csum_start: Offset from skb->head where checksumming should start csum_offset: Offset from csum_start where checksum should be store
/* Don't change this without changing skb_csum_unnecessary! */ #define CHECKSUM_NONE 0 #define CHECKSUM_UNNECESSARY 1 #define CHECKSUM_COMPLETE 2 #define CHECKSUM_PARTIAL 3
TCP收包时:
- CHECKSUM_UNNECESSARY
CHECKSUM_UNNECESSARY表示底层硬件或者协议栈已经计算了CSUM,也就是计算了tcp udp的伪头;所以TCP层在收到包后,发现skb->ip_summed为CHECKSUM_UNNECESSARY就不会再检查checksum;还有一种情况就是回环,因为在回环中错误发生的概率太低了,因此就不需要计算校验来节省cpu事件。
- CHECKSUM_NONE
csum中的校验和无效,需要L4层自己校验payload和伪头;可能有以下几种原因:设备不支持硬件校验和计算;设备计算了硬件校验和,但发现该数据帧已经损坏。部分驱动不会丢弃,而是将ip_summed设置为CHECKSUM_NONE,然后交给上层协议栈重新计算并处理这种错误。
- CHECKSUM_COMPLETE
网卡已经计算了L4层报头和payload的校验和,并且skb->csum已经被赋值,此时L4层的接收者只需要加伪头并验证校验结果。
1) 在L4层发现skb->ip_summed==CHECKSUM_UNNECESSARY,或者skb的csum_valid字段有效, 则放行该报文。skb->ip_summed==CHECKSUM_PARTIAL,但是checksum_start_offset存在,也放行。
2) 如果skb->ip_summed为CHECKSUM_COMPLETE,则把skb->csum加上伪头进行校验,成功则将skb->ip_summed设为CHECKSUM_UNNECESSARY,同时设置 skb->csum_valid=1 并 放行该数据包。
3) 如果skb->ip_summed是CHECKSUM_NONE且 skb->csum_bad已经置位,则不能放行-丢弃。
4) 如是为CHECKSUM_NONE且 csum_bad==0 ;则需要将数据报文的payload加上skb->csum进行checksum计算,成功将设为CHECKSUM_COMPLETE并放行,失败则丢弃。
skb->csum:存放硬件或者软件计算的payload的checksum不包括伪头,或者是只有伪头,但是是否有意义由skb->ip_summed的值决定,同时不同版本内核代码其值也不一样
int tcp_v4_rcv(struct sk_buff *skb) { ------------------------------ if (skb_checksum_init(skb, IPPROTO_TCP, inet_compute_pseudo)) goto csum_error; -------------------------- }
skb_checksum_init(skb, IPPROTO_TCP, inet_compute_pseudo) 函数实质上调用的是:__skb_checksum_validate(skb, IPPROTO_TCP, false, false, 0, inet_compute_pseudo)

__skb_checksum_validate(skb, IPPROTO_TCP, false, false, 0, inet_compute_pseudo) ({ \ __sum16 __ret = 0; \ skb->csum_valid = 0; \ if (__skb_checksum_validate_needed(skb, false, 0)) \ __ret = __skb_checksum_validate_complete(skb, \ complete, inet_compute_pseudo(skb, proto)); \ __ret; \ }) static inline void __skb_decr_checksum_unnecessary(struct sk_buff *skb) { if (skb->ip_summed == CHECKSUM_UNNECESSARY) { if (skb->csum_level == 0) skb->ip_summed = CHECKSUM_NONE; else skb->csum_level--; } } static inline int skb_csum_unnecessary(const struct sk_buff *skb) { return ((skb->ip_summed == CHECKSUM_UNNECESSARY) || skb->csum_valid || (skb->ip_summed == CHECKSUM_PARTIAL && skb_checksum_start_offset(skb) >= 0)); } static inline bool __skb_checksum_validate_needed(struct sk_buff *skb, bool zero_okay, __sum16 check) { if (skb_csum_unnecessary(skb) || (zero_okay && !check)) { skb->csum_valid = 1; __skb_decr_checksum_unnecessary(skb); return false; } return true; } static inline __wsum inet_compute_pseudo(struct sk_buff *skb, int proto) { return csum_tcpudp_nofold(ip_hdr(skb)->saddr, ip_hdr(skb)->daddr, skb->len, proto, 0); } /* Validate (init) checksum based on checksum complete. * * Return values: * 0: checksum is validated or try to in skb_checksum_complete. In the