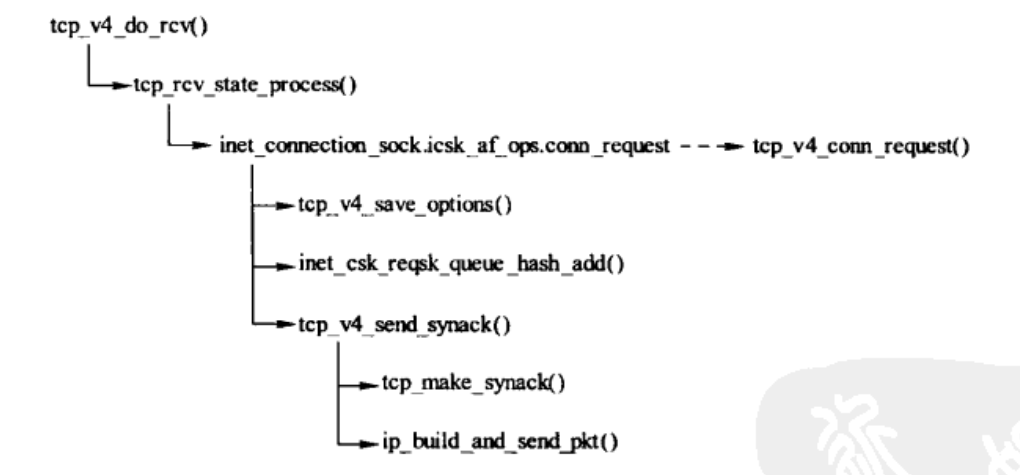
tcp syn-synack-ack 服务端 接收 SYN tcp_v4_do_rcv分析
rcv 分析:
/* The socket must have it's spinlock held when we get * here, unless it is a TCP_LISTEN socket. * * We have a potential double-lock case here, so even when * doing backlog processing we use the BH locking scheme. * This is because we cannot sleep with the original spinlock * held. Tcp的处理中使用了三个队列,receive_queue,backlog_queue,pre_queue,在数据包到达tcp协议栈时,持有sk自旋锁, 然后检查当前使用有进程上下文操作sk的逻辑,通过sock_owned_by_user判断,如果sk_lock.owned被赋值说明进程持有sk, 如果为0则可以在当前软中断上下文中,继续数据报文的处理。 */ /* * TCP传输层接收到段之后,经过了简单的 * 校验,并确定接收处理该段的传输控制 * 块之后,除非处于FIN_WAIT_2或TIME_WAIT状态, * 否则都会调用tcp_v4_do_rcv()作具体的处理 对于协议栈的接收路径,syn包的处理路径如下 tcp_v4_rcv ->__inet_lookup_skb() //listen hash中找到对应的TCP_LISTEN的sk ->tcp_v4_do_rcv() ->tcp_v4_cookie_check() //syncookie检查,因为没有syn包没有ack选项,因此忽略, 如果syncookie验证通过则创建新的sock ->tcp_rcv_state_process() ->tcp_v4_conn_request() 对于syncookie,服务端不保存任何状态 对于fastopen,新建sock进入TCP_SYN_RCV状态, 并插入等待accpet队列,并把数据部分放倒接收队列中, 并设置重传定时器 对于一般的syn包,request_sock设置为TCP_NEW_SYN_RECV,插入ehash表, 设置req_timer定时器,重传synack */ int tcp_v4_do_rcv(struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb) { struct sock *rsk; if (sk->sk_state == TCP_ESTABLISHED) { /* Fast path */ struct dst_entry *dst = sk->sk_rx_dst; sock_rps_save_rxhash(sk, skb); sk_mark_napi_id(sk, skb); if (dst) { if (inet_sk(sk)->rx_dst_ifindex != skb->skb_iif || !dst->ops->check(dst, 0)) { dst_release(dst); sk->sk_rx_dst = NULL; } } tcp_rcv_established(sk, skb, tcp_hdr(skb), skb->len); return 0; } if (tcp_checksum_complete(skb)) goto csum_err; if (sk->sk_state == TCP_LISTEN) {//说明收到的是三次握手第一步SYN或者第三步ACK,这里是服务器端的情况 struct sock *nsk = tcp_v4_cookie_check(sk, skb); //syncookie检查,因为没有syn包没有ack选项,因此忽略, 如果syncookie验证通过则创建新的 if (!nsk) goto discard; /*/如果是第一次握手的SYN,这里的nsk应该是'父'sk, 如果这里是三次握手的第三步ACK,则这里的nsk是‘子'sk */ if (nsk != sk) { sock_rps_save_rxhash(nsk, skb); sk_mark_napi_id(nsk, skb); if (tcp_child_process(sk, nsk, skb)) { //这里面还是会调用tcp_rcv_state_proces rsk = nsk; goto reset; } return 0;//如果是握手的第三步,这里直接退出 } //如果是三次握手中的第一步SYN,则继续后面的操作 } else sock_rps_save_rxhash(sk, skb); //走到这里说明只能是客户端收到SYN+ACK,或者是服务器端收到SYN if (tcp_rcv_state_process(sk, skb)) { rsk = sk; goto reset; } return 0; reset: tcp_v4_send_reset(rsk, skb); discard: kfree_skb(skb); /* Be careful here. If this function gets more complicated and * gcc suffers from register pressure on the x86, sk (in %ebx) * might be destroyed here. This current version compiles correctly, * but you have been warned. */ return 0; csum_err: TCP_INC_STATS(sock_net(sk), TCP_MIB_CSUMERRORS); TCP_INC_STATS(sock_net(sk), TCP_MIB_INERRS); goto discard;