latter * case the ip_summed will not be CHECKSUM_UNNECESSARY and the pseudo * checksum is stored in skb->csum for use in __skb_checksum_complete * non-zero: value of invalid checksum * */ static inline __sum16 __skb_checksum_validate_complete(struct sk_buff *skb, bool complete, __wsum psum) { if (skb->ip_summed == CHECKSUM_COMPLETE) { if (!csum_fold(csum_add(psum, skb->csum))) { skb->csum_valid = 1; return 0; } } else if (skb->csum_bad) { /* ip_summed == CHECKSUM_NONE in this case */ return (__force __sum16)1; } skb->csum = psum; if (complete || skb->len <= CHECKSUM_BREAK) { __sum16 csum; csum = __skb_checksum_complete(skb); skb->csum_valid = !csum; return csum; } return 0; } __sum16 __skb_checksum_complete(struct sk_buff *skb) { __wsum csum; __sum16 sum; csum = skb_checksum(skb, 0, skb->len, 0); /* skb->csum holds pseudo checksum */ sum = csum_fold(csum_add(skb->csum, csum)); if (likely(!sum)) { if (unlikely(skb->ip_summed == CHECKSUM_COMPLETE) && !skb->csum_complete_sw) netdev_rx_csum_fault(skb->dev); } if (!skb_shared(skb)) { /* Save full packet checksum */ skb->csum = csum; skb->ip_summed = CHECKSUM_COMPLETE; skb->csum_complete_sw = 1; skb->csum_valid = !sum; } return sum; }
/* Check if we need to perform checksum complete validation. * * Returns true if checksum complete is needed, false otherwise * (either checksum is unnecessary or zero checksum is allowed). */ static inline bool __skb_checksum_validate_needed(struct sk_buff *skb, bool zero_okay, __sum16 check) { if (skb_csum_unnecessary(skb) || (zero_okay && !check)) { skb->csum_valid = 1; __skb_decr_checksum_unnecessary(skb); return false; } return true; } static inline int skb_csum_unnecessary(const struct sk_buff *skb) { return ((skb->ip_summed == CHECKSUM_UNNECESSARY) || skb->csum_valid || (skb->ip_summed == CHECKSUM_PARTIAL && skb_checksum_start_offset(skb) >= 0)); } static inline int skb_checksum_start_offset(const struct sk_buff *skb) { return skb->csum_start - skb_headroom(skb); } static inline void __skb_decr_checksum_unnecessary(struct sk_buff *skb) { if (skb->ip_summed == CHECKSUM_UNNECESSARY) { if (skb->csum_level == 0) skb->ip_summed = CHECKSUM_NONE; else skb->csum_level--; }View Cod
TCP发包时:
skb->ip_summed用于L4校验和的状态,以通知底层网卡是否还需要处理校验和;此时ip_summed可以被设置的值有下面两种
- CHECKSUM_NONE
CHECKSUM_NONE表示协议栈已经计算了校验和,设备不需要做任何事情
- CHECKSUM_PARTIAL
CHECKSUM_PARTIAL表示使用硬件checksum ,协议栈已经计算L4层的伪头的校验和,only compute IP header, not include data
skb->csum表示为csum_start和csum_offset,它表示硬件网卡将要计算的校验值的地址,和最后填充的偏移。这个域在输出包时使用,只在校验值在硬件计算的情况下才对于网卡真正有意义。硬件checksum功能只能用于非分片报文