tcp_rcv_state_process
/* * This function implements the receiving procedure of RFC 793 for * all states except ESTABLISHED and TIME_WAIT. * It's called from both tcp_v4_rcv and tcp_v6_rcv and should be * address independent. */ int tcp_rcv_state_process(struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb) { struct tcp_sock *tp = tcp_sk(sk); struct inet_connection_sock *icsk = inet_csk(sk); const struct tcphdr *th = tcp_hdr(skb); struct request_sock *req; int queued = 0; bool acceptable; switch (sk->sk_state) { case TCP_CLOSE: goto discard; case TCP_LISTEN: //服务器端收到SYN /* * 在半连接的LISTEN状态下,只处理SYN段。如果是 * ACK段,此时连接尚未开始建立,因此返回1。在调用 * tcp_rcv_state_process()函数中会给对方发送RST段; * 如果接收的是RST段,则丢弃 */ if (th->ack) return 1; if (th->rst) goto discard; if (th->syn) { if (th->fin) goto discard; /* * 处理SYN段,主要由conn_request接口(TCP中为tcp_v4_conn_request)处理, * icsk_af_ops成员在创建套接字时被初始化,参见tcp_v4_init_sock() */ /*收到三次握手的第一步SYN, 则在tcp_v4_conn_request中创建连接请求控制块request_sock */ if (icsk->icsk_af_ops->conn_request(sk, skb) < 0)//ipv4_specific--->tcp_v4_conn_request return 1; consume_skb(skb); return 0; } goto discard; case TCP_SYN_SENT://客户端收到SYN+ACK /* 对于TCP_SYN_SENT状态的sock,会调用tcp_rcv_synsent_state_process来进行处理 解析tcp选项,获取服务端的支持情况, 比如sack, TFO, wscale, MSS, timestamp等 如果有ack, 进行tcp_ack, 这时候可能fastopen确认了之前的数据 调用tcp_finish_connect,TCP_SYN_SENT->TCP_ESTABLISHED 如果包含fastopen cookie则保存 判断是否需要立即ack还是延时ack 如果包里没有ack,只有syn,则表示相互connect, TCP_SYN_SENT->TCP_SYN_RECV, 并发送synack */ tp->rx_opt.saw_tstamp = 0; queued = tcp_rcv_synsent_state_process(sk, skb, th); if (queued >= 0) return queued; /* Do step6 onward by hand. */ tcp_urg(sk, skb, th); __kfree_skb(skb); tcp_data_snd_check(sk); return 0; } tp->rx_opt.saw_tstamp = 0; req = tp->fastopen_rsk; if (req) { WARN_ON_ONCE(sk->sk_state != TCP_SYN_RECV && sk->sk_state != TCP_FIN_WAIT1); if (!tcp_check_req(sk, skb, req, true)) goto discard; } if (!th->ack && !th->rst && !th->syn) goto discard; if (!tcp_validate_incoming(sk, skb, th, 0)) return 0; /* * 处理TCP段ACK标志,tcp_ack()返回非零值表示处理 * ACK段成功,是正常的第三次握手TCP段 */ /* step 5: check the ACK field */ acceptable = tcp_ack(sk, skb, FLAG_SLOWPATH | FLAG_UPDATE_TS_RECENT) > 0; /* tcp_rcv_state_process函数中对于ack的处理步骤中,假如连接处于FIN_WAIT_1, 且数据均已经被确认完,则进入TIME_WAIT_2状态;如果无需在该状态等待(linger2<0), 或者收到了乱序数据段,则直接关闭连接;如果需要等待, 则需要判断等待时间与TIMEWAIT时间的大小关系,若>TIMEWAIT_LEN, 则添加TIME_WAIT_2定时器,否则直接进入TIME_WAIT接管(其子状态仍然是FIN_WAIT_2), 接管之后会添加TIME_WAIT定时器; */ switch (sk->sk_state) { case TCP_SYN_RECV: if (!acceptable) return 1; if (!tp->srtt_us) tcp_synack_rtt_meas(sk, req); /*/这里是由tcp_v4_do_rcv里面的tcp_child_process走到这里, 