void __tcp_v4_send_check(struct sk_buff *skb, __be32 saddr, __be32 daddr) { struct tcphdr *th = tcp_hdr(skb); if (skb->ip_summed == CHECKSUM_PARTIAL) {//HW CSUM th->check = ~tcp_v4_check(skb->len, saddr, daddr, 0);// 计算伪头部 skb->csum_start = skb_transport_header(skb) - skb->head;// palyload 计算校验和的起始地址 相对于head的偏移 skb->csum_offset = offsetof(struct tcphdr, check);// 存放csum的地址 } else { th->check = tcp_v4_check(skb->len, saddr, daddr, csum_partial(th, th->doff << 2, skb->csum)); } } /* This routine computes an IPv4 TCP checksum. */ void tcp_v4_send_check(struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb) { const struct inet_sock *inet = inet_sk(sk); __tcp_v4_send_check(skb, inet->inet_saddr, inet->inet_daddr); } static int tcp_transmit_skb(struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb, int clone_it, gfp_t gfp_mask) { ///... icsk->icsk_af_ops->send_check(sk, skb); ///tcp_v4_send_check }
Sk_buf中的csum字段
- 该字段代表的是以太网发送数据包时,在将数据从用户控件复制到内核空间时,以相应算法计算数据包检验和,存放于 csum
接收数据包时,csum 存放网络设备计算的检验和。linux内核对于ip或者tcp或者udp的校验和都是采用的同一校验的方法(累加再进行取反)。因为网络数据包可能进行分片,那么linux内核就将校验和分为了两个函数,分别是累加csum_partial和取反csum_fold
我们可以使用csum_partial(const void *buff, int len, __wsum sum)来计算。使用例子:skb->csum = csum_partial((unsigned char *)tcph, ntohs(iph->tot_len) - iph_lenip_hdrlen(skb), 0)
ip头部中的check字段
- IP的头部校验和是用来检测IP头部的完整性和正确性,数据的完整性是高层协议校验的,比如TCP/UDP(多数LV4的校验和是包含报头和数据的)。数据包在二层有检验,在三层也有校验,在4层也是存在校验的。
IP层的校验和函数使用ip_fast_csum函数。该函数的参数是ip报头的指针及其长度。返回值就是检验和。在计算校验和的时候应该先将ip头部的check字段设置为0
L4层check字段
- TCP和UDP协议所计算的校验和会包括其报头、有效负载以及所谓的伪报头。伪报头基本上就是一个区块,为了方便起见,其中的字段是从IP报头中取来的,换言之,IP头部中出现的一些信息最后会整合到L4检验和中。注意:伪报头只是为了计算校验和而定义;伪报头并不存在于网络中的传输的封包内。
因为L4层的校验和会用到L3层的头部信息,所以改变了L3层的头部,最好再次计算一下校验和
TCP和UDP的校验和主要用到的函数为csum_tcpudp_magic。
说明:对于TCP而言,我们可以采用更加上层的函数,例如tcp_v4_check。该函数在内核中用两种调用方式,这两种情况可以查看__tcp_v4_send_check。一种是只计算伪首部,另一种是计算完成的TCP校验和。采用何种方式取决于ip_summed的值
PS:当我们修改数据包的时候,需要注意一下几个字段需要做相应的调整。我们首先来看ip头部信息中的tot_len字段,该字段ip头部加数据段。我们如果修改了数据包的长度,我们就需要更新该字段。同时,在tcp的头部信息中没有长度字段,所以我们不用更新tcp的长度字段。但是如果我们修改的udp的报文,我们需要修改udp头部中的长度(udp头部中有udp数据包长度字段)。如果我们没有调用内核提供的api函数来操作skb,那么我们需要手动修改skb中的head、tail、以及len字段。
net_device->features
net_device->features字段表示设备的各种特性。其中一些位用于表示硬件校验和的计算能力:
#define NETIF_F_IP_CSUM __NETIF_F(HW_CSUM) #define NETIF_F_IP_CSUM __NETIF_F(IP_CSUM) ///ipv4 + TCP/UDP #define NETIF_F_IPV6_CSUM __NETIF_F(IPV6_CSUM)
NETIF_F_IP_CSUM表示硬件可以计算L4 checksum,但是只针对IPV4的TCP和UDP。但是一些设备扩展支持VXLAN和NVGRE。 NETIF_F_IP_CSUM是一种协议感知的计算checksum的方法。具体来说,上层提供两个CSUM的参数(csum_start和csum_offset)。
- TCP校验和覆盖TCP首部和TCP数据,而IP首部中的校验和只覆盖IP的首部,不覆盖IP数据报中的任何数据。
- TCP的校验和是必需的,而UDP的校验和是可选的。
- TCP和UDP计算校验和时,都要加上一个12字节的伪首部。
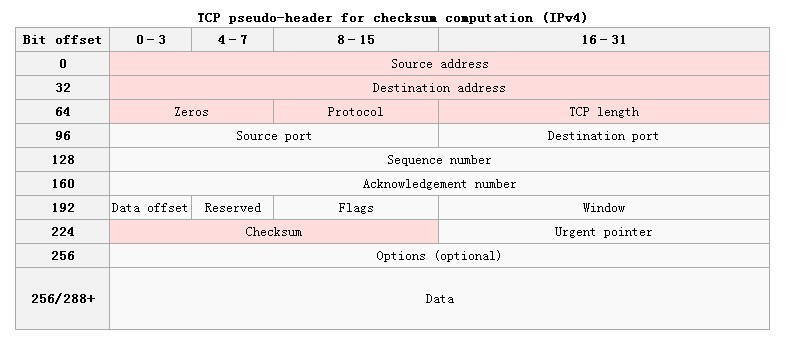
伪首部共有12字节,包含如下信息:源IP地址、目的IP地址、保留字节(置0)、传输层协议号(TCP是6)、TCP报文长度(报头+数据)。伪首部是为了增加TCP校验和的检错能力:如检查TCP报文是否收错了(目的IP地址)、传输层协议是否选对了(传输层协议号)等。
RFC 793的TCP校验和定义
The checksum field is the 16 bit one's complement of the one's complement sum of all 16-bit words in the header and text. If a segment contains an odd number of header and text octets to be checksummed, the last octet is padded on the right with zeros to form a 16-bit word for checksum purposes. The pad is not transmitted as part of the segment. While computingthe checksum, the checksum field itself is replaced with zeros.
把伪首部、TCP报头、TCP数据分为16位的字,如果总长度为奇数个字节,则在最后增添一个位都为0的字节。把TCP报头中的校验和字段置为0;
校验和的计算与顺序无关, 可以从数据块开始计算, 也可以从未尾开始向前计算
RFC 1071的IP校验和定义
1. Adjacent octets to be checksummed are paired to form 16-bit integers, and the 1's complement sum of these 16-bit integers is formed.
2. To generate a checksum, the checksum field itself is cleared, the 16-bit 1's complement sum is computed over the octets concerned, and the 1's complement of this sum is placed in the checksum field.
3. To check a checksum, the 1's complement sum is computed over the same set of octets, including the checksum field. If the result is all 1 bits (-0 in 1's complement arithmetic), the check succeeds.
内核协议栈中:
为了提高计算效率, TCP包的校验和并不一次算出,而是采用32位部分累加和(sk->csum)进行增量计算.
csum_partial()用来计算数据块的32位部分累加和, 累加和可以用csum_fold()折叠为16位校验和.csum_partial_copy_nocheck()可在拷贝用户数据的同时计算出它的部分累加和. 为了加快执行速度, csum_partial()将8个32位字分为一组用分立的指令进行32位累加,这样可加长循环体中指令长度, 提高CPU指令流水线的效率
代码实现如下:

TCP包接收校验的初始化 static __sum16 tcp_v4_checksum_init(struct sk_buff *skb) { const struct iphdr *iph = ip_hdr(skb); //如果TCP包本身的校验已经完成 if (skb->ip_summed == CHECKSUM_COMPLETE) { if (!tcp_v4_check(skb->len, iph->saddr, iph->daddr, skb->csum)) { //附加伪头进行校验 skb->ip_summed = CHECKSUM_UNNECESSARY; return 0; } } //生成包含伪头的累加和 skb->csum = csum_tcpudp_nofold(iph->saddr, iph->daddr, skb->len, IPPROTO_TCP, 0); if (skb->len <= 76) { return __skb_checksum_complete(skb); //计算数据部分校验和伪头累加和(skb->csum)计算整个skb的校验和 } return 0; } 附加伪头进行校验 static inline __sum16 tcp_v4_check(int len, __be32 saddr, __be32 daddr, __wsum base) { return csum_tcpudp_magic(saddr, daddr, len, IPPROTO_TCP, base); } static inline __sum16 csum_tcpudp_magic(__be32 saddr, __be32 daddr, unsigned short len, unsigned short proto, __wsum sum) { return csum_fold(csum_tcpudp_nofold(saddr, daddr, len, proto, sum)); } 生成包含伪头的累加和(源,目的,长度,协议号) static inline __wsum csum_tcpudp_nofold(__be32 saddr, __be32 daddr, unsigned short len, unsigned short proto, __wsum sum) { __asm__( "addl %1, %0 ;\n" //addl 加法 "adcl %2, %0 ;\n" //adcl 带进位的加法 "adcl %3, %0 ;\n" "adcl $0, %0 ;\n" //如果有进位,进行累加 : "=r" (sum) : "g" (daddr), "g"(saddr), "g"((len + proto) << 8), "0"(sum) ); return sum; } 将32位累加和折叠成16位校验和 static inline __sum16 csum_fold(__wsum sum) { __asm__( "addl %1, %0 ;\n" "adcl $0xffff, %0 ;\n" : "=r" (sum) : "r" ((__force u32)sum << 16), "0" ((__force u32)sum & 0xffff0000) ); return (__force __sum16)(~(__force u32)sum >> 16); } 基于伪头累加和,完成全包校验 static __inline__ int tcp_checksum_complete(struct sk_buff *skb) { return skb->ip_summed != CHECKSUM_UNNECESSARY && __tcp_checksum_complete(skb); } __sum16 __skb_checksum_complete(struct sk_buff *skb) { return __skb_checksum_complete_head(skb, skb->len); } __sum16 __skb_checksum_complete_head(struct sk_buff *skb, int len) { __sum16 sum; sum = csum_fold(skb_checksum(skb, 0, len, skb->csum)); if (likely(!sum)) { if (unlikely(skb->ip_summed == CHECKSUM_COMPLETE)) netdev_rx_csum_fault(skb->dev); skb->ip_summed = CHECKSUM_UNNECESSARY; } return sum; } __wsum skb_checksum(const struct sk_buff *skb, int offset, int len, __wsum csum) { int start = skb_headlen(skb); int i, copy = start - offset; int pos = 0; /* Checksum header. */ if (copy > 0) { if (copy > len) copy = len; csum = csum_partial(skb->data + offset, copy, csum); if ((len -= copy) == 0) return