在tcp_child_process前会通过tcp_check_req创建一个新的struct sock Once we leave TCP_SYN_RECV, we no longer need req * so release it. */ if (req) { tp->total_retrans = req->num_retrans; reqsk_fastopen_remove(sk, req, false); } else { /* Make sure socket is routed, for correct metrics. */ icsk->icsk_af_ops->rebuild_header(sk); tcp_init_congestion_control(sk); tcp_mtup_init(sk); tp->copied_seq = tp->rcv_nxt; tcp_init_buffer_space(sk); } smp_mb(); tcp_set_state(sk, TCP_ESTABLISHED);// TCP_SYN_RECV->TCP_ESTABLISHED sk->sk_state_change(sk);//sock_def_wakeup, 唤醒epoll /* sock_init_data中 有 sk->sk_state_change = sock_def_wakeup; sk->sk_data_ready = sock_def_readable; sk->sk_write_space = sock_def_write_space; sk->sk_error_report = sock_def_error_report; sk->sk_destruct = sock_def_destruct; */ //epoll然后调用ep_send_events->ep_scan_ready_list->ep_send_events_proc->ep_item_poll->tcp_poll /* * 设置"子"传输控制块为ESTABLISHED状态 */ /* Note, that this wakeup is only for marginal crossed SYN case. * Passively open sockets are not waked up, because * sk->sk_sleep == NULL and sk->sk_socket == NULL. */ /* * 发信号给那些将通过该套接字发送数据的进程, * 通知他们套接字目前已经可以发送数据了 sk_state_change()->sock_def_wakeup()->ep_poll_callback(), 添加到epoll的ready list中,并唤醒阻塞中的epoll。 epoll然后调用ep_send_events->ep_scan_ready_list->ep_send_events_proc->ep_item_poll->tcp_poll */ if (sk->sk_socket) sk_wake_async(sk, SOCK_WAKE_IO, POLL_OUT); /* * 初始化传输控制块各字段,如果存在时间戳选项, * 同时平滑RTT为零,则需计算重传超时时间等 */ tp->snd_una = TCP_SKB_CB(skb)->ack_seq; tp->snd_wnd = ntohs(th->window) << tp->rx_opt.snd_wscale; tcp_init_wl(tp, TCP_SKB_CB(skb)->seq); if (tp->rx_opt.tstamp_ok) tp->advmss -= TCPOLEN_TSTAMP_ALIGNED; if (req) { /* Re-arm the timer because data may have been sent out. * This is similar to the regular data transmission case * when new data has just been ack'ed. * * (TFO) - we could try to be more aggressive and * retransmitting any data sooner based on when they * are sent out. */ tcp_rearm_rto(sk); } else tcp_init_metrics(sk); /* * 为该套接字建立路由,初始化拥塞控制模块 */ /* * 初始化与路径MTU有关的成员 */ tcp_update_pacing_rate(sk); /* * 更新最近一次发送数据包的时间 */ /* Prevent spurious tcp_cwnd_restart() on first data packet */ tp->lsndtime = tcp_time_stamp; tcp_initialize_rcv_mss(sk); /* * 计算有关TCP首部预测的标志 */ tcp_fast_path_on(tp); break; case TCP_FIN_WAIT1: { struct dst_entry *dst; int tmo; /* If we enter the TCP_FIN_WAIT1 state and we are a * Fast Open socket and this is the first acceptable * ACK we have received, this would have acknowledged * our SYNACK so stop the SYNACK timer. */ if (req) { /* Return RST if ack_seq is invalid. * Note