csum; offset += copy; pos = copy; } ...... } 计算32位中间累加和 unsigned int csum_partial(const unsigned char * buff, int len, unsigned int sum) { //arch/x86/lib/checksum_32.S 汇编文件 } 基于TCP用户数据的中间累加和, 生成TCP包校验码 void tcp_v4_send_check(struct sock *sk, int len, struct sk_buff *skb) { struct inet_sock *inet = inet_sk(sk); struct tcphdr *th = tcp_hdr(skb); if (skb->ip_summed == CHECKSUM_PARTIAL) { th->check = ~tcp_v4_check(len, inet->saddr, inet->daddr, 0); //附加伪头进行校验 skb->csum_start = skb_transport_header(skb) - skb->head; skb->csum_offset = offsetof(struct tcphdr, check); } else { //完整的tcp校验和计算方法 th->check = tcp_v4_check(len, inet->saddr, inet->daddr, csum_partial((char *)th, th->doff << 2, skb->csum)); } } 在拷贝用户数据时同时计算累加和 unsigned int csum_partial_copy_nocheck(const char *src, char *dst, int len, int sum) { return csum_partial_copy_generic(src, dst, len, sum, NULL, NULL); // arch/x86/lib/checksum_32.S } ip头校验和计算 static inline __sum16 ip_fast_csum(const void *iph, unsigned int ihl) { unsigned int sum; __asm__ __volatile__( "movl (%1), %0 ;\n" "subl $4, %2 ;\n" "jbe 2f ;\n" "addl 4(%1), %0 ;\n" //sum = sum + *(iph+4) "adcl 8(%1), %0 ;\n" //sum = sum + *(iph+8) + carry "adcl 12(%1), %0 ;\n" //sum = sum + *(iph+12) + carry "1: adcl 16(%1), %0 ;\n" //sum = sum + *(iph+16) + carry "lea 4(%1), %1 ;\n" //iph = iph + 4 "decl %2 ;\n" "jne 1b ;\n" "adcl $0, %0 ;\n" "movl %0, %2 ;\n" "shrl $16, %0 ;\n" "addw %w2, %w0 ;\n" "adcl $0, %0 ;\n" "notl %0 ;\n" "2: ;\n" /* Since the input registers which are loaded with iph and ihl are modified, we must also specify them as outputs, or gcc will assume they contain their original values. */ : "=r" (sum), "=r" (iph), "=r" (ihl) : "1" (iph), "2" (ihl) : "memory" ); return (__force __sum16)sum; } 递减ip->ttl,更新校验和 static inline int ip_decrease_ttl(struct iphdr *iph) { u32 check = (__force u32)iph->check; check += (__force u32)htons(0x0100); iph->check = (__force __sum16)(check + (check>=0xFFFF)); return --iph->ttl; } static inline __wsum csum_add(__wsum csum, __wsum addend) { u32 res = (__force u32)csum; res += (__force u32)addend; return (__force __wsum)(res + (res < (__force u32)addend)); } static inline __wsum csum_sub(__wsum csum, __wsum addend) { return csum_add(csum, ~addend); } static inline __wsum csum_block_add(__wsum csum, __wsum csum2, int offset) { u32 sum = (__force u32)csum2; if (offset & 1) sum = ((sum & 0xFF00FF)<<8) + ((sum>>8) & 0xFF00FF); return csum_add(csum, (__force __wsum)sum); } static inline __wsum csum_block_sub(__wsum csum, __wsum csum2, int offset) { u32 sum = (__force u32)csum2; if (offset & 1) sum = ((sum & 0xFF00FF)<<8) + ((sum>>8) & 0xFF00FF); return csum_sub(csum, (__force __wsum)sum); } [/函数实现] 转载:https://www.cnblogs.com/super-king/p/3284884.html
对于IP层计算校验和,其调用函数如下:
ip_send_check(iph);
https://hustcat.github.io/checksum-in-kernel/
https://www.kernel.org/doc/Documentation/networking/checksum-offloads.txt
https://w180112.pixnet.net/blog/post/200083785
http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-25518484-id-5709671.html
/* A. Checksumming of received packets by device. * * CHECKSUM_NONE: * * Device failed to checksum this packet e.g. due to lack of capabilities. * The packet contains full (though not verified) checksum in packet but * not in skb->csum. Thus, skb->csum is undefined in this case. * * CHECKSUM_UNNECESSARY: * * The hardware you're dealing with doesn't calculate the full checksum * (as in CHECKSUM_COMPLETE), but it does parse headers and verify checksums * for specific protocols. For such packets it will set CHECKSUM_UNNECESSARY * if their checksums are okay. skb->csum is still undefined in this case * though. It is a bad option, but, unfortunately, nowadays most vendors do * this. Apparently with the secret goal to sell you new devices, when you * will add new protocol to your host, f.e. IPv6 8) * * CHECKSUM_UNNECESSARY is applicable to following protocols: * TCP: IPv6 and IPv4. * UDP: IPv4 and IPv6. A device may apply CHECKSUM_UNNECESSARY to a * zero UDP checksum for either IPv4 or IPv6, the networking stack * may perform further validation in this case. * GRE: only if the checksum is present in the header. * SCTP: indicates the CRC in SCTP header has been validated. * * skb->csum_level indicates the number of consecutive checksums found in * the packet minus one that have been verified as CHECKSUM_UNNECESSARY. * For instance if a device receives an IPv6->UDP->GRE->IPv4->TCP packet * and a device is able to verify the checksums for UDP (possibly zero), * GRE (checksum flag is set), and TCP-- skb->csum_level would be set to * two. If the device were only able to verify the UDP checksum and not * GRE, either because it doesn't support GRE checksum of because GRE * checksum is bad, skb->csum_level would be set to zero (TCP checksum is * not considered in this case). * * CHECKSUM_COMPLETE: * * This is the most generic way. The device supplied checksum of the _whole_ * packet as seen by netif_rx() and fills out in skb->csum. Meaning, the * hardware doesn't need to parse L3/L4 headers to implement this. * * Note: Even if device supports only some protocols, but is able to produce * skb->csum, it MUST use CHECKSUM_COMPLETE, not CHECKSUM_UNNECESSARY. * * CHECKSUM_PARTIAL: * * A checksum is set up to be offloaded to a device as described in the * output description for CHECKSUM_PARTIAL. This may occur on a packet * received directly from another Linux OS, e.g., a virtualized Linux kernel * on the same host, or it may be set in the input path in GRO or remote * checksum offload. For the purposes of checksum verification, the checksum * referred to by skb->csum_start + skb->csum_offset and any preceding * checksums in the packet are considered verified. Any checksums in the * packet that are after the checksum being offloaded are not considered to * be verified. * * B. Checksumming on output. * * CHECKSUM_NONE: * * The skb was already checksummed by the protocol, or a checksum is not * required. * * CHECKSUM_PARTIAL: * * The device is required to checksum the packet as seen by hard_start_xmit() * from skb->csum_start up to the end, and to record/write the checksum at * offset skb->csum_start + skb->csum_offset. * * The device must show its capabilities in dev->features, set up at device * setup time, e.g. netdev_features.h: * * NETIF_F_HW_CSUM - It's a clever device, it's able to checksum everything. * NETIF_F_IP_CSUM - Device is dumb, it's able to checksum only TCP/UDP over * IPv4. Sigh. Vendors like this way for an unknown reason. * Though, see comment above about CHECKSUM_UNNECESSARY. 