that RFC793 only says to generate a * DUPACK for it but for TCP Fast Open it seems * better to treat this case like TCP_SYN_RECV * above. */ if (!acceptable) return 1; /* We no longer need the request sock. */ reqsk_fastopen_remove(sk, req, false); tcp_rearm_rto(sk); } /* 发送数据未确认完毕 */ if (tp->snd_una != tp->write_seq) break; tcp_set_state(sk, TCP_FIN_WAIT2); /* 进入FIN_WAIT_2状态 */ sk->sk_shutdown |= SEND_SHUTDOWN;/* 关闭发送端 */ dst = __sk_dst_get(sk); if (dst)/* 路由缓存确认 */ dst_confirm(dst); if (!sock_flag(sk, SOCK_DEAD)) { /* Wake up lingering close() */ sk->sk_state_change(sk); /* 套接口不是DEAD状态,状态发生变化,唤醒等待进程 */ break; } /* linger2<0,无需在FIN_WAIT_2等待 */ if (tp->linger2 < 0 || /* 收到期望序号以后的数据段(data, fin) */ (TCP_SKB_CB(skb)->end_seq != TCP_SKB_CB(skb)->seq && after(TCP_SKB_CB(skb)->end_seq - th->fin, tp->rcv_nxt))) { tcp_done(sk);/* 关闭连接 */ NET_INC_STATS(sock_net(sk), LINUX_MIB_TCPABORTONDATA); return 1; } tmo = tcp_fin_time(sk); /* 获取FIN_WAIT_2等待时间 */ if (tmo > TCP_TIMEWAIT_LEN) { /* > TIMEWAIT_LEN,加入FIN_WAIT_2定时器 */ inet_csk_reset_keepalive_timer(sk, tmo - TCP_TIMEWAIT_LEN); } else if (th->fin || sock_owned_by_user(sk)) { /* Bad case. We could lose such FIN otherwise. * It is not a big problem, but it looks confusing * and not so rare event. We still can lose it now, * if it spins in bh_lock_sock(), but it is really * marginal case. */ /* 有fin?? 或者 被用户进程锁定,加入FIN_WAIT_2定时器 */ inet_csk_reset_keepalive_timer(sk, tmo); } else { /* 正常等待时间< TIMEWAIT_LEN,进入TIMEWAIT接管状态 */ tcp_time_wait(sk, TCP_FIN_WAIT2, tmo); goto discard; } break; } case TCP_CLOSING: if (tp->snd_una == tp->write_seq) { tcp_time_wait(sk, TCP_TIME_WAIT, 0); goto discard; } break; case TCP_LAST_ACK: if (tp->snd_una == tp->write_seq) { tcp_update_metrics(sk); tcp_done(sk); goto discard; } break; } /* step 6: check the URG bit */ tcp_urg(sk, skb, th); /* FIN_WAIT_2状态的走向有以下几个流程触发点, (1)TIME_WAIT_2定时器未超时时间内,收到数据段触发; (2)TIME_WAIT_2定时器超时触发; (3)TIME_WAIT定时器未超时时间内,收到数据段触发; (4)TIME_WAIT定时器超时触发; */ /* step 7: process the segment text */ switch (sk->sk_state) { case TCP_CLOSE_WAIT: case TCP_CLOSING: case TCP_LAST_ACK: if (!before(TCP_SKB_CB(skb)->seq, tp->rcv_nxt)) break; case TCP_FIN_WAIT1: case TCP_FIN_WAIT2://TIME_WAIT_2定时器未超时时间内,收到数据段触发,如果设置FIN标记,则直接进入TIME_WAIT状态; /* RFC 793 says to queue data in these states, * RFC 1122 says we MUST send a reset. * BSD 4.4 also does reset. */ if (sk->sk_shutdown & RCV_SHUTDOWN) { if (TCP_SKB_CB(skb)->end_seq != TCP_SKB_CB(skb)->seq && after(TCP_SKB_CB(skb)->end_seq - th->fin, tp->rcv_nxt)) { NET_INC_STATS(sock_net(sk), LINUX_MIB_TCPABORTONDATA); tcp_reset(sk); return 1; } } /* Fall through */ case TCP_ESTABLISHED: tcp_data_queue(sk, skb); queued = 1; break; } /* tcp_data could move socket to TIME-WAIT */ if (sk->sk_state != TCP_CLOSE) { tcp_data_snd_check(sk); tcp_ack_snd_check(sk); } if (!queued) { discard: tcp_drop(sk, skb); } return 0; }