8) * NETIF_F_IPV6_CSUM - About as dumb as the last one but does IPv6 instead. * NETIF_F_... - Well, you get the picture. * * CHECKSUM_UNNECESSARY: * * Normally, the device will do per protocol specific checksumming. Protocol * implementations that do not want the NIC to perform the checksum * calculation should use this flag in their outgoing skbs. * * NETIF_F_FCOE_CRC - This indicates that the device can do FCoE FC CRC * offload. Correspondingly, the FCoE protocol driver * stack should use CHECKSUM_UNNECESSARY. * * Any questions? No questions, good. --ANK */ /* Don't change this without changing skb_csum_unnecessary! */ #define CHECKSUM_NONE 0 #define CHECKSUM_UNNECESSARY 1 #define CHECKSUM_COMPLETE 2 #define CHECKSUM_PARTIAL 3
在做nat的时候,由于只是替换了ip port,所以:TCP校验和快速计算法,因为只修改了端口一个参数,可根据RFC1141方法快速计算
static inline void tcp_fast_csum_update(int af, struct tcphdr *tcph, const union nf_inet_addr *oldip, const union nf_inet_addr *newip, __be16 oldport, __be16 newport) { #ifdef CONFIG_IP_VS_IPV6 if (af == AF_INET6) tcph->check = csum_fold(ip_vs_check_diff16(oldip->ip6, newip->ip6, ip_vs_check_diff2(oldport, newport, ~csum_unfold(tcph->check)))); else #endif tcph->check = csum_fold(ip_vs_check_diff4(oldip->ip, newip->ip, ip_vs_check_diff2(oldport, newport, ~csum_unfold(tcph->check)))); }

static int tcp_dnat_handler(struct sk_buff *skb, struct ip_vs_protocol *pp, struct ip_vs_conn *cp, struct ip_vs_iphdr *iph) { struct tcphdr *tcph; unsigned int tcphoff = iph->len; bool payload_csum = false; int oldlen; #ifdef CONFIG_IP_VS_IPV6 if (cp->af == AF_INET6 && iph->fragoffs) return 1; #endif oldlen = skb->len - tcphoff; /* csum_check requires unshared skb */ if (skb_ensure_writable(skb, tcphoff + sizeof(*tcph))) return 0; if (unlikely(cp->app != NULL)) { int ret; /* Some checks before mangling */ if (!tcp_csum_check(cp->af, skb, pp)) return 0; /* * Attempt ip_vs_app call. * It will fix ip_vs_conn and iph ack_seq stuff */ if (!(ret = ip_vs_app_pkt_in(cp, skb, iph))) return 0; /* ret=2: csum update is needed after payload mangling */ if (ret == 1) oldlen = skb->len - tcphoff; else payload_csum = true; } tcph = (void *)skb_network_header(skb) + tcphoff; tcph->dest = cp->dport; /* * Adjust TCP checksums */ if (skb->ip_summed == CHECKSUM_PARTIAL) { tcp_partial_csum_update(cp->af, tcph, &cp->vaddr, &cp->daddr, htons(oldlen), htons(skb->len - tcphoff)); } else if (!payload_csum) { /* Only port and addr are changed, do fast csum update TCP校验和快速计算法,因为只修改了端口一个参数,可根据RFC1141方法快速计算*/ tcp_fast_csum_update(cp->af, tcph, &cp->vaddr, &cp->daddr, cp->vport, cp->dport); if (skb->ip_summed == CHECKSUM_COMPLETE) skb->ip_summed = cp->app ? CHECKSUM_UNNECESSARY : CHECKSUM_NONE; } else { /* full checksum calculation // 如果修改了协议内容部分数据,需要根据全部数据重新计算TCP校验和*/ tcph->check = 0; skb->csum = skb_checksum(skb, tcphoff, skb->len - tcphoff, 0); #ifdef CONFIG_IP_VS_IPV6 if (cp->af == AF_INET6) tcph->check = csum_ipv6_magic(&cp->caddr.in6, &cp->daddr.in6, skb->len - tcphoff, cp->protocol, skb->csum); else #endif tcph->check = csum_tcpudp_magic(cp->caddr.ip, cp->daddr.ip, skb->len - tcphoff, cp->protocol, skb->csum); skb->ip_summed = CHECKSUM_UNNECESSARY; } return 1; }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号