tcp_v4_conn_request
/* //服务器端收到SYN后,创建连接控制块request_sock 。也就是收到第一步SYN的时候只是建立的连接控制块request_sock ,当收到第三次ack的时候,才创建新的struct sock */ int tcp_conn_request(struct request_sock_ops *rsk_ops, const struct tcp_request_sock_ops *af_ops, struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb) { struct tcp_fastopen_cookie foc = { .len = -1 }; __u32 isn = TCP_SKB_CB(skb)->tcp_tw_isn; struct tcp_options_received tmp_opt; struct tcp_sock *tp = tcp_sk(sk); struct net *net = sock_net(sk); struct sock *fastopen_sk = NULL; struct dst_entry *dst = NULL; struct request_sock *req; bool want_cookie = false; /*如果启用了cookie机制,则会在第三步收到ACK的时候在tcp_v4_hnd_req中 的cookie_v4_check对之前发送的ack+syn进行检查,检查过程见cookie_v4_check */struct flowi fl; /* TW buckets are converted to open requests without * limitations, they conserve resources and peer is * evidently real one. */ if ((net->ipv4.sysctl_tcp_syncookies == 2 ||//sysctl_tcp_syncookies=2无条件生成syncookie inet_csk_reqsk_queue_is_full(sk)) && !isn) {//或者请求队列太长, 并且当前不是timewait want_cookie = tcp_syn_flood_action(sk, skb, rsk_ops->slab_name);//sysctl_tcp_syncookies>0, 并未当前socket打印一次告警 if (!want_cookie)//队列满了,但不使用syncookie,则丢弃 goto drop; } /* Accept backlog is full. If we have already queued enough * of warm entries in syn queue, drop request. It is better than * clogging syn queue with openreqs with exponentially increasing * timeout. */ /* * 如果连接队列长度已达到上限且SYN请求队列中至少有一个握手过程中 * 没有重传过的段,则丢弃当前连接请求. * 如果半连接队列中未重传的请求块数量大于1, * 则表示未来可能有2个完成的连接,这些新完成 * 的连接要放到连接队列中,但此时连接队列已满 * 。如果在接收到三次握手中最后的ACK后连接队列 * 中没有空闲的位置,会忽略接收到的ACK包,连接 * 建立会推迟,所以此时最好丢掉部分新的连接请 * 求,空出资源以完成正在进行的连接建立过程。 * 还要注意,这个判断并没有考虑半连接队列是否 * 已满的问题。从这里可以看出,即使开启了 * SYN cookies机制并不意味着一定可以完成连接的建立。 * */ if (sk_acceptq_is_full(sk) && inet_csk_reqsk_queue_young(sk) > 1) {//accept队列满,但是syn队列依然有可能被accept的连接,此时丢弃 NET_INC_STATS(sock_net(sk), LINUX_MIB_LISTENOVERFLOWS); goto drop; } /* * 可以接收并处理连接请求,调用inet_reqsk_alloc()分配一个连接请求 * 块,用于保存连接请求信息,同时初始化在建立连接过程中用来发送 * ACK、RST段的操作集合,以便在建立连接过程中能方便地调用这些接口 */ //rsk_ops ===tcp_request_sock_ops req = inet_reqsk_alloc(rsk_ops, sk, !want_cookie);//分配request_sock, 进入TCP_NEW_SYN_RECV状态 if (!req) goto drop; //af_ops====tcp_request_sock_ipv4_opss tcp_rsk(req)->af_specific = af_ops;//tcp_request_sock_ipv4_ops /* * 清除TCP选项后初始化mss_clamp和user_mss。 */ tcp_clear_options(&tmp_opt); tmp_opt.mss_clamp = af_ops->mss_clamp;//TCP_MSS_DEFAULT=536 tmp_opt.user_mss = tp->rx_opt.user_mss;//listen sock设置的或是tw的 /* * 解析SYN段中的TCP选项 */ tcp_parse_options(skb, &tmp_opt, 0, want_cookie ? NULL : &foc);//开启syncookie后则不用考虑fastopen, syncookie不允许使用tcp扩展 if (want_cookie && !tmp_opt.saw_tstamp) //开启syncookie,但是不带timestamp tcp_clear_options(&tmp_opt);//清除wscale,sack_ok等选项,因为没地方存 /* * 初始化该连接中是否启用时间戳的选项tstamp_ok */ tmp_opt.tstamp_ok = tmp_opt.saw_tstamp; /* * 根据接收到SYN段中的选项和序号来初始化连接请求块信息 */ tcp_openreq_init(req, &tmp_opt, skb, sk); /* Note: tcp_v6_init_req() might override ir_iif for link locals */ inet_rsk(req)->ir_iif = inet_request_bound_dev_if(sk, skb); /* * 初始化TCP层次的连接请求信息块,包括目的地址、源地址, * 并调用tcp_v4_save_options从IP层私有控制块中获取IP * 选项保存到传输控制块的opt中,包括MSS、窗口扩大 * 因子、显式拥塞通知等 */ af_ops->init_req(req, sk, skb);//tcp_v4_init_req 会调用tcp_v4_save_options if (security_inet_conn_request(sk, skb, req)) goto drop_and_free; if (!want_cookie && !isn) {//不需要生成syncookie,也不是从timewait recycle的新的sock /* VJ's idea. We save last timestamp seen * from the destination in peer table, when entering * state TIME-WAIT, and check against it before * accepting new connection request. * * If "isn" is not zero, this request hit alive * timewait bucket, so that all the necessary checks * are made in the function processing timewait state. */ /* * 进入TIMEWAIT状态时,从对端信息块中获取时间戳,在新的 * 连接请求之前检测PAWS */ if (tcp_death_row.sysctl_tw_recycle) { bool strict; dst = af_ops->route_req(sk, &fl, req, &strict); //tcp_v4_route_req //当起了快速回收tw_recycle的时候,这里可能有问题,可能连接建立不上,针对TCP时间戳PAWS漏洞的代码。 见:http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-736168-id-376061.html //针对TCP时间戳PAWS漏洞,造成服务器端收到SYN的时候不回收SYN+ACK,解决办法是对方不要发送时间戳选项,同时关闭tcp_timestamps见tcp_v4_conn_request if (dst && strict && !tcp_peer_is_proven(req, dst, true, tmp_opt.saw_tstamp)) { NET_INC_STATS(sock_net(sk), LINUX_MIB_PAWSPASSIVEREJECTED); goto drop_and_release; /* 1 tcp的option有 time stamp字段. 2 tcp_tw_recycle有设置。 3 在路由表中是否存在完全相同的流(如果打开了xfrm的话, 还要比较端口,默认xfrm应该是打开的),如果存在则直接返回. 4 并且数据包的源地址和新请求的源地址相同. 5 根据路由表以及源地址能够查找到保存的peer (这个可以看我以前的blog,也就是保存了一些连接统计信息). 6 当前时间(接收到syn)比最后一次的时间(time stamp)小于60秒. 7 已经存在peer的最近一次时间戳要大于当前请求进来的时间戳. 从上面可以看到,上面的条件中1/2都是 server端可以控制的,而其他的条件, 都是很容易就满足的,因此我们举个例子。 如果客户端是NAT出来的,并且我们server端有打开tcp_tw_recycle , 并且time stamp也没有关闭,那么假设第一个连接进来,然后关闭,此时这个句柄处于time wait状态,然后很快(小于60秒)又一个客户端(相同的源地址,如果打开了xfrm还要相同的端口号)发一个syn包,此时linux内核就会认为这个数据包异常的,因此就会丢掉这个包,并发送rst。 而现在大部分的客户端都是NAT出来的,因此建议tw_recycle还 是关闭,或者说server段关闭掉time stamp(/proc/sys/net/ipv4/tcp_timestamps). */ } } /* Kill the following clause, if you dislike this way. */ //如果没开启sysctl_tw_recycle和syncookie,最后1/4的syn请求需要验证过去的连接信? /* * 未启动syncookies的情况下受到synflood攻击,则丢弃接收到的段 */ else if (!net->ipv4.sysctl_tcp_syncookies && (sysctl_max_syn_backlog - inet_csk_reqsk_queue_len(sk) < (sysctl_max_syn_backlog >> 2)) && !tcp_peer_is_proven(req, dst, false, tmp_opt.saw_tstamp)) {//如果不存在tcp metric或者过去的连接信息则丢弃 /* Without syncookies last quarter of * backlog is filled with destinations, * proven to be alive. * It means that we continue to communicate * to destinations, already remembered * to the moment of synflood. */ pr_drop_req(req, ntohs(tcp_hdr(skb)->source), rsk_ops->family); goto drop_and_release; } isn = af_ops->init_seq(skb);//tcp_v4_init_sequence,根据四元组,随机数,当前高精度时间来生成isn } if (!dst) { dst = af_ops->route_req(sk, &fl, req, NULL);//tcp_v4_route_req if (!dst) goto drop_and_free; } tcp_ecn_create_request(req, skb, sk, dst); if (want_cookie) { /* * 如果启动了syncookies,则每60秒警告一次可能受 * synflood攻击,同时由客户端IP地址、客户端端口、 * 服务器IP地址、服务器端口、客户端初始序列号 * 等要素经hash运算后加密得到服务端初始化序列号 */ //如果开启了syncookie选项,则需要检查收到的第三步ack和这个isn值是否一致 isn = cookie_init_sequence(af_ops, sk, skb, &req->mss); //cookie_v4_init_sequence生成syncookie,并作为ack的起始序号 req->cookie_ts = tmp_opt.tstamp_ok; if (!tmp_opt.tstamp_ok) inet_rsk(req)->ecn_ok = 0; } tcp_rsk(req)->snt_isn = isn; tcp_rsk(req)->txhash = net_tx_rndhash(); tcp_openreq_init_rwin(req, sk, dst);//设置初始化rwnd if (!want_cookie) { tcp_reqsk_record_syn(sk, req, skb);//如果设置保存TCP_SAVE_SYN标记,则保存 fastopen_sk = tcp_try_fastopen(sk, skb, req, &foc, dst); //验证后创建fastopen sock,并把数据部分放入接收队列中 } if (fastopen_sk) {//验证并创建fastsocket成功, 进入TCP_SYN_RCV状态 af_ops->send_synack(fastopen_sk, dst, &fl, req, &foc, TCP_SYNACK_FASTOPEN);//tcp_v4_send_synac /* Add the child socket directly into the accept queue */ inet_csk_reqsk_queue_add(sk, req, fastopen_sk);//添加到等待accept的队列 sk->sk_data_ready(sk); bh_unlock_sock(fastopen_sk); sock_put(fastopen_sk); } else { tcp_rsk(req)->tfo_listener = false; if (!want_cookie) inet_csk_reqsk_queue_hash_add(sk, req, TCP_TIMEOUT_INIT);//插入ehash,并设置定时器 af_ops->send_synack(sk, dst, &fl, req, &foc, !want_cookie ? TCP_SYNACK_NORMAL : TCP_SYNACK_COOKIE);//tcp_v4_send_synack if (want_cookie) { reqsk_free(req);//启用syncookie的话,可以直接释放req return 0; } } reqsk_put(req); return 0; drop_and_release: dst_release(dst); drop_and_free: reqsk_free(req); drop: tcp_listendrop(sk); return 0; } EXPORT_SYMBOL(tcp_conn_request);
inet_csk_reqsk_queue_hash_add
把req放入ehash中,并设置rsk_timer定时器
http代理服务器(3-4-7层代理)-网络事件库公共组件、内核kernel驱动 摄像头驱动 tcpip网络协议栈、netfilter、bridge 好像看过!!!!
但行好事 莫问前程
--身高体重180的胖子


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号